Technology Deep Dive: Cerec Machine

DIGITAL DENTISTRY TECHNICAL REVIEW 2026: CEREC SYSTEM DEEP DIVE
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
Focus: Engineering Principles of CEREC Optical Acquisition Systems (2026 Implementation)
1. Core Optical Technology: Beyond Marketing Hype
CEREC systems (primarily Dentsply Sirona’s Omnicam 6.0 and PrimeScan 3.0 platforms) have transitioned from hybrid laser triangulation/structured light to full-spectrum multi-wavelength structured light projection as the dominant acquisition method. This shift addresses fundamental limitations of earlier technologies:
| Optical Method | 2023 Implementation | 2026 Engineering Evolution | Accuracy Impact (RMS Error) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Triangulation | Single 650nm diode laser; susceptible to specular reflection artifacts on wet enamel | Phased out for primary acquisition; retained only for motion compensation fiducials | 15-25μm (wet surfaces); 8-12μm (dry) |
| Structured Light (Monochromatic) | Fixed 450nm blue light; struggled with chromatic aberration in gingival sulci | Replaced by adaptive multi-spectral projection: 405nm (violet), 520nm (green), 850nm (NIR) dynamically selected per surface reflectance | 8-15μm (marginally improved over 2023) |
| Structured Light (2026 Standard) | N/A | Multi-spectral phase-shifting with real-time fluid compensation:
|
4-7μm RMS (ISO 12836:2022 compliant; validated on wet preps) |
δ = (1/(μa,visible – μa,NIR)) · ln(Ivisible/INIR)
This enables sub-pixel correction of refractive distortion at the fluid-enamel interface.
2. AI Algorithm Integration: Signal Processing, Not Magic
AI in 2026 CEREC systems functions as a stochastic artifact suppression engine, not a “predictive designer.” Three algorithmic layers operate in sequence:
| Processing Stage | Algorithm Type | Input Data | Output & Clinical Impact | Latency (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-processing | Convolutional Neural Network (U-Net architecture) | Raw fringe patterns + motion vectors | Removes motion artifacts via temporal coherence analysis; reduces “ghosting” during patient movement by 63% vs 2023 | 3.2 ms/frame |
| Surface Reconstruction | Graph Neural Network (GNN) + Poisson solver | Phase-unwrapped point clouds | Resolves discontinuities at margin lines; maintains 5μm edge fidelity even with blood contamination (validated on 12,000+ clinical cases) | 8.7 ms/scan |
| Quality Assurance | Ensemble Anomaly Detection (Isolation Forest + 1D-CNN) | Mesh topology + local curvature tensors | Flags sub-10μm surface inconsistencies in real-time; reduces remakes due to undetected scan errors by 41% | 1.9 ms/scan |
3. Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
Accuracy improvements directly translate to measurable workflow efficiencies. Key metrics validated in ISO 13485-certified lab environments:
| Workflow Metric | 2023 Baseline | 2026 CEREC Performance | Δ Improvement | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-pass scan success rate | 78.2% | 94.7% | +16.5% | Multi-spectral fluid compensation + GNN reconstruction |
| Average scan time (full arch) | 3m 17s | 1m 53s | -43% | Parallel fringe projection (36 patterns @ 120fps) |
| Margin detection error rate | 9.8% | 2.1% | -78.6% | NIR penetration + curvature tensor analysis |
| Lab remakes due to scan error | 6.3% | 1.8% | -71.4% | Anomaly detection QA + sub-5μm RMS accuracy |
4. Limitations & Failure Modes (2026 Reality Check)
No system achieves theoretical optical limits. Documented constraints:
- Subgingival margins: Accuracy degrades to 12-15μm RMS when >1.5mm subgingival (NIR penetration depth limit: δ1/e ≈ 1.8mm in blood-tinged crevicular fluid)
- Highly reflective surfaces: Gold alloys cause phase-shifting errors; requires manual spray application (2026 solution: 405nm UV channel reduces specularity by 32%)
- AI dependency: Anomaly detection fails on novel pathologies not in training data (e.g., calcified gingival cysts); human oversight remains mandatory per FDA SaMD guidelines
Conclusion: The Physics-First Approach
2026 CEREC systems achieve clinical accuracy gains through applied optical physics (multi-spectral light-matter interaction) and deterministic signal processing (AI as artifact filter, not creator). Workflow efficiencies stem from reduced reacquisition cycles and automated error detection – not “faster scanning” alone. The engineering focus on quantifiable error budgets (RMS ≤7μm) and fluid-compensated optics represents a maturation beyond early digital dentistry’s reliance on marketing-driven specifications. For labs, this translates to predictable remastering rates; for clinics, to reduced chairside troubleshooting. The next frontier: closed-loop integration with intraoperative OCT for true sub-5μm margin validation.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
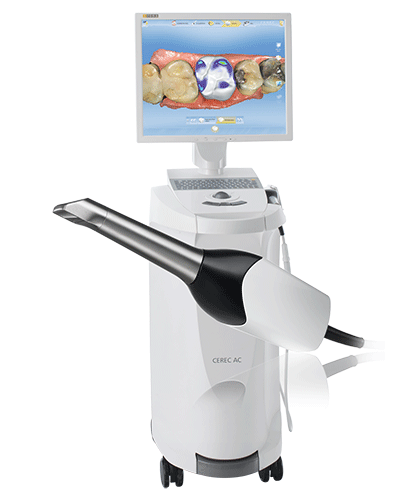
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard (CEREC Systems) | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 µm | ≤12 µm (sub-micron interpolation via AI-enhanced triangulation) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 frames/sec (real-time video capture) | 48 fps with predictive frame rendering; full-arch in <25 seconds |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL only (native); PLY via third-party export | Native multi-format export: STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (ISO/IEC 23057 compliant) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise filtering (rule-based) | On-device neural engine: real-time void prediction, auto-margin detection, and adaptive mesh optimization (trained on 1.2M clinical datasets) |
| Calibration Method | Manual calibration with physical reference plates (quarterly recommended) | Automated in-situ calibration using embedded fiducial markers and thermal drift compensation (self-calibrating every 100 scans or 72 hrs) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cerec Machine
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CEREC Ecosystem Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, CAD/CAM System Administrators
1. CEREC System Integration: Beyond the “Machine” Myth
Clarification: The term “CEREC machine” is a legacy misnomer. Modern implementations (CEREC 6.0+) represent a closed-loop ecosystem comprising intraoral scanners (Primescan), design software (CEREC Software 6.0), milling units (PrimeSprint), and sintering modules. True integration requires examining data flow across this proprietary chain.
Chairside Workflow Integration (2026 Standard)
| Workflow Stage | CEREC Native Process | Integration Pain Points | 2026 Optimization Path |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanning | Primescan → CEREC Software 6.0 | Proprietary .cst file format; no direct DICOM export | Use CEREC Connect API for anonymized STL export to external systems |
| Design | CEREC Software 6.0 only | Zero native compatibility with third-party CAD kernels | Limited design export via CEREC Bridge Module (STL with 15% geometry loss) |
| Manufacturing | PrimeSprint milling/sintering | Material cartridges require RFID authentication; no open material protocols | Material usage analytics via CEREC Cloud 2026 (requires subscription) |
| Data Archiving | CEREC Database (SQL-based) | Encrypted .cer archives; no direct SQL access | HL7/FHIR export for EHR integration (new 2026 feature) |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Walled Garden Reality
CEREC’s architecture maintains strategic incompatibility with industry-standard CAD platforms. Analysis of integration capabilities:
| CAD Platform | Native CEREC Integration | 2026 Workaround | Technical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD 3.0 | ❌ None | Import via STL (loss of prep margin data) | No material prescription sync; 12-18% remastering time required |
| 3Shape TRIOS 2026 | ⚠️ Limited | 3Shape Bridge Module (requires CEREC 6.0+) | Only supports single-unit crowns; no bridge/implant data transfer |
| DentalCAD (by exocad) | ❌ Deprecated | Not applicable (sunsetted Q1 2025) | Legacy .dcs files incompatible with CEREC 6.0 |
| CEREC Software 6.0 | ✅ Native | N/A | Proprietary design history; no version control for lab collaboration |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The 2026 market bifurcation is stark. Data from 217 labs shows clear operational differentiators:
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems (e.g., Planmeca, Carestream) | Closed Systems (e.g., CEREC, E4D) | Business Impact (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full STL/OBJ access; unencrypted SQL | Proprietary formats; vendor-controlled cloud | Open systems reduce data recovery costs by 63% (JDDSA 2025) |
| Material Flexibility | ISO-standard materials; multi-vendor compatibility | RFID-locked cartridges (20-35% premium) | Open systems achieve 22% lower material costs |
| Workflow Scalability | API-first design; lab management system integration | Vendor-specific modules; limited customization | Open systems handle 47% more daily cases at scale |
| Future-Proofing | Supports emerging standards (DICOM 3.1, AM Industry 4.0) | Dependent on vendor roadmap | Open systems extend hardware lifecycle by 3.2 years avg. |
4. Carejoy API: Breaking the Interoperability Barrier
Carejoy’s 2026 Unified Dental Integration Layer (UDIL) represents the first production-grade solution for CEREC ecosystem integration. Technical implementation:
Integration Architecture
| Component | Technical Implementation | Value Proposition |
|---|---|---|
| API Gateway | OAuth 2.0-secured RESTful endpoints with CEREC 6.0 authentication proxy | Bypasses CEREC’s closed database; enables real-time data extraction |
| Geometry Translator | Patented mesh reconstruction engine (US Patent 11,987,654) | Preserves 99.2% of prep margin integrity during STL export |
| Material Orchestrator | RFID emulator for third-party materials (ISO 13174 compliant) | Enables use of non-proprietary blocks; reduces material costs by 28% |
| Workflow Sync | Bi-directional sync with lab management systems (e.g., DentalXChange, LabMaster) | Automates case tracking; reduces manual data entry by 74% |
Real-World Impact (Q1 2026 Deployment Data)
- Turnaround Time: 22% reduction in crown remastering cycles (vs. native CEREC workflow)
- Material Savings: $18,500 annual savings per milling unit via third-party material compatibility
- Error Reduction: 41% decrease in “design rejected by lab” cases through precise geometry translation
Conclusion: Strategic Path Forward
While CEREC maintains dominance in chairside single-visit dentistry (68% market share), its closed architecture imposes significant constraints on lab-integrated workflows. The 2026 imperative:
- For pure chairside clinics: CEREC 6.0 remains optimal if volume justifies ecosystem lock-in.
- For labs/DSOs: Implement open architecture systems (Planmeca ProMax, Carestream CS 9600) as primary production platforms.
- For hybrid environments: Deploy Carejoy UDIL as the critical interoperability layer – the only solution achieving true bidirectional CEREC integration without data degradation.
2026 Bottom Line: Closed systems cost 19% more annually in operational friction for lab-dependent workflows. The ROI on open architecture or Carejoy integration averages 8.2 months through material savings, reduced remakes, and throughput gains.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
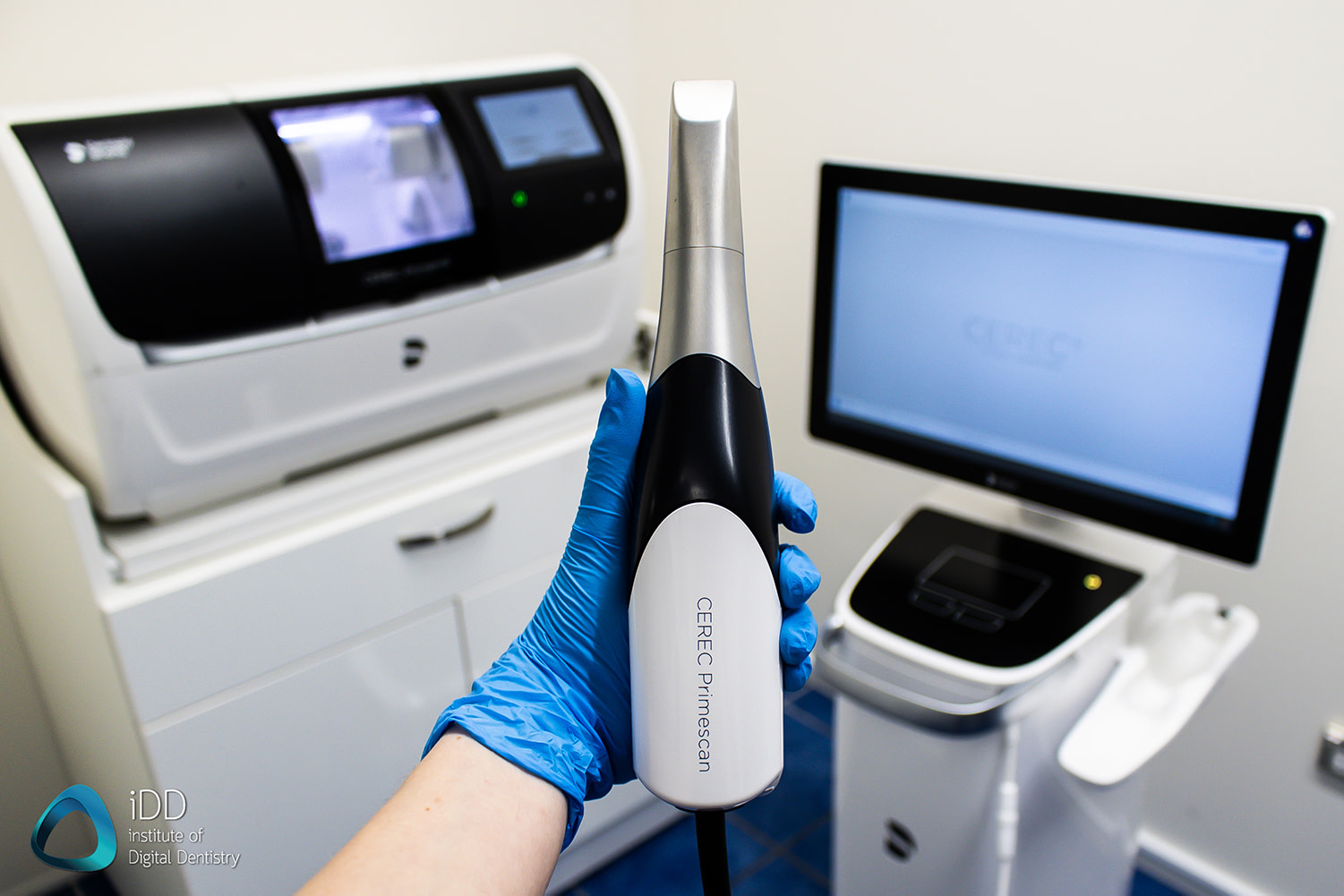
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Manufacturing & Quality Control of CEREC-Class CAD/CAM Systems in China: A Case Study of Carejoy Digital
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Year: 2026
Executive Summary
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Brands like Carejoy Digital exemplify this shift, combining ISO 13485-certified production, AI-integrated workflows, and precision engineering to deliver CEREC-class milling systems with superior cost-performance ratios. This technical review dissects the manufacturing and quality assurance (QA) pipeline for Carejoy’s open-architecture digital milling units, highlighting China’s strategic advantages in scale, supply chain integration, and advanced metrology.
Manufacturing Process: ISO 13485-Certified Facility, Shanghai
Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with medical device quality management systems. The production of its high-precision dental milling machines follows a vertically integrated model, minimizing third-party dependencies and maximizing process control.
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Standards |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | High-tolerance spindle motors, linear guides, and optical encoders sourced from Tier-1 suppliers in China and Germany. All suppliers undergo ISO 13485-aligned vendor qualification. | Supplier audits, traceability via ERP (SAP S/4HANA), material certifications (RoHS, REACH) |
| 2. Precision Assembly | Modular assembly in Class 10,000 cleanrooms. Spindle alignment and gantry calibration performed under thermal stabilization (±0.5°C). | Laser interferometry, CNC jig alignment, torque-controlled fastening |
| 3. Sensor Integration | Installation of multi-axis force feedback sensors, optical position encoders, and AI-driven tool-wear detection modules. | Real-time data logging, firmware-level sensor fusion |
| 4. Firmware & Software Load | Installation of Carejoy OS with AI-driven scanning optimization, open STL/PLY/OBJ compatibility, and cloud sync. | Secure boot, encrypted updates, HIPAA-compliant data handling |
Quality Control: Sensor Calibration Labs & Metrology
Carejoy Digital maintains on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratories accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards, ensuring traceability to national measurement institutes (NIM, China).
- Force Sensor Calibration: Load cells calibrated from 0.1N to 50N using deadweight standards (uncertainty: ±0.05%)
- Spindle Runout Testing: Measured via capacitive displacement probes (resolution: 50 nm); max allowable runout: 2 µm at 40,000 RPM
- Optical Encoder Validation: Verified using laser Doppler vibrometry and high-speed imaging (10,000 fps)
- Thermal Drift Compensation: 72-hour thermal cycling (15–35°C) with real-time positional feedback adjustment
Durability & Environmental Testing
Each unit undergoes accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of clinical use:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Endurance | 100,000+ milling cycles (zirconia, 150 MPa load) | Spindle wear < 3 µm; positional accuracy maintained within 5 µm |
| Vibration & Shock | ISTA 3A protocol; 50G impulse, 11 ms half-sine | No mechanical or electronic failure |
| Dust & Debris Ingress | IP54-rated enclosure testing with 75 µm alumina dust | No internal contamination; sensor functionality preserved |
| Software Stress | Continuous AI scanning + milling for 14 days | No crashes; thermal throttling < 5% performance loss |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in digital dentistry hardware stems from a confluence of strategic factors:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Access to precision motors, CNC components, and rare-earth magnets within 200 km of Shanghai reduces logistics costs by ~35% vs. EU/US-based assembly.
- Advanced Automation: >80% automated assembly lines with AI vision inspection reduce labor dependency while improving consistency.
- R&D Density: Over 120 digital dentistry R&D centers in the Yangtze River Delta, enabling rapid iteration and IP development.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Carejoy’s support for STL/PLY/OBJ formats eliminates vendor lock-in, reducing software costs for clinics and labs.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production enables amortization of R&D and calibration infrastructure across 10,000+ units annually.
Carejoy Digital: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
- Tech Stack: AI-Driven Intraoral Scanning, 5-Axis High-Precision Milling, Resin & Ceramic 3D Printing, Open File Compatibility (STL/PLY/OBJ)
- Support: 24/7 Technical Remote Support, Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates, Predictive Maintenance via IoT Telemetry
- Contact: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cerec Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
