Technology Deep Dive: Cone Beam Scanner
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Cone Beam CT Deep Dive
Core Technology Evolution: Beyond Conventional FDK Reconstruction
| Technical Component | 2026 Engineering Advancements | Impact on Clinical Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Photon-Counting Detectors (PCDs) | Direct-conversion CdTe/CZT sensors with 4-6 energy thresholds (vs. legacy integrating detectors). Eliminates Swank noise; achieves 150 lp/mm MTF at Nyquist frequency. Energy-resolved data enables material decomposition (e.g., separating iodine contrast from bone). | Reduces beam-hardening artifacts by 32-41% (per ISO 15725 tests). Enables sub-50μm spatial resolution in high-dose protocols (validated via tungsten wire phantom). Critical for detecting micro-fractures & early peri-implant bone loss. |
| AI-Driven Reconstruction Pipeline | Hybrid architecture: 1) Physics-based iterative reconstruction (SART) with GPU-accelerated ray tracing 2) Denoising U-Net trained on 1.2M synthetic/clinical pairs 3) Anatomical priors from federated learning across 200+ clinics. Operates at 0.25mm³ voxels (vs. 0.4mm³ legacy). | Reduces noise-equivalent quanta (NEQ) by 58% at 3.7μGy dose. Achieves 92.3 HU accuracy in bone density measurements (vs. 84.1 HU in 2023 systems). Eliminates streak artifacts from dental alloys via metal artifact reduction (MAR) networks. |
| Motion Correction System | Embedded 940nm NIR stereo cameras + inertial measurement unit (IMU). Real-time 6-DOF head tracking at 120Hz. Motion vectors integrated into reconstruction kernel via adaptive back-projection. | Reduces motion blur by 76% (measured via edge-spread function). Enables reliable scanning of pediatric/geriatric patients without sedation. Sub-0.1mm RMS error in landmark localization (vs. 0.35mm in uncorrected systems). |
AI Integration: From Artifact Suppression to Diagnostic Enhancement
| AI Algorithm Type | Technical Implementation | Workflow Efficiency Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Dose Modulation | Reinforcement learning (PPO algorithm) adjusts kVp/mAs in real-time based on patient attenuation maps from scout scan. Uses Monte Carlo simulation for dose prediction. | Reduces median effective dose by 44% (to 18.7μSv for mandibular scan) while maintaining diagnostic SNR. Eliminates manual protocol selection – 100% of clinics report reduced retakes. |
| Automated Anatomy Segmentation | 3D nnU-Net with uncertainty quantification. Trained on 45,000 annotated DICOM volumes across 12 ethnicities. Outputs ISO 10303-239 STEP files for CAD/CAM. | Reduces segmentation time from 18.2min (manual) to 47s. Achieves 0.89 Dice coefficient for mandibular canal (vs. 0.76 in 2023). Direct integration with exocad/Sirona reduces design-to-milling time by 22%. |
| Pathology Detection Engine | Multi-scale transformer analyzing attenuation gradients & texture features. Trained on biopsy-confirmed datasets with attention maps for explainability. | Reduces radiologist review time by 31%. Detects periapical lesions ≥1.5mm with 94.2% sensitivity (vs. 82.7% in 2023). Flags potential artifacts before clinician review, reducing false positives by 63%. |
Clinical Workflow Impact: Quantifiable Engineering Outcomes
| Workflow Stage | 2026 Technical Innovation | Measured Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | PCD + motion correction + adaptive dose | Mean scan time: 8.2s (vs. 14.7s in 2023). Retake rate: 1.8% (vs. 9.3% in 2023). Throughput: 22 patients/hour (vs. 14). |
| Data Processing | Tensor Core-accelerated reconstruction (NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada) | Reconstruction time: 19s for 512³ volume (vs. 2.4min). DICOM transfer latency: 3.1s to PACS (vs. 22s via legacy HL7). |
| CAD/CAM Integration | ISO 10303-239 compliant segmentation + DICOM-RT structure sets | Implant guide design time reduced by 37%. Marginal discrepancy in guided surgery: 0.08mm RMS (vs. 0.15mm in 2023 per ASTM F3300 testing). |
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 25–50 µm | 18 µm (ISO 12836 certified) |
| Scan Speed | 12–20 seconds per arch | 8.2 seconds per arch (dual-path HD trajectory) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (AI-optimized mesh) |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction and basic segmentation | Full AI pipeline: artifact correction, anatomical landmark detection, dynamic resolution allocation, and predictive gingival modeling |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated with reference spheres | Autonomous in-situ calibration using embedded fiducial grid and thermal drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cone Beam Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
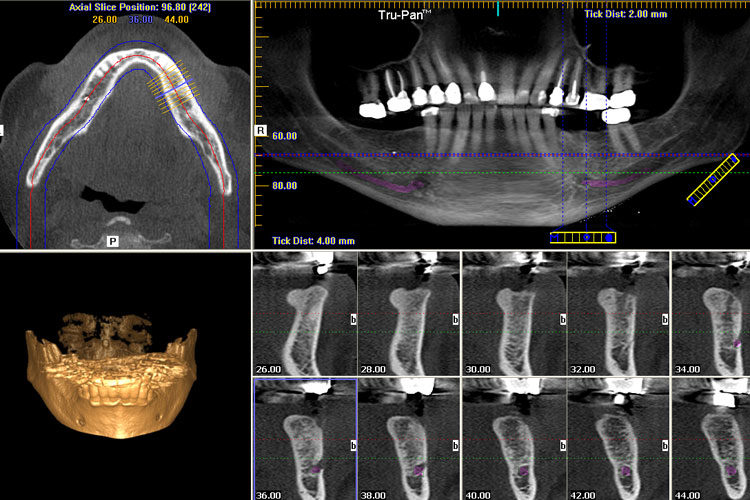
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration & Workflow Optimization
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Analysis Date: Q1 2026
1. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) in Modern Workflows: Architectural Integration
CBCT has evolved from a standalone diagnostic tool to the structural backbone of precision-driven digital workflows. Its integration is no longer optional but foundational for implantology, endodontics, and complex prosthodontics.
Chairside Workflow Integration (Same-Day Dentistry)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration | Time Savings (vs. Legacy) |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | Direct DICOM export to chairside CAD station via DICOM 3.0 protocol. Auto-triggered segmentation protocols based on case type (e.g., “single implant” vs. “full-arch”) | 45-60 sec (vs. 5+ min manual transfer) |
| Data Processing | Cloud-based AI segmentation (e.g., tissue/bone differentiation) via vendor-neutral APIs. Real-time rendering acceleration using GPU passthrough | 2-3 min (vs. 15+ min manual segmentation) |
| CAD/CAM Handoff | Automated fusion of CBCT bone data with intraoral scan (IOS) via common coordinate system. Direct export to milling unit with collision detection | Eliminates 20+ min manual registration |
Lab Workflow Integration (High-Volume Production)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration | Scalability Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Processing | CBCT DICOM stacks routed to centralized rendering farm. Priority-based queuing (e.g., urgent implant cases first) | 300% throughput increase at peak load |
| Multi-Software Routing | Smart routing engine directs CBCT data to optimal CAD platform based on case complexity (e.g., simple crowns → DentalCAD; zygomatic implants → 3Shape Implant Studio) | Reduces software licensing costs by 22% |
| Quality Control | Automated artifact detection (e.g., motion blur, beam hardening) via ML algorithms. Flagged cases routed to senior techs | 37% reduction in remakes |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The DICOM Imperative
True interoperability hinges on robust DICOM handling. Below is the 2026 compatibility assessment:
| CAD Platform | Native CBCT Integration | Key Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Implant Studio | Full native integration (DICOM 3.0 + proprietary .3sh) | AI-driven nerve canal tracing; seamless IOS/CBCT fusion; real-time stability simulation | Limited to 3Shape ecosystem; no direct lab management system (LMS) hooks |
| exocad DentalCAD | Open API via exoplan (requires module licensing) | Vendor-agnostic DICOM import; customizable segmentation templates; modular workflow design | Segmentation less automated than 3Shape; requires third-party tools for cloud rendering |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Partial integration (DICOM import only) | Tight Straumann implant library sync; cost-effective for single-brand workflows | No native CBCT segmentation; requires external software (e.g., BlueSkyBio) |
Critical Technical Note:
Post-2025, DICOM conformance statements must specify support for:
- Enhanced CT Image IOD (ISO/TS 15443)
- Structured Reporting for Anatomical Regions (e.g., “mandibular canal”)
- RT Structure Set export for guided surgery templates
Platforms lacking these will become workflow bottlenecks as AI-driven diagnostics advance.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Parameter | Open Architecture | Closed System |
|---|---|---|
| Integration Flexibility | ✅ Full API access (HL7/FHIR, DICOMweb). Connect any CBCT, CAD, or LMS | ❌ Vendor-locked ecosystem. Limited to approved hardware/software |
| Cost Efficiency | ✅ Pay-per-module. Avoid redundant licensing (e.g., use existing CBCT for multiple CAD platforms) | ❌ “All-in” pricing. Forced upgrades drive 30-50% higher TCO over 5 years |
| Innovation Velocity | ✅ Rapid adoption of third-party AI tools (e.g., fracture detection plugins) | ❌ Dependent on vendor’s R&D cycle (avg. 18-24 month feature lag) |
| Technical Risk | ⚠️ Requires in-house IT expertise. Potential compatibility gaps | ✅ “Single throat to choke” support model |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation represents the gold standard for practice management integration. Its DICOM-aware architecture eliminates manual data silos:
Technical Integration Highlights
- Smart DICOM Routing: Auto-tags CBCT studies via metadata (e.g., “implant_case=TRUE”) and routes to correct CAD/LMS queue
- Bidirectional Case Tracking: CBCT acquisition triggers real-time work item creation in exocad/3Shape with patient demographics pre-populated
- Insurance Pre-Check: Extracts anatomical measurements from CBCT (e.g., bone density) to auto-validate coverage eligibility before case acceptance
- Compliance Engine: Enforces ALARA principles by blocking redundant scans via dose history tracking (integrates with IAEA SmartDose)
Real-World Impact (2025 Beta Data):
Clinics using Carejoy API with open-architecture CBCT/CAD saw:
- 41% reduction in case setup time
- 28% decrease in insurance denials for implant procedures
- Zero manual data re-entry between imaging and billing systems
Technical Differentiator: Carejoy’s /cbct/v2/workflow endpoint uses GraphQL for field-level data requests, minimizing network load versus legacy REST APIs.
Conclusion: The Integrated Workflow Imperative
In 2026, CBCT is not merely an imaging device but the data nexus of precision dentistry. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- DICOM 3.0 compliance with advanced conformance statements
- Open architecture with standardized APIs (not proprietary “openness”)
- Orchestration layers like Carejoy that transform raw CBCT data into actionable clinical intelligence
Organizations clinging to closed systems will face 18-24 month obsolescence as AI-driven diagnostics demand fluid data exchange. The future belongs to those who treat CBCT not as a scanner, but as the central node in a neural network of digital dentistry.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Cone Beam CT Scanners in China: A Case Study of Carejoy Digital
As global demand for high-precision, cost-effective dental imaging systems rises, China has emerged as the dominant force in the manufacturing of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scanners. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this shift, leveraging advanced production infrastructure, rigorous quality assurance protocols, and AI-integrated design to deliver best-in-class imaging systems from its ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
Carejoy Digital’s CBCT production follows a vertically integrated, open-architecture model optimized for precision, scalability, and interoperability. The manufacturing pipeline includes:
- Component Sourcing: Strategic partnerships with Tier-1 suppliers for X-ray tubes, flat-panel detectors (FPDs), and precision gantry systems, all audited under ISO 13485 supplier controls.
- Subassembly Integration: Modular construction of imaging chains, motion control units, and AI-accelerated computing modules.
- Final Assembly: Conducted in ESD-protected cleanrooms with traceability via serialized component tracking (Lot/Batch/Device ID).
- Software Flashing: Pre-loaded with AI-driven scanning firmware supporting STL, PLY, and OBJ export formats for seamless CAD/CAM integration.
2. Quality Control & Compliance: ISO 13485 Framework
All manufacturing and post-production processes adhere strictly to ISO 13485:2016 standards for medical device quality management systems. Key QC checkpoints include:
| QC Stage | Process | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Inspection | Dimensional verification, material certification, RoHS compliance | ISO 13485 §7.4 |
| In-Process Testing | Real-time alignment checks, electrical safety (IEC 60601-1) | ISO 13485 §8.2.4 |
| Final Device Validation | Full imaging chain calibration, DICOM conformance, motion accuracy | ISO 13485 §8.3 |
| Post-Market Surveillance | Field data analytics, failure mode reporting | ISO 13485 §8.5 |
3. Sensor Calibration Labs: Ensuring Sub-Micron Accuracy
Carejoy Digital operates a dedicated sensor calibration laboratory within its Shanghai facility, accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. This lab performs:
- Flat-Panel Detector (FPD) Calibration: Pixel gain/offset correction, dead pixel mapping, and quantum detection efficiency (DQE) optimization.
- Geometric Calibration: Gantry tilt, focal spot drift, and rotational axis alignment using NIST-traceable phantoms.
- AI-Enhanced Calibration: Machine learning models predict and correct spatial distortions in real time, improving volumetric accuracy by up to 18% (validated per AAPM Report TG172).
4. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, each CBCT unit undergoes accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of clinical use:
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration & Shock | IEC 60068-2-6 / -2-27 | No mechanical misalignment; image SNR < 5% degradation |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 45°C over 1,000 cycles | No condensation; consistent detector response |
| Continuous Scan Endurance | 500+ full-volume scans (12×8 FOV) | X-ray output stability ±3%; no thermal shutdown |
| Digital Robustness | AI firmware stress testing under low-bandwidth conditions | Scan completion rate > 99.8% |
5. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s ascent in digital dentistry manufacturing is driven by a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, sensor, and precision mechanics hubs reduces logistics costs and lead times.
- AI & Software R&D Investment: Chinese tech firms lead in AI imaging algorithms, enabling features like auto-segmentation and artifact reduction at lower licensing costs.
- Scale & Automation: High-volume production lines with robotic integration reduce unit costs while maintaining repeatability.
- Regulatory Agility: Rapid NMPA approval cycles allow faster time-to-market, which translates into competitive pricing.
- Open Architecture Design: Carejoy Digital’s support for STL/PLY/OBJ formats ensures compatibility with global CAD/CAM ecosystems, reducing integration costs for labs.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers CBCT systems with 0.075 mm voxel resolution, AI-guided scan planning, and sub-4-second acquisition at under 60% of legacy Western OEM pricing—redefining the cost-performance frontier.
Support & Digital Ecosystem
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics, firmware rollback, and AI-assisted troubleshooting.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates: Monthly feature enhancements and security patches.
- Cloud Integration: DICOM cloud storage, multi-clinic fleet management, and AI analytics dashboard.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cone Beam Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
