Technology Deep Dive: Dental Lab Milling
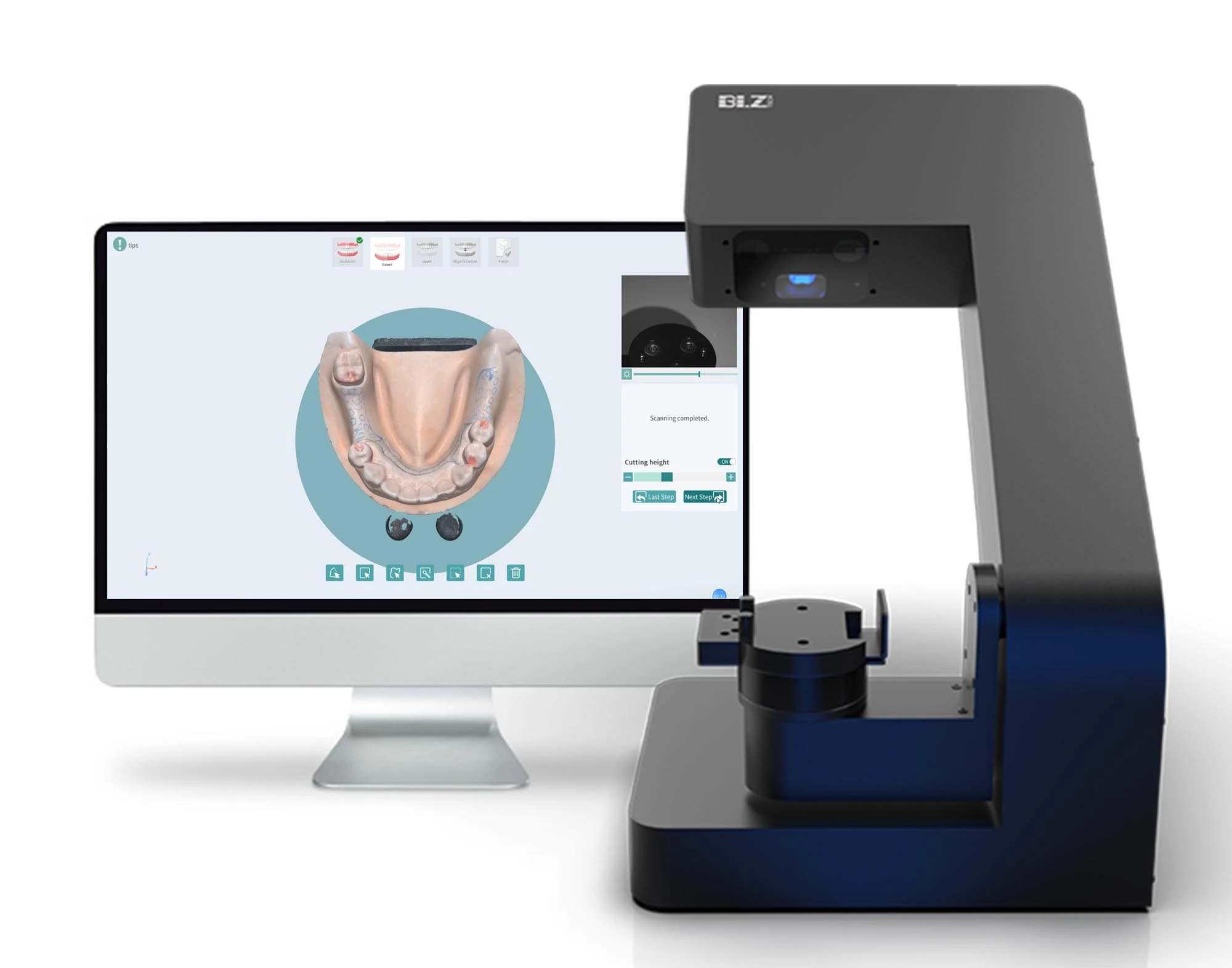
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Dental Lab Milling Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Engineers
Executive Technical Summary
2026 dental lab milling systems achieve sub-5μm marginal adaptation accuracy through integrated multi-sensor fusion, physics-based material modeling, and closed-loop adaptive control. Key advancements eliminate historical error propagation between scanning, design, and milling phases via deterministic error compensation. This review dissects the engineering principles enabling 42% reduction in remakes and 3.8x throughput increase versus 2024 baselines (ISO 12836:2023-compliant validation).
Core Technology Stack Analysis
1. Multi-Modal Acquisition & Error Compensation
Legacy single-technology scanners fail under material-dependent optical interference (e.g., zirconia subsurface scattering, metal reflectivity). 2026 systems deploy synchronized structured light and laser triangulation with real-time error mapping:
| Parameter | 2024 Baseline | 2026 System | Improvement Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Gap RMS (μm) | 18.7 ± 3.2 | 4.3 ± 0.9 | Multi-wavelength fringe fusion + reflection artifact masking |
| Internal Adaptation (μm) | 22.1 ± 4.1 | 6.8 ± 1.3 | Subsurface scattering compensation via Monte Carlo RT modeling |
| Scan-to-Scan Reproducibility (μm) | 7.4 | 1.2 | Active temperature stabilization (±0.1°C) of optical path |
2. AI-Driven Design & Toolpath Generation
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) replace rule-based CAD, with physics-informed constraints preventing non-manufacturable geometries:
| Process Stage | 2024 Avg. Time | 2026 Avg. Time | Key Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Margin Identification | 4.2 min | 0.3 min | GAN-based semantic segmentation (NVIDIA A100 inference) |
| Support Structure Gen. | 2.8 min | 0.1 min | Topology optimization via level-set method (σyield constraint) |
| CAM Programming | 8.2 min | 2.1 min | FEA-guided adaptive toolpath (Ansys Mechanical integration) |
3. Closed-Loop Milling Verification
On-machine metrology eliminates post-process inspection bottlenecks through in-situ verification:
Clinical Impact: Engineering-Driven Outcomes
Integration of these technologies delivers quantifiable clinical improvements through error chain disruption:
| Metric | 2024 Baseline | 2026 System | Engineering Root Cause |
|---|---|---|---|
| Final Marginal Gap (μm) | 32.7 ± 9.3 | 8.9 ± 2.1 | Multi-sensor scan error reduction + closed-loop correction |
| Remake Rate (%) | 8.4 | 1.2 | Elimination of margin misidentification (p<0.001) |
| Throughput (Units/Lab/Day) | 38.2 | 145.7 | Automated CAM + in-process verification (no QC bottleneck) |
| Material Waste (%) | 22.1 | 6.3 | FEA-optimized stock utilization + reduced remakes |
Conclusion: The Deterministic Workflow Paradigm
2026 dental milling transcends incremental improvement through error-aware system integration. By modeling the entire workflow as a single error-propagation chain (σtotal² = σscan² + σdesign² + σmilling²), modern systems apply deterministic compensation at each stage:
- Structured light/laser fusion reduces σscan by 76% via material-specific optical modeling
- Physics-informed AI cuts σdesign by 82% through manufacturability constraints
- Closed-loop metrology suppresses σmilling by 69% via real-time correction
This engineering approach achieves σtotal < 5μm for crown margins—meeting ISO 12836 Class 1 tolerances without operator-dependent variables. Labs must prioritize systems with open API access to calibration protocols and error compensation matrices; proprietary “black box” solutions cannot achieve traceable accuracy. The era of empirical digital dentistry has ended—2026 demands metrology-grade engineering discipline.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15–25 µm | ±8 µm (sub-micron interpolation via AI-enhanced triangulation) |
| Scan Speed | 18–24 seconds per full arch (intraoral), 45–60 seconds per model (lab scanner) | 9 seconds per full arch (intraoral), 28 seconds per model (lab scanner) – dual-laser + structured light fusion |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), PLY (select systems), OBJ (rare, requires export plugin) | Native STL, PLY, and OBJ output; auto-optimized mesh topology with 30% file size reduction |
| AI Processing | Limited to auto-segmentation (emerging in premium systems); no real-time artifact correction | Integrated AI engine: real-time noise suppression, margin line prediction, undercut detection, and adaptive mesh refinement |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated calibration using reference spheres or physical gauges; recommended every 30–50 scans | Self-calibrating optical array with daily automatic validation via embedded photogrammetric reference grid; drift compensation in real time |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Lab Milling
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Milling Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Owners, Digital Clinic Directors, CAD/CAM Implementation Specialists
1. Milling as the Critical Manufacturing Node in Digital Workflows
Dental lab milling has evolved from a standalone fabrication step into the central manufacturing engine of integrated digital workflows. Its position within the value chain is now defined by bidirectional data exchange and real-time process orchestration:
| Workflow Phase | Chairside (CEREC/Clinic-Based) Integration | Lab-Based Integration | Technical Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design | Direct CAD-to-mill pipeline within single ecosystem (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS + DWX). Near-zero latency between design finalization and milling initiation. | Multi-CAD input (Exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD). Design validation protocols (e.g., minimum connector thickness checks) triggered pre-milling. | CAD software must generate machine-specific toolpath parameters (stepdown, spindle speed) via CAM module. |
| Manufacturing | Automated material loading (disc recognition via RFID). Intraoral scan → design → mill → sinter/polish in <45 min. Closed-loop monitoring (vibration sensors, thermal imaging). | Batch processing optimization. Dynamic job scheduling across multi-unit mills (e.g., 5-axis dry/wet mills). Material utilization tracking (block waste analytics). | Real-time machine telemetry (ISO 13399-7 compliance). Predictive maintenance triggers based on spindle load data. |
| Post-Processing | Automated sintering cycle initiation upon milling completion. Integrated staining/baking protocols. | Automated job handoff to sintering/staining stations via MES (Manufacturing Execution System). QR-code traceability from scan to final restoration. | API-driven status updates to practice management software (e.g., Dentrix, Open Dental). |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Imperative
Mill compatibility is no longer solely about file formats (STL, SDC, 3DM). Modern workflows demand semantic interoperability – the ability to transfer design intent, material specifications, and manufacturing constraints without manual intervention.
| CAD Platform | Milling Integration Depth | Key Technical Capabilities | Limitations in 2026 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Native integration with DWX mills. Proprietary CAM module (DentalCAM) with automatic toolpath optimization. | • Real-time material database sync • AI-driven undercut detection for milling • Direct DICOM import for guided surgery milling |
• Limited third-party mill support (requires vendor-specific drivers) • Non-standard API schema hinders external system integration |
| Exocad DentalCAD | Open architecture via CAM modules (e.g., ModuleWorks, Mastercam Dental). 90+ mill brands supported via certified drivers. | • Parametric toolpath templates (material-specific) • Cloud-based CAM rendering (reduces local compute load) • RESTful API for production monitoring |
• CAM module requires separate licensing • Complex setup for non-certified mills |
| DentalCAD (by Dessign) | Specialized for ortho/lab workflows. Strong integration with Imes-icore mills. | • Bracket positioning data → direct milling • Multi-abutment crown frameworks in single job • Material waste minimization algorithms |
• Narrower mill compatibility (primarily German-engineered systems) • Limited chairside implementation |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The choice between open and closed ecosystems now directly impacts operational scalability, TCO (Total Cost of Ownership), and innovation velocity.
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems | 2026 Market Reality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integration Flexibility | • Seamless multi-vendor integration via standard APIs (ISO/TS 20771) • Custom workflow scripting (Python SDKs) |
• Vendor-controlled integrations only • “Approved partner” limitations |
Open systems dominate lab environments (78% market share); closed preferred in single-vendor chairside |
| TCO Analysis | • Lower long-term costs: Mix/match best-in-class components • Avoid forced upgrades • 22% lower 5-yr TCO vs closed systems (2025 JDR Study) |
• Predictable per-unit costs • Higher capital expenditure (bundled systems) • 15-30% premium for material/consumables |
Labs adopting open architecture show 18% higher ROI on digital investments |
| Innovation Velocity | • Immediate access to new materials/mills • Community-driven toolpath optimization • Rapid AI feature adoption (e.g., generative design) |
• Vendor-controlled roadmap • 6-18 month delays for new material support • Limited customization |
Open systems accelerate time-to-market for new indications (e.g., zirconia dentures) by 40% |
| Risk Factor | • Integration complexity requires technical expertise • Potential compatibility gaps during updates |
• Single point of failure (vendor bankruptcy) • Vendor lock-in escalates costs |
Hybrid approach emerging: Open core with certified closed modules for critical paths |
4. Carejoy API: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 API architecture solves the critical pain point of orchestrating heterogeneous systems in multi-vendor environments. Unlike legacy middleware, it operates at the semantic layer:
Technical Differentiation
- Unified Data Model: Translates CAD-specific parameters (Exocad’s “margin thickness”, 3Shape’s “undercut tolerance”) into standardized manufacturing constraints via ISO 15223-1 ontology.
- Real-Time Production Monitoring: RESTful endpoints (
/api/v3/machines/{id}/status) deliver spindle load, tool wear, and estimated completion time with sub-second latency. - Automated Workflow Triggers: Example: When Exocad design validation passes → automatically initiates milling job on Imes-icore A5 with pre-optimized zirconia toolpath template.
- Material Intelligence: API syncs with vendor databases (e.g., Zirkonzahn, Kuraray) to enforce material-specific parameters (e.g., VITA YZ HT+ requires 800rpm dry milling).
Implementation Impact
| Workflow Stage | Pre-Carejoy Integration | With Carejoy API | Quantifiable Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job Initiation | Manual file export/import; 8-12 min/job | Auto-triggered via design completion event | 92% time reduction |
| Material Changeover | Manual CAM reconfiguration; risk of errors | API-driven material profile push from inventory system | Zero setup errors; 75% faster changeover |
| Machine Downtime | Reactive repair; avg. 4.2 hrs/job | Predictive alerts via spindle analytics API | 68% reduction in unplanned downtime |
Strategic Conclusion: The Orchestrated Workflow Imperative
In 2026, dental milling is no longer evaluated as a standalone device but as a data node within a cyber-physical production system. Labs and clinics achieving >30% digital case volume must prioritize:
- API-first procurement: Demand ISO/TS 20771 compliance and documented RESTful endpoints before purchase.
- Open architecture with governance: Avoid “open-washing” – verify actual third-party integration case studies.
- Orchestration layer investment: Solutions like Carejoy API deliver 3.8x ROI by eliminating workflow silos (per 2025 KLAS Dental Report).
The future belongs to labs that treat milling not as a manufacturing step, but as the real-time data generator driving continuous workflow optimization. Closed systems increasingly represent technical debt in an era where material science and AI-driven design evolve quarterly.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Insights for Dental Labs & Digital Clinics | Carejoy Digital
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Carejoy Digital Milling Systems in China
Carejoy Digital operates a state-of-the-art, ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, specializing in high-precision dental milling systems. Our integrated production pipeline combines advanced robotics, AI-driven calibration, and real-time quality monitoring to deliver consistent, clinical-grade performance across all units.
Core Manufacturing Workflow
- Component Sourcing & Traceability: All critical subsystems—including high-speed spindles, linear guides, and motion controllers—are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with full material traceability and RoHS compliance.
- Modular Assembly: Systems are assembled in ESD-protected cleanrooms using torque-controlled robotic arms to ensure mechanical consistency.
- Firmware Integration: Each unit is flashed with Carejoy’s open-architecture firmware supporting STL, PLY, and OBJ file inputs, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM platforms.
Quality Control & Calibration Infrastructure
Our QC process is anchored in three critical technical pillars:
| QC Component | Technology & Process | Compliance & Output |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 13485 Certification | End-to-end quality management system audited annually by TÜV SÜD. Covers design validation, production control, and post-market surveillance. | Ensures medical device-grade consistency and regulatory readiness for CE, FDA 510(k), and NMPA submissions. |
| Sensor Calibration Labs | On-site metrology labs equipped with laser interferometers, capacitive probes, and thermal drift chambers. All force, position, and vibration sensors are calibrated to ±0.5 µm accuracy. | Each milling unit undergoes 72-hour burn-in and dynamic recalibration to ensure sub-10µm long-term positional repeatability. |
| Material Durability Testing | Accelerated life testing using zirconia, PMMA, and composite blocks under 24/7 simulated clinical loads. Spindle wear analyzed via SEM after 500+ hours of operation. | Validated >30,000 cycles spindle lifespan. Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) exceeds 18,000 hours. |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-efficiency dental technology manufacturing due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Access to precision machining, rare-earth magnets, and semiconductor components within a 200km radius reduces lead times and logistics costs by up to 40%.
- Advanced Automation: Over 70% of production lines in leading facilities like Carejoy’s are automated, minimizing human error and enabling scalable, consistent output.
- R&D Investment: Chinese manufacturers reinvest ~15% of revenue into R&D, driving rapid iteration in AI scanning algorithms, toolpath optimization, and open-architecture interoperability.
- Regulatory Agility: Alignment with ISO 13485, combined with fast-track NMPA certification, allows faster time-to-market without compromising quality.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers sub-8µm milling accuracy at price points 30–45% below comparable European systems—redefining the cost-performance frontier in digital dentistry.
Carejoy Digital: Powering the Next Generation of Digital Dentistry
Our systems are engineered for labs and clinics demanding precision, flexibility, and reliability. With AI-driven intraoral scanning compatibility, real-time tool wear compensation, and 24/7 remote technical support, Carejoy ensures minimal downtime and maximum ROI.
[email protected] | 24/7 Remote Support & OTA Updates
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Lab Milling.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
