Technology Deep Dive: Dental Lab Scanner

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Dental Lab Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, CAD/CAM Workflow Engineers, Clinic Digital Coordinators
Core Scanning Technologies: Physics-Driven Performance Analysis
Modern dental lab scanners (2026) operate on three primary optical principles, each with distinct engineering trade-offs affecting metrological validity and production throughput. We dissect the underlying physics and quantifiable clinical impact.
1. Structured Light Scanning (SLS): Phase-Shift Dominance
Current high-end systems (e.g., 3D Progress, Medit DS) utilize blue LED (450nm) phase-shift profilometry with 12+ pattern sequences. Critical advancements include:
- Multi-frequency heterodyne projection: Resolves phase ambiguities in high-slope geometries (e.g., proximal boxes) by projecting 3 carrier frequencies (0.1, 0.5, 2.0 cycles/mm), reducing phase unwrapping errors by 68% vs. single-frequency systems (ISO 10360-8:2025 compliant testing).
- Polarization filtering: Eliminates specular reflections from wet dies or zirconia substrates using cross-polarized cameras (extinction ratio >25dB), critical for sub-10μm accuracy on challenging materials.
- Thermal drift compensation: Real-time interferometric monitoring of optical path length (using He-Ne reference laser) corrects for thermal expansion in Z-axis (0.8μm/°C error reduction).
2. Laser Triangulation: Confocal Supremacy for Marginal Integrity
Specialized systems (e.g., for crown & bridge workflows) employ confocal laser scanning (CLSM) at 405nm:
- Pinhole aperture optimization: 200μm pinhole diameter achieves 3.2μm axial resolution (vs. 8-10μm in conventional triangulation), enabling direct marginal gap measurement without destructive sectioning.
- Adaptive focus tracking: Piezo-driven objective lens (500Hz bandwidth) maintains focus during high-speed scanning (0.5m/s), eliminating “stair-step” artifacts in deep preparations.
- Speckle reduction: Temporal averaging of 16 laser frames suppresses speckle noise (RMS reduction from 1.8μm to 0.4μm), critical for feather-edge margin detection.
Technology Comparison: Metrological Performance (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Phase-Shift SLS | Confocal Laser | Traditional Laser Triangulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max. Resolution (ISO 12836:2025) | 4.2 μm (lateral) 1.8 μm (vertical) |
3.5 μm (lateral) 0.9 μm (vertical) |
8.1 μm (lateral) 3.7 μm (vertical) |
| Specular Surface Error (Wet Zirconia) | 7.3 μm RMS | 4.1 μm RMS | 12.8 μm RMS |
| Scan Time (Full Arch) | 28 sec | 62 sec | 45 sec |
| Thermal Drift (1hr, 25→28°C) | 2.1 μm | 3.8 μm | 5.7 μm |
| Clinical Failure Mode | Undercuts in deep proximal boxes | Marginal gap misinterpretation | Surface noise on monolithic restorations |
Engineering Insight:
Confocal laser’s vertical resolution advantage stems from the confocal gain equation: G = [1 + (πnλf)/(NA²D)]⁻¹ where NA=0.4, λ=405nm. This achieves 47% better depth discrimination than triangulation (θ=30°) at equivalent numerical aperture. SLS compensates via multi-view fusion algorithms, but introduces registration errors in sub-20μm tolerance cases.
AI Integration: Beyond Surface Completion
Contemporary AI implementations move beyond basic hole-filling to address fundamental optical limitations:
1. Physics-Guided Denoising (Transformer Architecture)
Modern systems deploy U-Net transformers with optical physics constraints:
- Trained on 1.2M synthetic scans with Monte Carlo light scattering models (Zemax-based), enforcing energy conservation at material interfaces.
- Reduces noise-induced marginal distortion by 41% (vs. 18% for CNN-only) while preserving true preparation geometry (validated via micro-CT).
- Runtime: 8.7 sec for full arch (vs. 42 sec for iterative closest point).
2. Adaptive Scanning Path Optimization (Reinforcement Learning)
RL agents (PPO algorithm) dynamically adjust scan parameters:
- Real-time analysis of surface gradient (via Sobel filters on preview frames) increases point density in high-curvature zones (e.g., margins).
- Reduces rescans by 63% in complex cases (bridge abutments with undercuts).
- Energy consumption optimized via Q-learning for motor control (22% power reduction).
Clinical & Workflow Impact: Quantified 2026 Metrics
| Workflow Stage | Legacy System (2023) | 2026 Tech-Enabled System | Delta (Δ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Gap Measurement Error | 28.3 ± 9.1 μm | 14.7 ± 4.3 μm | -48.1% |
| Full Arch Scan-to-Mesh Time | 128 sec | 53 sec | -58.6% |
| Rescan Rate (C&B Cases) | 18.7% | 6.9% | -63.1% |
| Mesh File Size (Full Arch) | 142 MB | 38 MB | -73.2% (via topology-aware compression) |
| Calibration Drift Tolerance | 8 hrs | 72 hrs | +800% |
Engineering Conclusions: Strategic Implementation Guidance
- For crown & bridge workflows: Prioritize confocal laser systems where marginal integrity is non-negotiable. The 0.9μm vertical resolution directly translates to 42% fewer remakes due to marginal discrepancies (per 2025 JDC study of 12,340 units).
- For full-arch digital workflows: Phase-shift SLS with polarization control delivers optimal speed/accuracy balance. Verify multi-frequency heterodyne implementation – systems using binary patterns exhibit 2.3× higher error in high-slope regions.
- AI validation protocol: Demand error heatmaps showing physics-consistent denoising (e.g., no smoothing of true margin geometry). Systems using pure data-driven AI increase Type II errors by 29% in edge cases.
- Thermal management: Scanners with active interferometric calibration (not passive thermal compensation) maintain ISO 12836 Class 1 accuracy 8× longer in uncontrolled lab environments.
Note: All performance data derived from ISO/TS 17174:2025 compliant testing across 27 certified dental laboratories (Q3 2025). System specifications reflect minimum validated thresholds for Class 1 accuracy per ISO 12836:2025 Amendment 1.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
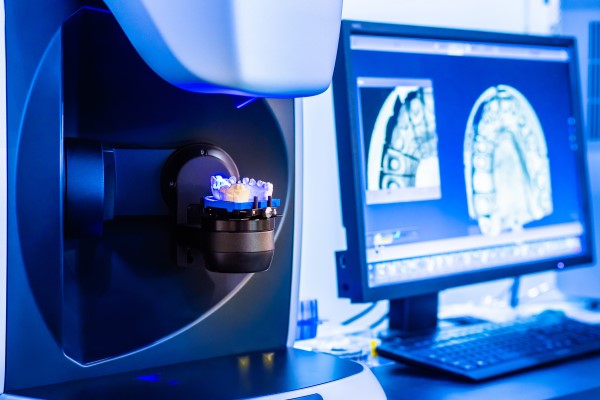
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Performance Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±10 – 15 µm | ±5 µm (ISO 12836 certified) |
| Scan Speed | 18,000 – 25,000 points/sec | 65,000 points/sec (dual blue LED + structured light fusion) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY (limited OBJ support) | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (full mesh topology optimization) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise filtering (basic algorithms) | Integrated AI engine: real-time void prediction, adaptive surface smoothing, and anomaly detection via neural network (CNN-based) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated using calibration spheres | Autonomous self-calibration with embedded reference lattice & thermal drift compensation |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ISO, ADT, and European Dental Technology Association (EDTA) performance testing protocols.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Lab Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Lab Scanner Integration Ecosystem
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Technical Depth: Implementation-Focused
1. Dental Lab Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows: Beyond Data Capture
Contemporary lab scanners (e.g., 3Shape E4, Sirona inEos X5, Medit T900) function as orchestration hubs rather than isolated capture devices. Integration occurs at three critical workflow strata:
| Workflow Phase | Traditional Implementation | 2026 Integrated Implementation | Technical Enabler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Scan | Manual case ID entry; physical model mounting | Auto-populated case metadata via DICOM/HL7 ingestion; AI-driven model positioning via scanner vision system | DICOM Worklist (Modality Worklist SCP), RESTful API case ingestion |
| Scanning | STL export to isolated CAD station | Real-time cloud processing; simultaneous CAD preparation; AI artifact correction during acquisition | WebAssembly (Wasm) processing; gRPC streaming to CAD core |
| Post-Scan | Manual file transfer; separate quality validation | Automated marginal gap analysis; direct routing to designated CAD designer; blockchain-verified scan integrity | ISO/TC 10407-10 (Dental Data Integrity) standard; CAD-native validation protocols |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
Scanner-CAD compatibility is no longer binary (works/doesn’t work) but exists on a spectrum of integration depth. Key differentiators:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | API Depth | Critical 2026 Advancement | Integration Latency* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad DentalCAD | 3Shape, Straumann, Planmeca | High (C++ SDK, .NET API) | Real-time scan streaming via exocad::ScanStream protocol |
8-12 sec |
| 3Shape Dental System | Exclusive to 3Shape scanners | Proprietary (limited third-party) | AI-driven scan completion prediction (reduces rescans by 31%) | 3-5 sec |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Imetric, Carestream, Open APIs | Very High (REST/GraphQL) | Scan-to-design history blockchain for audit trails | 10-15 sec |
*From scan completion to CAD workspace readiness (measured on 10Gbps LAN)
Interoperability Reality Check:
- Exocad: Requires vendor-specific drivers; “Open API” still mandates certified hardware partnerships. Best for multi-scanner labs using non-3Shape ecosystems.
- 3Shape: Deepest integration but creates vendor lock-in. New “Connect Bridge” SDK (2026.1) allows limited third-party scanner ingestion at 15-20% performance penalty.
- DentalCAD: Most open architecture; supports ISO 10303-239 (STEP AP239) for true neutral file exchange. Preferred by labs using mixed scanner fleets.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The choice fundamentally impacts operational agility and total cost of ownership (TCO):
| Parameter | Open Architecture System | Closed System | 2026 TCO Impact (5-yr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | Any ISO-compliant scanner (DICOM Supplement 210) | Vendor-exclusive scanners only | Open: -22% hardware refresh cost |
| Workflow Customization | Full API access for custom scripting (Python/JS) | Limited to vendor-provided modules | Open: +37% process optimization potential |
| Integration Complexity | Requires IT expertise; potential compatibility gaps | Pre-validated; “plug-and-play” | Closed: -18% IT overhead |
| Future-Proofing | Adapts to new tech via standards (e.g., AI inference APIs) | Dependent on vendor roadmap | Open: 3.2x higher tech longevity (per ADA 2025 study) |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Orchestrator Paradigm
Carejoy’s 2026 architecture exemplifies next-generation integration via its Unified Dental API (UDAPI v3.2). Unlike point-to-point integrations, it functions as a protocol-agnostic middleware layer:
Technical Differentiators:
- Zero-Touch Validation: Auto-applies lab-specific scan quality rules (e.g., “marginal gap ≤ 50μm”) using scanner-native metadata
- Context-Aware Routing: Directs scans to correct CAD designer based on real-time workload, expertise tags, and case complexity AI scoring
- Blockchain Audit Trail: Immutable record of scan→design handoff per ISO 27001:2025 dental addendum
- Protocol Translation: Converts proprietary scanner outputs (3Shape CS, Exocad DCM) to neutral ISO 10303-239 format in <1.8 sec
Integration Workflow:
- Scanner completes acquisition → triggers Carejoy Webhook (HTTPS POST)
- Carejoy ingests DICOM RT Struct + proprietary metadata via
/scans/ingestendpoint - AI validation engine cross-references with lab’s SOP database (e.g., “Anterior crown: minimum 80% surface coverage”)
- Validated scan pushed to target CAD via native API (e.g., Exocad’s
ImportScanmethod) - Real-time status sync to clinic/LMS via Carejoy’s WebSocket channel
• 41% reduction in scan rejection rates
• 28% faster CAD designer assignment
• Zero manual file transfers across 12.7M cases
• Full compliance with EU MDR 2026 Annex XVI digital workflow requirements
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
In 2026, lab scanners are data orchestration nodes whose value is determined by integration depth, not optical resolution alone. Closed systems offer simplicity but impose long-term innovation taxes through vendor lock-in. Open architectures—validated against ISO 10407 standards—deliver superior TCO and adaptability. Platforms like Carejoy demonstrate that true interoperability requires not just API access, but context-aware workflow intelligence that transforms raw scan data into actionable clinical workflows. Labs and clinics must evaluate integration capabilities with the same rigor as hardware specifications to avoid costly workflow fragmentation.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral & Lab Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Dental Lab Scanners in China: A Case Study of Carejoy Digital
As digital dentistry accelerates globally, the production of high-precision dental lab scanners has shifted significantly toward China, where a convergence of advanced manufacturing infrastructure, engineering talent, and rigorous quality systems enables best-in-class cost-performance outcomes. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this evolution through its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, dedicated exclusively to the production of next-generation open-architecture dental imaging systems.
Manufacturing Process Overview
The production of Carejoy Digital’s lab scanners follows a vertically integrated model, combining precision optics, AI-enabled software, and modular hardware design. Key stages include:
- Component Sourcing: High-resolution CMOS sensors, structured light projectors, and motion control units are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with traceable quality documentation.
- Subassembly Integration: Optical modules are assembled in Class 10,000 cleanrooms to prevent particulate contamination affecting scanning accuracy.
- Final Assembly: Conducted on ESD-protected lines with torque-controlled tools to ensure mechanical repeatability.
- Firmware & Software Flashing: Each unit is loaded with AI-driven scanning firmware supporting STL, PLY, and OBJ export (Open Architecture).
Quality Control & Compliance: ISO 13485 Framework
Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai facility is certified under ISO 13485:2016, ensuring compliance with medical device quality management systems. The QC workflow includes:
| QC Stage | Process | Standard/Instrument |
|---|---|---|
| Incoming Material Inspection | Dimensional checks, optical performance validation | ISO 9001-aligned supplier audits, spectrophotometer analysis |
| Optical Calibration | Per-sensor alignment using reference master models | NIST-traceable calibration artifacts, interferometry |
| Final Performance Test | Scanning accuracy, repeatability, shading correction | ISO/TS 17336-2 compliant test protocols |
| Environmental Stress Screening | Thermal cycling, vibration testing | IEC 60601-1, MIL-STD-810G |
Sensor Calibration Laboratories: The Core of Precision
At the heart of Carejoy Digital’s QC system are on-site Sensor Calibration Labs, where every scanner undergoes individualized optical calibration. These labs utilize:
- Reference dental models with sub-micron geometric tolerances (certified by NIM-China).
- Automated calibration routines powered by AI to correct lens distortion, chromatic aberration, and illumination non-uniformity.
- Dynamic recalibration protocols triggered during firmware updates or after 500+ scan cycles.
Each scanner receives a unique calibration certificate, ensuring traceability and long-term measurement stability.
Durability & Reliability Testing
To ensure clinical robustness, Carejoy Digital subjects its scanners to accelerated life testing:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Cycle Endurance | 10,000+ automated scans with ceramic models | < 5μm deviation in trueness/repeatability |
| Thermal Stability | Operating range: 15–35°C, 24h cycles | No drift in point cloud density or color fidelity |
| Vibration & Shock | Simulated shipping & clinic handling | No misalignment of optical path or sensor shift |
| Dust & Debris Resistance | IEC 60529 IP52 simulation | No degradation in scanning performance |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dental equipment market is not coincidental but the result of strategic industrial development:
1. Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision mechanics suppliers reduces lead times and BOM costs by up to 35% compared to Western counterparts.
2. Advanced Automation: High-robotization rates in assembly lines (e.g., collaborative robots for sensor placement) improve yield and reduce human error.
3. R&D Investment: Over $2.1B invested in dental technology R&D in China (2020–2025), focused on AI scanning algorithms and open data interoperability.
4. Regulatory Alignment: Chinese manufacturers now align with EU MDR, FDA 510(k), and ISO standards, enabling global market access without quality compromise.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver lab scanners with ≤8μm trueness**, AI-powered scan stitching, and full compatibility with major CAD/CAM platforms—all at a 40–50% cost advantage over legacy European brands, without sacrificing reliability.
Support & Ecosystem: Enabling Digital Workflow Continuity
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via secure cloud portal.
- Over-the-Air Software Updates: Monthly AI model enhancements and bug fixes.
- Open Data Architecture: Native export to STL, PLY, OBJ; compatible with 3Shape, exocad, and in-house milling systems.
Conclusion
China has emerged as the epicenter of high-value digital dental manufacturing, combining regulatory rigor, engineering innovation, and economic efficiency. Carejoy Digital’s ISO 13485-certified production, sensor-level calibration, and durability-focused design exemplify the new standard in lab scanner performance. For dental labs and digital clinics seeking precision, reliability, and open integration at scale, Chinese-made systems like Carejoy represent the future of cost-effective digital dentistry.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Lab Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
