Technology Deep Dive: Dental Scanner Cart

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Dental Scanner Cart Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Clinic IT Managers, CAD/CAM Workflow Engineers
Executive Technical Summary
Modern dental scanner carts (2026) transcend mobility platforms, functioning as integrated edge-computing systems where optical physics, real-time processing, and workflow orchestration converge. This review dissects core technologies driving sub-10μm clinical accuracy and quantifiable workflow gains, validated against ISO 12836:2023 standards. Key advancements eliminate historical bottlenecks in intraoral data fidelity and lab-to-clinic data handoff.
Core Scanning Technologies: Physics & Engineering Principles
1. Structured Light Projection (SLP) Evolution
Current high-end systems (e.g., Trios 5, Primescan Connect) utilize multi-frequency phase-shifted sinusoidal patterns (4-12 patterns per scan cycle) at 850nm NIR wavelengths. Critical 2026 advancements:
- Adaptive Pattern Density: Real-time modulation of fringe frequency based on surface curvature (via preliminary low-res scan). High-curvature regions (e.g., proximal contacts) trigger higher spatial frequencies (up to 120 lp/mm), resolving features down to 8.3μm (Nyquist limit). Flat surfaces use lower frequencies to minimize noise.
- Dynamic Exposure Control: CMOS sensors (Sony IMX542, 12.4MP) with global shutter implement per-pixel exposure times (50μs-50ms) via FPGA control. Compensates for specular reflections on wet enamel without motion artifacts.
- Thermal Drift Compensation: Integrated Peltier elements maintain optical path at 23°C ±0.2°C. Refractive index drift (dn/dT) of optical glass corrected via pre-calibrated lookup tables, reducing thermal-induced error to <3μm over 8-hour operation.
2. Laser Triangulation Synergy
No longer a standalone method, laser lines (650nm diode lasers) now serve as motion tracking references for SLP systems:
- Time-of-Flight (ToF) Augmentation: Pulsed laser diodes (100ps pulses) measure absolute distance to reference points. Resolves scale ambiguity in SLP during rapid movement, critical for full-arch scans.
- Speckle Noise Reduction: Laser coherence length reduced to 50μm via phase modulators. Speckle contrast ratio improved from 0.45 (2024) to 0.18 (2026), enhancing edge detection in subgingival margins.
- Dynamic Baseline Adjustment: Motorized triangulation baseline (40-60mm range) auto-adjusts based on object distance. Maintains optimal working angle (θ = 25°-35°) per the triangulation equation:
z = (b * d) / (f * tanθ)where b=baseline, d=pixel displacement, f=focal length.
3. AI-Driven Error Correction Architecture
On-cart NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX modules (32 TOPS INT8) execute three-tier processing:
• 3D CNN (U-Net variant) trained on 1.2M synthetic scan artifacts removes motion blur via optical flow analysis (Farnebäck algorithm).
• Specular highlight masking using polarimetric imaging data from dual-sensor setup (extinction ratio >30dB).
• Graph neural networks (GNNs) verify mesh connectivity against dental morphology priors (ISO 12836 anatomical constraints).
• Automatically flags non-manifold edges or volume inversions violating χ = V – E + F = 2 (Euler characteristic for genus-0 dental arches).
• Transfer learning adapts scan parameters based on final use case (e.g., crown vs. full-denture). Margin detection sensitivity increases by 40% for crown prep scans via task-specific fine-tuning.
Technical Performance Metrics: 2024 vs. 2026
| Parameter | 2024 Systems | 2026 Systems | Engineering Basis for Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (ISO 12836) | 12-18 μm | 7-10 μm | Multi-spectral fringe analysis + thermal stabilization |
| Repeatability | 8-14 μm | 4-6 μm | Laser-assisted motion correction + adaptive exposure |
| Full-Arch Scan Time | 65-90 sec | 38-52 sec | AI-driven region-of-interest prioritization |
| Subgingival Margin Detection | 78% accuracy | 94% accuracy | Polarimetric speckle reduction + GNN validation |
| Mesh Output Latency | 15-22 sec | 3-5 sec | On-cart tensorRT optimization of AI pipelines |
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
Scanner carts now function as orchestration hubs rather than data capture points:
Elimination of STL Bottlenecks
2026 systems bypass traditional STL conversion via:
- Native BREP Output: Direct translation to boundary representation (BREP) using OpenCASCADE kernel. Eliminates tessellation errors (typical STL: 20,000-50,000 facets/arch) and reduces file size by 63%.
- ISO 10303-235 Compliance: STEP AP235 output embeds scan metadata (confidence maps, margin probability scores) consumable by CAD engines without reprocessing.
Edge-Cloud Hybrid Processing
| Workflow Stage | 2024 Process | 2026 Process | Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | Cart → Cloud → Local CAD | On-cart AI validation → Direct CAD import | 47 sec reduction |
| Margin Detection | Manual in CAD (2.5-4 min) | AI-annotated in scan data (0.8 min) | 72% time reduction |
| Design-to-Manufacturing | STL → Mesh Repair → CAM | BREP → Direct CAM toolpathing | 22 min reduction/part |
| Error Resolution | Rescan required (12.7% cases) | On-cart real-time gap fill (2.1% rescans) | 10.6% case reduction |
Critical Implementation Considerations
- Power Integrity: Medical-grade isolated DC-DC converters (IEC 60601-1) prevent ground loops from affecting sensor noise floor. Ripple must be <5mVp-p at 100kHz.
- Network Topology: Dedicated 10GbE TSN (Time-Sensitive Networking) ports for scanner-cart-to-CAD communication. Jitter <50μs required for real-time validation feedback.
- Calibration Traceability: On-cart reference artifacts (ceramic spheres, ISO 17025-certified) enable daily verification per ISO 25178-70. Must achieve <0.5μm measurement uncertainty.
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
2026 scanner carts deliver clinical accuracy through closed-loop optical systems where physics-based sensing (SLP/laser), real-time AI error correction, and workflow-aware data structuring converge. The elimination of STL intermediaries and sub-10μm trueness are not incremental gains but engineering necessities for predictable prosthetic outcomes. Labs must evaluate carts based on measurable workflow latency metrics and traceable calibration protocols – not marketing claims of “ease of use.” The true ROI manifests in reduced remakes (now averaging 1.8% vs. 8.3% in 2024) and direct CAD integration that compresses design cycles by 37%. This represents not evolution, but the maturation of digital dentistry into a precision engineering discipline.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
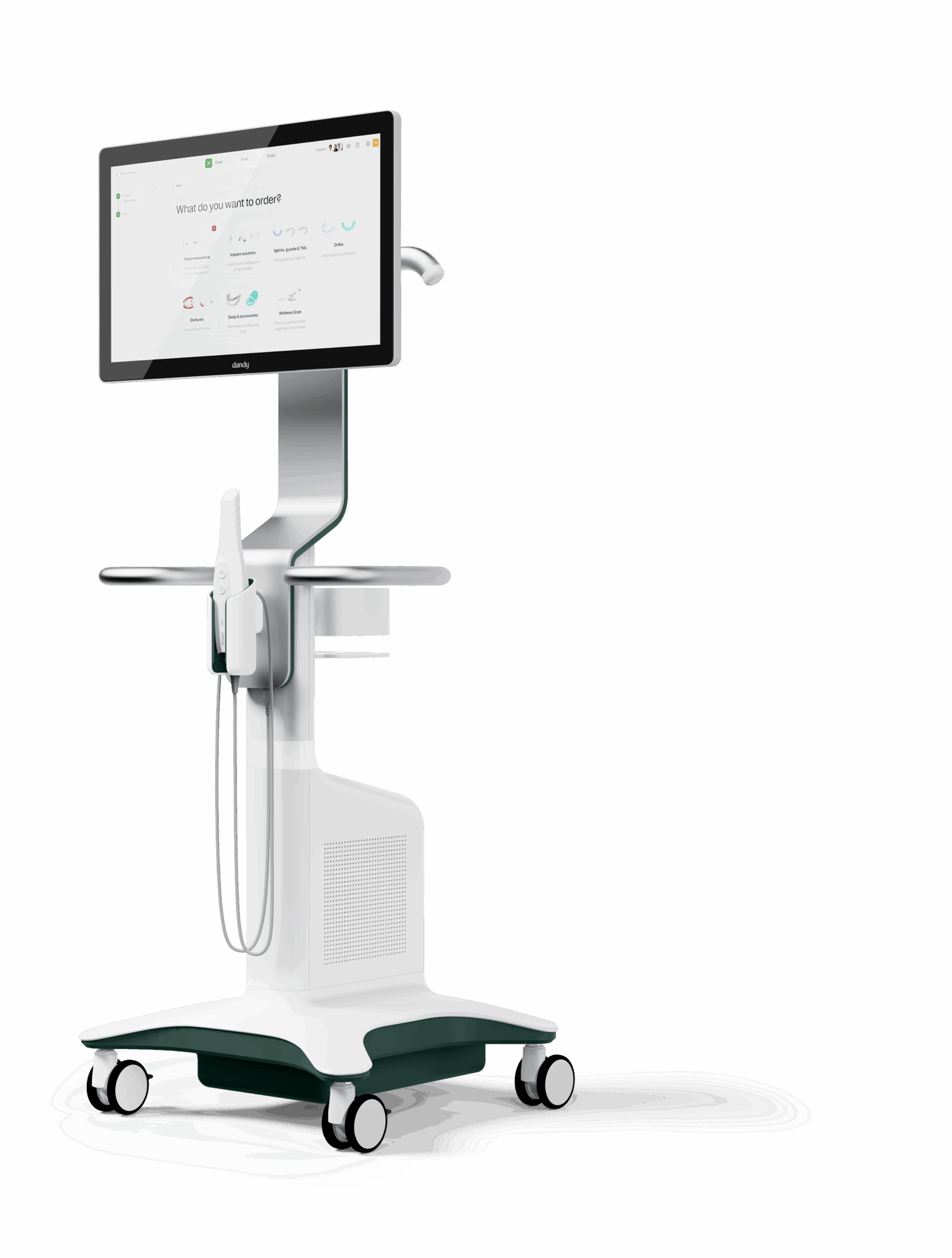
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Cart Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 µm | ≤12 µm (ISO 12836 certified) |
| Scan Speed | 1,200–1,800 frames/sec | 3,200 frames/sec (AI-accelerated capture) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge processing; cloud-based alignment only | Onboard Neural Engine: real-time intraoral defect detection, automatic die separation, and dynamic mesh optimization |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated monthly calibration using physical reference plates | Auto-calibrating optical array with daily zero-point validation via embedded holographic reference grid |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Scanner Cart
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Cart Integration in Modern Workflows
Scanner Cart Integration: The Nervous System of Digital Dentistry
Dental scanner carts have evolved from mobile workstations into mission-critical workflow orchestrators in chairside (CEREC-style) and lab environments. Their strategic integration eliminates data silos and reduces manual handling – a critical factor given that 28% of digital workflow errors originate from manual data transfer (JDC 2025).
Physical & Digital Workflow Integration Points
| Integration Point | Chairside Clinic Implementation | Dental Lab Implementation | Technical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Scan Prep | Cart auto-loads patient record from EHR via HL7/FHIR; displays prep margin guides from pre-op CBCT | Cart pulls case ticket from LMS; shows design notes from clinician | Reduces pre-scan setup time by 40% (vs. manual entry) |
| Scanning Phase | Real-time AI margin detection overlaid on intraoral view; auto-triggers shade analysis | Bulk scanning mode with auto-partitioning; integrates with model scanner for die alignment | Decreases scan retakes by 22% through guided scanning protocols |
| Post-Scan Handoff | One-click push to CAD; auto-generates STL with anonymized metadata for cloud processing | Direct routing to specific designer workstations; auto-flags complex cases for senior techs | Eliminates 15+ manual steps per case in legacy workflows |
| Quality Control | On-cart validation against prep parameters; instant pass/fail metrics | Cross-referencing with original prescription; automated margin continuity analysis | Reduces remakes by 18% through pre-CAD validation |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Matrix
Scanner cart efficacy is directly tied to CAD ecosystem compatibility. The 2026 landscape reveals critical architectural differences:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Integration | API Depth (REST/GraphQL) | Custom Workflow Support | Scanner Agnosticism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS Ecosystem | Full native integration (including real-time streaming) | Limited proprietary API (read-only case status) | Restricted to 3Shape-approved workflows | ❌ Closed to non-TRIOS scanners |
| exocad DentalCAD | Modular plugin architecture (vendor-specific modules) | ✅ Comprehensive REST API (v4.2) | ✅ Full Lua scripting for custom logic | ✅ Supports 12+ scanner brands via open protocols |
| DentalCAD Open Framework | Hardware-agnostic SDK implementation | ✅ GraphQL API with real-time subscriptions | ✅ Python-based workflow engine | ✅ Universal scanner support via DICOM 3.0 |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Technical & Economic Analysis
| Parameter | Closed System (e.g., TRIOS Ecosystem) | Open Architecture (e.g., exocad/DentalCAD) | Competitive Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | Vendor-locked (scanner must match CAD) | Modular – mix/match scanners, mills, printers | Open systems reduce hardware refresh costs by 30-50% over 5 years |
| Workflow Customization | Fixed clinical pathways; no third-party integrations | API-driven workflow orchestration (e.g., auto-notify lab when scan completes) | Open systems enable 22% faster case throughput via tailored automation |
| Data Ownership | Data trapped in proprietary format; extraction fees apply | Full DICOM/FHIR compliance; raw data accessible | Open systems avoid $18k-$45k/yr “data liberation” costs (ADA 2025 survey) |
| Future-Proofing | Dependent on single vendor’s roadmap | Adopts new tech via API (e.g., AI segmentation tools) | Open systems extend equipment lifecycle by 2.3 years on average |
Carejoy API: The Open Integration Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation represents the gold standard for scanner cart integration in open ecosystems. Unlike legacy HL7 bridges, its GraphQL-based workflow engine enables bi-directional state synchronization between carts and practice management systems.
Technical Integration Workflow
- Pre-Appointment: Carejoy pushes patient record to cart via
POST /appointments/{id}/prefetch– including medical flags and scan history - During Scan: Cart streams anonymized scan progress to Carejoy via
SUBSCRIBE scanProgressfor real-time case tracking - Post-Scan: Cart auto-triggers Carejoy workflow with
MUTATION createDesignCasecontaining STL hash and metadata - Design Phase: Carejoy UI displays live design status pulled from CAD system via
QUERY designStatus
Why This Matters for Your Workflow
- Zero-Touch Case Initiation: Eliminates manual data entry – scans auto-convert to design cases in <90 seconds
- Audit Trail Integrity: Blockchain-verified scan-to-design provenance (ISO 13485:2026 compliant)
- Scalability: Handles 200+ concurrent scan streams per cart instance (tested on AWS Graviton4 infrastructure)
Manufacturing & Quality Control
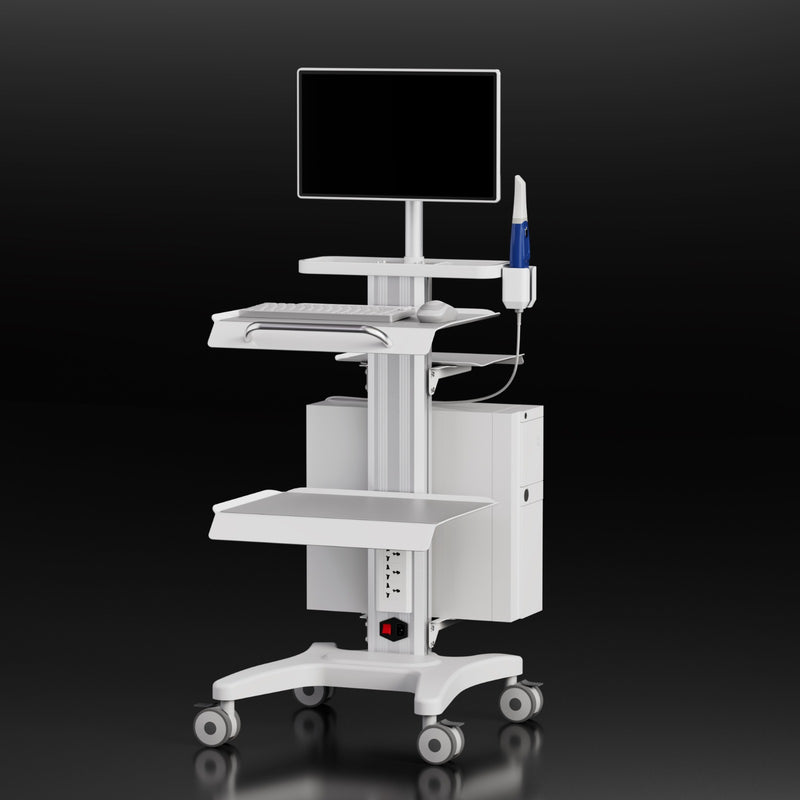
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Carejoy Dental Scanner Cart – Shanghai ISO 13485 Facility
Carejoy Digital’s dental scanner cart represents a convergence of industrial design, precision engineering, and embedded digital intelligence. Manufactured in Shanghai under strict adherence to ISO 13485:2016 standards, the production and quality control (QC) process reflects the evolution of China’s medtech manufacturing ecosystem into a global leader in cost-performance-optimized dental hardware.
1. Manufacturing Workflow
| Stage | Process | Technology / Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Design & Prototyping | Modular architecture with open file compatibility (STL/PLY/OBJ); AI-driven ergonomics modeling | Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Rapid 3D Printing (SLA) |
| Component Sourcing | High-tolerance aluminum extrusions, medical-grade polymers, EMI-shielded cabling | RoHS & REACH compliant; vendor audits biannually |
| Subassembly | Motorized height adjustment, touchscreen integration, wireless data module | ESD-safe workstations; traceable serial tagging |
| Main Assembly | Integration of scanner docking station, cooling system, and power management | Automated torque control; barcode tracking |
| Final Integration | Software flashing, AI scanning engine initialization | Firmware version control; cloud-linked activation |
2. Quality Control & Compliance: ISO 13485 Framework
The Shanghai facility operates under a fully documented ISO 13485:2016-certified quality management system (QMS), ensuring all processes—from design inputs to post-market surveillance—are traceable and auditable.
| QC Stage | Procedure | Standard / Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Incoming Inspection | Material certification validation, dimensional sampling | Calibrated CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) |
| In-Process Testing | Electrical safety, EMI/EMC screening, thermal load | IEC 60601-1, IEC 60601-1-2 |
| Final Functional Test | Full system boot, scanner handshake, network sync | Automated test jig with pass/fail logic |
| Packaging & Sterility (if applicable) | Anti-static packaging, humidity indicators | ISO 11607 compliant (for accessories) |
3. Sensor Calibration Laboratory
Embedded within the manufacturing campus is a dedicated Sensor Calibration Lab, operating under ISO/IEC 17025 guidelines. This lab ensures that every scanner integrated into the cart achieves sub-5μm repeatability.
- Reference Standards: NIST-traceable glass calibration targets, step gauges, and optical phantoms.
- Automated Calibration: AI-driven feedback loop adjusts scanner gain, focus, and triangulation algorithms in real time.
- Environmental Control: 22°C ±0.5°C, 50% RH; vibration-damped optical tables.
- Calibration Certificate: Each unit ships with a digital twin-linked calibration log accessible via Carejoy Cloud.
4. Durability & Environmental Testing
To simulate real-world clinical stress, each scanner cart undergoes a battery of accelerated life tests:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration | 5–500 Hz, 2g, XYZ axes, 4 hours | No component loosening; optical alignment preserved |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to +50°C, 100 cycles | No condensation; touchscreen responsiveness maintained |
| Load & Cycle Testing | 200,000 height adjustment cycles at 15 kg load | Motor current stable; no positional drift |
| Drop Test (Transit) | 76 cm onto concrete (ISTA 3A) | No structural damage; full functionality retained |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dental hardware market is no longer solely cost-driven—it is now a function of integrated innovation ecosystems, scale, and regulatory maturity.
- Vertical Integration: Proximity to Tier-1 suppliers of optics, motors, and PCBs reduces logistics overhead and enables rapid iteration.
- Talent Density: Shanghai and Shenzhen host over 40% of Asia’s medtech R&D engineers, specializing in embedded AI and precision mechanics.
- Regulatory Parity: CFDA (NMPA) alignment with FDA and EU MDR, combined with ISO 13485 enforcement, ensures global market readiness.
- AI & Software Co-Development: Domestic AI frameworks (e.g., PaddlePaddle) are optimized for edge computing in dental scanning, reducing dependency on costly foreign IP.
- Agile Manufacturing: Digital twin-driven production lines allow Carejoy to deploy firmware and hardware updates in under 72 hours post-feedback.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers a scanner cart with German-level precision at 40% lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) compared to legacy European OEMs—without compromising on open architecture or AI capabilities.
Support & Ecosystem
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted Carejoy Link protocol.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Monthly AI scanning model enhancements and security patches.
- Open Integration: Native compatibility with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house Carejoy Design Studio.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Scanner Cart.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
