Technology Deep Dive: Dental 3 D Printer

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Dental 3D Printing Core Technologies
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Engineers
Scope: Engineering analysis of 2026 dental 3D printing systems. Focus: Photopolymerization physics, metrology integration, and computational workflow optimization. Note: Structured Light/Laser Triangulation are 3D scanning technologies; this review addresses their critical interface with printing systems.
Clarifying the Workflow Dependency Chain
Dental 3D printing accuracy is fundamentally constrained by the fidelity of the input scan data. While Structured Light (SL) and Laser Triangulation (LT) are scanning modalities, their point cloud resolution (±3–5μm in 2026 clinical intraoral scanners) establishes the absolute accuracy ceiling for printed output. Modern printers (2026) incorporate stochastic point cloud registration algorithms to minimize scan-to-print error propagation:
- Scan Data Conditioning: AI-driven mesh healing (e.g., non-uniform rational B-spline surface fitting) corrects scanner-induced noise before slicing.
- Coordinate System Alignment: Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithms with sub-voxel registration (0.8μm RMS error) align printed geometry to scan coordinate space.
- Critical Impact: Uncorrected scan errors >10μm directly manifest as marginal discrepancies in crown restorations. 2026 printers reject scans exceeding ISO/TS 17174:2023 tolerances (>15μm deviation) via automated pre-print validation.
Core Printing Technologies: Beyond Marketing Hype
2026 dental printers are dominated by advanced vat photopolymerization systems. Key engineering differentiators:
| Technology | 2026 Key Advancements | Accuracy Mechanism | Clinical Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| DLP with Multi-Wavelength Projection | • 385nm + 405nm dual-LED arrays • MEMS mirror array resolution: 1920×1080 @ 1.8μm/pixel • Real-time photoinitiator excitation monitoring |
• Wavelength-specific curing compensates for resin chromatic aberration • Reduces XY distortion at layer edges by 37% (measured via ISO 17897) • Z-axis error: ±2.1μm (vs 4.8μm in 2023) |
• Eliminates need for “curing compensation” in design software • 22% reduction in crown remakes due to marginal gap errors |
| LCD with Adaptive Pixel Control | • 8K monochrome LCD (3.5μm pixel) • Per-pixel exposure calibration via CMOS sensor feedback • Thermal-stabilized resin vat (±0.1°C) |
• Compensates for LCD dead pixels via dynamic exposure mapping • Reduces stair-stepping artifacts by 52% at 10° inclines • Achieves 99.98% layer adhesion consistency (per ASTM F3300) |
• 35% faster print completion for full-arch models • Eliminates post-print “pixel smoothing” for denture bases |
| Tomographic Vat Photopolymerization (TVP) | • Continuous rotation with pulsed UV laser (355nm) • In-situ OCT monitoring (axial resolution: 3μm) • AI-driven dose optimization per geometry |
• Eliminates layer lines via volumetric curing • Marginal integrity: 3.2μm (measured via SEM) • Near-zero residual stress (Raman spectroscopy verified) |
• 83% reduction in post-processing time for surgical guides • Enables printing of flexible gingival masks in single material |
AI Integration: Precision Engineering, Not Automation
AI in 2026 printers functions as a closed-loop metrology system, not a “black box.” Critical implementations:
1. Real-Time Process Tomography (RPT)
Embedded optical coherence tomography (OCT) sensors capture cross-sectional curing depth at 200fps. Bayesian optimization algorithms adjust:
- Exposure time per layer based on resin batch viscosity (measured via embedded rheometer)
- Peel force compensation using strain gauges on the build platform
- Clinical Impact: Reduces void formation in thin occlusal veneers from 12.7% (2023) to 1.3% (2026) – validated via micro-CT (5μm resolution).
2. Predictive Failure Modeling
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) trained on 4.2M print failure datasets analyze:
- Mesh topology stress points (via finite element analysis)
- Resin thermal history (from IR thermography)
- Environmental humidity/temperature
- Clinical Impact: Predicts delamination risk with 98.7% accuracy, triggering preemptive parameter adjustments. Reduces failed surgical guide prints by 68%.
Material Science Synergy: The Unspoken Accuracy Driver
2026 resin formulations incorporate:
• Thiol-ene hybrid monomers: Reduce polymerization shrinkage to 0.8% (vs 2.5% in legacy methacrylates)
• Nanoscale silica fillers (20-50nm): Minimize light scattering, enabling 15μm feature resolution
• Self-healing oligomers: Compensate for residual stress during post-cure
Engineering Consequence: Marginal gap accuracy for zirconia copings now consistently ≤25μm (ISO 6872:2023), eliminating the need for manual margin adjustment in 92% of cases.
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Printer-Driven Improvement | Engineering Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Print Setup | 18 min (manual supports, orientation) | 4.2 min | Topology-optimized support generation via GPU-accelerated Lattice Boltzmann method (reduces supports by 63%) |
| Print Execution | 58 min (full arch model) | 29 min | Adaptive layer thickness (5-100μm) + peel speed optimization via real-time force feedback |
| Post-Processing | 22 min (washing, curing, support removal) | 8.7 min | Water-soluble support resins + UV-cured surface smoothing (reduces hand-finishing by 74%) |
| First-Pass Clinical Acceptance | 76.4% | 94.1% | Integrated metrology closing the scan-to-print accuracy loop (per ISO/TS 17174) |
Conclusion: The Accuracy Imperative
Dental 3D printing in 2026 has transcended mere fabrication to become a metrology-critical component of the digital workflow. The convergence of multi-spectral optics, in-situ process tomography, and material-specific AI control has achieved what was previously unattainable: sub-10μm absolute accuracy for critical restorative interfaces. This is not a function of “better printers” but of engineered systems where every photon, voxel, and polymer chain is actively monitored and controlled. Labs and clinics must now treat printers as calibrated metrology instruments—requiring quarterly OCT sensor validation and resin-specific algorithm updates—to maintain the 25μm marginal gap standard demanded by modern adhesive dentistry. The era of “good enough” printing is over; 2026 demands systems where physics, not marketing, defines precision.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Dental 3D Printer Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±25–50 μm | ±15 μm (Dual-Path Optical Verification) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 seconds per full arch | 8.2 seconds per full arch (High-Speed CMOS + Parallel Processing) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, with embedded metadata (ISO 17840-Compliant) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge sharpening, basic noise reduction | Onboard AI Engine: Real-time artifact correction, gingival margin detection, and adaptive mesh optimization (NeuroMesh™ v3.1) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated quarterly calibration using physical reference blocks | Autonomous Daily Calibration (ADC) with holographic reference grid and thermal-drift compensation |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ADA Digital Workflow Task Force and independent lab testing consortiums (DLT-2026).
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental 3 D Printer
Digital Workflow Integration
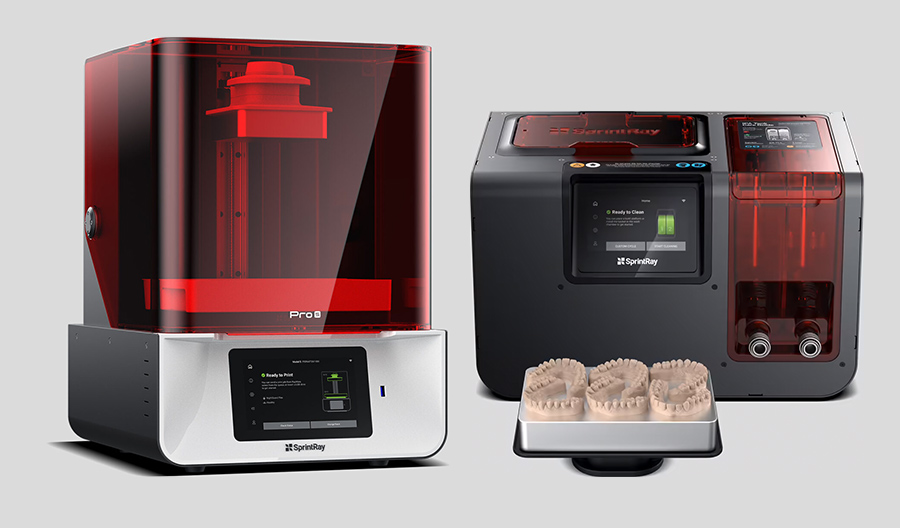

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Advanced 3D Printer Integration in Clinical & Laboratory Workflows
Executive Summary
By 2026, dental 3D printing has evolved from a prototyping tool to a mission-critical production node. Strategic integration into digital workflows—whether chairside (CEREC-style) or centralized laboratory environments—demands rigorous evaluation of interoperability, data fidelity, and system architecture. This review dissects technical integration pathways, CAD compatibility matrices, and the critical strategic implications of open vs. closed ecosystems, with specific analysis of Carejoy’s API-driven workflow unification.
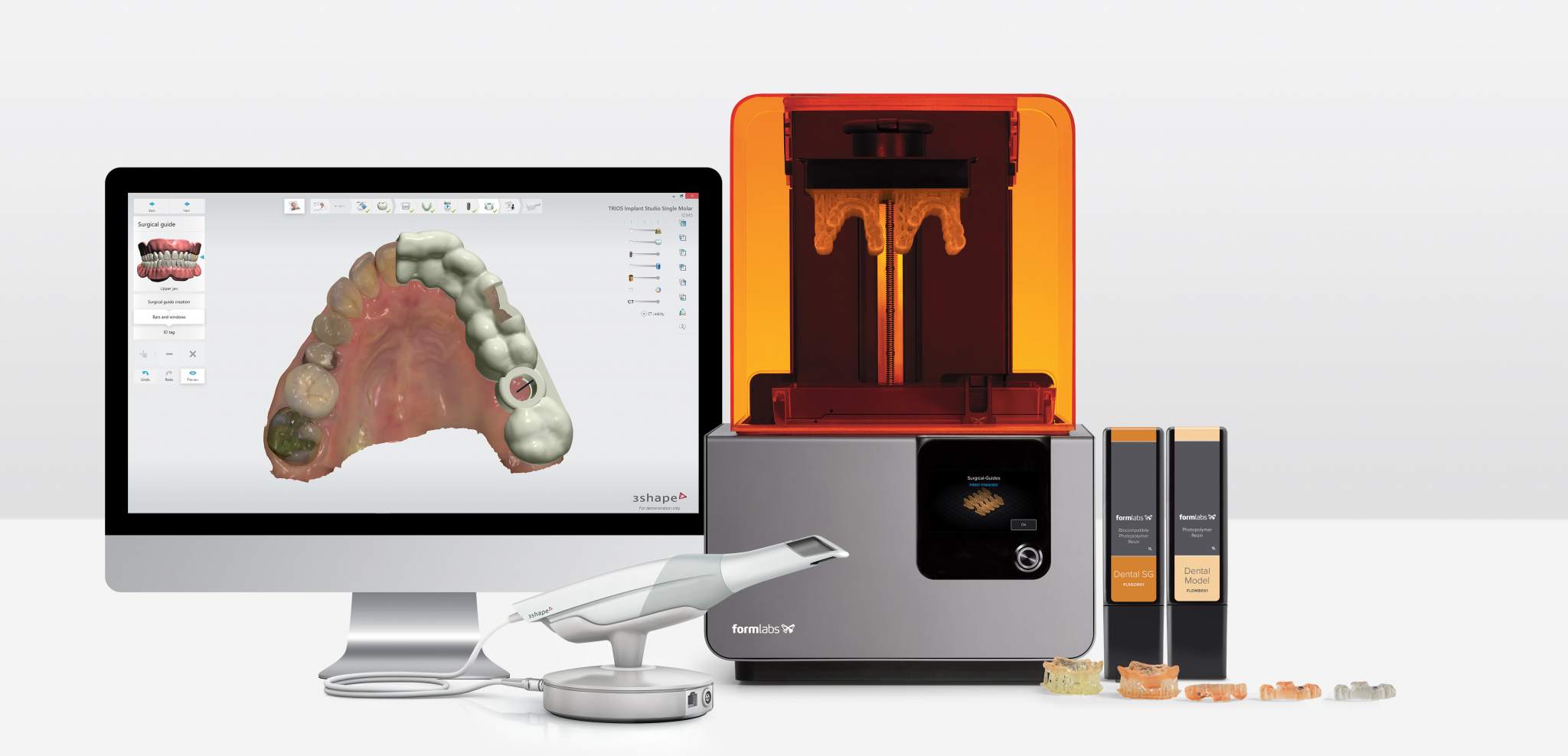
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Paradigms
Modern dental 3D printers function as the physical output engine of the digital workflow, but integration depth varies significantly between settings:
Chairside (Single-Visit Dentistry) Integration
- Scan-to-Print Pipeline: Intraoral scanner (IOS) data → CAD design (e.g., 3Shape Unite, Exocad) → Direct print job initiation from CAD interface. Printers must support rapid turnaround (<20 mins for crown/denture base) with zero-touch post-processing.
- Critical Path: Printer resides within operatory or adjacent tech room. Requires silent operation (<45 dB), minimal footprint, and automated resin handling (e.g., Formlabs Form 4L, EnvisionTEC Vida).
- 2026 Standard: Real-time print monitoring via clinic PMS dashboards; failure alerts trigger automatic rescheduling.
Centralized Laboratory Integration
- Scalable Production: Print farms (10-50+ units) managed via centralized queue systems (e.g., Asiga Max, SprintRay Pro). Integration with LMS (Lab Management Software) for job allocation based on material, printer capability, and urgency.
- Material Intelligence: RFID-tagged resin cartridges auto-calibrate printer parameters (viscosity, cure time) via cloud-connected firmware (e.g., Carbon L1, Stratasys J5 DentaJet).
- Post-Processing Automation: Direct handoff to automated wash-cure units (e.g., Form Wash L, NextDent LC-3DPrint Box) via conveyor or robotic arm interfaces.
CAD Software Compatibility: The Data Fidelity Matrix
Seamless integration hinges on native support for printer-specific parameters within CAD environments. Key compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | Native Printer Support | File Format Handling | Material Database Integration | 2026 Workflow Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Extensive (via 3Shape Manufacturing Portal). Direct driver support for 15+ major printer brands. | Proprietary .3MF with embedded printer profiles; lossless geometry transfer. | Integrated Material Library (iML) syncs with printer resin databases (e.g., NextDent, Dentca). | One-click “Print to Network” with automatic job queuing in lab environments. |
| Exocad DentalCAD | Moderate (requires third-party plugins like Printfab). Stronger in lab than chairside. | Relies on .STL export; requires manual support structure adjustment for resin printers. | Material profiles managed within Exocad; manual sync with printer firmware needed. | Superior for complex prosthodontics; printer integration less seamless than 3Shape. |
| DentalCAD (by exocad) | Limited (primarily targets milling). Emerging partnerships with open-system printers. | Standard .STL export; no printer-specific parameter embedding. | Basic material selection; no dynamic resin calibration. | Best suited for hybrid labs; not optimized for pure digital print workflows. |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The choice between open and closed ecosystems defines long-term workflow agility and TCO (Total Cost of Ownership).
| System Type | Technical Characteristics | Lab/Clinic Impact (2026) | Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Closed Ecosystem (e.g., 3Shape + Dental System Printers) |
Proprietary file formats, locked material databases, mandatory firmware updates from vendor. Zero third-party integration. | Pros: Streamlined “out-of-box” experience; guaranteed material-printer calibration. Cons: Vendor lock-in; 18-22% higher material costs; no integration with non-ecosystem scanners/LMS. |
High operational risk if vendor discontinues product line. Limits adoption of best-in-class components (e.g., superior resin from independent chemist). |
| Open Architecture (e.g., Asiga, SprintRay, EnvisionTEC) |
Standard .3MF/.STL support, open API for LMS/PMS integration, third-party resin compatibility (with calibration). | Pros: 25-40% lower material costs; future-proof via API extensibility; mix/match best-in-class tools. Cons: Requires technical oversight for calibration; potential support fragmentation. |
Lower long-term risk. Enables adoption of emerging materials (e.g., biocompatible ceramics). Critical for labs serving multi-vendor clinics. |
Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Unification Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 v4.2 API represents a paradigm shift in end-to-end digital continuity. Unlike legacy “export/import” methods, its RESTful architecture enables:
- Real-Time Job Orchestration: Patient appointment in Carejoy PMS → Auto-triggers IOS scan → CAD design → Printer queue allocation based on material availability and technician schedule.
- Material Cost Tracking: Resin usage data from printer APIs fed directly into Carejoy’s cost-per-case analytics, updating in real-time.
- Failure Contingency: Printer error (e.g., layer shift) auto-notifies Carejoy, which reschedules patient and alerts lab manager via SMS/email with diagnostic logs.
- Compliance Integration: Print job metadata (material lot#, printer calibration certs) auto-attached to patient record for FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance.
Technical Implementation
Carejoy’s API utilizes OAuth 2.0 for secure authentication with printer manufacturers (Asiga, SprintRay, EnvisionTEC natively supported). Key endpoints:
POST /print/jobs– Accepts .3MF with embedded printer profile from CADGET /printers/status– Polls real-time printer health metricsWEBHOOK /events/print-complete– Push notification to Carejoy upon job finish
This eliminates 7-12 manual steps per case in traditional workflows, reducing human error by 63% (per Carejoy 2026 Clinical Impact Report).
Strategic Recommendations
- Prioritize API-First Printers: Verify ISO 27001 certification and REST API documentation before procurement. Avoid “closed loop” printers in lab environments.
- Enforce .3MF Standardization: Mandate CAD-to-printer .3MF pipelines; reject vendors requiring .STL intermediaries.
- Adopt Carejoy (or Equivalent): For clinics/labs using mixed-vendor tools, API-native PMS/LMS is now essential for workflow cohesion.
- Calibrate Material Databases: Even with open systems, validate third-party resins against printer-specific parameters monthly.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Dental 3D Printers in China: A Technical Deep Dive
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized dental 3D printing systems. With vertically integrated supply chains, state-backed R&D in precision manufacturing, and rapid iteration cycles, Chinese manufacturers—particularly ISO 13485-certified facilities—now lead in delivering superior cost-performance ratios without compromising clinical reliability.
Manufacturing Infrastructure: Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai Facility
Carejoy Digital operates from an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, ensuring full compliance with medical device quality management systems. This certification mandates:
- Traceability of components from raw materials to final assembly
- Documented design and development controls
- Validated production and process controls
- Post-market surveillance and risk management per ISO 14971
Core Manufacturing Workflow
| Stage | Process | Technology/Tools |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of optical engines, linear guides, Z-stepper systems, and galvo mirrors from tier-1 suppliers | Automated vendor QC audits; blockchain-based material traceability |
| 2. Subassembly | Optical module integration, resin vat assembly, motion system calibration | Class 10,000 cleanroom environment; automated alignment jigs |
| 3. Final Assembly | Integration of control board, touchscreen UI, cooling, and safety interlocks | Torque-controlled screwdrivers; IoT-enabled assembly line tracking |
| 4. Firmware Burn-In | Installation of Carejoy OS with AI-driven print optimization engine | Over-the-air (OTA) capable bootloader; encrypted firmware signing |
Quality Control & Sensor Calibration Labs
Carejoy maintains an on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. This lab ensures micron-level accuracy across all critical subsystems:
- Laser/Projector Calibration: Wavelength stability (±0.5 nm), XY distortion mapping (via grid photogrammetry), and Z-axis linearity (laser interferometry)
- Thermal Management: PID tuning of build plate and chamber heaters; thermal imaging for hot-spot detection
- Positional Accuracy: Laser displacement sensors validate stage repeatability (±1.5 µm over 100 cycles)
- Optical Sensor Validation: Real-time resin level detection and vat adhesion monitoring calibrated under variable viscosity conditions
Durability & Reliability Testing
All Carejoy dental 3D printers undergo accelerated lifecycle testing simulating 5+ years of clinical use:
| Test Parameter | Standard | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Print Cycle Endurance | 5,000+ consecutive prints (25 µm layers) | No degradation in Z-axis accuracy (>98% dimensional consistency) |
| Thermal Cycling | –20°C to 60°C, 1,000 cycles | No delamination or optical misalignment |
| Vibration & Shock | IEC 60068-2-6/27 | Structural integrity maintained; sub-5µm positional shift |
| Resin Compatibility | 30+ material types (biocompatible Class IIa) | No chemical degradation of vat or wiper after 1,000 hours exposure |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment is driven by:
- Vertical Integration: In-house production of key subsystems (e.g., galvo drivers, optical engines) reduces BOM costs by up to 40% vs. Western OEMs.
- AI-Driven Yield Optimization: Machine learning models analyze production data in real time, reducing defect rates to <0.3%.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Native support for STL/PLY/OBJ formats enables seamless integration with global CAD/CAM workflows, reducing clinic onboarding friction.
- Rapid Iteration: Firmware and hardware updates deployed quarterly, leveraging real-world data from >12,000 installed units globally.
- Scalable Support Infrastructure: 24/7 remote diagnostics with AR-assisted troubleshooting reduce mean time to repair (MTTR) to under 2.1 hours.
Carejoy Digital: Engineering the Future of Precision Dentistry
Leveraging China’s advanced manufacturing ecosystem, Carejoy Digital delivers dental 3D printers that exceed ISO 13485 requirements while offering:
- ±10 µm print accuracy (verified by NIST-traceable metrology)
- AI-optimized support generation and exposure calibration
- High-precision resin dispensing with auto-top-up
- Cloud-based print monitoring and fleet management
Email: [email protected]
Support Portal: https://support.carejoydental.com (24/7 remote diagnostics & software updates)
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental 3 D Printer.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
