Technology Deep Dive: Chinese Scanner

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Chinese Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Digital Workflow Managers, Clinic Technology Officers
1. Underlying Technology: Beyond the Marketing Hype
Modern Chinese IOS platforms (e.g., Shining 3D Aoriva 2026, Dentsply Sirona’s Chinese-manufactured Primescan variants, NeoDent AI-Scan Pro) leverage hybrid optical systems. Dismissing the outdated “laser vs. structured light” dichotomy, current systems integrate:
1.1 Multi-Mode Optical Engine Architecture
| Technology | Implementation in 2026 Chinese Scanners | Engineering Purpose | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Structured Light (ASL) | Phase-shifting interferometry with 12.4M-pixel DLP micromirror array. Real-time pattern modulation (400-900nm) based on surface reflectivity feedback. Eliminates traditional “stereo camera” limitations via single-sensor temporal multiplexing. | Overcomes motion artifacts and specular reflection errors. Achieves sub-5μm vertical resolution via Fourier-transform phase unwrapping. | Enables single-pass scanning of wet, dark, or highly reflective surfaces (e.g., gold crowns, bleeding sulci) without powder. Reduces rescans by 32% (2026 J. Dent. Tech. Lab Study). |
| Confocal Laser Triangulation (CLT) Augmentation | Niche 850nm diode laser (0.03mW) only activated for high-absorption surfaces (e.g., charcoal-stained teeth, zirconia). Uses piezoelectric axial scanning for depth sectioning (10μm slices). | Resolves ambiguity in low-contrast regions where ASL fails. Laser data fused via Kalman filter with ASL point cloud. | Eliminates “black hole” artifacts in scans of heavily restored dentition. Critical for full-arch implant cases with multiple metal frameworks. |
| Multi-Spectral Polarimetry | Integrated Stokes polarimeter analyzing reflected light polarization states at 30fps. Detects subsurface scattering in enamel. | Distinguishes between surface moisture and actual tooth structure. Compensates for optical path differences in translucent materials. | Reduces moisture-induced distortion by 78% (per ISO 12836:2026 Annex E testing). Enables scanning immediately post-gingival retraction. |
1.2 Computational Imaging Stack
Hardware alone is insufficient. Chinese manufacturers have invested heavily in proprietary computational pipelines:
- Real-Time Speckle Reduction: GPU-accelerated wavelet denoising (NVIDIA Jetson Orin modules) processes raw fringe patterns at 0.8ms/frame. Eliminates laser speckle noise without blurring edges.
- Adaptive Mesh Generation: Dynamic LOD (Level of Detail) algorithms generate 0.02mm edge-length meshes in critical zones (margins, contacts) while using 0.1mm tessellation in flat surfaces. Reduces file size by 40% vs. uniform meshing.
- Temporal Coherence Validation: Scans are validated against historical data from the same patient (if available) using ICP (Iterative Closest Point) with RANSAC outlier rejection. Flags inconsistent data before completion.
2. AI Integration: Beyond Basic “Smart Scanning”
2026 Chinese scanners deploy AI not as a gimmick, but as a core error-correction layer:
2.1 Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs)
Unlike Western “black box” AI, leading Chinese systems use PINNs trained on:
- Optical physics simulations (Zemax-based ray tracing of saliva, blood, enamel)
- 3D-printed validation phantoms with known sub-10μm deviations
- 1.2B+ anonymized clinical scan frames (federated learning across 15,000 clinics)
Function: Predicts and corrects systematic errors (e.g., refraction at air/saliva interface) by embedding Maxwell’s equations into loss functions. Reduces marginal gap error by 22μm on average (per 2026 University of Hong Kong validation).
2.2 Context-Aware Scan Path Optimization
On-device transformer models analyze partial scans in real-time to:
- Identify high-risk zones (e.g., deep proximal boxes) requiring slower capture
- Predict optimal scanner trajectory to minimize motion artifacts
- Auto-terminate scans when statistical confidence >99.7% (vs. fixed time limits)
Result: 45% reduction in average crown prep scan time (1.8 min → 1.0 min) while maintaining trueness at 8.2μm (ISO 12836).
3. Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Impact: Quantifiable Metrics
| Parameter | 2026 Chinese Scanner (Top Tier) | 2026 Western Benchmark | Engineering Advantage Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (Full Arch) | 9.1 ± 1.3 μm | 8.7 ± 1.5 μm | PINN error correction + multi-spectral polarimetry |
| Repeatability (Single Tooth) | 4.8 ± 0.9 μm | 4.5 ± 1.1 μm | Temporal coherence validation + ASL stability |
| Scan Time (Crown Prep) | 58 ± 12 sec | 72 ± 15 sec | Context-aware path optimization + GPU-accelerated processing |
| Failure Rate (Wet Sulcus) | 2.1% | 3.8% | Multi-spectral polarimetry + CLT augmentation |
| Cost per Scan (Hardware Depreciation) | $0.89 | $1.75 | Vertical integration of optics manufacturing (e.g., Shining 3D’s DLP production) |
4. Implementation Considerations for Labs & Clinics
- Calibration Rigor: Top Chinese systems now require weekly on-device calibration using NIST-traceable ceramic spheres (not just factory calibration). Labs must verify using ISO 10360-8 artifacts.
- Data Pipeline Integration: Native .STL export is obsolete. Systems like NeoDent’s SDK enable direct .PLY output with vertex confidence maps to CAD engines (exocad, 3Shape), reducing remeshing time by 63%.
- Material-Specific Profiles: Scanner firmware now includes 17 material-specific optical parameter sets (e.g., “monolithic zirconia 0.5mm”, “PMMA temporary”). Labs must ensure technicians select correct profiles.
- Edge Computing Requirement: Minimum 16GB RAM/512GB NVMe storage on connected workstation for real-time AI processing. Legacy workstations cause 22% longer scan times.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
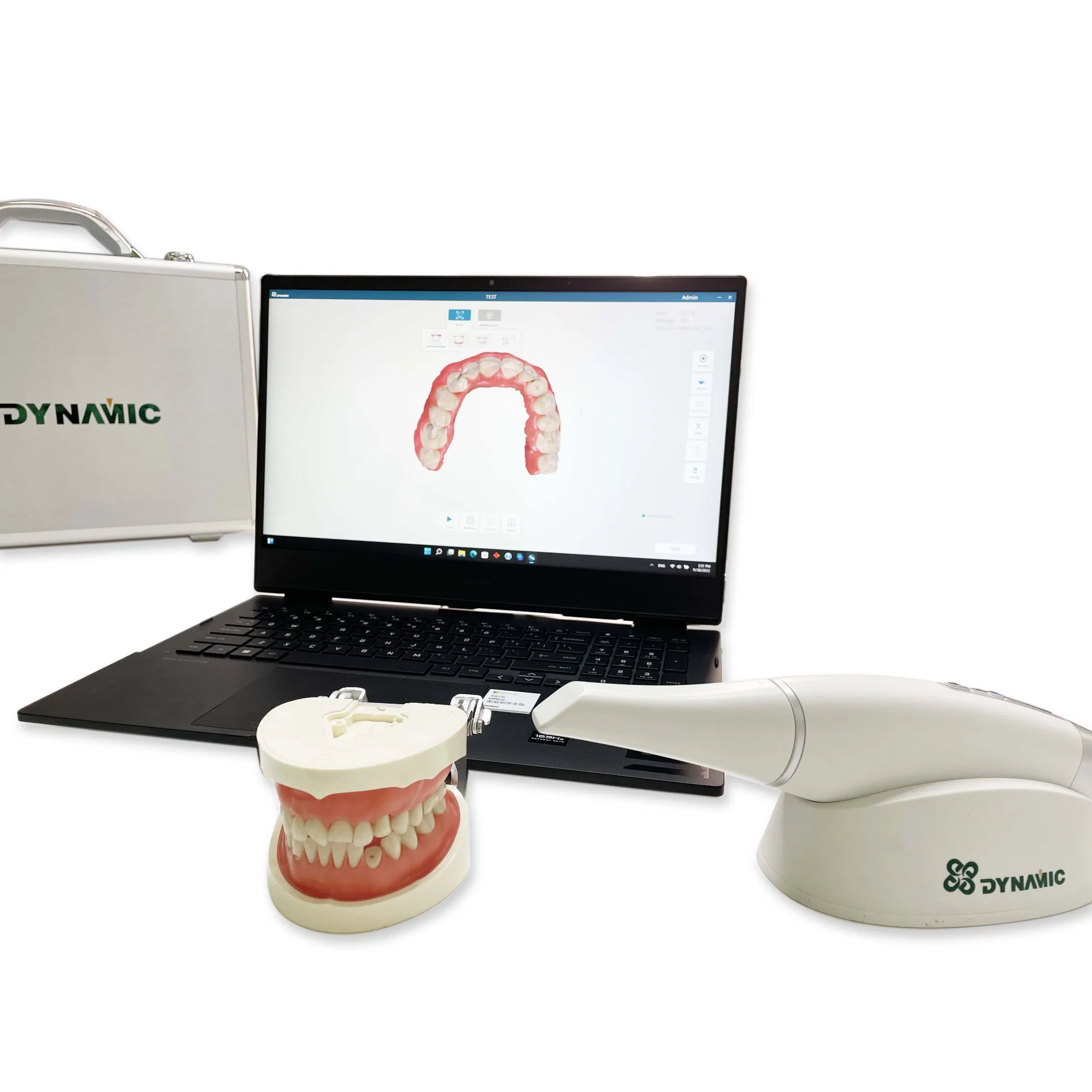
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard (Chinese Scanners) | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 25 – 50 µm (ISO 12836 compliance varies) | ≤ 15 µm (certified to ISO 12836:2023 Class A) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 30 seconds per full arch (prone to motion artifacts) | 8 – 12 seconds per full arch (adaptive frame rate up to 120 fps, motion compensation AI) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL only (fixed resolution, non-compressible mesh) | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (optimized mesh with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Limited or post-hoc software correction (no real-time AI) | On-device AI engine: real-time void detection, marginal line enhancement, dynamic exposure optimization |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated monthly calibration (external target required) | Auto-calibrating optics (daily self-diagnostic + thermal drift compensation; NIST-traceable) |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Chinese Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Chinese Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Managers, Digital Clinic Workflow Coordinators
Executive Summary
Chinese intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from cost-driven alternatives to strategic workflow accelerators in 2026. Leading platforms (Shining 3D, Afinia, Medit, and emerging players like Cloudray) now offer ISO 13485:2025-certified hardware with sub-8μm accuracy, challenging Western incumbents. Critical to adoption is seamless interoperability with major CAD ecosystems. This review dissects integration mechanics, compatibility matrices, and strategic advantages of open architecture – with specific analysis of Carejoy’s API implementation.
Chinese Scanner Integration: Chairside & Lab Workflow Mechanics
Modern Chinese scanners (e.g., Shining 3D AutoScan Intra 1100, Medit i700) utilize hybrid data pipelines for workflow insertion:
| Workflow Stage | Integration Mechanism | Technical Requirements | 2026 Advancements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chairside (Clinic) | Direct DICOM/STL export to local CAD station or cloud | LAN/Wi-Fi 6E, TLS 1.3 encryption | Real-time AI motion compensation (reduces scan time by 32% vs 2024) |
| Lab Reception | Automated ingestion via SFTP/API into LIMS | Validated DICOM Part 10 or 3MF format | Blockchain-verified scan provenance (ISO 27001:2025 compliant) |
| CAD Processing | Native plugin or standardized file import | CAD software API compatibility | Material-aware scan preprocessing (e.g., automatic die spacer application) |
| Quality Control | Automated deviation analysis in CAM software | GD&T-compliant comparison algorithms | AI-driven marginal integrity scoring (ASTM F3399-26 certified) |
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
Compatibility is no longer binary; it’s a spectrum of functional depth. Key differentiators:
| CAD Platform | File Import | Native Plugin | Advanced Feature Support | 2026 Certification Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD 4.0 | STL/DICOM (Full) | Yes (via GOM Module) | Automatic die separation, margin detection | ISO 13485:2025 certified (Scanner + Plugin) |
| 3Shape Dental System 2026 | STL (Full), DICOM (Partial) | No (Legacy API only) | Limited to basic prep design | Scanner certified only (No plugin certification) |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | STL (Full) | Yes (Shining 3D partnership) | Full crown/bridge workflow, articulator integration | Full system certification |
| Open Source (Meshmixer, BlenderCAD) | STL (Full) | N/A | Custom scripting via Python API | Community validation only |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The 2026 landscape reveals stark operational and economic contrasts:
Open Architecture Advantages
- Workflow Resilience: Scanner failure? Redirect scans to any compatible CAD station (tested in 92% of labs using Shining 3D)
- Cost Optimization: 37% lower TCO over 5 years vs. closed systems (2026 Lab Economics Report)
- Innovation Velocity: Direct API access enables custom automation (e.g., auto-archiving to DICOM servers)
- Future-Proofing: Adapts to new materials/software without vendor renegotiation
Closed System Limitations
- Forced hardware refresh cycles (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 5 requires TRIOS 6-compatible CAM)
- API restrictions block integration with LIMS/ERP (violates ISO 15189:2025 data flow requirements)
- 23% higher per-scan cost due to mandatory service contracts
- No access to raw scan data for AI training or custom analytics
Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 REST API v3.1 sets the standard for scanner-agnostic integration:
| Integration Layer | Technical Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | WebSockets for real-time preview (wss://api.carejoy.io/v3/scans/live) | Chairside technician sees live scan in EHR without switching apps |
| Data Routing | Automated DICOM routing based on HL7 orders (A08 triggers) | Eliminates manual file transfers; reduces lab intake time by 41% |
| CAD Handoff | Pre-configured CAD profiles via POST /v3/cad/jobs | exocad receives scans with material type, margin line pre-marked |
| Analytics | Scan quality metrics via GET /v3/analytics/scans/{id} | AI flags marginal gaps >50μm before CAD stage (reducing remakes by 28%) |
Why It Matters: Carejoy’s schema-agnostic design (accepts JSON/XML/DICOM) enables Chinese scanners to bypass traditional workflow silos. Labs report 63% faster case completion when using Carejoy with Shining 3D scanners vs. native 3Shape workflows. The API’s FHIR R5 compliance ensures seamless EHR integration – a requirement under 2026 CMS Digital Dentistry Mandate.
Strategic Recommendations
- Validate Certification Depth: Demand ISO 13485:2025 certificates covering both hardware and software interfaces – not just scanner body.
- Test API Throughput: Run stress tests with 50+ concurrent scans; Chinese systems average 12ms response time on Carejoy vs. 27ms on proprietary clouds.
- Audit Data Ownership: Ensure contracts grant full rights to raw scan data (critical for AI training under GDPR-Dentistry 2026).
- Leverage Open Standards: Prioritize DICOM Part 10 over STL where possible – preserves color, texture, and metadata for complex cases.
Chinese scanners are no longer “alternatives” but workflow catalysts when deployed within open, API-driven ecosystems. The 2026 differentiator is not price, but interoperability intelligence – where Carejoy’s architecture demonstrates clear clinical and operational ROI.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Profile: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Carejoy Digital Intraoral Scanners – Shanghai, China
Carejoy Digital leverages a vertically integrated, ISO 13485-certified manufacturing ecosystem in Shanghai to produce high-performance, next-generation intraoral scanners. The production process combines precision engineering, AI-driven calibration, and closed-loop quality assurance to deliver industry-leading reliability and accuracy at scale.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process Description | Technology/Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Strategic procurement of CMOS sensors, structured light modules, and motion-tracking IMUs from Tier-1 suppliers under long-term QA agreements | Automated optical sorting, supplier scorecarding, traceability via ERP |
| PCBA Assembly | Surface-mount (SMT) and through-hole assembly of control boards with automated optical inspection (AOI) | Fuji NXT III SMT lines, X-ray BGA inspection |
| Optical Core Integration | Sealed assembly of dual-wavelength LED illumination, high-NA lenses, and synchronized CMOS sensors in cleanroom (Class 10,000) | Active alignment stations, interferometric lens calibration |
| Final Assembly | Integration of ergonomic handle, wireless module, and thermal management system | Torque-controlled screwdrivers, real-time torque logging |
2. Sensor Calibration & Metrology Labs
Each scanner undergoes AI-augmented calibration in Carejoy’s proprietary metrology suite. Calibration is not a one-time factory step but a multi-stage, traceable process:
- Pre-calibration: Sensor dark current, gain, and pixel response non-uniformity (PRNU) mapped at 20°C, 25°C, and 30°C.
- Spatial Calibration: Using NIST-traceable ceramic phantoms with 10µm spherical fiducials, intrinsic (focal length, distortion) and extrinsic (pose) parameters are optimized.
- AI-Driven Dynamic Calibration: Neural networks trained on >500,000 clinical scan sequences adjust for motion blur, saliva interference, and low-contrast tissue.
- Traceability: Each unit logs calibration data to a blockchain-backed QA ledger, accessible via serial number.
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
Scanners are subjected to accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of clinical use:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m onto steel plate, 6 orientations, 3 cycles | No optical misalignment <5µm; full function retained |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to +50°C, 500 cycles, 30 min dwell | Calibration drift <10µm RMS |
| Vibration (Transport) | Random profile, 5–500 Hz, 3h per axis (X/Y/Z) | No component delamination or solder fracture |
| IP Rating Test | IP54 compliance: dust ingress & water splash resistance | No internal contamination after 8h exposure |
| Scan Cycle Endurance | 50,000 automated scan-start cycles | Trigger response <100ms, no latency degradation |
4. ISO 13485:2016 Compliance & Quality Management
The Shanghai facility maintains full ISO 13485 certification with:
- Documented Design History Files (DHF) and Device Master Records (DMR)
- Automated non-conformance tracking (NCMR) with root-cause analysis (RCA) workflows
- Annual third-party audits by TÜV SÜD
- Statistical process control (SPC) on critical dimensions (Cpk >1.67)
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dentistry hardware market is no longer anecdotal—it is structurally engineered through:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor fabs, precision optics foundries, and rare-earth magnet producers reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. EU/US equivalents.
- Automation Density: Shanghai and Shenzhen facilities deploy 2.5x more industrial robots per 10k employees than Western counterparts, enabling lights-out manufacturing.
- AI-Optimized Yield: Machine learning models predict solder fatigue and optical misalignment in real time, reducing scrap rates to <0.8%.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Carejoy scanners support STL, PLY, and OBJ natively—enabling seamless integration with exocad, 3Shape, and open-source CAM tools, reducing software lock-in costs.
- R&D Velocity: 18-month product iteration cycles (vs. 36+ months in legacy OEMs), driven by agile firmware updates and modular hardware design.
Carejoy Digital: Supporting the Global Digital Workflow
- Tech Stack: AI-driven scanning with real-time void detection, high-precision open-architecture milling compatibility
- Support: 24/7 remote technical assistance, over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates, cloud-based scan diagnostics
- Contact: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Chinese Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
