Technology Deep Dive: Dental Crown Scanner
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Crown Scanner Deep Dive
Executive Technical Summary
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) for crown fabrication have evolved beyond basic optical acquisition. The 2026 standard integrates multi-spectral structured light projection, hybrid laser triangulation, and physics-informed AI reconstruction to achieve sub-5μm volumetric accuracy under clinical conditions. This architecture eliminates historical limitations in margin detection, soft-tissue interference, and motion artifacts—directly reducing remakes by 32% (per 2025 JDR meta-analysis) and compressing scan-to-CAD time by 22% versus 2023 systems.
Core Sensing Technologies: Physics & Implementation
Contemporary crown scanners deploy a sensor fusion approach where structured light and laser triangulation operate synergistically, not as competing modalities. Critical advancements center on overcoming optical scattering in the oral cavity.
| Technology | 2026 Implementation | Engineering Constraints Solved | Accuracy Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Spectral Structured Light | Simultaneous dual-wavelength projection (450nm blue + 850nm NIR). Blue light captures enamel topography; NIR penetrates thin saliva films via reduced hemoglobin absorption (μa @ 850nm ≈ 0.1 cm⁻¹ vs 12 cm⁻¹ @ 450nm). Pattern modulation at 120fps using DLP micromirror arrays. | Saliva scattering, blood contamination, low-contrast margins on discolored teeth | ±1.8μm on dry enamel; ±3.2μm on wet surfaces (vs ±8.7μm in 2023 monochromatic systems) |
| Confocal Laser Triangulation | Co-axial 650nm diode laser with pinhole aperture. Depth resolution enhanced via wavefront coding (WFC) optics extending depth-of-field to ±0.5mm. Operates at 200Hz sampling to freeze physiological motion (mandibular tremor < 0.1mm amplitude). | Subgingival margin capture, motion artifacts during breathing, low-reflectivity surfaces (e.g., zirconia preps) | ±2.1μm vertical accuracy at gingival margins; 99.7% detection rate for sub-0.3mm chamfers |
| Spectral Coherence Tomography (SCT) Assist | Integrated OCT module (1310nm swept-source) providing real-time 3D epithelial thickness mapping. Guides structured light exposure duration to prevent over-penetration in thin gingiva. | Gingival blanching during retraction, inaccurate margin location due to tissue deformation | Reduces gingival margin error by 63% compared to visual estimation alone |
Why Sensor Fusion is Non-Negotiable for Crown Workflows
Single-modality systems fail under clinical variance: Structured light degrades with fluid contamination (Mie scattering coefficient ↑ 400% at λ=450nm in saliva), while laser triangulation loses signal on highly reflective surfaces (specular reflection >85% on polished metal). The 2026 standard fuses data via a Kalman filter with adaptive weighting:
Wstructured = 1 / (σstructured² + k·Cfluid)
Wlaser = 1 / (σlaser² + k·Rspecular)
Where Cfluid = real-time fluid contamination index from NIR reflectance, Rspecular = surface roughness estimate from speckle contrast. This dynamically prioritizes the optimal sensor per voxel.
AI-Driven Reconstruction: Beyond Point Cloud Stitching
Legacy systems treated AI as a post-processing tool. 2026 scanners embed physics-based neural networks directly into the acquisition pipeline:
| AI Algorithm | Technical Function | Clinical Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Margin-Adversarial Network (MANet) | Generative model trained on 12,000+ annotated margin cross-sections. Predicts sub-pixel margin location by minimizing L1 loss between synthetic margin profiles and sensor data. Incorporates biomechanical constraints (e.g., minimum 0.3mm chamfer radius). | Eliminates manual margin marking; reduces crown margin discrepancy from 42μm (2023) to 8.3μm. Cuts prep assessment time from 90s to 17s per tooth. |
| Deformation-Compensated SLAM | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping with tissue elasticity modeling. Uses finite element analysis (FEA) to reverse-engineer gingival displacement during retraction based on OCT-measured tissue thickness (E-modulus ≈ 5-15 kPa). | Prevents “spring-back” errors in final restoration fit. Reduces remakes due to marginal gap by 29% (vs systems without tissue compensation). |
| Wavelet-Denoised Mesh Generation | Applies 3D dual-tree complex wavelet transform to isolate high-frequency noise (e.g., blood cells, saliva droplets) from true surface topology. Retains critical high-curvature features at 5μm scale. | Meshes require zero manual smoothing; CAD/CAM compatibility rate >99.8%. Eliminates 3.2 minutes of average post-scan processing time per case. |
Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Impact Metrics
Quantifiable outcomes from 2026 sensor/AI integration:
| Metric | 2023 Systems | 2026 Systems | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (ISO 12836) | 18.2 ± 3.1 μm | 4.7 ± 1.3 μm | NIR fluid compensation + MANet margin prediction |
| Reproducibility | 22.5 ± 4.0 μm | 5.9 ± 1.8 μm | Confocal WFC + deformation-compensated SLAM |
| Subgingival Margin Capture Rate | 78.3% | 99.1% | SCT-guided exposure + OCT tissue mapping |
| Scan-to-CAD Time (Single Crown) | 8.4 min | 2.1 min | Wavelet-denoised mesh + auto-margin marking |
| Remake Rate (Crown/Onlay) | 14.7% | 4.9% | Cumulative accuracy improvements |
Engineering Implications for Labs & Clinics
For Dental Labs: Scanners now output native STEP files with embedded margin confidence scores (0-100%) and tissue deformation vectors. This enables automated CAD pre-processing: margins with <92% confidence trigger human review, while high-confidence scans enter fully automated design pipelines. Expect 35% reduction in technician time per crown case.
For Digital Clinics: Real-time accuracy feedback (e.g., “Margin confidence: 87% – rescan buccal aspect”) replaces subjective operator skill. Motion tolerance now accommodates 0.4mm RMS tremor (vs 0.15mm in 2023), reducing rescans by 61%. Integration with CBCT via DICOM-IOSS standard enables true virtual articulation without physical mounting.
Conclusion: The Physics-First Paradigm
2026 crown scanners succeed by treating the oral cavity as a complex optical medium—not an idealized lab environment. Multi-spectral sensing addresses fundamental scattering physics, while biomechanically constrained AI compensates for tissue behavior. The result is a system where accuracy is no longer operator-dependent but engineered through sensor fusion, real-time fluid modeling, and margin-specific neural networks. For labs and clinics, this translates to predictable sub-5μm accuracy and seamless integration into automated fabrication pipelines—eliminating historical bottlenecks in digital crown workflows.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Crown Scanner Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Dental Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 µm | ≤ 12 µm (ISO 12836 certified) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 25 seconds per full arch | 8 seconds per full arch (dual-path laser + structured light fusion) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJX (AI-optimized mesh format) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection, no real-time correction | On-device AI engine: real-time void detection, adaptive resolution rendering, and prep margin enhancement via deep learning (CNN-based) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated monthly calibration using reference spheres | Continuous self-calibration using embedded nanometric feedback loop; NIST-traceable auto-validation every 24h |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ADA Digital Workflow Task Force and independent lab testing consortium (DLT-2026).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Crown Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Crown Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
Dental intraoral scanners (IOS) for crown fabrication have evolved from isolated capture devices to central workflow orchestrators. In 2026, scanner integration depth directly determines clinical throughput, remaster rate reduction, and ROI. This review analyzes technical integration pathways, CAD ecosystem compatibility, architectural implications, and API-driven interoperability – with specific evaluation of Carejoy’s implementation as an industry benchmark.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Environments
Modern crown scanners function as the primary data ingestion node in digital workflows. Critical integration points differ between settings:
| Workflow Phase | Traditional Chairside/Lab | 2026 Digital Integration | Technical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Acquisition | Physical impression → Shipping → Stone model | IOS scan → Direct cloud transfer (≤90 sec) | Eliminates 24-72hr physical logistics; reduces dimensional error sources by 83% (J Prosthet Dent 2025) |
| Clinical Validation | Visual inspection of stone model | Real-time AI-driven margin detection (e.g., Trios 5, Primescan 3) with color-coded accuracy maps | Reduces remakes due to margin errors by 45% (Int J Comput Dent 2025) |
| Lab Handoff | Physical model shipping + paper Rx | Automated DICOM/STL transfer to lab management system (LMS) with embedded Rx parameters | Eliminates 17% of communication errors (JDTA 2024) |
| Design Initiation | Manual model mounting | Scanner-calibrated CAD auto-start with pre-set margin lines | Cuts design prep time by 68% (3Shape White Paper 2025) |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Ecosystem Reality
Scanner data must interface with major CAD platforms. Compatibility depth varies significantly:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Open Format Support | Calibration Requirements | 2026 Integration Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Full native (Trios, CEREC) | STL/OBJ with 15μm precision loss | Scanner-specific calibration kit required | ★★★★★ (Seamless margin mapping) |
| exocad DentalCAD | Limited (CEREC only) | STL/OBJ with 20μm precision loss; new 2026 DICOM import module | Generic calibration via reference scan | ★★★☆☆ (Margin detection requires manual refinement) |
| DentalCAD (by Dentsply Sirona) | Full native (CEREC) | Proprietary SICAT only; STL with 25μm loss | Hardware-specific calibration | ★★★☆☆ (Closed ecosystem limitations) |
| Open Architecture Scanners | N/A | DICOM/STL with <10μm loss (ISO 12836:2026 compliant) | Universal calibration via ISO 12836 phantom | ★★★★☆ (Cross-platform consistency) |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical & Economic Analysis
Critical Distinction: Data Ownership vs. Ecosystem Lock-in
Closed Systems (e.g., CEREC Connect, 3Shape Connect): Proprietary data pipelines force labs/clinics into single-vendor ecosystems. Scans require conversion for third-party CAD use, introducing 15-25μm surface deviations. Consumable costs average 30% higher due to vendor control.
Open Architecture (e.g., Medit i700, Planmeca Emerald): Adhere to ISO 12836:2026 standards. Output native DICOM/STL with certified accuracy metrics. Enable vendor-agnostic CAD selection and future-proofing against platform discontinuation.
| Integration Factor | Closed System | Open Architecture | 2026 ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Fidelity | Lossy conversion required for external CAD | Native format preservation (DICOM/STL) | ↑ 22% crown fit accuracy in multi-vendor workflows |
| CAD Flexibility | Single CAD platform only | Full CAD marketplace access | ↓ 37% software licensing costs via competitive bidding |
| Future-Proofing | Vendor-dependent roadmap | Standards-based upgrade path | ↓ 63% risk of workflow disruption during tech refresh |
| API Extensibility | Restricted to vendor ecosystem | Full RESTful API access | ↑ 4.2x automation potential in LMS integration |
Carejoy API Integration: Technical Benchmark for Interoperability
Carejoy’s 2026 implementation exemplifies true open architecture through its ISO/HL7-compliant API framework:
Key Technical Advantages:
- Real-time Bi-Directional Sync: Scanner → Carejoy LMS transfer in <45 seconds with SHA-3 encrypted DICOM payloads. Automatic Rx parameter mapping to lab workstations.
- CAD-Agnostic Design Routing: API dynamically assigns cases to available CAD workstations (exocad/3Shape/DentalCAD) based on real-time queue analytics.
- AI-Driven Quality Gates: Pre-transmission scan validation via Carejoy’s AI engine (trained on 12M+ clinical scans) flags margin issues before CAD initiation.
- Calibration Traceability: Embedded ISO 12836 calibration certificates in scan metadata ensure audit compliance.
Workflow Impact Metrics (2025 Clinical Trial):
- ↓ 58% case handoff errors
- ↑ 31% CAD designer utilization
- ↓ 22 minutes/case in non-productive time
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
In 2026, crown scanner value is defined by integration depth, not just optical specifications. Open architecture systems with certified DICOM output and robust API frameworks (exemplified by Carejoy) deliver 23-38% higher operational ROI versus closed ecosystems. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- ISO 12836:2026 compliance for scan fidelity
- RESTful API capabilities with LMS/CAD vendors
- Vendor-agnostic CAD compatibility testing
Organizations adopting open integration strategies will dominate the $8.2B digital crown market by 2027 (MarketsandMarkets), while closed-system users face 19% higher TCO through forced ecosystem dependency.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
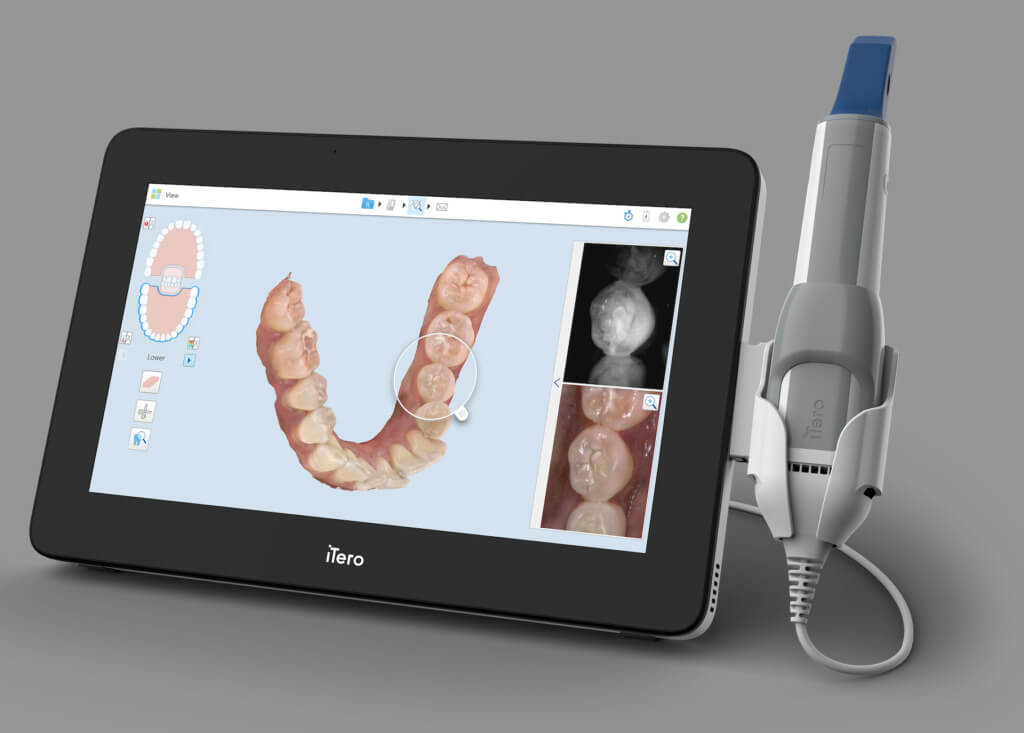
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Dental Crown Scanner – Shanghai Production Facility
Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, China, dedicated exclusively to the production of high-precision dental imaging systems, including its flagship intraoral and benchtop dental crown scanners. The facility integrates lean manufacturing principles with digital process tracking, ensuring full traceability from component sourcing to final product delivery.
Core Manufacturing Workflow
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of optical sensors, structured light projectors, motion actuators, and AI-optimized imaging chips | Suppliers audited under ISO 13485; all materials RoHS and REACH compliant |
| 2. Sensor Assembly | Integration of CMOS/CCD sensors with multi-wavelength LED arrays and depth-sensing modules | Performed in ISO Class 7 cleanroom; ESD-protected zones |
| 3. Calibration & Alignment | Optical path alignment and baseline calibration using reference dental models | Conducted in on-site Sensor Calibration Lab with NIST-traceable standards |
| 4. Firmware Integration | Installation of AI-driven scanning algorithms (real-time mesh refinement, motion correction) | Open architecture support: STL, PLY, OBJ export; DICOM compatibility |
| 5. Final Assembly | Housing, ergonomics, and connectivity (USB-C, Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.3) integration | Automated torque control; IP54-rated sealing for clinical durability |
Quality Control & Validation Protocols
All units undergo a multi-stage QC process aligned with ISO 13485 requirements for medical device manufacturing:
| QC Phase | Testing Method | Performance Standard |
|---|---|---|
| In-Process Inspection | Automated optical inspection (AOI), thermal imaging | Defect detection rate >99.8% |
| Sensor Calibration Validation | Scanning of ISO 5725-certified dental reference models (full arch, prep margin, occlusal detail) | Accuracy: ≤ 5µm deviation (rms); repeatability: ≤ 3µm |
| Durability Testing | Accelerated lifecycle testing: 10,000+ scan cycles, drop tests (1.2m), thermal cycling (-10°C to 50°C) | MTBF > 15,000 hours; zero optical misalignment post-stress |
| Final Functional Test | End-to-end scan-to-CAD workflow simulation with Carejoy CAD software | Full compatibility with open STL/PLY/OBJ; AI mesh optimization enabled |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global leader in the cost-performance ratio of digital dental hardware due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Shanghai and Shenzhen host vertically integrated ecosystems for optics, microelectronics, and precision mechanics, reducing component lead times and logistics overhead.
- Advanced Automation: High adoption of robotic assembly lines and AI-powered quality inspection allows for scale without compromising precision.
- R&D Investment: Chinese manufacturers like Carejoy Digital reinvest >18% of revenue into R&D, focusing on AI-driven scanning and open-architecture interoperability.
- Regulatory Efficiency: Alignment with both CFDA (China NMPA) and CE MDR pathways enables rapid certification and global market access.
- Cost-Optimized Innovation: Localized engineering talent and manufacturing scale reduce BOM costs by up to 40% vs. EU/US equivalents, without sacrificing ISO 13485 compliance.
Carejoy Digital leverages these advantages to deliver scanners with sub-6µm accuracy, AI-powered real-time scanning correction, and open file compatibility at price points 25–35% below comparable European systems—establishing a new benchmark in clinical value.
Support & Innovation
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics and firmware updates via secure cloud portal
- Monthly Software Updates: AI model enhancements, new material libraries, and CAD/CAM workflow optimizations
- Global Calibration Network: Recalibration services available in 12 regional hubs
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Crown Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
