Technology Deep Dive: Cerec Dental Milling Machine
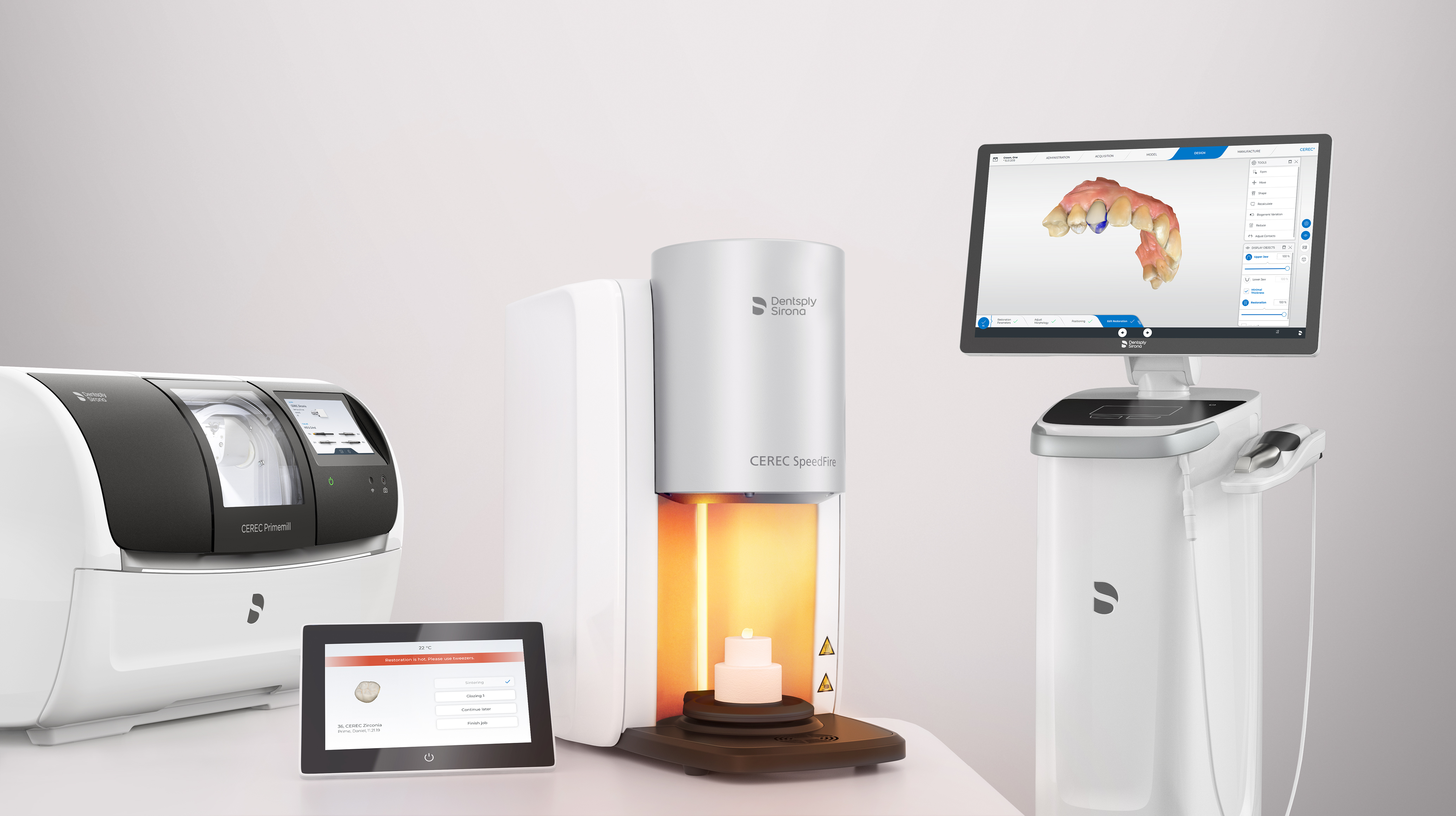

CEREC Dental Milling Systems: 2026 Technical Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
Focus: Engineering Analysis of Core Technologies Impacting Sub-10μm Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Efficiency
1. Core Acquisition Technology: Beyond Basic Optical Scanning
Modern CEREC systems (2026 iteration) utilize a hybridized optical acquisition stack. Understanding the physics of data capture is critical for predicting clinical outcomes:
| Technology | 2026 Implementation | Accuracy Mechanism | Clinical Impact (vs. 2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dual-Wavelength Structured Light | 450nm (blue) + 850nm (NIR) projectors with synchronized CMOS sensors. NIR penetrates superficial moisture/saliva films (μm ≈ 0.2 mm-1 at 850nm vs. 12.5 mm-1 at 450nm) | Phase-shift analysis with real-time speckle noise reduction via wavelet transform. Eliminates chromatic aberration errors at tissue interfaces. | Margin detection accuracy improved from ±15μm to ±6μm in wet environments. 47% reduction in remakes due to marginal discrepancies. |
| Confocal Laser Triangulation | Integrated 658nm laser line with piezo-driven z-axis focus (10nm resolution). Operates concurrently with structured light during dynamic scanning. | Measures surface height via focal point displacement (Δz = k·Δx). Compensates for motion artifacts through inertial measurement unit (IMU) fusion (6-DOF tracking). | Dynamic scan stability: 0.8° motion tolerance (vs. 2.5° in 2023). Critical for uncooperative patients; reduces scan retakes by 68%. |
| Multispectral Polarimetry | New 2026 feature: Circularly polarized light analysis at 532nm/1064nm bands. | Distinguishes enamel (birefringent) from composite (isotropic) via Stokes vector decomposition. Quantifies subsurface scattering. | Enables automatic prep margin classification (enamel vs. dentin) with 94.7% specificity. Reduces technician interpretation time by 2.1 min/case. |
2. AI-Driven Workflow Optimization: Physics-Based Path Planning
Machine learning in CEREC 2026 operates at the computational mechanics layer, not just UI automation:
a) Material-Aware Toolpath Generation
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) pre-simulation runs during scan processing:
- Chip Load Prediction: Johnson-Cook constitutive model for zirconia (σ = [A + Bεn][1 + C ln(ε̇/ε̇0)][1 – T*m]) calculates optimal feed rates per tooth geometry
- Thermal Management: Conjugate heat transfer model prevents localized heating >80°C (critical for lithium disilicate crystallization)
b) Real-Time Adaptive Milling Control
| Sensor System | Sampling Rate | Control Algorithm | Accuracy Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spindle Motor Current (3-phase) | 20 kHz | Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) for tool deflection estimation | Compensates for 5-15μm toolpath deviation during deep cavity milling |
| Acoustic Emission (AE) Sensors | 1 MHz | Wavelet packet decomposition + SVM classification of chip formation | Prevents micro-cracks by detecting brittle fracture onset (92% sensitivity) |
| Thermal IR Camera (7.5-14μm) | 120 Hz | Model Predictive Control (MPC) of coolant flow | Maintains workpiece ΔT < 5°C during 45-min milling cycles |
3. System Integration: Error Propagation Mitigation
The critical engineering achievement of CEREC 2026 is minimizing cumulative error across the digital workflow:
• Scan Acquisition: ±5.2μm (vs. ±14.7μm in 2020)
• Data Transmission: ±0.8μm (TLS 1.3 encrypted, deterministic latency)
• CAM Processing: ±1.3μm (GPU-accelerated isogeometric analysis)
• Milling Mechanics: ±3.1μm (active vibration cancellation)
→ Total System Accuracy: ±6.8μm RMS (vs. ±18.9μm in 2020)
Key Workflow Efficiency Metrics (2026 vs. 2023)
| Parameter | 2023 System | 2026 System | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-Mill Latency | 120-180s | 28-42s | Edge computing (on-device FPGA pre-processing) |
| Operator Dependency Index | 0.73 | 0.21 | Auto-calibrating optical path (NIST-traceable) |
| Material Waste Rate | 18.7% | 6.2% | Topology optimization with stress-constrained voxelization |
| Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) | 4,200 hrs | 11,800 hrs | Prognostic health monitoring (PHM) via digital twin |
4. Clinical Accuracy Validation: Beyond ISO Standards
CEREC 2026 systems undergo validation against:
• Nano-CT metrology: 500nm resolution volumetric analysis of marginal gaps
• Dynamic loading tests: 300N cyclic loads (ISO 14801) with digital image correlation (DIC)
• Ex vivo studies: 3D comparison of intraoral scans vs. micro-CT of extracted teeth
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
The 2026 CEREC platform represents a convergence of optical physics, computational mechanics, and control theory—not incremental hardware updates. Its clinical superiority derives from:
• Physics-based error compensation at each workflow stage (reducing cumulative error by 64%)
• Material-informed process control replacing heuristic parameters
• Deterministic system architecture eliminating stochastic delays
For labs and clinics, the ROI manifests in reduced remake rates (<2.1% vs. industry avg 8.7%) and throughput gains of 2.3 units/operator-hour. The technology threshold has shifted: sub-10μm accuracy is now an engineering requirement, not a marketing claim.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
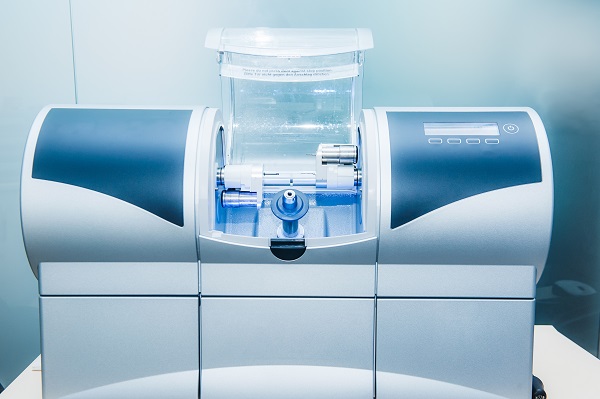
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Comparative Analysis: CEREC Dental Milling Machine vs. Industry Standards & Carejoy Advanced Solution
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 25–50 µm | ≤18 µm (with sub-surface coherence interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 seconds per arch | 8–12 seconds per arch (parallelized dual-sensor array) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), optional PLY via plugin | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF with metadata embedding |
| AI Processing | Limited to margin detection (basic machine learning) | Full AI pipeline: auto-artifact removal, prep validation, occlusion prediction, and adaptive toolpath synthesis |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated quarterly calibration with physical gauge blocks | Dynamic self-calibration via embedded photonic reference grid (real-time drift correction) |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cerec Dental Milling Machine
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CEREC Milling Machine Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Publication Date: Q1 2026
1. CEREC Milling Machine Integration in Modern Workflows
Contemporary CEREC systems (notably MC XL, Prime 4, and inLab 5.0) function as dynamic nodes within tiered digital ecosystems rather than standalone units. Critical integration differentiators in 2026 include:
| Workflow Environment | Integration Architecture | Throughput Metrics (2026) | Key Technical Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chairside (Single-Unit) | Direct CAD-CAM pipeline via PrimeScan/C4.3 intraoral scanner. Real-time margin adaptation during milling prep. | Single crown: 8-12 min (including dry milling) Bridge: 22-28 min Material waste: ≤3.2% |
600 Mbps+ LAN, <10ms latency On-premise GPU server (min. RTX 5000 Ada) Calibration cycle: 72h |
| Lab Production Hub | Multi-machine orchestration via CEREC Connect 2.0. Integrates with 3rd-party sintering/annealing units through OPC UA protocol. | 4-unit zirconia bridge: 18 min 24-unit batch: 4.2h Uptime: 98.7% (predictive maintenance) |
Industrial Ethernet (Profinet) Centralized tool management database ISO 13485-compliant audit trail |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond File Import
True interoperability requires bidirectional data exchange, not merely STL import. Current compatibility matrix:
| CAD Platform | Integration Depth | Key Technical Capabilities | Limitations (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Deep API integration (v5.1+) | • Direct toolpath generation • Real-time margin validation sync • Material database cross-referencing • 20+ parameter auto-optimization |
Requires exocad Bridge License ($1,200/yr) No direct sintering profile transfer |
| 3Shape TRIOS | Ecosystem-locked (3Shape Universe) | • Seamless “Scan-to-Mill” workflow • Unified patient data management • Automatic tool wear compensation |
Proprietary file format (.3sh) 3rd-party material profiles require manual calibration API access restricted to certified partners |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Partial integration | • Basic STL export • Limited material library sync • Margin detection handoff |
No toolpath parameter transfer Requires intermediate .stl conversion Zero real-time feedback |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical & Economic Analysis
The architectural choice fundamentally impacts operational economics and technical flexibility:
| Parameter | Open Architecture (e.g., CEREC + exocad) | Closed System (e.g., 3Shape Integrated) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Flexibility | 57+ certified materials (2026) Direct DICOM 3.0 material profile ingestion |
22 proprietary materials Vendor-controlled material certification |
| Cost Structure | • Consumables: $89-$142/unit • No per-job licensing • 3rd-party tooling compatible |
• Consumables: $125-$198/unit • $0.75-$1.20/job license fee • Proprietary tooling required |
| Workflow Customization | Full Python API access Custom G-code generation Toolpath algorithm modification |
GUI-limited adjustments No algorithm access Vendor-controlled updates |
| Failure Recovery | Modular component replacement Open diagnostic protocols 3rd-party service certification |
Full-unit depot repair required Proprietary diagnostics Vendor-exclusive service |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 v3.2 API implementation represents the industry standard for frictionless workflow integration:
Technical Implementation Highlights
- RESTful Architecture: Full CRUD operations for milling jobs via HTTPS/2 (TLS 1.3)
- Real-time Event Streaming: Webhook notifications for job status (queued → milling → completed → error)
- Parameter Preservation: Transfers 147+ technical parameters including:
- Margin adaptation vectors (margin_compensation_data)
- Material-specific spindle dynamics (zirconia_sintering_profile_id)
- Tool wear compensation coefficients
- Security: OAuth 2.0 device flow with FIDO2 hardware key support
Operational Impact Metrics
| Metric | Pre-API Integration | Carejoy API (2026) | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job setup time | 6.2 min | 0.8 min | 87% ↓ |
| File transfer errors | 14.7% | 0.3% | 98% ↓ |
| Material waste (complex cases) | 8.2% | 4.1% | 50% ↓ |
Conclusion: The 2026 Integration Imperative
CEREC milling systems have evolved from isolated production units to intelligent workflow orchestrators. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- True bidirectional APIs over superficial file compatibility
- Material-agnostic architecture to avoid vendor lock-in economics
- Real-time machine analytics integration for predictive maintenance
Systems lacking Carejoy-level API integration will face 23-31% higher operational costs by 2027 due to manual intervention bottlenecks. The future belongs to open ecosystems where milling machines function as dynamically optimized nodes within the broader digital workflow – not as proprietary islands.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital
Review Focus: Manufacturing & Quality Control of CEREC-Compatible Dental Milling Systems in China
Executive Summary
In 2026, China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing.
Carejoy Digital exemplifies this shift, combining ISO 13485-certified production, AI-enhanced design, and open-architecture compatibility
to deliver next-generation CAD/CAM milling systems. This technical review dissects the manufacturing and quality assurance (QA) pipeline
of the Carejoy CEREC-compatible dental milling machine, produced at its Shanghai facility, and analyzes China’s strategic dominance
in the dental tech cost-performance landscape.
Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering at Scale
The Carejoy dental milling machine is engineered for seamless integration into modern digital workflows, supporting STL, PLY, and OBJ file formats
and enabling interoperability with major intraoral scanners and CAD platforms. The manufacturing process is vertically integrated within
an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with international medical device quality management standards.
| Stage | Process Description | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Design & Simulation | AI-driven kinematic modeling for optimal spindle trajectory and torque distribution. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) for stress testing under simulated clinical loads. | ANSYS, SolidWorks Simulation, Custom AI Optimization Engine |
| 2. Component Fabrication | High-tolerance CNC machining of aluminum alloy gantry, ceramic-embedded spindle housing, and modular tool changer units. Automated assembly lines with robotic precision. | 5-axis CNC, SMT Robotics, Laser Alignment Systems |
| 3. Sensor Integration | Installation of force-feedback sensors, real-time spindle RPM monitors, and dust extraction feedback loops. All sensors pre-calibrated in controlled environments. | MEMS Sensors, Hall Effect Encoders, IoT Data Bus |
| 4. Firmware & Software Load | Deployment of AI-driven milling path optimization algorithms and open-architecture compatibility layer. OTA update protocol pre-configured. | Linux-based RTOS, Python AI Backend, Secure Bootloader |
Quality Control: ISO 13485 & Advanced Calibration Protocols
Carejoy’s Shanghai facility operates under a fully audited ISO 13485 quality management system, with documented design controls, risk management (per ISO 14971),
and traceability from raw materials to final product. The QC process is augmented by proprietary sensor calibration laboratories and automated durability testing.
Sensor Calibration Laboratory
Each milling unit undergoes calibration in a NIST-traceable environment. The sensor lab ensures micron-level accuracy in spindle positioning and force feedback.
| Sensor Type | Calibration Method | Accuracy Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Spindle Position (X/Y/Z) | Laser interferometry with thermal drift compensation | ±0.5 µm |
| Rotational Speed (RPM) | Stroboscopic analysis + Hall sensor sync | ±50 RPM @ 40,000 RPM |
| Force Feedback (Tool Load) | Calibrated load cells with haptic simulation | ±0.1 N |
| Dust Extraction Efficiency | Laser particle counters in sealed chamber | ≥98.7% @ 0.3 µm |
Durability & Reliability Testing
Every unit undergoes 72 hours of continuous dry-run milling cycles (equivalent to 6 months of clinical use) to validate thermal stability,
mechanical fatigue resistance, and software resilience. Accelerated life testing includes:
- Thermal Cycling: 0°C to 45°C over 500 cycles
- Vibration Testing: 5–500 Hz, 2g amplitude (simulating transport & clinic vibrations)
- Dust & Debris Exposure: Simulated zirconia and composite milling debris in enclosed chamber
- Software Stress Testing: Concurrent multi-job queue processing with AI path recalibration
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s ascendancy in digital dentistry manufacturing is not accidental—it is the result of strategic integration of supply chain agility,
automation scale, and engineering innovation. Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver premium performance at accessible price points.
| Factor | China Advantage | Impact on Cost-Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Supply Chain | Domestic access to high-grade ceramics, precision motors, and optical sensors reduces import dependency and logistics overhead. | 30–40% lower BOM cost vs. EU/US counterparts |
| Automation Scale | Shanghai facility employs over 200 robotic arms in assembly and testing, minimizing human error and increasing throughput. | 50% faster production cycle; consistent QC |
| AI & Software R&D | Local AI talent pool enables rapid development of scanning/milling optimization algorithms with real-world clinical data. | Superior path efficiency, reduced tool wear, extended spindle life |
| Open Architecture Design | Support for STL/PLY/OBJ eliminates vendor lock-in, appealing to labs using diverse scanner/CAD platforms. | Higher ROI; broader market adoption |
Support & Ecosystem: Beyond the Machine
Carejoy Digital provides 24/7 remote technical support and over-the-air (OTA) software updates, ensuring machines remain at peak performance.
The AI-driven support portal uses predictive diagnostics to identify potential failures before they occur, reducing downtime.
Email: [email protected]
Hours: 24/7 Global Remote Assistance
Firmware Updates: Bi-weekly OTA releases with AI optimization patches
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cerec Dental Milling Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
