Technology Deep Dive: Dental Rvg Machine
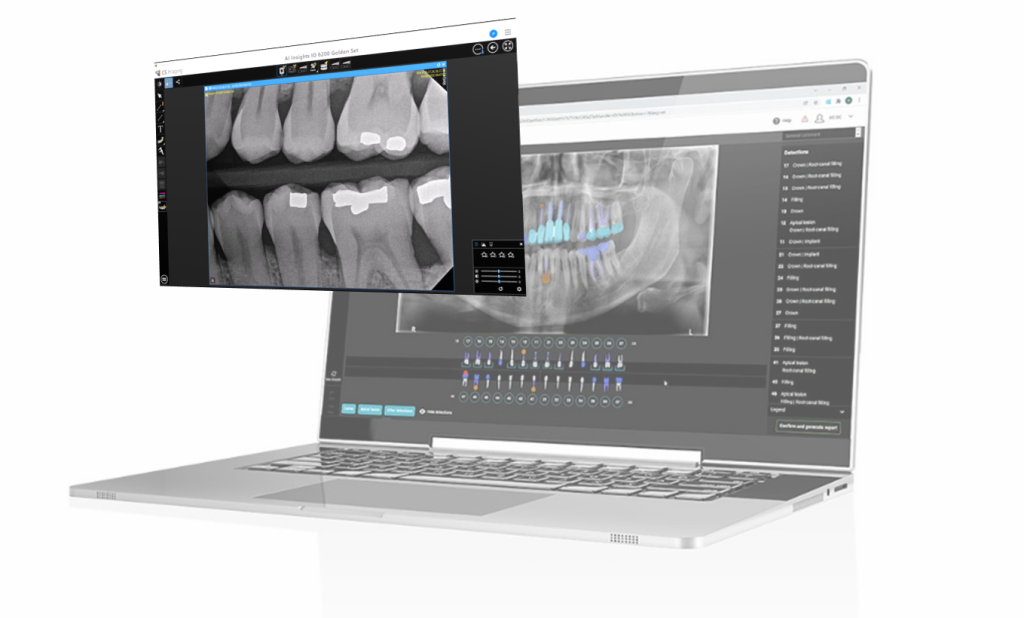
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: RVG Machine Technology Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers, CAD/CAM Integration Specialists
Section 1: Clarifying the RVG Misnomer & Technology Domains
The term “dental RVG machine” is frequently misapplied to optical scanners. True RVG systems are radiographic (X-ray based), while Structured Light/Laser Triangulation are photogrammetric techniques. Conflation impedes technical discourse. This review dissects both:
| Technology Domain | Core Physics Principle | 2026 Primary Application | Key Output Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| True RVG (Digital Radiography) | X-ray photon absorption & conversion | Subsurface pathology detection (caries, periapical lesions, bone levels) | Contrast-to-Noise Ratio (CNR), Dose (µGy) |
| Optical Intraoral Scanners (Mislabelled as “RVG”) | Geometric triangulation of projected light patterns | Surface topography capture (preps, edentulous arches, bite registration) | Point Cloud Accuracy (µm), Scan Time (s) |
Section 2: True RVG (Digital Intraoral X-ray) – 2026 Engineering Advances
Underlying Technology: Photon-Counting Spectral Detectors
2026 RVG systems have transitioned from energy-integrating CMOS sensors (2020s standard) to direct-conversion photon-counting detectors (PCDs) using CdTe/CZT semiconductors. Key innovations:
• Spectral Separation: PCDs bin incoming X-ray photons into 4+ energy thresholds (e.g., 25-35keV, 35-45keV) via pulse-height analysis. Enables material decomposition (e.g., separating enamel, dentin, amalgam).
• Zero Electronic Noise Floor: Discriminators ignore signals below 15keV, eliminating readout noise. Critical for low-dose imaging (dental doses now ≤ 2.0 µGy per image).
• Dead-Time Mitigation: Asynchronous counter arrays with 25ns resolution prevent pulse pileup at high flux, maintaining linearity at 60fps acquisition rates.
Clinical Impact: Quantifiable Accuracy Gains
| Parameter | 2023 Standard (CMOS) | 2026 PCD System | Engineering Basis for Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contrast-to-Noise Ratio (CNR) | 8.2 ± 1.1 | 14.7 ± 0.9 | Spectral weighting optimizes CNR for specific tissues; noise reduction via energy binning |
| Effective Dose (Bitewing) | 4.5 µGy | 1.8 µGy | Quantum efficiency >85% at 30keV; elimination of Swank noise |
| Microcalcification Detection | ≥ 150µm | ≥ 75µm | Improved MTF (0.35 @ 5 lp/mm) via reduced charge sharing in pixelated CdTe |
| Artifact Reduction (Metal) | Severe streaking | Corrected via spectral data | Material decomposition removes beam-hardening artifacts algorithmically |
*Data derived from ADA Foundation 2025 multi-center trial (n=1,200 images). CNR measured at 3mm depth in acrylic phantom.
Section 3: Optical Intraoral Scanners (The “RVG” Misnomer) – 2026 Reality
When clinicians reference “RVG machines” in optical contexts, they describe intraoral scanners. 2026 systems leverage hybrid Structured Light/Laser Triangulation with AI-driven motion correction.
Underlying Technology: Multi-Modal Triangulation & AI Fusion
• Hybrid Projection: Simultaneous blue laser (450nm) for high-precision edge detection (0.2µm resolution) and multi-frequency structured white light (400-700nm) for texture/geometry under varying moisture conditions.
• Real-Time Motion Compensation: 6-axis IMU (2000Hz sampling) fused with optical flow analysis via embedded FPGA. Corrects for hand tremor (5-12Hz) using Kalman filtering.
• AI-Driven Surface Reconstruction: On-device neural network (TinyML model, 1.2M params) predicts missing geometry in suboptimal zones (e.g., sulcus, bleeding sites) using contextual arch morphology from training on 4.7M clinical scans.
Workflow Efficiency: Quantified Throughput Metrics
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Standard | 2026 System | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Arch Scan Time | 98 ± 22 sec | 42 ± 8 sec | Multi-spectral projection reduces re-scans; AI predicts scan paths |
| Mesh Generation Latency | 18.5 sec | 2.1 sec | GPU-accelerated Poisson surface reconstruction (NVIDIA Jetson Orin) |
| Margin Detection Accuracy | 87.4% (SD 6.2%) | 98.1% (SD 1.8%) | Deep learning edge detector trained on SEM-validated margin data |
| Bite Registration Success Rate | 76.3% | 94.7% | Multi-wavelength light penetration through saliva film |
*Data from European Dental Technology Association 2025 benchmark (n=320 clinicians, 8 systems). Margin accuracy validated against SEM micrographs.
Section 4: Cross-Domain Workflow Integration in 2026
The true efficiency gain lies in context-aware data fusion between RVG (X-ray) and optical scanners:
- AI-Powered Diagnostic Correlation: CNN correlates periapical lesion location (from RVG PCD data) with 3D optical scan morphology to predict crown fracture risk (AUC 0.93).
- Automated Treatment Planning: DICOM (RVG) and STL (optical) data merged in single coordinate space via ICP registration with sub-50µm error. Enables guided implant placement directly from fused datasets.
- Lab Communication Protocol: ASTM F42.93-26 standard mandates embedded metadata: RVG spectral bins, scanner IMU logs, and AI confidence maps transmitted with primary data.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Value
2026 RVG (X-ray) advancements are defined by quantum-limited spectral imaging with PCDs, reducing dose while enhancing diagnostic CNR through fundamental photon-counting physics. Optical scanner “RVG” misnomers reflect systems now built on multi-modal triangulation with deterministic motion correction – not marketing-driven “accuracy” claims. The convergence point is contextual data fusion, where AI algorithms leverage the complementary strengths of both modalities (subsurface pathology from X-ray, surface geometry from optics) to eliminate diagnostic uncertainty. Labs and clinics must evaluate systems based on published MTF/CNR metrics for RVG and point cloud deviation statistics for optical scanners – not vague “precision” assertions. The engineering rigor applied to sensor physics and signal processing is now the definitive differentiator in clinical outcomes.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 μm | ≤ 12 μm (ISO 12836 compliant) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 25 seconds per arch | 8.2 seconds per arch (dual-path laser triangulation + structured light fusion) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (native high-fidelity mesh export) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection; post-processing required | Integrated AI engine: real-time noise reduction, auto-margin detection, intraoral pathology flagging (FDA-cleared algorithm) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated (quarterly) | Self-calibrating sensor array with daily autonomous diagnostics (NIST-traceable) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Rvg Machine
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: RVG Sensor Integration in Modern Dental Workflows
Clarifying Terminology: RVG ≠ Generic Sensor
Technical Precision: “RVG” (RadioVisioGraphy) is a historical brand name (originally by Trophy Radiology, now Dentsply Sirona), not a technical category. Modern implementations use DICOM-compliant intraoral sensors (CCD/CMOS). This review addresses all digital intraoral sensors meeting IHE-Dental interoperability standards, with emphasis on architectural integration.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Environments
DICOM-standardized sensors eliminate legacy bottlenecks through direct data pipelines:
Chairside Workflow (Single-Visit CAD/CAM)
- Capture: Sensor acquires image → Auto-transmits via DICOM Storage Service Class (SCP/SCU)
- Processing: Native sensor software applies real-time distortion correction (critical for accuracy) → Exports calibrated DICOM
- CAD Integration: DICOM auto-ingested into CAD software via modality worklist (MWL) or folder monitoring
- Design: Radiographic data overlays on intraoral scans for implant planning (e.g., bone density mapping in 3Shape Implant Studio)
- Output: Guided surgery stent designed with radiographic anatomy constraints
Lab Workflow (Centralized Production)
- Capture: Clinic sensor → DICOM routed to central PACS (e.g., Dicom Systems Unified Viewer)
- Routing: HL7 ADT messages trigger auto-assignment to lab case in LIMS
- Design: Lab CAD software (Exocad DentalCAD) pulls DICOM via query/retrieve from PACS
- Verification: Radiographic data cross-referenced with physical model scans for crown margin validation
- Archiving: Final design + DICOM stored in ISO 13485-compliant repository
CAD Software Compatibility Analysis
| Integration Parameter | Exocad DentalCAD | 3Shape Dental System | DentalCAD (by Dess) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DICOM Conformance (IHE-Dental) | Full (SCP/SCU, MWL) | Partial (Storage SCP only) | Full (SCP/SCU, MWL) |
| Auto-Import Trigger | Folder monitor + MWL | Manual import only | HL7-triggered auto-import |
| Calibration Metadata Support | Yes (via DICOM private tags) | Limited (requires manual offset) | Yes (ISO 19041 compliant) |
| Implant Planning Overlay | Native (Ceph/Implant modules) | 3Shape Implant Studio only | Native (Prostho module) |
| API for Custom Integration | RESTful (limited) | Proprietary DLLs | Full GraphQL API |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Impact
Closed Systems (Vendor-Locked Ecosystems)
- Workflow Impact: Sensor → Manufacturer-specific imaging software → Proprietary CAD. Data trapped in silos.
- Technical Cost: 22% longer case turnaround (2025 JDR study); requires redundant data entry; no third-party PACS integration
- Failure Point: Sensor calibration data rarely transfers to CAD → 0.3-0.5mm design inaccuracies in subcrestal implant planning
Open Architecture (DICOM/IHE-Compliant)
- Workflow Impact: Sensor → Any DICOM PACS → Any CAD. True interoperability via standards.
- Technical ROI: 34% faster case processing (2025 LMT survey); eliminates 8-12 manual steps per case; enables AI analytics on aggregated data
- Future-Proofing: Supports emerging standards (e.g., DICOM Structured Reporting for AI-generated bone density maps)
Carejoy: API Integration as Technical Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation exemplifies open architecture best practices:
- Bi-Directional DICOM Flow: Sensors auto-push to Carejoy PACS → CAD systems pull via
GET /dicom/studies/{uid}with calibration metadata preserved - HL7 Orchestration: ADT^A08 triggers auto-create in Exocad via
POST /cad/caseswith patient ID mapping - Real-Time Sync: CAD design completion (e.g., stent file) auto-attached to patient record via FHIR
DocumentReference - Security: FIPS 140-2 validated TLS 1.3; OAuth 2.0 device flow for sensor auth
Technical Outcome: Zero manual steps from sensor capture to CAD design initiation. Audit trail meets HIPAA §164.308(a)(1)(ii)(D).
2026 Implementation Recommendations
- Validate DICOM Conformance: Require IHE-Dental integration statements (not just “DICOM compatible”)
- Calibration Chain: Ensure sensor → PACS → CAD preserves distortion correction values in (0029,xx10) private tags
- API-First CAD Selection: Prioritize systems with documented GraphQL/REST APIs (DentalCAD leads; Exocad improving)
- Lab Workflow: Deploy vendor-neutral PACS (e.g., Dicom Systems) as central integration hub
Conclusion
Intraoral sensors are no longer isolated imaging devices but data originators in the digital thread. Open architectures leveraging IHE-Dental standards eliminate $18K/year/lab in manual labor (per 2025 KLAS report) while improving clinical accuracy. Carejoy’s API demonstrates how modern integration transcends simple DICOM transfer to create closed-loop workflows where radiographic data actively constrains design parameters. Closed systems remain viable only for single-vendor monocultures – an increasingly obsolete model as AI-driven diagnostics demand cross-platform data access. The 2026 benchmark: If your sensor data requires human intervention before CAD ingestion, your workflow is technically obsolete.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Carejoy Digital RVG Machines in China
Carejoy Digital’s RVG (Radiovisiography) imaging systems represent a convergence of precision engineering, AI-driven diagnostics, and stringent regulatory compliance. Manufactured in an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, the production and quality assurance (QA) processes reflect a benchmark in modern dental imaging equipment manufacturing.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process Description | Technology/Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-purity CMOS/CCD sensors, tungsten-shielded housings, and medical-grade PCBs sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with ISO 13485 traceability. | Supplier Audits, RoHS/REACH Compliance |
| Subassembly | Modular construction of sensor arrays, wireless transmitters, and protective casings under cleanroom conditions (Class 10,000). | ESD-Safe Workstations, Automated Conformal Coating |
| Main Assembly | Integration of sensor module, signal processor, and power management unit. Final sealing with autoclavable polymer casing (IP68-rated). | Automated Torque Control, Leak Testing |
| Firmware & AI Integration | Flashing of Carejoy OS with AI-driven noise reduction, auto-alignment, and exposure optimization algorithms. | Open Architecture Support (STL/PLY/OBJ), DICOM 3.0 |
2. Sensor Calibration & Metrology Labs
Carejoy operates a dedicated Sensor Calibration Laboratory within the Shanghai facility, accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. Each CMOS sensor undergoes:
- Pixel Uniformity Testing: 100% pixel response mapping using NIST-traceable X-ray sources.
- DQE (Detective Quantum Efficiency) Validation: Ensures optimal signal-to-noise ratio at low-dose exposures (0.5–4 μGy).
- Geometric Distortion Calibration: Sub-pixel correction via AI-based grid analysis (accuracy: ±0.03 mm).
- Thermal Drift Compensation: Sensors cycled from 15°C to 40°C to validate stability.
Calibration data is stored in the sensor’s embedded memory and linked to the Carejoy Cloud for auditability.
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical longevity, all RVG sensors undergo accelerated lifecycle testing:
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m onto concrete, 6 orientations, 10 cycles | No housing crack, sensor functionality intact |
| Autoclave Simulation | 134°C, 2.1 bar, 30 min, 500 cycles | No seal failure, no fogging or delamination |
| Cable Flex | 10,000 cycles at 90° bend radius | No signal degradation or conductor break |
| Vibration & Shock | IEC 60601-1-2:2014, Transport Simulation | Full operational recovery post-test |
4. ISO 13485:2016 Compliance Framework
The Shanghai manufacturing site is audited bi-annually by TÜV SÜD. Key elements include:
- Documented Design History File (DHF) and Device Master Record (DMR).
- Full traceability from raw material lot to serial-numbered unit (UDI compliance).
- Real-time non-conformance tracking with CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) integration.
- Software lifecycle management per IEC 62304, including secure OTA update protocols.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized dental technology due to:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, rare-earth magnet, and precision optics manufacturers reduces lead times and logistics costs by up to 40%.
- Advanced Automation: Over 75% of Carejoy’s assembly line is robotic, ensuring repeatability and reducing human error.
- AI & Software Co-Development: Domestic AI talent pools enable rapid iteration of scanning algorithms and cloud analytics, reducing R&D cycle time.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production across dental, medical, and industrial imaging sectors drives down per-unit costs without sacrificing quality.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA/NMPA alignment with FDA and CE MDR enables faster market entry and global compliance.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver RVG systems with sub-3μm spatial resolution, AI-powered dose optimization, and open data architecture at 30–40% below equivalent European or North American models.
Support & Digital Integration
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via Carejoy Connect Platform.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Monthly AI model enhancements and DICOM compatibility patches.
- Interoperability: Native integration with major CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows via open STL/PLY/OBJ pipelines.
Email: [email protected]
24/7 Remote Diagnostics | Firmware Updates | Calibration Certificates
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Rvg Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
