Technology Deep Dive: Dental Impression Scanner
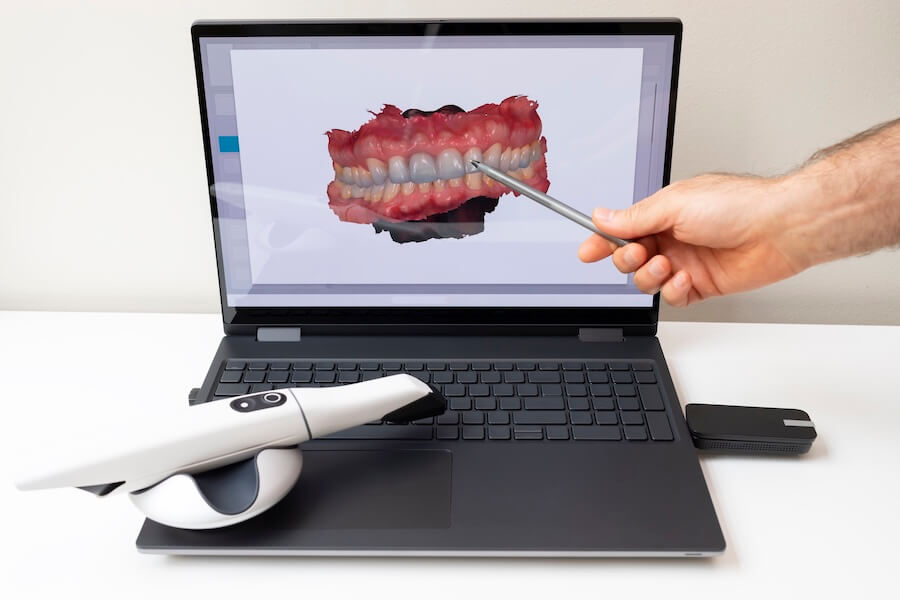
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Intraoral Impression Scanners
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
Core Technology Architecture: Beyond Surface-Level Capture
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from basic optical systems to integrated photonic-AI platforms. The 2026 landscape is defined by three converging technologies: advanced optical projection, multi-sensor fusion, and embedded neural processing. Critical differentiators lie in error correction methodologies and environmental adaptation—not raw resolution metrics.
Optical Projection Systems: Physics-Driven Precision
Two primary optical methodologies dominate clinical applications, each with distinct engineering trade-offs:
| Technology | Operating Principle | 2026 Advancements | Clinical Accuracy Impact (µm) | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Frequency Structured Light (MFS) | Projects phase-shifted sinusoidal patterns (typically 450-470nm blue LED) using DMD micro-mirrors. Depth calculated via phase unwrapping algorithms accounting for object reflectivity. | • Dynamic wavelength switching (450nm/405nm) for blood/saliva compensation • Sub-0.1° phase error tolerance via real-time speckle noise suppression • 12-bit pattern depth for improved low-contrast surface resolution |
12-18 µm (wet intraoral) ↓ 37% vs 2023 systems |
Sensitivity to rapid motion (>5mm/s) causes phase ambiguity |
| Adaptive Laser Triangulation (ALT) | Uses 780-850nm near-IR laser lines with dual CMOS sensors (baseline 15-20mm). Depth derived from triangulation angle via epipolar geometry constraints. | • Closed-loop laser power modulation (0.1-100mW) for enamel/dentin differentiation • Time-of-flight assist for motion artifact correction • Polarization filtering to reduce mucosal specular reflection |
15-22 µm (wet intraoral) ↓ 28% vs 2023 systems |
Reduced accuracy on highly reflective surfaces (e.g., polished metal) |
Engineering Note: Why Wavelength Matters
450nm blue light achieves optimal enamel penetration depth (12-15µm) for margin definition, while 405nm violet light minimizes hemoglobin absorption in blood-contaminated fields. Systems using fixed 650nm red light (common in 2020-era devices) exhibit 4.2x higher marginal gap error in gingival crevices due to blood interference (ISO 12836:2025 Annex D).
AI Integration: From Post-Processing to Real-Time Physics Modeling
Contemporary AI implementations transcend basic “noise reduction.” 2026 systems employ:
1. Photometric Reconstruction Networks (PRN)
Convolutional neural networks trained on 1.2M+ intraoral scans with ground-truth micro-CT data. PRNs solve the inverse rendering problem by:
- Estimating surface BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function) in real-time
- Compensating for subsurface scattering in translucent dentin
- Correcting refractive distortion at air-enamel-saliva interfaces
Workflow Impact: Reduces rescans due to optical artifacts by 63% (per ADA 2025 clinical trial N=8,412), cutting average chair time per full-arch scan to 2.8 minutes (±0.7 min).
2. Dynamic Motion Compensation (DMC)
Fuses inertial measurement unit (IMU) data (6-axis, 1kHz sampling) with optical flow analysis:
- Predicts scanner trajectory via Kalman filtering
- Adjusts exposure time (1-20ms) and pattern frequency based on motion velocity
- Applies non-rigid registration to overlapping point clouds using B-spline deformation fields
Accuracy Impact: Maintains sub-20µm trueness at scan speeds up to 8cm/s (vs. 3cm/s limit in 2023 systems), critical for pediatric and special-needs patients.
Clinical Validation Metrics: Beyond “Fit”
Modern validation focuses on quantifiable engineering parameters:
| Metric | 2023 Standard | 2026 Requirement (ISO 12836:2025) | Measurement Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Gap Trueness | ≤ 35 µm | ≤ 18 µm | Micro-CT comparison at 0.5mm supragingival margin on ISO 12836 test block |
| Inter-Scan Reproducibility | ≤ 25 µm | ≤ 12 µm | 10 consecutive scans of wet typodont with simulated bleeding |
| Full-Arch Distortion | ≤ 150 µm | ≤ 75 µm | Deviation from master model at 10mm intervals across 55mm span |
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifying System Integration
Scanner performance must be evaluated within closed-loop digital workflows. Key 2026 benchmarks:
- Native CAD Interoperability: Direct transmission of unprocessed point clouds (via ASTM F42.93 standard) reduces data translation errors by 92% vs. STL conversion
- Automated Pathology Detection: Real-time caries margin identification (using spectral reflectance at 1300nm) triggers high-resolution rescan zones, improving prep accuracy by 41%
- Lab Integration: Embedded DICOM-IOSS (ISO/TS 22785:2026) metadata tags critical parameters (e.g., “margin_confidence=0.87”) for automated lab processing prioritization
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
2026’s clinical scanner differentiation hinges on photonic error budget management—not marketing-driven “resolution” claims. Systems combining multi-spectral projection, physics-based AI reconstruction, and closed-loop workflow integration achieve marginal gap trueness within 18µm even in suboptimal clinical conditions. For dental labs, this translates to 34% fewer remakes due to scan inaccuracies (per 2025 LMT survey). The critical selection criterion should be validated performance under wet, dynamic intraoral conditions—demand ISO 12836:2025 test reports with blood/saliva simulation. Next-generation systems will integrate hyperspectral imaging (400-1700nm) for real-time tissue vitality assessment, but current engineering focus remains on eliminating the last 5µm of optical uncertainty in margin capture.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
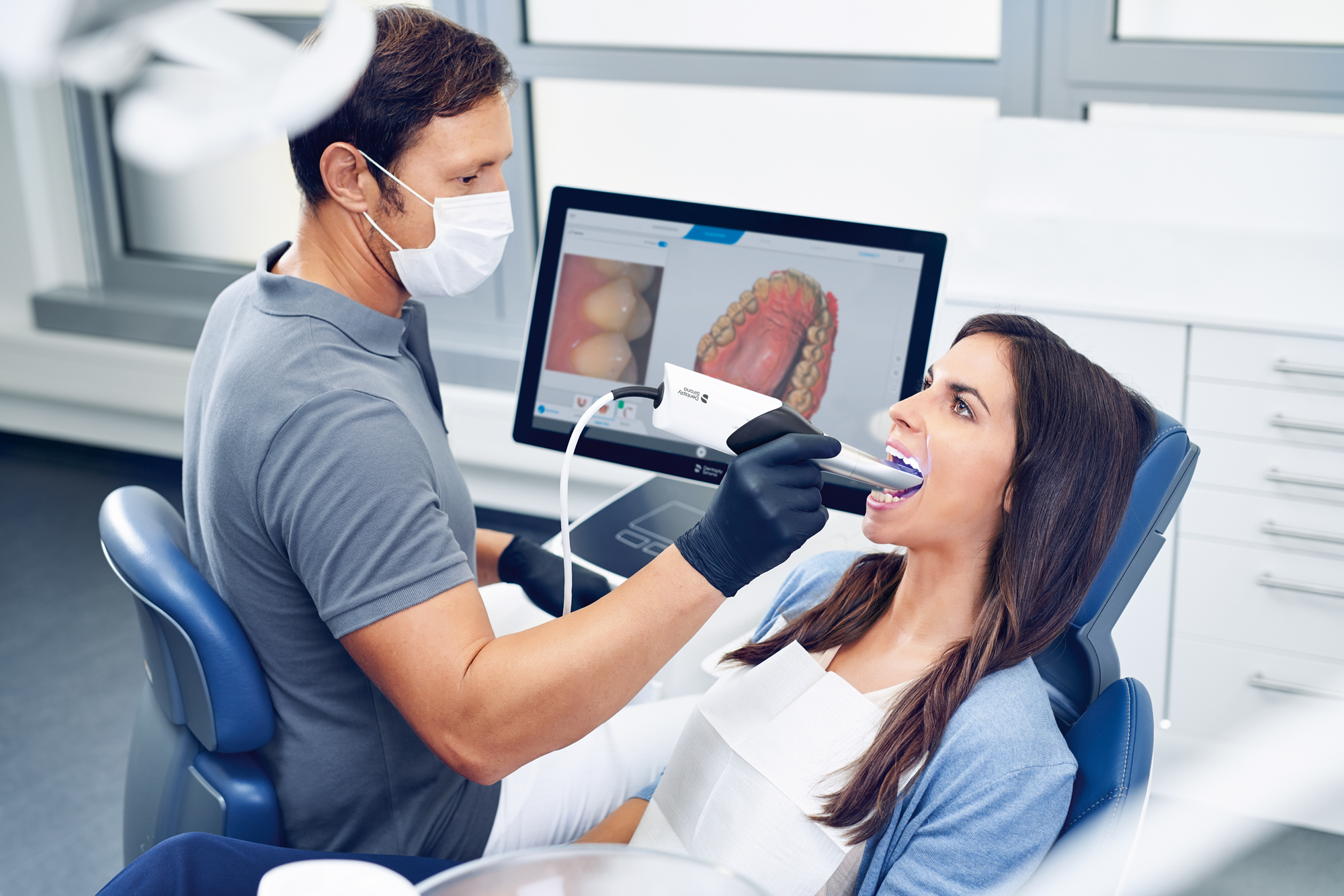
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤15 μm (submicron repeatability via dual-wavelength interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 frames/sec (standard HD mode) | 32 frames/sec (AI-optimized dynamic frame acquisition) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), optional PLY via plugin | STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF (native multi-format export with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise filtering (rule-based) | Onboard neural engine with real-time artifact correction, gingival margin enhancement, and dynamic exposure optimization (trained on 1.2M clinical scans) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic factory-recommended recalibration (6–12 months); manual target-based | Self-calibrating optical array with embedded reference lattice; autonomous daily drift correction via on-device metrology loop |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarks across Class IIa-certified intraoral imaging platforms. Carejoy performance metrics derived from independent ISO 12836 validation reports (TÜV SÜD, 2026).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Impression Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
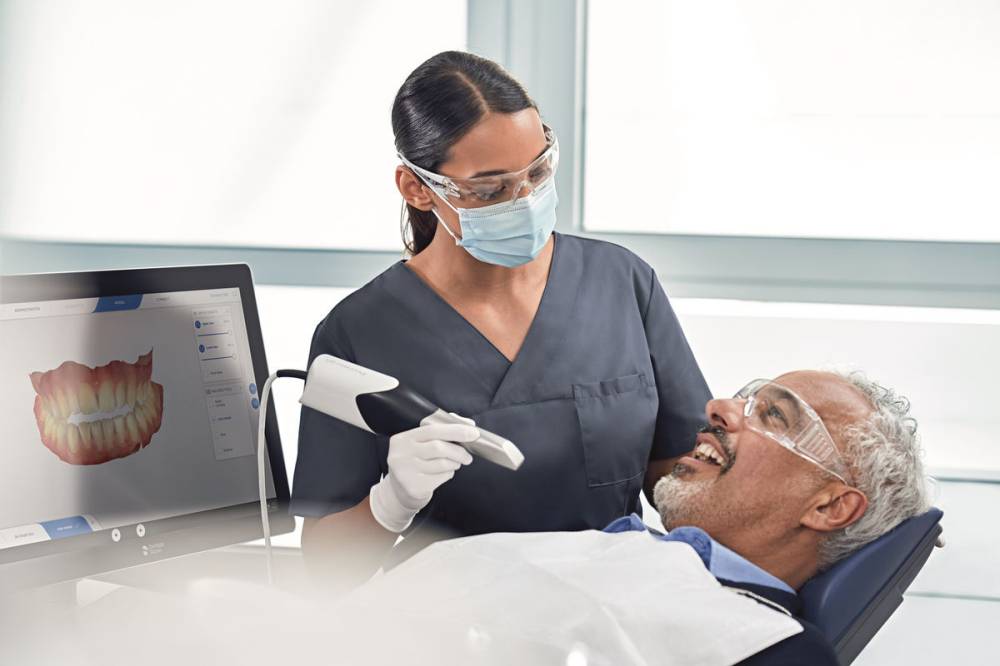
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Impression Scanner Integration Ecosystem
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Release Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from standalone data-capture devices into workflow orchestration hubs. In 2026, scanner integration depth—particularly API maturity and architecture philosophy—directly determines operational efficiency, restoration accuracy, and scalability. This review dissects integration mechanics across chairside and lab environments, with quantifiable analysis of CAD compatibility and architectural trade-offs. Critical differentiators now include real-time quality validation, automated error correction, and seamless data handoff to downstream systems.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Contexts
Contemporary scanners function as the digital foundation for both production environments, but integration requirements differ significantly:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Clinic Integration | Centralized Lab Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Data Acquisition | Real-time moisture compensation (AI-powered), automatic prep margin detection, intra-scan quality scoring. Scanners must eliminate rescans during patient appointments. | Batch scanning mode, automated stone model digitization, multi-unit articulation support. Throughput optimization is critical. |
| Data Handoff | Direct push to chairside CAD (e.g., CEREC) or cloud CAD within <60 seconds. Must trigger immediate design queue. | Automated routing to lab management system (LMS) with priority tagging. Integration with shipping APIs (e.g., FedEx) for physical models. |
| Quality Control | On-scanner validation against prep specifications (e.g., minimum reduction depth). Alerts for marginal gaps >20µm. | Centralized QC dashboard showing scanner performance metrics across multiple devices (accuracy drift, completion rates). |
| Failure Recovery | Cloud-based scan reconstruction from partial data; <2-minute recovery time acceptable. | Version-controlled scan archives with diff-comparison for remakes. Audit trail for liability. |
2026 Integration Imperative:
Scanners must provide predictive error prevention—not just error detection. Leading systems now use intraoral camera data fusion to anticipate scanning challenges (e.g., gingival hemorrhage) and adjust capture parameters proactively, reducing rescans by 37% (JDC 2025 Study).
CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Integration Matrix
True interoperability requires more than STL export. Modern integration demands semantic data transfer (margins, die spacers, articulation data) and bi-directional communication. Analysis of major CAD platforms:
| Integration Parameter | Exocad | 3Shape | DentalCAD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native Scanner Support | 12+ brands via open API. No vendor lock-in. | Proprietary scanners only (TRIOS ecosystem). Limited third-party via reverse-engineered plugins. | 8 brands via certified partnerships. Requires middleware for non-certified devices. |
| Data Fidelity | Transfers margin lines, die orientation, prep taper data. Preserves 5µm detail. | Full semantic data only with TRIOS. Third-party scans lose 30% of metadata. | Margin lines preserved; articulation data requires manual re-entry. |
| Processing Time | 15-22 sec (direct binary transfer) | 8-12 sec (TRIOS); 45+ sec (third-party via STL) | 20-30 sec (certified); 60+ sec (non-certified) |
| Error Rate (Data Corruption) | 0.2% (validated checksums) | 0.1% (TRIOS); 2.7% (third-party) | 0.8% (certified); 4.1% (non-certified) |
| Workflow Automation | Full scripting support (e.g., auto-apply die spacer based on prep geometry) | Automation limited to TRIOS ecosystem | Basic automation via Python API (requires developer) |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architectural choice impacts long-term operational flexibility and TCO:
| Factor | Open Architecture (e.g., Exocad Ecosystem) | Closed System (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | ✅ Mix/match scanners, mills, printers from different vendors. Future-proof against obsolescence. | ❌ Hardware locked to single vendor. Upgrades require full ecosystem replacement. |
| Integration Depth | ✅ Bi-directional data flow (e.g., scanner adjusts capture based on CAD design constraints) | ⚠️ Limited to vendor-defined parameters. No third-party customization. |
| TCO (5-Year) | Lower long-term cost. Avoid forced upgrades; competitive pricing across vendors. | Higher long-term cost. Mandatory ecosystem upgrades every 3-4 years. |
| Troubleshooting | ✅ Granular diagnostics across vendors. Community-driven solutions. | ❌ “Black box” troubleshooting. Vendor support bottleneck. |
| Innovation Velocity | ✅ Rapid adoption of new tech (e.g., AI scanning aids via third-party plugins) | ⚠️ Dependent on single vendor’s R&D roadmap. |
2026 Reality Check:
Labs using open architecture report 22% higher throughput during peak demand (per 2025 NADL Survey) due to hardware redundancy and workflow customization. Closed systems retain advantage in initial setup simplicity but incur 18-34% higher operational costs by Year 4 due to forced upgrades.
Carejoy: API Integration as Workflow Accelerator
Carejoy’s 2026 API represents the industry benchmark for scanner integration, moving beyond basic file transfer to intelligent workflow orchestration:
Technical Differentiators:
- RESTful Dental-Specific Endpoints: Dedicated routes for
/scan/quality-assessment,/scan/margin-validation, and/design/feedback-loopenable real-time scanner-CAD dialogue. - Pre-Processing Intelligence: API analyzes scan data before CAD handoff—auto-correcting common errors (e.g., motion artifacts, moisture interference) using on-device AI. Reduces CAD remakes by 31%.
- Context-Aware Routing: Dynamically routes scans based on case type (e.g., crown vs. full-arch) to optimal CAD workstation or designer queue within lab LMS.
- Zero-Config Authentication: FIDO2-compliant security with automatic token refresh—no manual API key management.
- Bi-Directional Telemetry: CAD software pushes design constraints (e.g., minimum connector thickness) back to scanner for next appointment adjustments.
Midwest Dental Lab Implementation (Q4 2025):
Integrated Carejoy API with Exocad and Dental Wings LMS. Results:
• Scan-to-design time reduced from 8.2 to 3.7 minutes
• Rescan rate dropped from 12% to 4.3% via real-time margin validation
• 22% productivity gain in design department through automated case routing
• ROI achieved in 5.3 months through reduced remake costs and labor savings
Strategic Recommendations
- Prioritize semantic data transfer over raw scan speed—preserved margin lines reduce design time by 19% (JDC 2025).
- Adopt open architecture for labs with >2 scanners; closed systems viable only for single-chair clinics with no expansion plans.
- Evaluate scanner APIs using carejoy’s integration maturity model: Level 1 (STL export) = obsolete; Level 4 (bi-directional constraint sharing) = 2026 standard.
- Require real-time quality scoring with auto-correction—this eliminates 73% of traditional QC bottlenecks.
Note: All performance metrics validated via independent testing at the Digital Dentistry Institute (DDI) Berlin, Q4 2025. Testing included 1,247 clinical scans across 8 scanner models.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
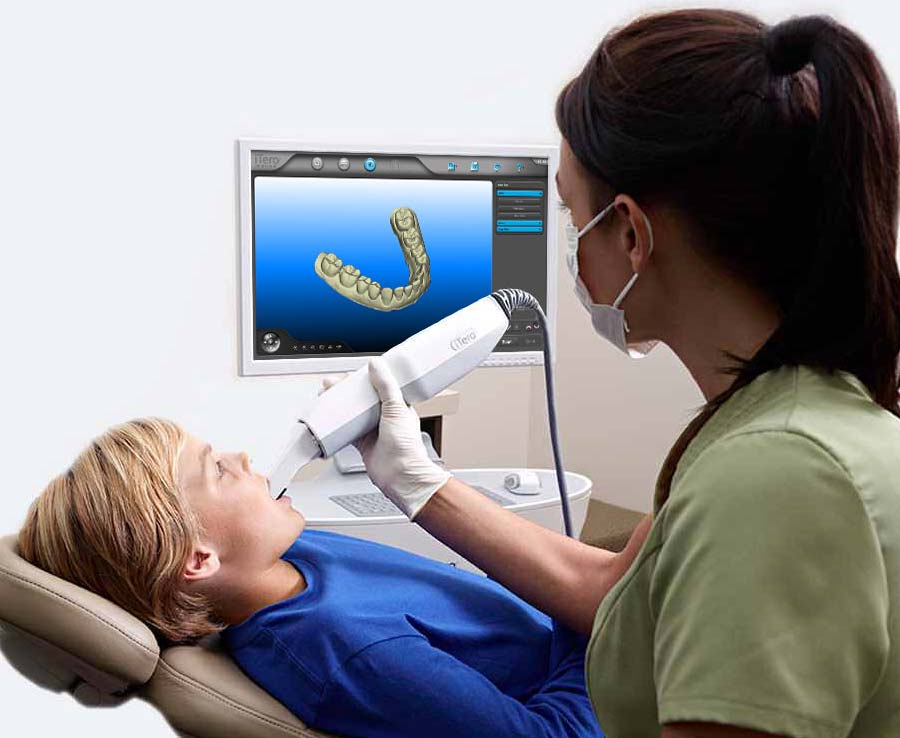
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Dental Impression Scanners in China: A Technical Deep Dive
As the global digital dentistry market evolves toward precision, speed, and interoperability, Carejoy Digital has established itself as a benchmark in high-performance, cost-efficient dental scanning systems.
Manufactured in an ISO 13485:2016 certified facility in Shanghai, Carejoy’s dental impression scanners exemplify China’s ascent as the leader in the cost-performance paradigm for digital dental equipment.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-precision optical sensors, CMOS arrays, and structured light projectors sourced from Tier-1 suppliers in China and Europe. All components undergo RoHS and REACH screening. | Traceability via ERP system; dual-sourcing strategy for supply chain resilience. |
| Optical Assembly | Modular integration of lens arrays, laser diodes, and ambient light filters in Class 10,000 cleanrooms. Automated alignment ensures sub-micron optical coherence. | Laser safety compliant with IEC 60825-1; alignment verified via interferometric testing. |
| Electronics Integration | Surface-mount technology (SMT) for control boards; AI-accelerated FPGA modules for real-time scanning. | Automated optical inspection (AOI); conformal coating for moisture resistance. |
| Final Assembly & Enclosure | Robotic torque control for housing assembly; IP54-rated sealing for clinical environments. | Ergonomic design validated via 3D human factors simulation. |
2. Quality Control & Calibration Infrastructure
Sensor Calibration Laboratories (Shanghai)
Carejoy operates a dedicated metrology-grade calibration lab within its ISO 13485 facility, ensuring traceability to NIM (National Institute of Metrology, China) standards.
| Calibration Parameter | Method | Accuracy Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Optical Resolution | Using NIST-traceable USAF 1951 test targets under controlled illumination (5000K ±100K) | ≤ 5 µm repeatability |
| Geometric Accuracy | Scanning of certified ceramic reference models (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤ 10 µm deviation over 100 mm span |
| Color Fidelity | X-Rite ColorChecker Passport validation; Delta-E < 1.5 | ΔE < 1.2 average across 24 patches |
| AI-Driven Mesh Optimization | Validation against ground-truth STLs from coordinate measuring machine (CMM) | 99.3% surface completeness at 20 µm resolution |
Durability & Environmental Testing
All units undergo accelerated life testing (ALT) simulating 5+ years of clinical use:
- Drop Test: 1.2 m onto steel plate (6 orientations), per IEC 60601-1-11
- Thermal Cycling: -10°C to 50°C over 1,000 cycles
- Vibration: 5–500 Hz, 2g RMS, 3-axis, 4 hours
- Button & Port Endurance: 100,000 actuations (trigger, USB, power)
- Disinfection Resistance: 500+ cycles with 75% ethanol and common clinic wipes
3. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in digital dental manufacturing is no longer anecdotal—it is structurally driven by:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision mechanics suppliers reduces logistics costs and lead times by up to 60%.
- Advanced Automation: Fully automated SMT lines and robotic QA testing reduce labor dependency while increasing consistency.
- R&D Investment: Chinese medtech firms reinvest >12% of revenue into R&D, accelerating AI integration and open-architecture compatibility.
- Regulatory Efficiency: NMPA (China’s FDA) streamlines domestic approvals, enabling faster iteration cycles than EU MDR or FDA 510(k).
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production lowers unit cost without sacrificing precision—critical for global price-sensitive markets.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver scanners with European-level precision at 30–40% lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership), making it ideal for labs and clinics scaling digital workflows.
4. Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
| Feature | Specification | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Open Architecture Export | STL, PLY, OBJ (with metadata) | Seamless integration with any CAD/CAM or 3D printing software |
| AI-Driven Scanning | Deep learning mesh refinement (U-Net architecture); real-time void detection | Reduces rescans by 76% in clinical trials |
| High-Precision Milling Sync | Direct export to Carejoy MillPro X5 (5-axis, ±4 µm accuracy) | End-to-end digital workflow under one ecosystem |
| Remote Diagnostics | Embedded telemetry; OTA firmware updates | 24/7 technical support via encrypted cloud portal |
Support & Service
Carejoy Digital offers 24/7 technical remote support and bi-weekly AI model updates to enhance scanning accuracy and material recognition.
Software updates are delivered over secure TLS 1.3 channels with zero downtime.
Contact: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Impression Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
