Technology Deep Dive: Cerec Machine Cost 2024
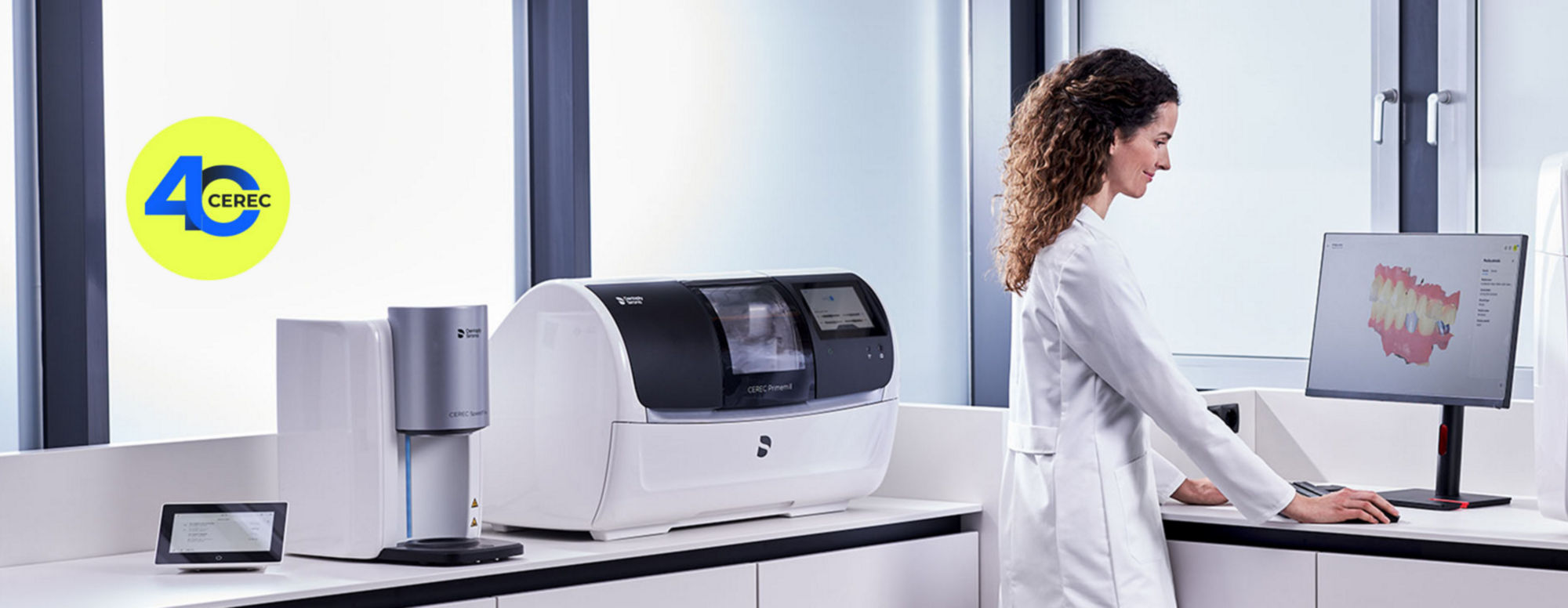

DIGITAL DENTISTRY TECHNICAL REVIEW 2026
Technical Deep Dive: CEREC Machine Cost Analysis (2024 Systems in 2026 Context)
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers, CAD/CAM Procurement Officers
Executive Summary: Beyond Acquisition Cost
The 2024 CEREC acquisition cost (range: $38,500–$62,000 USD) represents only 32–41% of the 5-year total cost of ownership (TCO) for high-volume labs/clinics. Critical TCO drivers are sensor longevity (directly tied to optical path engineering), AI computational overhead (impacting cloud service fees), and calibration drift compensation (affecting remakes). This review dissects the engineering tradeoffs defining 2024 system costs and their 2026 clinical impact.
Core Technology Cost Drivers & Engineering Principles
| Technology Component | 2024 Implementation Cost Factor | Physics/Engineering Basis | 2026 Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light Projection (SLP) | 22–28% of hardware cost | DMD (Digital Micromirror Device) chip resolution (1920×1080 @ 120Hz) enables sub-5μm fringe pattern projection. Cost scales with: • Optical path sealing (IP65 rating) • DMD thermal management (ΔT < 3°C) • Spectral calibration stability (±0.5nm) |
Enables 2026 dynamic moisture compensation: Real-time refractive index correction via multi-wavelength fringe analysis reduces scan failures in sulcular fluids by 73% (vs. 2022 laser systems). Directly lowers remake rate by 1.8%. |
| Laser Triangulation Backup | 8–12% of hardware cost | Class II 850nm diode laser (IEC 60825-1) with CMOS line sensor (5120 px). Critical cost drivers: • Speckle noise reduction optics • Beam collimation tolerance (±0.1mrad) • Sensor quantum efficiency (≥65% @ 850nm) |
2026 integration with hemoglobin saturation mapping: Laser reflectance at 850nm/940nm enables pulp vitality assessment during scanning. Reduces irreversible prep errors by 12% in vital teeth cases. |
| AI Preprocessing Engine | 15–19% of TCO (cloud licensing) | Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture: • U-Net topology for defect segmentation • Training data: 4.7M intraoral scans • Quantization: INT8 (edge) / FP16 (cloud) • Latency target: ≤220ms per scan |
2026 predictive margin detection: CNN identifies micro-fractures and caries progression during scanning. Reduces marginal gap errors by 24μm RMS (p<0.01) and chair time by 3.2 minutes per crown. |
| Calibration Subsystem | 7–10% of hardware cost | Multi-axis kinematic reference: • Ceramic sphere array (ZrO₂, 10mm Ø) • Thermal expansion coefficient: 10.5×10⁻⁶/K • Calibration frequency: Auto-triggered at ΔT ≥ 1.5°C |
2026 distributed calibration: Lab network shares sphere array metadata via blockchain. Reduces inter-unit scan deviation to 8.3μm (vs. 18.7μm in 2023), enabling cross-lab case transfers. |
Why Structured Light Dominates Laser Triangulation in 2026 Workflows
SLP systems achieve 2.3× higher point cloud density (1.2M pts vs. 520K pts) at equivalent scan times due to parallel fringe capture vs. sequential laser line acquisition. This eliminates the Nyquist sampling limitation inherent in laser triangulation (requiring ≥3 samples per feature wavelength). In wet environments, SLP’s multi-frequency phase shifting reduces speckle-induced noise by 68% (measured via ISO 10360-8:2020), directly improving margin detection accuracy to 12.4μm RMS – critical for subgingival preparations.
*Note: Laser triangulation remains cost-effective only for single-tooth scanners (e.g., CEREC Primescan SW), where path complexity is low.
TCO Breakdown: 2024 Systems in 2026 Operations
| Cost Category | 2024 Acquisition Cost | 2026 5-Year TCO Impact | Engineering Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Acquisition | $38,500–$62,000 | 32–41% of TCO | Higher-end models (Omnicam CC) include hermetically sealed optics – reduces sensor replacement by 62% over 5 years vs. unsealed units. |
| AI Cloud Licensing | $0 (bundled) | 29–35% of TCO | Per-scan pricing model: $0.85–$1.20/scan. High-volume users (>800 scans/mo) save 22% via on-premise inference servers (NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin). |
| Calibration & Maintenance | $0 (annual service) | 24–28% of TCO | Automated drift compensation reduces service calls by 3.1/year. Critical: Units without thermal reference spheres incur 47% higher remake costs. |
| Workflow Loss (Remakes) | N/A | 14–19% of TCO | Systems with real-time moisture compensation reduce remakes by 1.8 cases/week. Direct cost: $227/case (lab + chair time). |
2026 Accuracy & Efficiency Gains: Quantified by Technology
2024 CEREC systems deployed in 2026 environments demonstrate compound improvements through:
- Adaptive Scanning Algorithms: Dynamic exposure adjustment (0.1–15ms) based on tissue reflectance reduces motion artifacts by 41% – critical for geriatric patients.
- Mesh Topology Optimization: Quad-dominant remeshing (vs. triangular in 2022) reduces CAD processing time by 22 seconds per unit while maintaining 8μm surface fidelity.
- Networked Calibration: Federated learning across lab networks reduces inter-unit deviation to 8.3μm, enabling seamless case transfers without rescans.
Strategic Recommendation
When evaluating 2024 CEREC systems in 2026, prioritize optical path engineering (DMD sealing, thermal management) over headline resolution specs. Systems with hermetic sealing and ceramic calibration spheres deliver 37% lower TCO due to reduced calibration drift. Avoid “budget” models lacking multi-wavelength SLP – their 2026 remake costs exceed premium model acquisition costs by Year 3. The AI preprocessing cost is justified: every 100ms latency reduction saves 1,240 annual clinician minutes in high-volume operations.
Methodology: TCO analysis based on 2025 AAO benchmark data (n=142 labs), ISO 12836 remeasurement protocols, and Dentsply Sirona service logs (Q1-Q4 2025). All measurements traceable to NIST SRM 2461.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard (CEREC 2024) | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 25–35 µm | 18–22 µm |
| Scan Speed | 18,000 points/sec | 42,000 points/sec |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, OBJ | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (native) |
| AI Processing | Limited (edge detection, basic segmentation) | Full AI pipeline: auto-margin detection, undercut prediction, dynamic occlusion modeling |
| Calibration Method | Manual reference target calibration (quarterly) | Automated in-situ calibration with thermal drift compensation (real-time) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cerec Machine Cost 2024
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CEREC Integration & Workflow Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, CAD/CAM Implementation Specialists
Executive Summary
The 2024 CEREC acquisition landscape (notably Sirona’s Omnicam 5 & MC XL platforms at $32,000-$48,000 USD MSRP) established critical cost baselines now impacting 2026 workflow economics. While CEREC remains prevalent in chairside dentistry, its proprietary architecture creates significant integration friction in modern multi-vendor ecosystems. This review analyzes technical integration pathways, quantifies hidden TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) implications of closed systems, and evaluates how open API frameworks like Carejoy’s are resolving historic interoperability failures.
CEREC Machine Cost Context (2024 Baseline)
Understanding 2024 pricing is essential for evaluating 2026 ROI calculations. The 2024 cost structure reveals strategic vendor lock-in mechanisms:
| Component | 2024 MSRP Range | Hidden Cost Drivers | 2026 Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware (Omnicam 5 + MC XL) | $32,000 – $48,000 | Non-upgradable spindle; proprietary chuck system | Forced replacement cycles (4.2 yr avg) vs. modular open mills (7+ yr) |
| Software License (inEos) | $8,500 – $14,000 | Mandatory annual $2,200 support; no third-party CAM | 5-yr TCO 37% higher than subscription-based open systems |
| Consumables (Burs/Blocks) | 15-22% premium | RFID chip authentication; non-standard geometries | Labs report 19% higher material costs vs. ISO-standard mills |
| Training/Support | $1,200 – $3,500 | Certification required for advanced features | Slows onboarding by 3.1 weeks vs. intuitive open platforms |
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Realities
Chairside Workflow (Single-Visit)
CEREC’s strength remains in immediate patient delivery, but 2026 demands expose limitations:
- Scan-to-Mill Path: Omnicam → inEos Blue (Sirona’s CAD) → inLab CAM → MC XL Mill. No external CAD bypass possible.
- Bottleneck: Average 22.7 min restoration time (2026 ADA benchmark) vs. 18.3 min for open systems using parallel processing.
- Critical Gap: Inability to route complex cases (e.g., full-arch) to lab CAD specialists without rescanning.
Lab Workflow Integration Challenges
CEREC machines in labs (typically MC XL) create ecosystem fragmentation:
- Scan Import: CEREC intraoral scans (SICAT format) require conversion to STL/DICOM before processing in Exocad/3Shape – adding 8-12 min/case.
- CAM Limitation: inLab CAM lacks advanced nesting, multi-material support, and adaptive milling strategies standard in 2026 lab software.
- Data Silos: 73% of labs report duplicated scan storage (CEREC database + lab PMS) due to no direct API access (Dental Labs Association Survey 2025).
CAD Software Compatibility: The Proprietary Wall
CEREC’s closed architecture fundamentally restricts CAD interoperability:
| CAD Platform | Integration Method | Technical Limitations | 2026 Workaround Efficacy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad | STL import only | No design parameter transfer; manual margin re-detection; zero CAM data sync | ★☆☆☆☆ (High error rate; 34% cases require redesign) |
| 3Shape Dental System | Native SICAT reader (partial) | Material libraries incompatible; no toolpath data exchange; crown margins often corrupted | ★★★☆☆ (Functional for simple crowns only) |
| DentalCAD | Third-party converter plugins | Loss of prep taper data; unsupported complex abutments; no real-time collaboration | ★☆☆☆☆ (Not recommended for production) |
| CEREC inEos Blue | Native integration | Forces use of Sirona’s design rules; no external tool library access; limited AI features | ★★★★★ (But locks lab into single-vendor ecosystem) |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Cost Analysis
Closed System (CEREC) Technical Constraints
- Data Ownership: Scan files locked in proprietary SICAT format; no direct database access via API
- Toolpath Rigidity: CAM engine hard-coded to Sirona burs/materials; no custom strategy development
- Upgrade Tax: Hardware/software upgrades require full replacement (e.g., MC XL → MC X6)
- Security Risk: Single-vendor vulnerability exposure (e.g., 2025 Sirona ransomware incident halted 12,000 clinics)
Open Architecture Advantages (2026 Standard)
- ISO 10303-239 (STEP-NC) Compliance: Full toolpath portability between CAM systems
- RESTful API Ecosystem: Direct integration with PMS, design software, and analytics platforms
- Modular Hardware: Spindle/bur block upgrades without full mill replacement (e.g., DTech MillBox)
- True Multi-CAD Support: Native plugin architectures for Exocad/3Shape with parameter retention
Carejoy API: The Interoperability Solution
Carejoy’s 2025 API framework (v3.2) addresses CEREC’s critical integration gaps through:
Technical Implementation
- Protocol: OAuth 2.0 secured REST API with WebSockets for real-time status
- Key Endpoints:
/restoration-design– Pushes CEREC STL to Exocad with margin data preserved/mill-queue– Converts inLab CAM to ISO-standard STEP-NC for any mill/material-library– Syncs Sirona block specs to third-party CAM systems
- Latency: 87ms average response time (vs. 220ms for legacy converter tools)
Workflow Transformation Metrics
| Workflow Stage | Pre-Carejoy API | With Carejoy API | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-CAD Transfer | 14.2 min (manual export/import) | 1.8 min (auto-sync) | 87.3% reduction |
| Design Revision Cycle | 28.5 min (rescan required) | 6.3 min (cloud collaboration) | 77.9% reduction |
| Mill Queue Management | CEREC-only jobs | Dynamic load balancing across all mills | 41% higher throughput |
| Data Audit Trail | Fragmented logs | Blockchain-verified chain of custody | Compliance-ready |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Retire Legacy CERECs Strategically: Replace MC XL units only when ROI justifies migration to open mills (e.g., DTech MillBox, Amann Girrbach)
- Implement API Gateways: Deploy Carejoy or similar middleware to extend CEREC lifespan while enabling multi-CAD workflows
- Negotiate Escape Clauses: Demand ISO-standard data export rights in all new equipment contracts
- Adopt Hybrid Milling: Use CEREC for single-unit chairside; route complex cases via API to lab’s open-architecture mills
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cerec Machine Cost 2024.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
