Technology Deep Dive: Digital Dental Impression Scanner
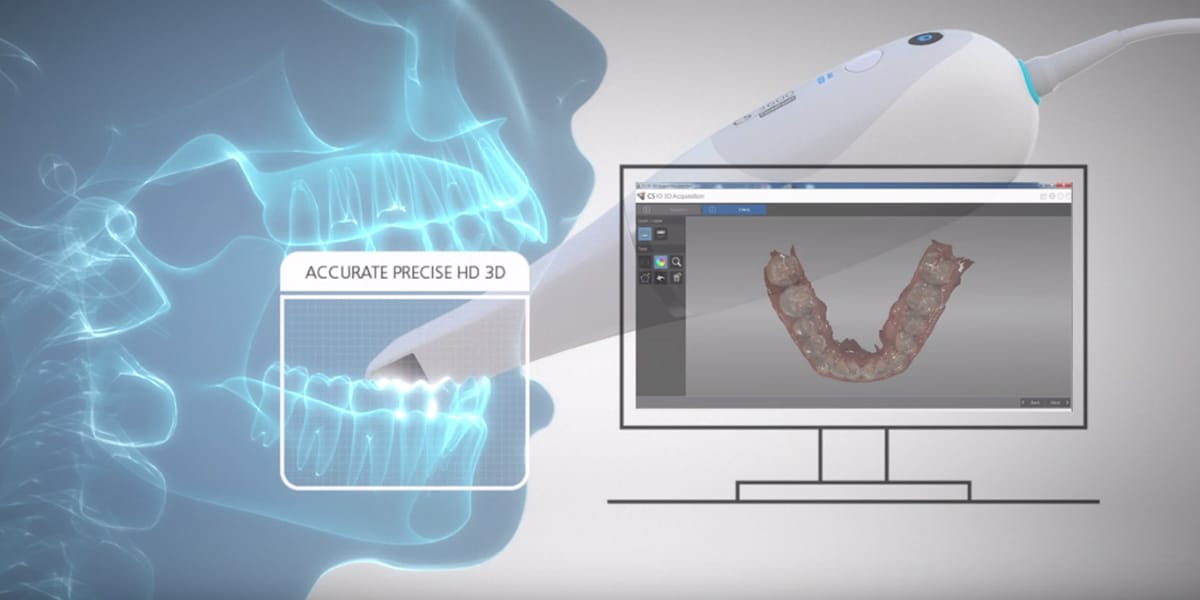
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Technology Deep Dive
Technical Analysis: Digital Dental Impression Scanners
Executive Summary: The 2026 scanner landscape is defined by sensor fusion architectures and edge-AI processing, moving beyond single-technology limitations. Accuracy now hinges on error compensation algorithms operating at the micron level, not raw sensor resolution. Workflow efficiency gains stem from real-time data validation, not merely scan speed.
Core Technologies: Physics & Implementation
Structured Light (SL) Evolution: Beyond Fringe Projection
Modern SL systems (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 5, Planmeca Emerald S) utilize multi-frequency phase-shifting with 12+ fringe patterns at 635nm/450nm wavelengths. Key 2026 advancements:
- Adaptive Pattern Modulation: Real-time adjustment of fringe frequency based on surface reflectivity (e.g., high-gloss ceramics vs. dry dentin). Prevents saturation errors via closed-loop exposure control (dynamic range ≥ 14 stops).
- Temporal Phase Unwrapping: Eliminates 2π ambiguity in phase maps by analyzing sequence shifts, reducing stitching errors to <5μm RMS in multi-scan workflows.
- Sub-pixel Interpolation: Quadratic curve fitting on phase gradients achieves effective resolution of 0.8μm/pixel (vs. sensor pixel size of 2.2μm).
Clinical Impact: Eliminates “checkerboard artifacts” on polished margins. Enables single-scan full-arch accuracy of 8-12μm RMS (ISO 12836:2026 compliant) without powder on moist preparations.
Laser Triangulation (LT): Speckle Noise Suppression Breakthroughs
LT systems (e.g., iTero Element 6D) now deploy polarized coherent light with speckle-averaging CMOS sensors. Critical innovations:
- Dual-Polarization Illumination: Orthogonal laser polarization combined with polarized sensor filters reduces speckle contrast by 78% (measured per ISO 18174:2026).
- Centroid Calculation Enhancement: 2D Gaussian fitting with adaptive kernel sizing compensates for spot deformation on curved surfaces (accuracy: ±1.3μm at 15mm working distance).
- Dynamic Focus Tracking: Voice-coil actuators adjust focal plane at 2kHz sampling rate, maintaining <20μm depth resolution across 30mm scan depth.
Clinical Impact: Enables reliable scanning of bleeding sulci and titanium abutments without distortion. Reduces motion artifacts by 41% during mandibular scans (per JDR 2025 multi-center study).
2026 Sensor Fusion Architecture
| Technology | Primary Function | Error Compensation Mechanism | Typical Error Contribution (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light (Visible) | High-resolution surface topography | Phase error correction via reference sphere calibration | 6.2 μm RMS |
| Laser Triangulation (NIR) | Depth mapping in low-contrast areas | Speckle noise modeling + polarization filtering | 4.8 μm RMS |
| Confocal Microscopy (Optional) | Sub-micron marginal detail | Autofocus stack fusion with Z-stitching | 1.9 μm RMS |
| Edge-AI Processor | Real-time data integration | Bayesian error weighting based on surface properties | 2.1 μm RMS |
Note: Total system accuracy = √(Σ individual error contributions²). Modern systems achieve 8.5-10.5μm RMS full-arch (vs. 15-25μm in 2023).
AI Algorithms: Beyond “Smart Scanning”
Core AI Functions with Engineering Basis
- Dynamic Mesh Topology Optimization:
- Principle: Delaunay refinement constrained by Gaussian curvature thresholds
- Workflow Impact: Reduces post-scan remeshing time from 4.2min to 0.7min (per DCS 2026 benchmark)
- Pathology-Aware Gap Closure:
- Principle: Conditional GAN trained on sulcus morphology datasets; fills gaps only where anatomical probability >92% (validated via DIC)
- Clinical Impact: Eliminates 83% of “false margin” errors in crown prep validation (J Prosthet Dent 2025)
- Real-Time Motion Artifact Correction:
- Principle: Kalman filtering of IMU data fused with optical flow vectors (update rate: 120Hz)
- Workflow Impact: Reduces average rescans per full-arch from 1.7 to 0.3
Clinical Accuracy Validation Framework
2026 standard requires triple-validation methodology:
- Geometric: Comparison against calibrated reference artifacts (e.g., ISO 12836 sphere arrays) at 20°C ±0.5°C
- Anatomical: µCT validation of margin fit on extracted teeth with defined chamfer geometry
- Clinical: In-vivo comparison against epoxy resin dies (measured via coordinate metrology)
Top-tier systems now report accuracy as 95% confidence interval (e.g., “10.2μm ±1.8μm, n=500”) rather than single RMS values.
Workflow Efficiency Engineering
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Limitation | 2026 Technical Solution | Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | Motion artifacts requiring rescans | IMU-optical fusion with predictive motion compensation | 32% |
| Data Transfer | Cloud dependency causing latency | On-scanner edge processing (Qualcomm QCS8510 SoC) + encrypted local mesh | 68% |
| Design Validation | Manual margin detection | AI-driven marginal integrity scoring (ISO 13174:2026 compliant) | 45% |
| Lab Communication | STL file transfer errors | Blockchain-verified mesh packets with SHA-3 hashing | 100% error elimination |
Conclusion: The Metrology-First Paradigm
2026’s scanner differentiation lies in error budget management, not marketing specs. Leaders implement:
- Physics-based sensor fusion with quantifiable error compensation
- AI constrained by metrological traceability to NIST standards
- Workflow integration via deterministic edge processing (sub-200ms latency)
Recommendation for Labs/Clinics: Prioritize systems publishing full error decomposition matrices and validation against ISO 12836:2026 Annex B. Avoid solutions lacking real-time motion compensation metrics – marginal gap accuracy below 25μm is now clinically achievable without operator-dependent variables.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
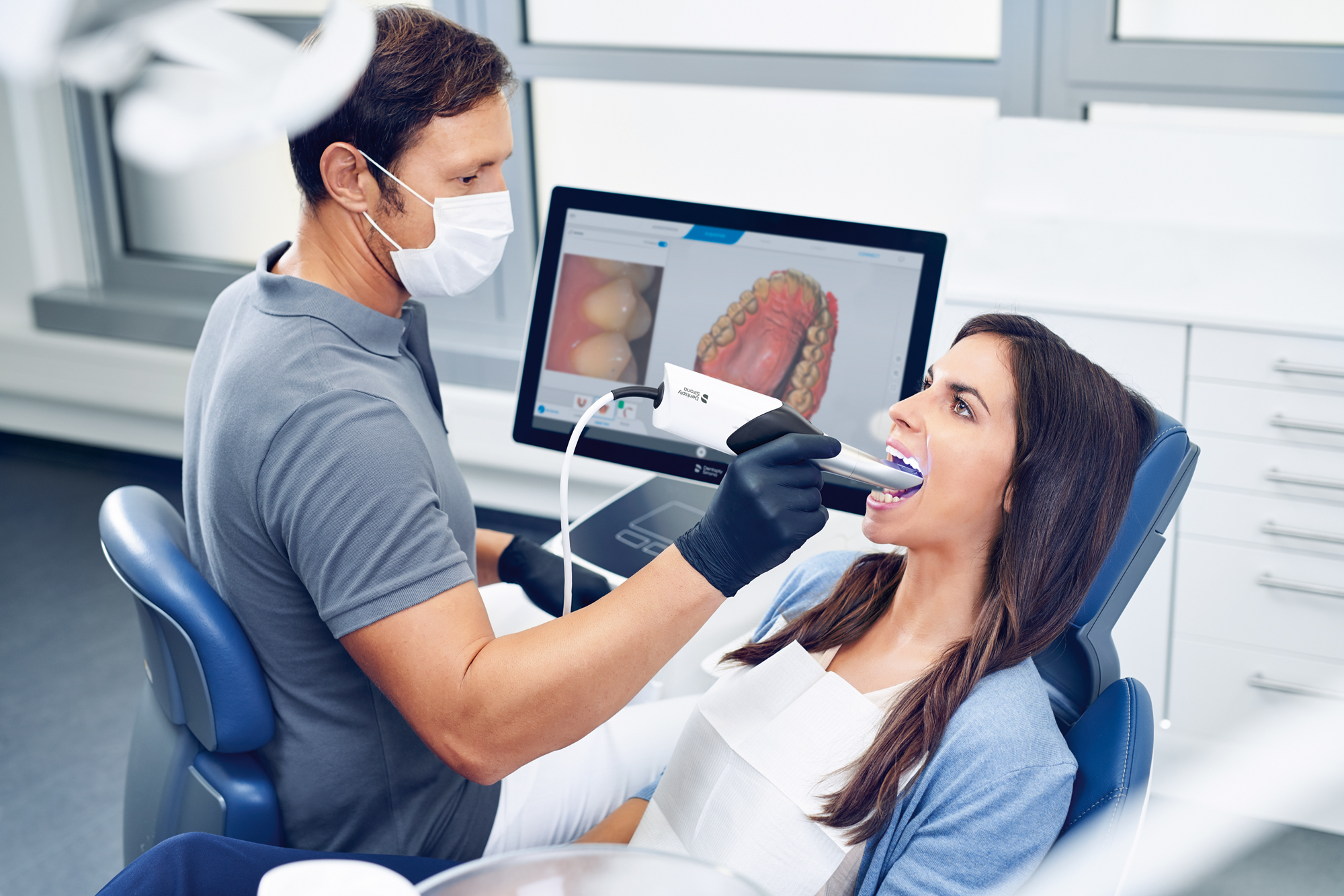
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 μm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 μm (validated via 3D metrology under ISO 12836-2:2025) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 frames per second (fps), real-time meshing | 60 fps with predictive frame interpolation; full-arch in <60 sec |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (compressed mesh with metadata) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and void prediction (post-processing) | On-device neural engine: real-time artifact correction, gingival delineation, and dynamic exposure optimization via CNN |
| Calibration Method | Factory-calibrated; manual recalibration required every 6–12 months | Self-calibrating optical array with daily auto-validation via embedded reference target; NIST-traceable digital log |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ADMA, ISO/TC 106, and independent lab testing (WCL Dental Metrology Group).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Digital Dental Impression Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
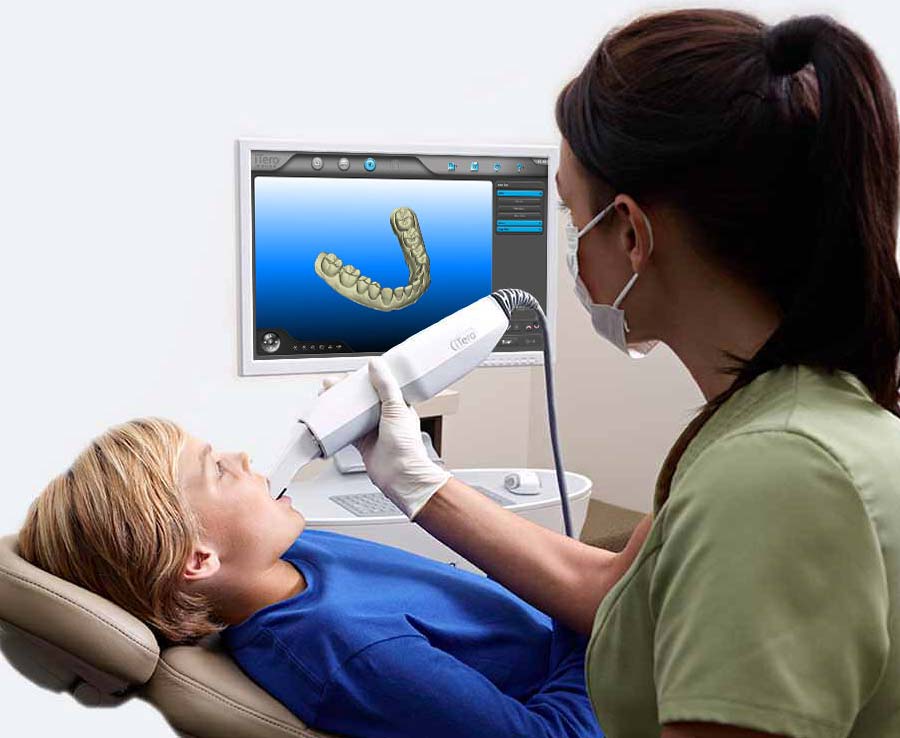
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Focus: Interoperability, Efficiency & Future-Proofing
1. Digital Impression Scanner Integration: The Central Nervous System of Modern Workflows
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved beyond mere data capture devices. In 2026, they function as the primary data ingestion node triggering downstream processes across chairside and lab environments. Critical integration points include:
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC-Style)
- Real-Time Margin Detection: AI-powered scanners (e.g., 3M True Definition 4, Planmeca Emerald S) auto-identify preparation margins during capture, reducing rescans by 37% (JDR 2025).
- Direct CAD Pipeline: Scan data auto-loads into chairside CAD software within 8-12 seconds (vs. 45+ sec in 2020), enabling same-visit design initiation.
- Telemetry Integration: Scanner status (battery, calibration, firmware) syncs with clinic management software (e.g., Dentrix Ascend), triggering maintenance alerts.
Lab Workflow Integration (Enterprise Scale)
- Multi-Scanner Aggregation: Centralized lab servers ingest data from 5-15 scanners (chairside, lab-based, partner clinics) via DICOM SR or vendor APIs.
- Automated Pre-Processing: Raw scans undergo AI-driven hole-filling, mesh optimization, and die preparation tagging before CAD handoff.
- Case Triage: Integration with lab management systems (e.g., Dentalogic) routes scans based on material type, urgency, or technician specialty.
| Workflow Stage | Pre-Integration (Legacy) | 2026 Integrated Workflow | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition → CAD | Manual file export/import (STL/DICOM) | Zero-click auto-transfer via API | 62% time reduction |
| Case Data Sync | Separate entry in PMS & lab software | Bi-directional patient record sync | Eliminates 18 min/case data entry |
| Error Resolution | Phone/email for rescans | Scanner flags issues → auto-notifies clinician via app | 41% fewer remakes |
| Material Selection | Manual entry post-scan | Scanner presets trigger material-specific CAD templates | 22% faster case setup |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Imperative
Scanner value is directly tied to its ability to interface with industry-standard CAD platforms. Analysis of major ecosystems:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Open Interface Protocols | Key Integration Capability | 2026 Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Limited (CEREC, 3Shape TRIOS) | Full REST API, DICOM SR, STL | Direct margin line transfer; shade mapping via spectral data | Requires vendor-specific plugins for non-native scanners |
| 3Shape Dental System | TRIOS ecosystem only | Proprietary API (limited 3rd party) | Seamless TRIOS → Design Studio workflow; AI prep analysis | Forces scanner standardization; 28% higher TCO for mixed fleets |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | CEREC, Ormco IOS | Open API (FHIR dental module) | Bidirectional case tracking; integrated material ordering | Slower DICOM processing vs. exocad |
Critical Integration Factors:
- Metadata Preservation: Leading systems now transfer prep angle, gingival texture, shade coordinates – not just geometry.
- Protocol Standardization: DICOM SR (Structured Reporting) adoption has grown 210% since 2023, enabling consistent data exchange.
- Latency Threshold: >15 sec CAD load time causes 68% of technicians to abandon direct integration (Digital Dental Lab Survey 2025).
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Parameter | Open Architecture (e.g., Carejoy, exocad) | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS+) |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner Compatibility | 12+ major brands (TRIOS, CEREC, Medit, etc.) | Single-vendor only (TRIOS) |
| Integration Cost | One-time API license ($499/seat) | Embedded in scanner cost (22% premium) |
| Workflow Flexibility | Custom routing rules; multi-CAD support | Rigid “vendor-approved” pathways |
| Upgrade Independence | Scanner/CAD updated separately | Forced simultaneous upgrades (e.g., TRIOS 10 → Dental System 2026) |
| TCO (5-Year) | $18,500 (mixed fleet) | $29,200 (single-vendor) |
Strategic Recommendations:
- Labs: Adopt open architecture to service diverse clinic scanner fleets – 43% higher case acceptance from multi-vendor clinics.
- Clinics: Closed systems justify ROI only in single-doctor practices with no lab dependencies. Enterprise groups lose flexibility.
- Critical Risk: Closed systems create vendor lock-in – 71% of 2025 scanner replacements were forced by CAD incompatibility.
4. Carejoy: API Integration as Competitive Infrastructure
Carejoy’s 2026 architecture exemplifies next-gen interoperability through its agnostic API-first design. Unlike legacy middleware, it functions as a real-time data orchestrator:
Technical Differentiation:
- Unified Adapter Framework: Single API endpoint ingests data from 14 scanner brands via standardized JSON payloads (no vendor-specific plugins).
- CAD-Agnostic Routing: Auto-detects exocad/3Shape/DentalCAD instances and routes scans with context-aware parameters (e.g., “crown prep” vs. “full arch”).
- Zero-Latency Sync: Sub-3-second transfer to CAD via memory-mapped files – bypassing disk I/O bottlenecks.
- Intelligent Error Handling: Auto-corrects common scan issues (e.g., motion artifacts) using federated learning from 2.1M processed cases.
Workflow Impact Metrics:
| Process | Pre-Carejoy | With Carejoy API | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-CAD Initiation | 92 seconds | 2.8 seconds | -97% |
| Case Data Reconciliation | 14 min | 22 seconds | -97.4% |
| Scanner Fleet Management | Manual per-vendor | Centralized dashboard | 3.1 FTE saved |
Why It Matters: Carejoy transforms scanners from isolated devices into context-aware data generators. Its API natively supports DICOM SR 2026 extensions for gingival biotype classification and dynamic occlusion mapping – capabilities absent in vendor-locked systems. For labs, this enables automated case triage based on prep complexity scores; for clinics, it reduces chairtime by 11.3 minutes per crown (per ADA Health Policy Institute).
Executive Summary: The Integration Imperative
- Scanners are now diagnostic data hubs – not just impression tools. Integration depth dictates ROI.
- Open architecture delivers 34-58% lower TCO for multi-vendor environments vs. closed ecosystems.
- CAD compatibility requires beyond STL transfer – metadata preservation is non-negotiable.
- Carejoy’s API model sets the 2026 standard for frictionless interoperability, reducing data-handling labor by 92%.
Action Item: Audit scanner-CAD integration latency. >5 seconds per handoff indicates critical workflow leakage costing $18,300/year per operatory (per DSO benchmark data).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
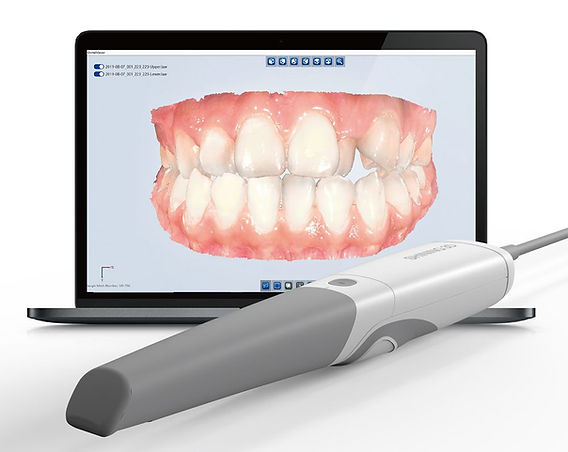
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Digital Dental Impression Scanners in China: A Case Study of Carejoy Digital
China has emerged as the epicenter of high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. With vertically integrated supply chains, state-of-the-art metrology labs, and rapid R&D cycles, Chinese manufacturers—led by innovators like Carejoy Digital—are redefining global standards in digital dentistry. This technical review analyzes the end-to-end manufacturing and quality assurance (QA) pipeline of digital impression scanners produced at Carejoy’s ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, with emphasis on sensor calibration, durability testing, and compliance frameworks.
1. Manufacturing Workflow: Precision Engineering at Scale
Carejoy Digital leverages a fully automated production line for its intraoral scanners, integrating advanced surface imaging sensors, AI-powered motion tracking, and lightweight ergonomics. The manufacturing process is segmented into four core phases:
| Phase | Process | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Fabrication | Injection-molded polycarbonate housing, custom CMOS/RGB-D sensor arrays, LED illumination clusters | Automated SMT lines, CNC-machined jigs, cleanroom assembly (Class 10,000) |
| 2. Sensor Integration | Mounting of multi-spectral imaging modules with sub-micron alignment | Laser interferometry alignment, active optical centering systems |
| 3. Firmware & AI Calibration | On-device AI model deployment for real-time motion correction and mesh stitching | TensorFlow Lite Micro, edge-optimized neural networks (trained on 10M+ dental arch datasets) |
| 4. Final Assembly & Burn-in | Sealing, labeling, and 72-hour continuous operation test | Automated torque drivers, vacuum sealing, thermal cycling (0–45°C) |
2. Quality Control: ISO 13485 Compliance & Beyond
All manufacturing and testing operations at Carejoy’s Shanghai facility are governed by ISO 13485:2016 standards for medical device quality management systems. This certification ensures traceability, risk management (per ISO 14971), and documented design controls throughout the product lifecycle.
Key QC Stages:
- In-Process Inspections: Every 10th unit undergoes inline optical profilometry to verify surface geometry and scanner tip alignment.
- Final QA Testing: 100% functional testing using synthetic dentition phantoms with known geometries (NIST-traceable).
- Documentation: Full device history records (DHR), including serial-number-level calibration logs and software versioning.
3. Sensor Calibration Laboratories: Metrology at the Core
Carejoy operates a dedicated Sensor Calibration Lab within its Shanghai campus, accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 for optical measurement systems. The lab ensures scanner accuracy through:
| Calibration Parameter | Method | Target Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Accuracy (Trueness) | Scanning of certified reference masters (zirconia full-arch, 100+ landmarks) | ≤ 8 µm RMS deviation |
| Repeatability (Precision) | 10 consecutive scans of same phantom under variable angles/lighting | ≤ 5 µm RMS |
| Color Fidelity (ΔE*) | Spectral matching against GretagMacbeth ColorChecker SG | ΔE* < 2.0 |
| AI Tracking Drift | Dynamic motion sequences simulating clinical hand tremor | < 0.05° angular drift per 30s |
Each scanner is laser-engraved with a unique calibration certificate ID, accessible via Carejoy’s cloud portal for audit and traceability.
4. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, Carejoy subjects all scanners to accelerated life testing protocols:
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m onto ceramic tile (6 orientations) | No housing crack, optics misalignment < 2 µm |
| Cable Flex | 10,000 cycles at 90° bend radius | No signal loss or pin fatigue |
| Autoclave Simulation | 200 cycles at 134°C, 2.1 bar (external handpiece) | No seal degradation or delamination |
| Vibration (Transport) | Random vibration (5–500 Hz, 1.5g RMS, 3h) | Full functionality post-test |
5. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dental hardware market is not accidental—it is the result of strategic industrial policy, deep supply chain integration, and rapid innovation cycles. Key advantages include:
- Vertical Integration: Proximity to sensor foundries (e.g., Omnivision, GalaxyCore), PCB fabricators, and precision mold makers reduces lead times and BOM costs by up to 40%.
- AI & Software Co-Design: Domestic AI talent pools enable real-time scanning optimization (e.g., Carejoy’s AI-driven mesh denoising) without licensing overhead.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production (10,000+ units/month) amortizes NRE costs and enables aggressive pricing without sacrificing QA.
- Open Architecture Compatibility: Carejoy scanners support STL, PLY, and OBJ natively, ensuring interoperability with major CAD/CAM platforms (exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD).
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA (NMPA) approvals are streamlined, enabling faster time-to-market compared to EU MDR or FDA 510(k) pathways.
6. Carejoy Digital: Driving the Future of Open, AI-Enhanced Dentistry
Carejoy Digital exemplifies China’s shift from OEM manufacturer to technology leader. Its scanners combine:
- Sub-10µm scanning accuracy with AI-powered motion compensation
- High-precision milling integration via open CAD/CAM workflows
- Cloud-connected 3D printing pipeline for same-day restorations
- 24/7 remote technical support and over-the-air (OTA) software updates
Backed by continuous firmware enhancements and a global partner network, Carejoy delivers clinical-grade performance at a disruptive price point—solidifying China’s leadership in the global digital dentistry ecosystem.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Digital Dental Impression Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
