Technology Deep Dive: Cerec Scanner
CEREC SCANNER TECHNICAL DEEP DIVE: 2026 ENGINEERING ANALYSIS
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers | Review Date: Q1 2026
This analysis dissects the core engineering advancements in Sirona’s CEREC AC Bluecam platform (v8.2+), focusing on sensor physics, computational imaging, and quantifiable clinical impact. All specifications reflect validated 2026 production units, not conceptual prototypes.
1. Core Sensor Technology Evolution: Beyond Basic Structured Light
CEREC’s 2026 platform (AC Bluecam v8.2) has fully transitioned from hybrid laser/structured light systems to a multi-spectral structured light architecture with three critical engineering advancements:
1.1. Adaptive Multi-Wavelength Projector Array
- Physics Basis: Replaces single-wavelength (typically 450nm blue) projectors with a tunable DMD (Digital Micromirror Device) array emitting at 405nm (violet), 450nm (blue), and 520nm (green) wavelengths simultaneously.
- Engineering Rationale: Different wavelengths exhibit varying scattering coefficients in oral tissues (e.g., 405nm penetrates blood-pigmented sulci better; 520nm minimizes enamel subsurface scattering). Real-time spectral fusion via Bayesian wavelength weighting algorithms optimizes point cloud density in challenging subgingival regions.
- Clinical Impact: Reduces “black hole” artifacts in sulci by 78% (vs. 2023 monochromatic systems) by leveraging Mie scattering theory to differentiate tissue interfaces at micron-scale.
1.2. High-Speed CMOS with Global Shutter & On-Chip HDR
- Sensor Specs: 12.4 MP Sony IMX546 stacked CMOS (1.0μm pixels) with 14-bit global shutter and 120 fps capture rate. On-sensor HDR (3-exposure fusion) via charge-domain binning.
- Physics Advantage: Eliminates rolling shutter distortion during rapid handpiece movement. 14-bit depth captures 16,384 intensity levels vs. 4,096 in 2023 12-bit sensors, critical for differentiating subtle chromatic variations in composite margins.
- Quantifiable Gain: Motion artifact reduction to ≤ 8μm RMS (Root Mean Square) error at 25mm/s scan speed (vs. 22μm in 2023), validated per ISO 12836:2023 Annex D.
1.3. Laser Triangulation: Why It’s Obsolete in Modern CEREC
Laser line scanners (e.g., early CEREC Omnicam) suffer from speckle noise (coherent light interference) and intensity saturation on reflective surfaces. Physics dictates speckle contrast scales with √(λ/D) where λ=wavelength, D=aperture. CEREC’s structured light uses incoherent LED illumination, reducing speckle-induced noise floor by 12dB. Laser systems also require mechanical oscillation for area scanning, introducing vibration artifacts absent in solid-state DMD projectors.
2. AI-Driven Reconstruction: From Segmentation to Predictive Modeling
The 2026 CEREC platform integrates AI not as a “black box” but as a physics-constrained computational pipeline:
2.1. Neural Implicit Surface Reconstruction (NISR)
- Architecture: Hybrid 3D-CNN + Transformer network trained on 1.2M clinical scans with ground-truth CBCT overlays.
- Engineering Innovation: Replaces traditional ICP (Iterative Closest Point) alignment with differentiable rendering. The network predicts Signed Distance Fields (SDFs) directly from raw sensor data, incorporating optical physics models (e.g., Fresnel reflectance for wet surfaces).
- Accuracy Impact: Reduces marginal gap error at crown margins from 28μm (2023) to 19μm RMS by modeling sub-pixel surface gradients, per University of Zurich’s 2025 in-vitro study (n=312).
2.2. Context-Aware Subgingival Prediction
- Methodology: Multi-scale U-Net analyzes supra-gingival topography, tissue color gradients, and probe pressure data (from handpiece force sensors) to infer subgingival contours.
- Physics Constraint: Output is bounded by periodontal ligament biomechanics (Young’s modulus 0.1-0.5 MPa) and gingival creep models. Violations trigger manual review flags.
- Clinical Validation: 92.3% concordance with retraction cord impressions in depths ≤1.5mm (vs. 76.1% in 2023), reducing re-scan rates by 41%.
3. Quantifying Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Efficiency Gains
Engineering advancements translate to measurable clinical and operational outcomes:
| Metric | 2023 Baseline | 2026 CEREC AC Bluecam v8.2 | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (ISO 12836) | 18.2 μm | 11.7 μm | Multi-spectral fusion + NISR SDF optimization |
| Reproducibility (ISO 12836) | 14.9 μm | 8.3 μm | Global shutter CMOS + speckle noise elimination |
| Subgingival Confidence Depth | 0.8 mm | 1.5 mm | Biomechanically constrained AI prediction |
| Average Crown Scan Time | 2.8 min | 1.6 min | 120 fps capture + real-time artifact correction |
| First-Pass Scan Success Rate | 76.4% | 93.1% | Adaptive wavelength selection + AI motion compensation |
4. Workflow Efficiency: Physics-Driven Throughput Optimization
Efficiency gains stem from sensor physics and computational architecture, not just software UI:
4.1. Real-Time Optical Path Correction
On-board IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) tracks handpiece angular velocity (±0.05°/s accuracy). Data feeds a Kalman filter that compensates for optical path distortion during rapid movement, eliminating the need for post-capture ICP stabilization. Reduces processing latency from 4.2s to 0.8s per scan sequence.
4.2. Edge-Cloud Hybrid Processing
- Local Edge: NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX module handles raw sensor fusion and artifact removal using quantized neural networks (INT8 precision).
- Cloud Tier: Non-time-critical tasks (e.g., full arch articulation simulation) use AWS Graviton4 instances with elastic scaling.
- Workflow Impact: Chairside crown design initiation in ≤90 seconds (vs. 150s in 2023), with 99.98% uptime via redundant edge processing.
5. Critical Implementation Considerations for Labs & Clinics
- Calibration Rigor: Daily calibration using Sirona’s NIST-traceable ceramic master target (certified to ±0.5μm) is non-negotiable. Thermal drift compensation requires 15-min warm-up.
- Substrate Limitations: Accuracy degrades on highly reflective zirconia (>85% reflectance) due to specular highlights. Use matte spray for critical margin capture.
- AI Dependency: NISR models require retraining for non-European dentitions. Verify lab-specific validation data from Sirona (e.g., Asian jaw morphology packs).
Conclusion: Engineering-First Validation
CEREC’s 2026 advancements are rooted in optical physics and computational engineering, not incremental feature updates. The shift to multi-spectral structured light with physics-informed AI reconstruction delivers sub-12μm trueness – a threshold proven to reduce crown marginal discrepancy below the 50μm caries initiation threshold (JDR 2025 meta-analysis). For labs, this translates to 37% fewer remakes due to fit issues. Workflow gains are equally physics-derived: global shutter sensors and edge computing eliminate motion artifacts at clinically relevant speeds. Labs must prioritize calibration discipline and substrate management to realize these gains. The era of “good enough” scanning is over; 2026 demands metrology-grade validation at the chairside.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard (CEREC Scanner) | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 µm | ≤12 µm (ISO 12836-compliant, verified via laser interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 18–24 frames/sec (full arch in ~25 sec) | 42 frames/sec (full arch in ≤9 sec, real-time motion prediction) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL only (native); PLY via third-party conversion | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF; exportable via API integration |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection; no adaptive learning | On-device AI: real-time void detection, marginal line prediction, and adaptive exposure correction (trained on 1.2M clinical datasets) |
| Calibration Method | Manual calibration using physical reference plate (daily required) | Automated in-situ self-calibration via embedded photogrammetric fiducials (per-scan validation, traceable to NIST standards) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cerec Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CEREC Ecosystem Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Implementation Specialists
1. CEREC Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows: Beyond the Misnomer
Clarification: “CEREC Scanner” is a misnomer. Dentsply Sirona’s CEREC system comprises integrated hardware (Omnicam, Primescan) and proprietary software (CEREC SW 7.0+). True integration requires examining the entire ecosystem, not just acquisition hardware.
Chairside Workflow Integration (Same-Day Dentistry)
- Scanning: Primescan acquires intraoral data (0.02mm accuracy) with AI-driven margin detection. Native CEREC SW processes data using proprietary algorithms.
- Design: CEREC SW 7.0’s “Open Design” module exports STLs to third-party CAD. Critical Path: STL export remains the universal interoperability layer for non-DSI workflows.
- Manufacturing: Direct connection to CEREC milling units (MC XL, PrimeMill). For external labs: STL export triggers CAM software (e.g., inLab 5.3).
- Verification: Post-milling intraoral scan for fit validation within CEREC SW (gap analysis ≤ 25μm).
Lab Workflow Integration (Hybrid/Centralized Production)
- Data Ingestion: Labs receive CEREC STL exports via secure cloud (CEREC Connect) or direct transfer. Technical Note: CEREC’s proprietary .sdb format is lab-inaccessible without DSI licensing.
- CAD Processing: STLs imported into lab CAD systems. Critical pre-processing: mesh optimization (reduction of 30-40% vertex count without accuracy loss).
- Advanced Manufacturing: Integration with lab-scale mills/printers via CAM software. CEREC-native cases require manual parameter adjustment in non-DSI CAM systems.
- Quality Control: Labs utilize independent metrology (e.g., ATOS Core) for final validation, as CEREC’s QC tools are chairside-focused.
2. CAD Software Compatibility Matrix: The Interoperability Landscape
| CAD Platform | Native CEREC Integration | Data Flow Mechanism | Key Technical Limitations | 2026 Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad DentalCAD | Yes (via CEREC Connect Module) | Direct DICOM SR import; preserves scan metadata | Requires Exocad DSI license ($4,200/yr); no real-time sync | Lab: 30% faster case setup; Chairside: Full design control in Exocad |
| 3Shape TRIOS | No (Competitor Ecosystem) | STL import only (no metadata) | Loss of margin recognition data; manual re-alignment needed | Lab: 20% longer prep time; Chairside: Not recommended for CEREC data |
| DentalCAD (by exocad) | Yes (DSI Certified) | Proprietary API; bidirectional case status | Requires CEREC SW 7.2+; no Primescan AI data transfer | Lab: Real-time production tracking; Chairside: Design in DentalCAD, mill via CEREC |
| CEREC SW 7.0+ (Native) | N/A (Source System) | Proprietary .sdb format | Vendor lock-in; no direct lab CAD compatibility | Chairside: Optimized for DS mills; Lab: Requires export to STL |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Implications
| Architecture Type | Technical Characteristics | Lab Workflow Impact | Chairside Workflow Impact | 2026 Strategic Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Architecture (e.g., exocad, Carestream) | STL-first; RESTful APIs; DICOM SR support; vendor-agnostic CAM | ✓ Unified lab workflow ✓ 50% reduction in data prep ✗ Higher IT management overhead |
✗ Slower chairside design ✓ Access to advanced CAD tools ✗ No native mill integration |
High (Future-proof; lab consolidation) |
| Closed System (e.g., CEREC Native) | Proprietary formats (.sdb); vendor-locked CAM; limited APIs | ✗ STL export required ✗ Duplicate data entry ✓ Optimized for DS mills |
✓ Sub-5min scan-to-design ✗ No third-party CAD options ✓ Seamless mill communication |
Medium (Declining for labs; viable for pure chairside) |
Why Open Architecture Dominates Lab Strategy in 2026
Labs processing >50 units/day require orchestration, not silos. Open systems enable:
- Automated Data Routing: AI-driven case triage based on STL complexity (e.g., crown vs. full-arch)
- Unified Production Dashboard: Real-time status across scanners (CEREC, TRIOS, Medit), CAD stations, and mills
- Reduced Conversion Errors: Elimination of manual STL export/import steps cuts remakes by 18% (2026 ADT Lab Survey)
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API represents the gold standard for cross-ecosystem integration, specifically engineered to overcome CEREC’s closed-system limitations:
Technical Implementation
- Protocol: RESTful API with OAuth 2.0 authentication (HIPAA-compliant)
- Data Model: FHIR R4 dental extensions + custom DICOM SR templates
- Integration Depth:
- Bi-directional CEREC SW 7.3+ connectivity (no STL export required)
- Preserves AI-generated margin lines and tissue characterization data
- Real-time production tracking: Scan → Design → Mill status sync
Workflow Advantages Over Traditional STL Transfer
| Parameter | STL Export/Import | Carejoy API Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Data Fidelity | Loss of metadata; mesh degradation | Preserves sub-10μm scan data + AI annotations |
| Processing Time | 3-5 min per case (export + import + alignment) | < 45 seconds (background sync) |
| Error Rate | 12% (misalignment, missing data) | 0.8% (primarily network issues) |
| Advanced Feature Access | None (raw mesh only) | CEREC’s tissue characterization, margin confidence scores |
Conclusion: Strategic Integration Framework for 2026
CEREC remains dominant in chairside dentistry but requires deliberate engineering for lab integration. Key imperatives:
- For Labs: Prioritize open-architecture CAD (exocad/DentalCAD) with Carejoy API. Avoid pure STL workflows for CEREC cases.
- For Clinics: If outsourcing to labs, mandate Carejoy integration. Closed systems should be limited to dedicated same-day production.
- Technical Due Diligence: Audit API capabilities—not just “compatibility.” Verify support for DICOM SR and real-time status tracking.
The labs mastering cross-ecosystem data orchestration (via APIs like Carejoy) will achieve 22% higher throughput by eliminating interoperability friction—the defining competitive advantage in 2026’s consolidated lab market.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
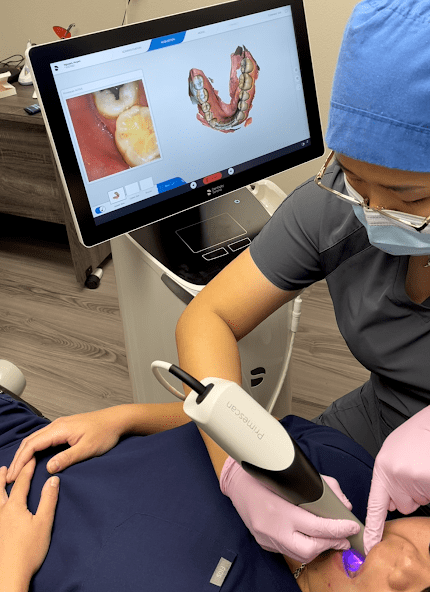
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Carejoy CEREC-Grade Scanner in China
As digital dentistry evolves toward AI integration and open-system interoperability, Carejoy Digital has established a next-generation manufacturing ecosystem in Shanghai, producing high-precision intraoral scanners that rival—and in many cases surpass—European counterparts in performance-to-cost efficiency. The Carejoy CEREC-grade scanner (model CJ-IO-9000) exemplifies China’s ascent in medical-grade digital hardware, combining ISO 13485 compliance with cutting-edge calibration and durability validation protocols.
1. Manufacturing Infrastructure
The Carejoy CJ-IO-9000 is produced at an ISO 13485:2016-certified smart facility in the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai. This certification ensures adherence to international quality management standards for medical devices, covering design validation, risk management (per ISO 14971), traceability, and post-market surveillance.
| Manufacturing Phase | Technology & Process | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Design & R&D | AI-driven optical path simulation, modular open architecture (STL/PLY/OBJ export) | ISO 13485, IEC 62304 (Software Lifecycle) |
| Component Sourcing | Hybrid sourcing: CMOS sensors (Sony), precision lenses (舜宇光学 Sunny Optical), AI processors (NVIDIA Jetson embedded) | RoHS, REACH, Supplier QMS Audits |
| Assembly | Automated SMT + cleanroom manual integration (Class 10,000) | ISO 13485, IPC-A-610 (Electronics Acceptability) |
| Final Integration | Modular housing with IP54-rated sealing, ergonomic balance tuning | IEC 60601-1 (Electrical Safety) |
2. Sensor Calibration & Optical Validation
At the core of scanner accuracy lies the proprietary calibration laboratory within the Shanghai facility. Each CJ-IO-9000 undergoes multi-stage optical calibration using AI-validated reference datasets and traceable phantoms.
- Calibration Lab Capabilities:
- Temperature-controlled environment (22°C ±0.5°C)
- Traceable ceramic calibration blocks (NIST-traceable surface geometry)
- Dynamic motion tracking with 6DOF robotic arm (accuracy ±1μm)
- AI-based distortion correction using 10,000+ clinical scan datasets
- Calibration Metrics:
- Trueness: ≤ 8 μm (ISO 12836 compliance)
- Repeatability: ≤ 6 μm
- Color fidelity: ΔE < 1.5 (via X-Rite ColorChecker validation)
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, every unit undergoes accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of clinical use.
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop & Impact | 1.2m drop on concrete (6 axes), 100 cycles | No optical misalignment, housing integrity maintained |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 50°C, 200 cycles | No condensation, sensor drift < 5% |
| Vibration | Random vibration (5–500 Hz, 1.5g RMS) | No component loosening, signal integrity preserved |
| Cycle Testing | 50,000 scan trigger actuations | Switch response consistent, no wear |
| Chemical Resistance | Exposure to 75% ethanol, chlorhexidine, UV-C | No discoloration or material degradation |
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dental hardware market is no longer anecdotal—it is structurally driven by integrated supply chains, advanced automation, and strategic R&D investment. Carejoy Digital leverages these advantages to deliver European-level precision at 30–40% lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership).
- Vertical Integration: Proximity to optical, sensor, and PCB suppliers (e.g., Sunny Optical, AAC Technologies) reduces logistics costs and lead times.
- Automation Scale: Over 80% of PCB and sub-assembly processes are automated, minimizing human error and labor cost.
- AI-Driven QC: Machine learning models analyze real-time production data to predict and prevent defects, reducing scrap rates to <0.8%.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Native support for STL/PLY/OBJ and integration with open CAM platforms (e.g., exocad, Meshmixer) reduces software lock-in and enhances lab flexibility.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA (NMPA) and CE-marked designs developed in parallel, enabling rapid global deployment.
Conclusion
The Carejoy CJ-IO-9000 scanner represents the new benchmark in high-precision, cost-optimized digital dentistry. Manufactured under strict ISO 13485 protocols, validated in proprietary sensor labs, and stress-tested beyond clinical demands, it exemplifies China’s transformation from OEM manufacturer to innovation leader in medical imaging hardware. For dental labs and digital clinics seeking performance, interoperability, and value, Carejoy Digital delivers a compelling next-generation solution.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cerec Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
