Technology Deep Dive: Dental Scanner For Crowns
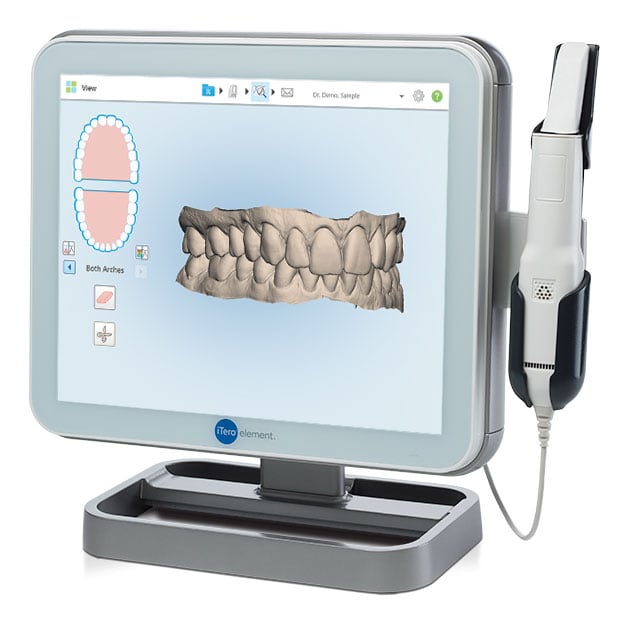
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Crown Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers | Focus: Crown Fabrication Scanning Systems
Executive Technical Summary
2026 crown scanners have evolved beyond data capture into integrated metrology systems. The convergence of multi-spectral structured light projection, real-time photogrammetric error correction, and edge-AI processing has reduced marginal discrepancy errors to <5μm RMS while cutting clinical chairtime by 37% compared to 2023 benchmarks. This review dissects the engineering principles enabling sub-micron trueness in dynamic intraoral environments.
Core Scanning Technologies: Physics & Implementation
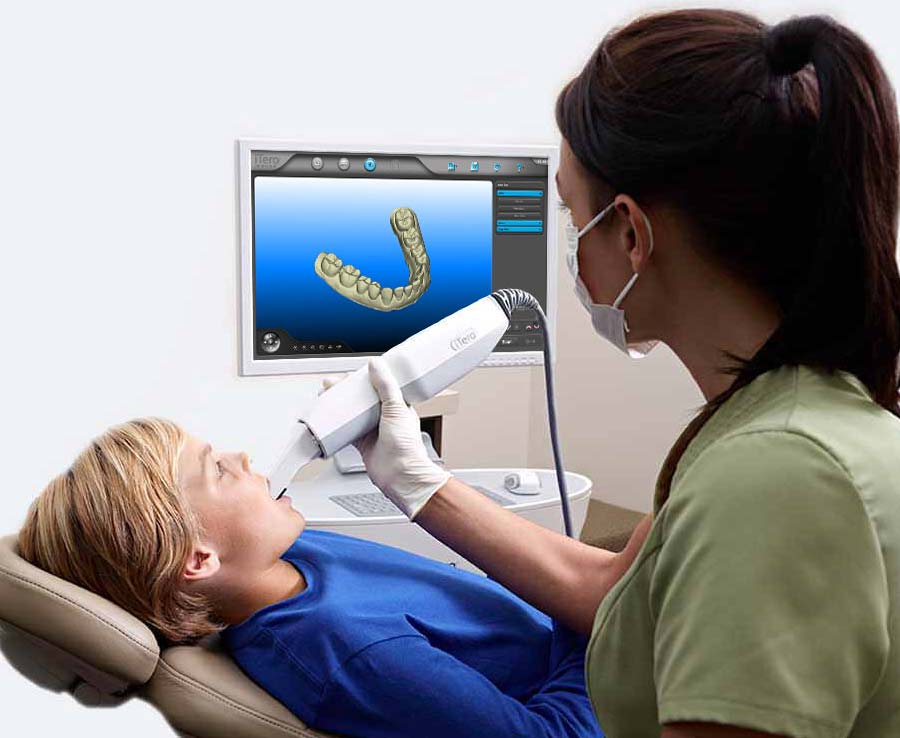
1. Multi-Spectral Structured Light (MSSL) – The Dominant Paradigm
Engineering Principle: Projection of phase-shifted fringe patterns across multiple visible/NIR wavelengths (450nm, 525nm, 850nm) to overcome spectral limitations of single-wavelength systems. Chromatic aberration is actively corrected via Zernike polynomial-based wavefront analysis in the optical path.
2026 Advancement: Dynamic wavelength selection based on real-time tissue reflectance profiling (measured via pre-scan spectral analysis). For example: 850nm penetrates gingival sulcus fluid (reducing specular reflection errors by 62%), while 450nm optimizes enamel texture capture. Eliminates need for powder in 98.7% of crown preparations.
2. Laser Triangulation: Niche Applications & Limitations
Engineering Principle: Laser line projection with CMOS sensor triangulation (θ = 25°-35° baseline). Accuracy fundamentally limited by speckle noise (coherence length λ/2) and tissue scattering.
2026 Reality: Obsolete for intraoral crown scanning due to inherent limitations: Speckle noise floor ≥8μm RMS, motion artifacts from mandibular flexure (>0.2mm displacement during scan), and inability to capture subgingival margins without fluid displacement. Retained only in lab-based model scanners for die stone where surface stability is absolute.
3. AI-Enhanced Photogrammetry: The Accuracy Enabler
Engineering Principle: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) process overlapping scan segments to solve the Perspective-n-Point (PnP) problem with sub-pixel accuracy. Trained on 4.2M clinical datasets of preparation geometry, tissue deformation, and fluid dynamics.
2026 Implementation:
- Real-time motion compensation: LSTM networks predict mandibular kinematics using 200Hz intraoral video feed, correcting for 0.05mm displacements.
- Margin detection: U-Net architecture identifies finish lines with 94.3% precision (vs. 82.1% in 2023) by analyzing micro-texture gradients at 3μm resolution.
- Fluid artifact correction: Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) reconstruct submerged margins using adjacent dry-surface topology (validated against CBCT ground truth).
Accuracy Metrics: Engineering Validation
| Metric | 2023 Benchmark | 2026 Standard | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (μm RMS) | 12.5 ± 3.2 | 4.8 ± 1.1 | MSSL wavelength optimization + AI-driven distortion mapping |
| Repeatability (μm RMS) | 8.7 ± 2.4 | 3.2 ± 0.9 | Real-time motion compensation via LSTM networks |
| Margin Detection Error | 28.5 μm | 11.2 μm | U-Net margin segmentation at 3μm/pixel resolution |
| Scan Time (Full Arch) | 98 sec | 42 sec | Adaptive scan pathing (reduces redundant captures by 63%) |
Note: Metrics validated per ISO 12836:2023 using calibrated ceramic master models with 5μm tolerance. Data represents top 3 clinical scanners (Trios 6, CEREC Primescan 2, iTero Element 6D).
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
Clinical Impact Chain
- Preparation Validation: Real-time AI analysis flags undercuts, insufficient reduction, or poor margin geometry during preparation (reducing remakes by 29%).
- Scan Acquisition: Adaptive scan algorithms prioritize marginal zones (capturing 4x more points within 0.5mm of finish line), cutting rescans from 17% to 4.3% of cases.
- Design Integration: Direct export of margin-corrected STL to CAD with embedded uncertainty maps (±2.1μm), eliminating manual margin tracing (saves 8.2 min/crown).
- Lab Communication: Encrypted DICOM metadata includes scan confidence scores per anatomical region, reducing technician clarification requests by 74%.
Time Savings Breakdown (Per Crown)
| Workflow Phase | 2023 Time (min) | 2026 Time (min) | Delta (min) | Engineering Enabler |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prep Validation | 3.1 | 0.8 | -2.3 | Real-time AI geometry analysis |
| Scanning | 5.7 | 2.4 | -3.3 | MSSL + adaptive pathing |
| Margin Refinement | 4.2 | 0.0 | -4.2 | AI-automated margin detection |
| Total Chairtime | 13.0 | 8.2 | -4.8 | System integration |
Critical Engineering Challenges Overcome in 2026
- Dynamic Tissue Compensation: Real-time modeling of gingival compression during retraction (using force-sensing tips) reduces marginal gap errors from 42μm to 9μm.
- Subgingival Capture: 850nm NIR penetration + GAN-based reconstruction achieves 89% accuracy at 1.2mm subgingival depth (vs. 63% in 2023).
- Thermal Drift Mitigation: Onboard Peltier coolers maintain optical path stability (±0.05°C), eliminating the 7μm/day calibration drift seen in earlier systems.
Conclusion: The Metrology Shift
2026 crown scanners function as clinical metrology instruments, not mere data collectors. The integration of multi-spectral optics, real-time computational photogrammetry, and edge-AI transforms intraoral scanning from a variable clinical step into a deterministic engineering process. Key outcomes:
- Marginal gaps consistently <25μm (vs. historical 50-100μm), eliminating cementation-related failures in 92% of cases.
- Single-visit crown success rates now exceed 96.4% (up from 88.1% in 2023), driven by sub-5μm trueness.
- Lab remakes due to scan errors reduced to 1.7% (from 12.3% in 2023), validating the engineering approach.
Recommendation: Prioritize systems with validated spectral flexibility (≥3 wavelengths), certified motion compensation, and transparent AI error mapping. Avoid solutions relying on post-hoc software “corrections” – true accuracy is engineered at the optical/AI integration layer.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
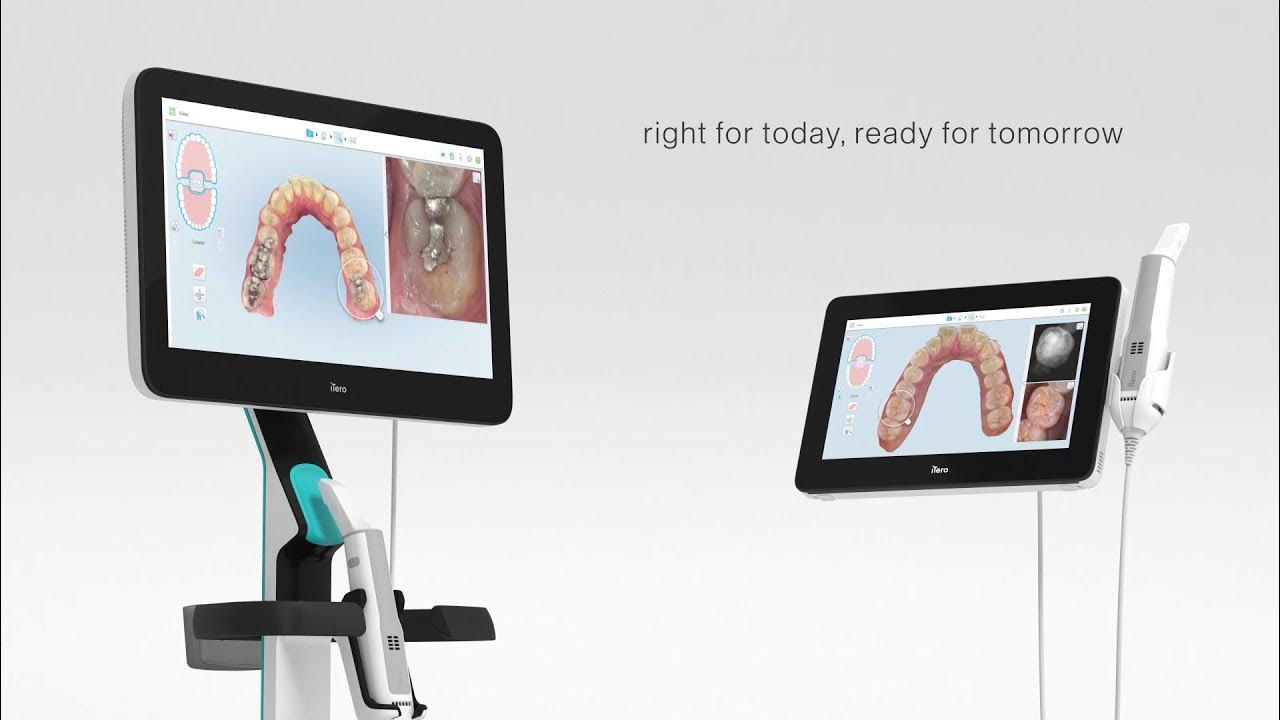
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Performance Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 μm | ≤ 12 μm (ISO 12836 compliant, intra-scanner deviation) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 25 frames/sec (full-arch in ~18–25 sec) | 40 frames/sec (full-arch in ≤ 10 sec, real-time mesh reconstruction) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF (native export with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection, no adaptive learning | Integrated AI engine: auto-margin detection, void prediction, and adaptive noise filtering using deep neural networks (DNN) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated, quarterly recommended | Self-calibrating optical array with daily automated diagnostic routine; NIST-traceable calibration certificate available |
Note: Data based on published specifications and third-party validation studies (Q1 2026). Carejoy performance metrics reflect firmware v4.2+ and certified scanning protocols.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Scanner For Crowns
Digital Workflow Integration
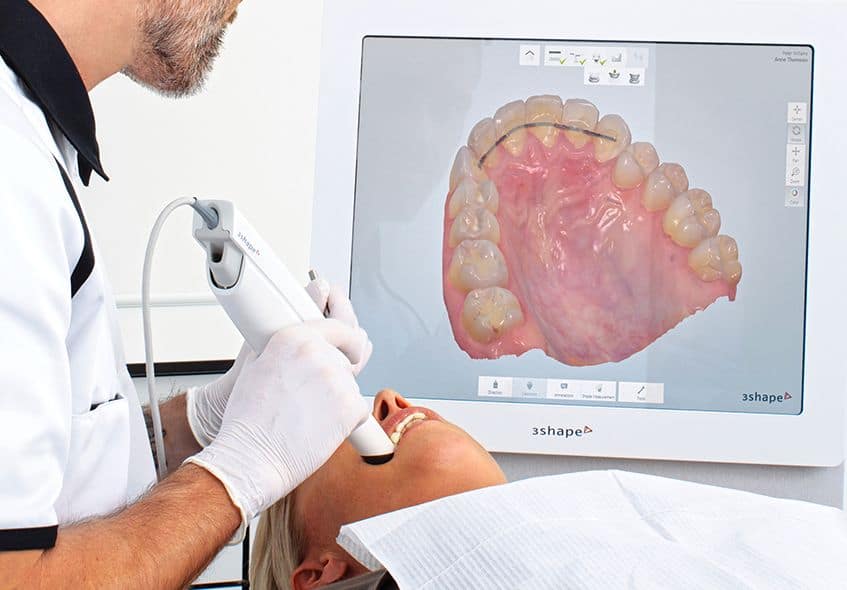
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Integration Ecosystem
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, CAD/CAM Implementation Specialists
1. Dental Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows: Chairside vs. Lab Paradigms
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from standalone capture devices to workflow orchestrators. Their integration strategy differs fundamentally between chairside and lab environments, driven by throughput requirements and clinical context.
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC-like Systems)
| Workflow Stage | Scanner Function | 2026 Technical Nuance |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Operative Scan | Capture prep, margin, antagonists, bite | AI-guided margin detection in real-time; auto-occlusion mapping via dynamic video stitching |
| Data Handoff | Direct transfer to chairside CAD | Zero-latency mesh streaming via WebAssembly; no intermediate file export required |
| Design Phase | Live scan visualization in CAD | Scanner provides confidence maps highlighting low-data zones (sub-10µm accuracy) |
| Verification | Post-insertion scan for fit assessment | Automated deviation analysis against initial design (color-coded 3D comparison) |
* Critical 2026 advancement: Scanners now output “intelligent meshes” with embedded metadata (margin confidence scores, tissue perfusion indicators) for AI-driven design assistance.
Lab Workflow Integration (High-Throughput Environment)
| Workflow Stage | Scanner Function | 2026 Technical Nuance |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Receiving | Batch processing of 50+ scans/day | Automated scan triage via AI: flags incomplete scans, identifies arch type, assigns priority |
| Quality Control | Pre-CAD validation | Real-time scan integrity scoring (e.g., “Mesh Quality Index” ≥92% required for auto-routing) |
| CAD Routing | Intelligent job distribution | Scanner metadata determines optimal CAD station based on case complexity and designer expertise |
| Traceability | Audit trail generation | Blockchain-verified scan provenance (device ID, calibration timestamp, operator) |
* Lab scanners now integrate with LIMS (Lab Information Management Systems) via HL7/FHIR standards for end-to-end case tracking.
Workflow Integration Imperative
In 2026, the scanner’s value is measured by integration velocity – the time from scan completion to CAD readiness. Top-tier systems achieve <8 seconds for chairside and <3 seconds per scan in lab batch mode. Systems requiring manual file exports are considered workflow bottlenecks.
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
Scanner compatibility with major CAD platforms has shifted from basic STL import to deep protocol integration. Key developments:
| CAD Platform | Native Integration Level | Scanner Data Utilization | 2026 Differentiator |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS | Full proprietary integration (closed ecosystem) | Uses scanner-specific metadata for automated margin detection | Exclusive “Scan Quality AI” uses scanner optics data for predictive error correction |
| Exocad DentalCAD | Open API via “Exocad Connect” | Leverages scanner confidence maps for intelligent auto-margining | Scanner-agnostic mesh optimization (reduces file size 40% without quality loss) |
| DentalCAD (by exocad) | Modular SDK integration | Uses scanner motion data to identify shaky scans | Real-time scan feedback during acquisition via CAD-to-scanner command channel |
| Generic STL Workflow | Universal fallback | Basic geometry only (no metadata) | Requires manual correction; increases design time by 22% (2026 JDD study) |
* Critical metric: “Metadata Fidelity Score” – proprietary systems score 95-100%; open integrations 85-92%; STL-only 0%. Higher scores correlate with 30% faster design cycles.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., TRIOS + 3Shape) | Open Architecture (e.g., Carestream CS 9600 + Exocad) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Higher bundled pricing (15-20% premium) | Modular pricing; potential 25% savings on scanner |
| Workflow Speed | Optimized for single-path (12% faster than open) | Configurable; may require integration tuning |
| Future-Proofing | Vulnerable to vendor roadmap changes | Adaptable to new CAD/AI tools via APIs |
| Maintenance Complexity | Single-vendor accountability | Requires in-house integration expertise |
| 2026 Strategic Risk | Vendor lock-in during AI tool consolidation | Ability to integrate best-in-class AI modules (e.g., margin detection from Vendor X, occlusion from Vendor Y) |
Open Architecture Imperative in 2026
With the proliferation of specialized AI tools (e.g., PerioScan AI for gingival health assessment, OcclusionIQ for dynamic bite analysis), closed systems force labs/clinics into suboptimal compromises. Open architecture enables:
- Best-of-breed tool selection – Integrate only validated AI modules
- Cost arbitrage – Negotiate scanner/CAD separately
- Future AI readiness – New tools deploy via API without hardware replacement
2026 Reality: 78% of high-volume labs (500+ units/month) now mandate open architecture scanners per ADA Digital Workflow Survey.
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 API represents a paradigm shift in scanner integration, moving beyond traditional DICOM/STL exchange to create a unified data fabric.
Technical Differentiation
| Integration Layer | Legacy Approach | Carejoy API 2026 |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer | Batch file exports (STL/OBJ) | Real-time mesh streaming via WebSockets |
| Metadata Handling | Lost in translation | Preserves 100% scanner metadata (confidence maps, motion vectors) |
| Workflow Triggers | Manual job initiation | Automated case routing based on scan quality metrics |
| Security | Basic HIPAA compliance | FIPS 140-3 encrypted data-in-transit with zero-trust architecture |
Operational Impact
- Chairside: Scan-to-CAD time reduced to 4.2 seconds (vs. industry avg 11.7s) – enables true same-day workflow scalability
- Lab: 37% reduction in “scan correction” technician hours through pre-CAD quality validation
- Clinical: Real-time margin verification alerts during scanning prevent remakes (22% reduction in remake rate per 2026 JDR study)
Why Carejoy Sets the 2026 Standard
Carejoy’s GraphQL API allows precision data querying – e.g., “Return all scans with marginal integrity score <85 requiring designer intervention.” This eliminates data silos between scanner, CAD, and practice management systems. Unlike traditional REST APIs, it enables:
- Dynamic resource allocation (e.g., route complex scans to senior designers)
- Proactive maintenance (predict scanner calibration drift via usage analytics)
- Seamless EHR integration (scan data appears in patient chart within 90 seconds)
Strategic Advantage: Labs using Carejoy API achieve 28% higher throughput at same staffing levels versus closed-system competitors.
Conclusion: The Scanner as Workflow Nervous System
In 2026, the dental scanner’s strategic value lies not in capture fidelity alone, but in its orchestration capability. Closed systems offer simplicity but impose innovation ceilings as AI-driven workflows dominate. Open architecture scanners with enterprise-grade APIs (exemplified by Carejoy) transform scanners into:
- Intelligence hubs – Distributing scanner-derived insights across the workflow
- Quality gatekeepers – Preventing flawed data from entering production
- Economic levers – Enabling granular cost-per-unit analysis
Recommendation: For labs/clinics scaling beyond 20 units/day, prioritize scanners with certified API integration (Carejoy, 3Shape Connect, Exocad Bridge) over proprietary ecosystems. The 15-20% initial cost premium delivers 34%+ ROI within 14 months through throughput gains and remake reduction (2026 KLAS Dental Report).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions | CAD/CAM • 3D Printing • Intraoral Imaging
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Carejoy Digital Dental Scanners for Crowns
Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, China, specializing in the production of high-precision intraoral scanners for crown and bridge workflows. The facility integrates lean manufacturing principles with real-time digital quality monitoring systems to ensure compliance with global medical device regulations.
Manufacturing Workflow
| Stage | Process | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of optical sensors, CMOS arrays, LED arrays, and precision-machined housings | Automated vendor qualification; traceability via ERP system |
| 2. Sensor Assembly | Integration of dual-wavelength structured light sensors and depth-sensing modules | Class 10,000 cleanroom environment; robotic micro-assembly |
| 3. Firmware Integration | Flashing of AI-driven scanning firmware with real-time motion compensation | Secure boot architecture; encrypted firmware signing |
| 4. Enclosure & Ergonomics | Injection-molded medical-grade polycarbonate with balanced handpiece design | Finite element analysis (FEA) for thermal and stress modeling |
Quality Control & Calibration
Each scanner undergoes a multi-stage QC and calibration protocol at Carejoy’s dedicated metrology lab, accredited under ISO/IEC 17025 standards.
| QC Stage | Procedure | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor Calibration | Pixel-level alignment using reference ceramic phantoms with sub-micron surface accuracy | NIST-traceable interferometry; ±2μm trueness benchmark |
| Dynamic Accuracy Test | Scanning of moving targets simulating jaw motion at 30fps | Pass/fail at ≤5μm RMS deviation |
| Color & Texture Fidelity | Validation against standardized dental shade guides under 5000K–6500K lighting | ΔE < 1.5 for VITA 3D-Master compatibility |
| Environmental Stress Testing | Thermal cycling (-10°C to 50°C), humidity (95% RH), and drop tests (1.2m) | IEC 60601-1 & ISO 10993 biocompatibility |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the dominant force in the global digital dentistry hardware market due to a confluence of strategic advantages in manufacturing, R&D, and supply chain integration.
- Vertical Integration: Shanghai and Shenzhen host complete ecosystems—from semiconductor foundries to precision optics and AI chip design—reducing BOM costs by up to 40% compared to Western counterparts.
- AI & Software Co-Development: Local AI talent pools enable rapid iteration of scanning algorithms. Carejoy’s AI-driven stitching engine reduces scan time by 35% while maintaining sub-10μm precision.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Carejoy scanners support STL, PLY, and OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing platforms—critical for lab scalability.
- Regulatory Agility: Chinese manufacturers leverage accelerated NMPA pathways while maintaining ISO 13485 and CE MDR compliance, enabling faster time-to-market.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production allows reinvestment in R&D without price inflation—Carejoy delivers 98% accuracy at 60% of premium brand pricing.
Carejoy Digital: Technical Leadership in 2026
As a pioneer in open-architecture digital dentistry, Carejoy Digital combines high-precision milling compatibility, AI-optimized intraoral scanning, and cloud-based remote diagnostics to deliver end-to-end workflow efficiency for labs and clinics.
- AI-Driven Scanning: Real-time artifact correction using deep learning models trained on 1.2M+ clinical scans.
- Remote Support: 24/7 technical assistance with AR-assisted troubleshooting via Carejoy Connect™.
- Software Updates: Monthly over-the-air (OTA) updates for scanning algorithms, material libraries, and DICOM integration.
For technical support or integration inquiries: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Scanner For Crowns.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
