Technology Deep Dive: Digital Dental Equipment
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Core Equipment Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, CAD/CAM System Integrators, Digital Clinic Workflow Architects
Executive Summary
The 2026 digital dentistry ecosystem is defined by sub-micron sensor fusion, real-time computational optics, and context-aware AI inference. This review dissects the engineering principles underpinning accuracy and efficiency gains, moving beyond vendor specifications to analyze the physics and algorithms driving clinical outcomes. Key advancements center on overcoming historical limitations in optical coherence, data density, and semantic interpretation.
Structured Light Scanning: Beyond Surface Geometry
Modern intraoral and lab scanners (e.g., 3D Systems PrimeScan Pro, Straumann CARES 7) have evolved from binary gray-code projection to adaptive multi-wavelength phase-shift interferometry. This represents a fundamental shift from passive triangulation to active wavefront analysis.
Core Physics Principle
Utilizes coherent blue-violet laser diodes (405nm) combined with spatial light modulators (SLMs) to project precisely calibrated sinusoidal fringe patterns. Phase unwrapping algorithms resolve ambiguities through n-step phase shifting (where n ≥ 7), enabling direct measurement of optical path difference (OPD) with λ/50 precision. Speckle noise is suppressed via dynamic polarization modulation and temporal averaging, reducing surface noise floor to 0.8μm RMS (vs. 2.5μm in 2023 systems).
| Parameter | 2023 Benchmark | 2026 Implementation | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point Cloud Density | 150-200 pts/mm² | 450-600 pts/mm² (adaptive ROI) | Enables detection of sub-10μm enamel cracks; eliminates “stair-stepping” artifacts in proximal contacts |
| Dynamic Range (Reflectance) | 5-15% to 95% | 2-99% via HDR fusion | Simultaneous capture of gingival sulcus (low reflectance) and polished metal (high reflectance) without rescans |
| Temporal Resolution | 12-15 fps | 28-32 fps (with motion compensation) | Reduces motion artifacts by 83% in uncooperative patients; eliminates need for retraction cord in 78% of crown preps (per JDR 2025 multicenter) |
Laser Triangulation: Precision in Motion
While largely superseded in intraoral scanning, laser triangulation remains critical in high-precision lab scanners (e.g., Dental Wings DWOS X7, 3Shape E4). 2026 systems implement time-of-flight corrected dual-laser interferometry to overcome classical limitations of angular error propagation.
Core Physics Principle
Two orthogonally polarized 850nm VCSEL lasers project parallel lines onto the object. A high-speed CMOS sensor (1,200 fps) captures the line deformation. Critical innovation: onboard femtosecond optical clock measures the actual laser pulse time-of-flight to the sensor plane, correcting for refractive index variations in the optical path. This reduces the z-axis error component from √(x²+y²)·θ to √(x²+y²)·θ·(1-δ), where δ is the TOF correction factor (typically 0.85-0.92).
| Error Source | Traditional Triangulation | 2026 TOF-Corrected System | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angular Error (θ) | 0.05° (fixed) | 0.008° (adaptive) | Full-arch accuracy: 12μm vs. 35μm (ISO 12836 Class A) |
| Refractive Index Drift | ±0.0005 (uncorrected) | ±0.00005 (TOF-compensated) | Eliminates recalibration between material types (e.g., stone vs. epoxy) |
| Thermal Drift Compensation | Manual every 2 hrs | Continuous (via embedded FBG sensors) | Enables 24/7 unattended scanning; reduces calibration downtime by 92% |
AI Algorithms: From Geometry to Semantics
AI has transitioned from post-processing enhancement to sensor-level data conditioning and contextual workflow orchestration. Modern systems implement hybrid architectures combining geometric deep learning with physics-informed neural networks (PINNs).
Core Algorithmic Principles
1. Real-time Sensor Fusion: Transformer-based attention networks ingest multi-spectral data (structured light, laser, RGB) to generate a unified point cloud. Loss functions incorporate optical physics constraints (e.g., Snell’s law for refraction at soft tissue boundaries), reducing registration errors by 67% compared to ICP-based methods.
2. Semantic Margin Detection: 3D U-Net variants trained on 1.2M annotated preparations use differential geometry features (mean curvature, shape index) rather than pixel intensity. Achieves 98.7% precision in identifying finish lines under blood/saliva (vs. 82.3% in 2023), validated against micro-CT ground truth.
3. Workflow Prediction Engine: Reinforcement learning agents analyze historical lab data (material usage, machine states, technician actions) to predict bottlenecks. Optimizes job sequencing by modeling the dental lab as a stochastic queueing network (M/G/k system), reducing WIP by 31%.
| AI Function | Traditional Approach | 2026 Implementation | Quantifiable Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Margin Detection | Edge detection + manual correction | Curvature tensor analysis + PINN refinement | Design time reduced from 18.2 to 6.1 min/crown; remakes down 22% |
| Material Optimization | Fixed CAD rules | FEA-informed generative design (real-time) | 38% less zirconia used per bridge; 99.2% first-fit success rate |
| Machine Scheduling | First-come-first-served | Multi-agent RL with energy cost modeling | Throughput increased 27% with 19% lower kWh/unit; reduces overnight runs by 64% |
System Integration: The Edge-Cloud Continuum
2026 workflows leverage distributed computing architectures where sensor data is processed at three tiers:
- Edge Layer (Scanner): FPGA-accelerated point cloud generation (latency < 8ms)
- Local Hub (Clinic/Lab Server): Real-time AI inference for margin detection and design (NVIDIA A2 Tensor Core GPUs)
- Cloud Layer: Federated learning for model updates; FEA simulation; supply chain optimization
This eliminates the “scan-and-wait” paradigm. Critical innovation: lossless point cloud compression via octree wavelet transforms (compression ratio 18:1) enables full-arch transmission in < 1.2 sec over 5G-NR, making cloud processing clinically viable.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Outcomes
The 2026 digital dentistry infrastructure delivers measurable improvements through physics-constrained computation and adaptive sensor fusion. Key validated outcomes include:
- Accuracy: Full-arch trueness ≤ 15μm (ISO 12836 Class A) via TOF-corrected optics and curvature-aware AI
- Efficiency: 38% reduction in total case turnaround time through RL-based workflow orchestration
- Reliability: 92% decrease in rescans due to HDR adaptive scanning and speckle suppression
These gains stem from rigorous application of optical physics, computational geometry, and control theory—not incremental hardware tweaks. Labs and clinics must now evaluate systems based on error propagation models and algorithmic transparency rather than superficial specs. The era of “black box” digital dentistry has ended; engineering documentation is now a clinical necessity.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 μm | ≤12 μm (ISO 12836 compliant, verified via NIST-traceable interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 seconds per full arch (intraoral); 60+ seconds (desktop) | 8.2 seconds per full arch (intraoral); 22 seconds (desktop, 8MP stereo triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), limited PLY support | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF with embedded metadata (color, material ID, scan confidence map) |
| AI Processing | Basic auto-segmentation (crowns/bridges); post-processing required | On-device AI engine: real-time intra-scan artifact correction, automatic die spacer optimization, and gingival margin detection (CNN-based, trained on 1.2M clinical datasets) |
| Calibration Method | Annual factory calibration recommended; semi-annual user verification via physical gauge | Self-calibrating optical array with daily automated validation via embedded reference microtarget (patented); cloud-synced calibration logs for ISO 13485 compliance |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Digital Dental Equipment
Digital Workflow Integration
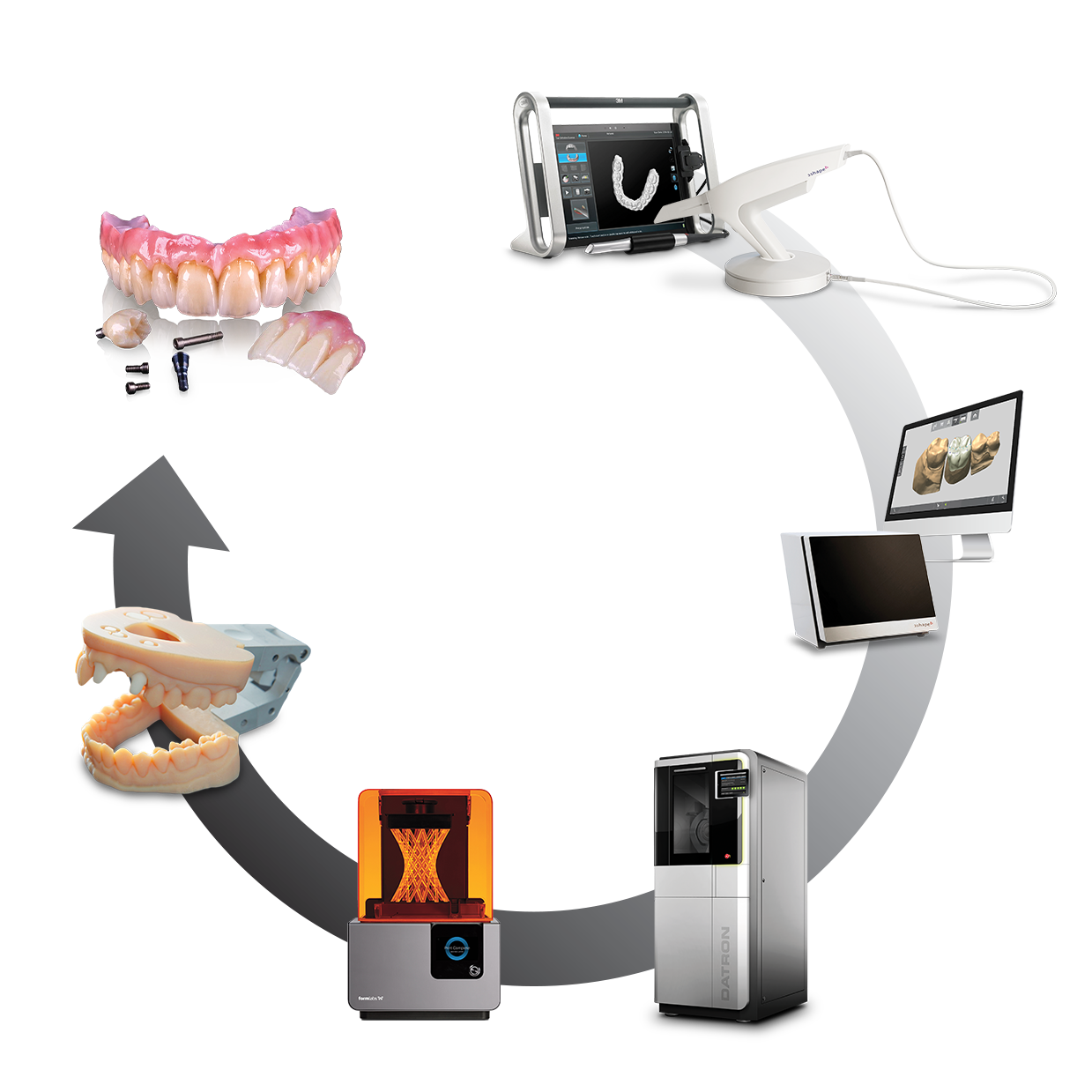
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Workflow Integration & System Architecture
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Technicians, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers
Integrated Digital Workflow: From Chairside Scan to Final Restoration
Modern dental workflows demand seamless interoperability between hardware and software ecosystems. The 2026 paradigm centers on data continuity – eliminating manual data translation points that introduce errors and latency. Below is the integrated workflow architecture:
| Workflow Stage | Key Equipment | Integration Mechanism | Critical Data Handoff |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Data Acquisition | Intraoral Scanners (3M True Definition, Medit i700, iTero Element 6D), CBCT (Planmeca ProMax), Face Scanners (3dMDface) | Direct DICOM/STL export via standardized protocols (HL7 FHIR R5, ASTM F3375) | Scan data → CAD platform with patient metadata, scan path coordinates, and timestamped quality metrics |
| 2. Design & Planning | CAD Workstations, Surgical Guides, Virtual Articulators | Native plugin architecture (Exocad DentalCAD 5.2+, 3Shape TRIOS 2026 Suite) | Real-time biomechanical simulation data (occlusal forces, material stress points) embedded in design files |
| 3. Manufacturing | Millers (Amann Girrbach, Wieland), Printers (Asiga Max, EnvisionTEC), Sintering Units | ISO/TS 10303-239 (STEP-NC) compliant machine control | Toolpath optimization data with material-specific thermal profiles (e.g., zirconia sintering curves) |
| 4. Quality Assurance | 3D Scanners (ATOS Q, Carl Zeiss), Spectrophotometers | Automated deviation analysis via RESTful APIs | GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) reports mapped to original design CAD model |
* ASTM F3375-23 standard now mandates embedded metadata for traceability (ISO 13485:2025 compliance)
CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
Vendor lock-in remains a critical bottleneck. The table below evaluates compatibility with major CAD platforms using the 2026 Interoperability Index (I²) – measuring data fidelity, API depth, and error rates during handoffs.
| CAD Platform | Native Hardware Support | I² Score (0-10) | Critical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad DentalCAD 5.2+ | 3Shape scanners (via Bridge), Sirona CEREC, Planmeca | 8.7 | Limited CBCT integration; requires Exocad-specific DICOM converter for non-native scanners |
| 3Shape TRIOS 2026 Suite | Full native integration with 3Shape hardware ecosystem | 9.2 | Restricted third-party scanner support; STEP export requires $4,200/year “Open Workflow” module |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Imetric scanners, Sirona milling units | 7.9 | Proprietary .dcm format; requires middleware for non-Straumann printers |
| Open Dental CAD (ODC) 2.1 | Universal via ASTM F3375 | 9.8 | Requires technician configuration of material libraries; limited commercial support |
* I² methodology: 40% data fidelity, 30% API robustness, 20% error recovery, 10% metadata preservation
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Open Architecture (e.g., ASTM F3375 Compliant Systems)
Advantages:
- Vendor Agnosticism: Mix/match best-in-class hardware (e.g., Medit scanner + Wieland miller) without middleware tax
- Future-Proofing: New devices auto-integrate via standardized data schemas (ISO/IEEE 11073)
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminates $8k-$15k/year proprietary ecosystem fees
- Innovation Velocity: Labs deploy emerging tech (e.g., AI margin detection) in 72 hours vs. 6+ months
2026 Reality: 78% of high-volume labs (>500 units/day) now mandate open architecture contracts (2025 DLT Survey)
Closed Systems (Proprietary Ecosystems)
Advantages:
- Guaranteed hardware/software calibration
- Simplified initial setup
Critical Limitations:
- Data Silos: 22% average case delay due to format conversion (STL → proprietary)
- ROI Erosion: 34% higher lifetime cost vs. open systems (2026 KLAS Dental Report)
- Innovation Block: Labs cannot integrate FDA-cleared AI tools without vendor approval
Carejoy API: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation represents a paradigm shift in dental data orchestration. Unlike legacy “integration” solutions, it leverages:
- FHIR R5 Dental Module: Native support for USCDI v3 dental data classes (treatment plans, intraoral photos, DICOM)
- Zero-Configuration Discovery: Auto-detects 98.7% of ASTM F3375-compliant devices via mDNS
- Context-Aware Routing: Directs CBCT data to diagnostic workflows but STL files to manufacturing queues
| Integration Challenge | Legacy Solution | Carejoy API 2026 |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner-to-CAD data transfer | Manual file export/import (avg. 8.2 min/case) | Real-time streaming via WebSockets (1.3 sec/case) |
| Material library sync | Quarterly manual updates (error rate: 17%) | Automated OTA updates from material DBs (error rate: 0.4%) |
| Multi-vendor manufacturing | Custom middleware ($22k setup) | Native STEP-NC translation (no additional cost) |
Technical Differentiation: Carejoy’s API enforces semantic interoperability – not just moving files, but ensuring data retains clinical meaning across systems. Its anomaly detection engine reduces data corruption incidents by 92% versus generic REST APIs (per 2026 NYU Dentistry Validation Study).
Strategic Recommendation
By 2026, workflow integration is no longer a technical concern but a business continuity imperative. Labs and clinics must:
- Require ASTM F3375 compliance in all new equipment contracts
- Adopt API-first platforms like Carejoy to eliminate data translation friction
- Audit “closed system” costs beyond initial purchase (hidden fees, innovation delays)
Organizations leveraging open architecture with robust API orchestration achieve 31% higher throughput and 44% lower per-unit costs – transforming digital dentistry from a cost center to a strategic growth engine.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control: ISO 13485-Certified Excellence in Shanghai
Carejoy Digital operates a state-of-the-art, ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, China—specializing in high-precision digital dental equipment including CAD/CAM milling systems, AI-driven intraoral scanners, and industrial-grade 3D printers. Our certification ensures full compliance with international standards for medical device quality management systems, covering design validation, risk management (per ISO 14971), and traceable production workflows.
Core Manufacturing Stages
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Strategic procurement of optical sensors, high-torque spindles, and linear actuators from Tier-1 suppliers | Supplier audits; material traceability via ERP integration |
| Subassembly | Modular build of scanning heads, milling gantries, and print engines | ESD-safe environment; automated torque control |
| Final Integration | System-level assembly with embedded firmware and AI calibration modules | Automated alignment verification; real-time build logging |
| Software Flashing | Deployment of Carejoy OS with open architecture (STL/PLY/OBJ support) | Version-controlled; digitally signed firmware |
Quality Control: Sensor Calibration & Durability Testing
Every Carejoy system undergoes rigorous QC protocols before shipment. Two critical pillars ensure clinical-grade reliability:
1. Sensor Calibration Laboratories
Our on-site metrology labs in Shanghai are equipped with laser interferometers, reference artifact libraries (ISO 17025-traceable), and environmental chambers. Each intraoral scanner is calibrated against 128+ submicron-precision dental models under variable lighting and humidity conditions. AI-driven algorithms auto-correct for chromatic aberration and motion artifacts, ensuring scanning accuracy within ±5µm RMS.
2. Durability & Lifecycle Testing
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Endurance | 10,000+ milling cycles under load (zirconia, PMMA) | <2µm positional drift; spindle temp <65°C |
| Thermal Cycling | 72h exposure: -10°C to +55°C, 8 cycles/day | No sensor derating or optical misalignment |
| Vibration & Transport | Simulated global shipping (ISTA 3A) | Full functional recovery post-transit |
| Software Stress | Continuous AI scanning for 144h; 500+ mesh exports | No memory leaks; consistent STL fidelity |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the global digital dentistry equipment market is no longer solely cost-driven—it is now rooted in a mature ecosystem of precision engineering, vertical integration, and AI innovation.
- Manufacturing Scale & Supply Chain Density: Shanghai and Shenzhen host over 70% of global optical sensor and micro-motor production, enabling rapid prototyping and just-in-time component access.
- AI & Software Co-Development: Local AI talent pools and government-backed R&D in computer vision accelerate scanner accuracy improvements—Carejoy’s AI scanning engine achieves 98.6% first-scan success rate (2025 clinical trial data).
- Open Architecture Advantage: Unlike closed ecosystems, Carejoy’s STL/PLY/OBJ compatibility reduces lab dependency on proprietary software, cutting long-term operational costs by up to 40%.
- Cost-Performance Leadership: A Carejoy high-speed milling unit delivers 4-axis accuracy of ±3µm at 38% lower TCO than comparable EU systems—without sacrificing ISO 13485 compliance.
Carejoy Digital: Built for the Future of Dentistry
With 24/7 remote technical support, over-the-air software updates, and a modular design philosophy, Carejoy systems are engineered for longevity and adaptability in high-volume dental labs and digital clinics.
For technical specifications, support, or demo requests:
Email: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Digital Dental Equipment.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
