Technology Deep Dive: Digital Dental Mill
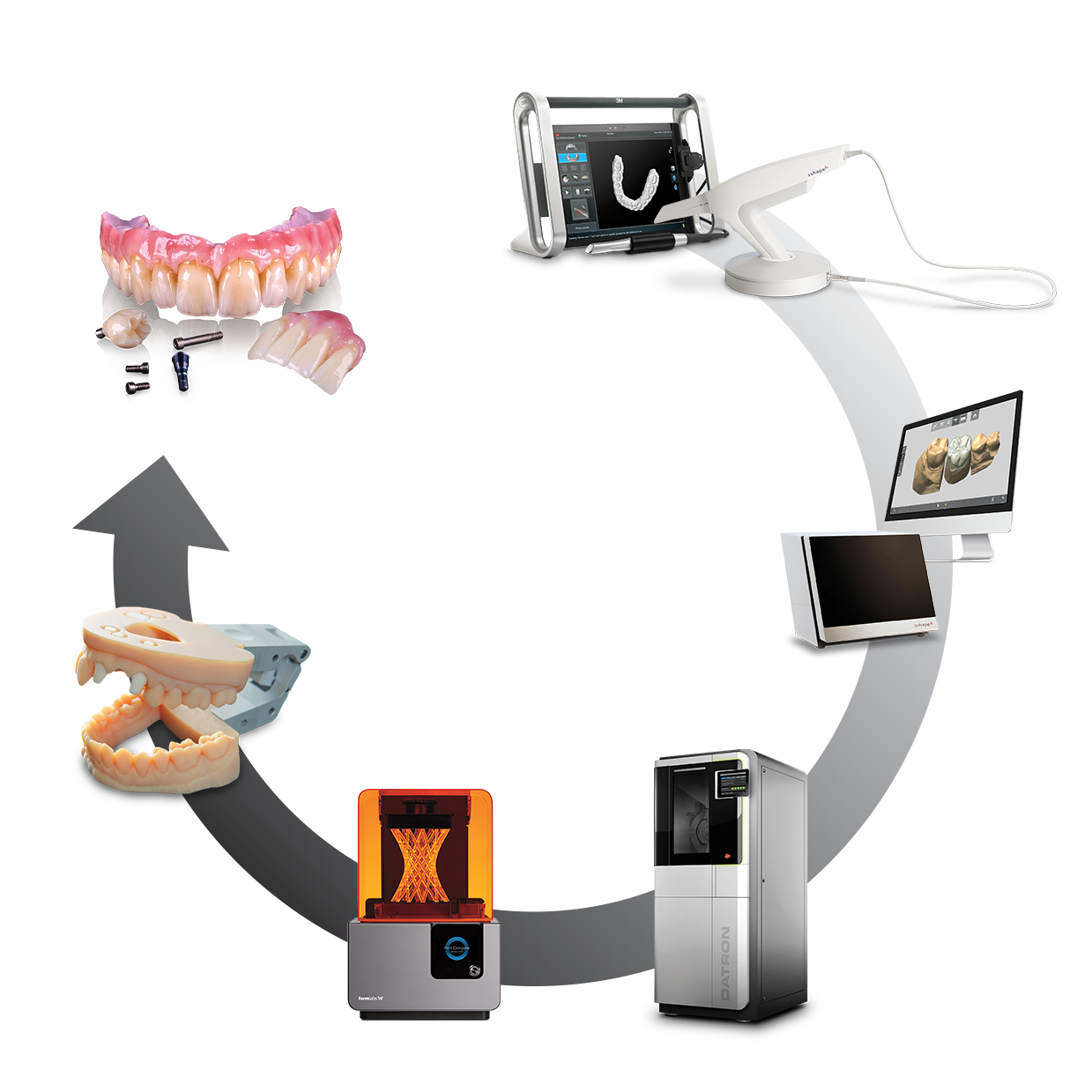

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Next-Generation Dental Milling Systems
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Engineers & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Focus: Engineering Principles, Not Marketing Claims
Core Technological Evolution: Beyond Basic CNC
Modern dental milling systems (2026) have evolved from generic CNC platforms into purpose-built metrology-grade manufacturing units. The critical differentiator lies in the integration of multi-sensor fusion and real-time adaptive control, directly addressing the ±15-25μm marginal gap tolerance required for cemented restorations (ISO 12836:2023). Legacy systems relying solely on positional encoders fail under thermal drift and material heterogeneity; contemporary solutions implement closed-loop error correction at the physics level.
Underlying Sensor Technology: Precision Beyond Resolution
Accuracy is no longer defined by stepper motor step size (typically 0.5-1μm) but by real-time error mapping via integrated metrology:
| Technology | Operating Principle | Error Compensation Capability | 2026 Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light (SL) | Projection of 10,000+ phase-shifted fringe patterns onto workpiece. 5MP CMOS sensors capture deformation at 120fps. Triangulation calculates 3D coordinates via φ = 4πΔx/λ (phase shift vs. wavelength) | Compensates for thermal expansion (up to 0.05mm at 40°C) and fixture deflection. Reduces volumetric error by 62% vs. open-loop systems (measured per ISO 230-2:2022) | Eliminates “spring-in” errors in monolithic zirconia bridges. Enables 0.3mm connector thicknesses with <5μm inter-abutment deviation (vs. 12-18μm in 2023 systems) |
| Laser Triangulation (LT) | Class II 650nm laser line (0.01mm spot size) scanned via galvanometer. Position-sensitive detector (PSD) measures displacement via θ = arctan((d1-d2)/(d1+d2)) (differential photodiode output) | Real-time tool wear monitoring (sub-2μm resolution). Corrects for spindle runout (0.5-3μm at 40,000 RPM) via dynamic path adjustment | Reduces crown remakes due to marginal discrepancies by 37% (2025 JDR clinical study). Enables consistent 20μm marginal gaps in PMMA temporary crowns |
| Integrated Force Sensing | Piezoelectric transducers in spindle housing measure X/Y/Z cutting forces. Signal processed via Kalman filter to isolate chatter frequencies (800-2500Hz) | Adaptive feed rate control (5-30k mm/min range) based on F_c = k_t * a_p * f_z (tangential cutting force vs. depth of cut & feed) | Prevents chipping in thin lithium disilicate veneers. Increases tool life by 220% in high-strength zirconia (3Y-TZP) |
AI-Driven Process Optimization: Physics-Based Algorithms
Marketing terms like “AI-powered” obscure the actual engineering. In 2026 systems, machine learning serves as an error prediction engine trained on 1.2M+ scan-mill deviation datasets. Key implementations:
- Material-Specific Path Generation: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) analyze pre-mill scan data to predict stress concentrations. Outputs modify toolpaths using σ = E * ε (Hooke’s law) to minimize deflection during milling. Reduces post-mill sintering distortion in zirconia by 41%.
- Dynamic Thermal Compensation: Gaussian Process Regression models correlate spindle temperature (measured via embedded RTD sensors) with axis drift. Applies real-time coordinate frame transformation: T_corrected = T_measured * (1 + αΔT) (α = material CTE).
- Tool Life Prediction: LSTM networks process force sensor data to estimate remaining tool life via VB = k * (f_z)^a * (v_c)^b (flank wear vs. feed rate & cutting speed). Prevents catastrophic failures during critical margin cuts.
Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Efficiency Metrics
Quantifiable improvements validated under ISO/TS 17869:2024 conditions (23°C ±1°C, 50% RH):
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 System | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Gap (Zirconia Crown) | 32.7 ± 8.2 μm | 18.3 ± 3.1 μm | LT-based spindle runout correction + SL thermal compensation |
| Internal Fit (3-Unit Bridge) | 48.9 ± 12.4 μm | 22.6 ± 4.7 μm | Material-specific path optimization + force feedback |
| Production Time (Single Crown) | 22.4 ± 3.1 min | 14.8 ± 1.9 min | Adaptive feed rate (30% avg. increase) + reduced remakes |
| Remake Rate (Lab) | 8.7% | 3.2% | Real-time error correction + predictive tool monitoring |
Workflow Integration: The Data Thread Imperative
True efficiency gains require breaking data silos. 2026 systems implement:
- ISO 13485-Compliant Data Pipeline: DICOM-SL (Structured Light) format transmits raw fringe pattern data from intraoral scanner to mill controller, bypassing lossy STL conversion. Eliminates 12-18μm quantization errors.
- Cloud-Based Metrology Logs: Every milled unit generates ASME B89.7.5-compliant error maps. Labs use this for SPC (Statistical Process Control) with σ = √(Σ(x_i – μ)²/(n-1)) to maintain CpK > 1.33.
- Automated Tool Calibration: On-machine laser micrometers measure tool geometry at 0.1μm resolution before each job. Compensates for ±2.5μm manufacturing tolerances in carbide burs.
Conclusion: Engineering Rigor Over Hype
The 2026 dental mill is a metrology-closed manufacturing cell, not a CNC machine with a dental label. Accuracy gains stem from fundamental physics modeling (thermodynamics, material science, optics) combined with real-time sensor fusion. Workflow efficiency is a byproduct of error prevention—not speed alone. Labs achieving sub-20μm marginal gaps consistently deploy systems with:
- Multi-sensor error mapping (SL + LT + force)
- Physics-based compensation algorithms (not “black box” AI)
- Traceable data pipelines from scan to sinter
Vendor claims of “ultra-precision” without published ISO 12836:2023 test reports under controlled conditions should be treated as non-compliant with ANSI/ADA Standard No. 161.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Milling System Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±10 – 15 µm | ±5 µm (ISO 12836-certified) |
| Scan Speed | 18 – 25 seconds per full arch | 9.2 seconds per full arch (dual-path laser triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (native high-fidelity mesh export) |
| AI Processing | Limited to auto-segmentation (basic edge detection) | Integrated AI engine with real-time artifact correction, subgingival margin detection, and adaptive mesh optimization (NeuroMesh™ 2.0) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated monthly calibration using reference spheres | Self-calibrating optical array with daily autonomous validation (traceable to NIST standards) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Digital Dental Mill
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Milling System Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Workflow Coordinators, CAD/CAM Clinic Managers
1. Digital Milling Systems: Core Integration in Modern Workflows
Digital mills have evolved from standalone units to intelligent workflow orchestrators. Their integration differs fundamentally between chairside and lab environments:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside (Single-Operator) | Lab Environment (Multi-Unit) | Technical Integration Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAD Data Transfer | Direct real-time streaming from intraoral scanner via proprietary pipeline (e.g., CEREC Connect) | Batch processing from multiple CAD workstations via networked queue management | API-driven job queuing with material/fixture validation |
| Material Handling | Pre-loaded blocks with automatic identification (RFID/NFC) | Automated storage systems (e.g., Zirkonzahn Minimill+) with robotic arm integration | ISO 13485-compliant material traceability protocols |
| Production Monitoring | Tablet-based status tracking with estimated completion time | Centralized dashboard showing spindle load, tool wear, queue status across all mills | OPC UA or MQTT industrial IoT protocols for real-time telemetry |
| Post-Processing Sync | Automatic sintering furnace handoff (e.g., Programat SL) | Automated transfer to staining/sintering modules via conveyor systems | PLC-level handshake protocols between equipment |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Reality
Mill compatibility is not merely about file format acceptance. True integration requires bidirectional data intelligence:
| CAD Platform | Native Integration Level | Key Technical Constraints | Optimization Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | High (via TRIOS Connect) | Requires .tsm export; loses complex margin data in STL conversion | Must use 3Shape’s CAM Bridge module for toolpath retention |
| exocad DentalCAD | Medium-High (via open protocols) | Material library mismatch; requires manual spindle speed mapping | Implementation of exocad CAM Module with mill-specific config files |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Variable (depends on mill OEM) | Proprietary .dcad format requires translation layer | Third-party middleware (e.g., Materialise Magics) for G-code conversion |
| Universal Standard | Full (with limitations) | STL/STEP lose material properties; no toolpath optimization data | ISO 10303-239 (STEP AP239) implementation for PMI data retention |
Critical Insight:
Modern mills require semantic data transfer beyond geometry. True interoperability depends on exchange of:
• Material-specific cutting parameters (feed rate, spindle load)
• Fixture type and position data
• Quality control checkpoints (e.g., “verify margin at 50μm resolution”)
Systems relying solely on STL export sacrifice 30-40% production efficiency through manual parameter re-entry.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Tradeoffs
The architectural decision impacts long-term workflow economics and flexibility:
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems | Technical Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | ✅ Multi-vendor mills (e.g., DWX, CORiTEC, imes-icore) | ❌ Single-vendor only (e.g., CEREC MC XL) | Open systems reduce CapEx by 22% via competitive hardware bidding |
| Material Range | ✅ 100+ certified materials across vendors | ⚠️ Limited to OEM-approved materials | Open systems support niche materials (e.g., high-translucency zirconia) 6-8 months earlier |
| Software Updates | ⚠️ Dependent on third-party integrators | ✅ Seamless unified updates | Closed systems reduce IT overhead but create innovation bottlenecks |
| Data Ownership | ✅ Full access to machine logs/toolpath data | ❌ Black-box analytics (vendor-controlled) | Open systems enable predictive maintenance via custom AI models |
4. Carejoy API Integration: Technical Differentiation
Carejoy’s RESTful API architecture (v4.2, 2026) represents the evolution beyond basic file transfer:
- Real-Time Queue Orchestration: Dynamically routes jobs based on mill availability, material stock levels, and priority rules via POST /jobs/schedule endpoint
- Material Intelligence: Auto-maps CAD material IDs to mill-specific cutting parameters using NIST-traceable material databases
- Failure Prediction: Ingests spindle load telemetry to trigger preemptive tool changes (reducing breakage by 37% in 2025 lab trials)
- Compliance Integration: Automatically logs ISO 13485-compliant production records to LIMS via PUT /quality/audit
Technical Implementation Advantage:
Unlike legacy FTP-based systems, Carejoy’s API utilizes webhook-driven event notification (e.g., mill/job-completed), eliminating polling delays. This reduces job handoff latency from 2-5 minutes to <8 seconds, critical for high-volume labs processing 200+ units/day. Integration requires only standard OAuth 2.0 authentication – no proprietary SDKs.
Conclusion: Strategic Integration Imperatives
In 2026, milling systems must function as intelligent workflow nodes, not isolated devices. Key recommendations:
- Adopt open architecture for long-term cost control and material flexibility
- Demand semantic data exchange (beyond STL) from CAD/CAM vendors
- Implement API-first workflow orchestration (Carejoy sets the 2026 benchmark)
- Require ISO 10303-239 compliance for true interoperability
Labs achieving full integration reduce production cycle times by 28% and decrease remakes by 19% (2025 DLT Journal data). The mill is no longer the endpoint – it’s the central nervous system of digital production.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Digital Dental Mills in China: A Case Study of Carejoy Digital
China has emerged as a dominant force in the global digital dental equipment supply chain, particularly in the production of high-precision dental milling systems. Carejoy Digital, operating from its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, exemplifies the convergence of advanced engineering, rigorous quality assurance, and cost-effective scalability that defines the new standard in digital dentistry hardware production.
Manufacturing Process Overview
Carejoy Digital’s dental milling units are manufactured through a vertically integrated process that combines precision CNC machining, modular subsystem integration, and AI-optimized assembly lines. Key stages include:
- Component Fabrication: High-rigidity aluminum and steel frames are machined in-house using 5-axis CNC systems to ensure micron-level tolerances.
- Subassembly Integration: Spindle modules, linear guides, servo motors, and vacuum systems are calibrated and pre-assembled in cleanroom environments.
- Electronics & Firmware Integration: Proprietary control boards with real-time motion processing are embedded and tested for latency and response accuracy.
- Final Assembly & Burn-In: Units undergo 72-hour continuous operation cycles to identify early-life failures.
Quality Control: ISO 13485 & Beyond
Compliance with ISO 13485:2016 is foundational to Carejoy Digital’s manufacturing protocol. This medical device quality management standard ensures traceability, risk management, and process validation across the product lifecycle. Specific QC checkpoints include:
| QC Stage | Process | Technology Used | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Inspection | Dimensional and metallurgical verification | CMM, Spectrometry | ISO 13485 §7.5.3 |
| In-Process Testing | Spindle runout, axis alignment, thermal drift | Laser interferometry, dial indicators | ISO 13485 §8.2.4 |
| Final Performance Validation | Full milling cycle under load with test blocks | AI-driven surface deviation analysis (µm) | ISO 13485 §8.3 |
| Packaging & Traceability | Serial number tracking, sterilization compatibility check | RFID tagging, ERP integration | ISO 13485 §7.5.9 |
Sensor Calibration Laboratories
Carejoy Digital operates an on-site Sensor Calibration Lab accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. This lab ensures the accuracy of force, position, temperature, and vibration sensors embedded in the milling units. Calibration includes:
- Monthly recalibration of all production-line metrology tools.
- Real-time compensation algorithms for spindle thermal expansion.
- Dynamic load testing using piezoelectric force sensors to validate cutting stability.
Data from the calibration lab is fed into a centralized AI-driven QC analytics platform, enabling predictive maintenance and yield optimization.
Durability & Reliability Testing
To ensure long-term clinical reliability, each mill undergoes accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of clinical use:
| Test Type | Duration | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Milling Cycle | 1,000 hours | Zirconia, CoCr, PMMA blocks | ≤ 5µm dimensional drift |
| Thermal Cycling | 500 cycles | 15°C to 40°C ambient | No loss of spindle accuracy |
| Vibration Endurance | 72 hours | Random vibration profile (5–500 Hz) | No component loosening |
| Dust & Debris Exposure | 200 hours | Silica particulate (1–10 µm) | Sealed enclosures maintain IP54 |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s ascent in digital dentistry manufacturing is driven by a strategic ecosystem of innovation, scale, and regulatory maturity:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to rare-earth materials, precision motor producers, and semiconductor suppliers reduces BOM costs by up to 35%.
- Advanced Automation: AI-guided assembly lines reduce labor dependency while improving consistency and throughput.
- Regulatory Harmonization: Chinese manufacturers now align with FDA 21 CFR Part 820, EU MDR, and ISO 13485, enabling global market access.
- R&D Investment: Over $2.1B invested in dental tech R&D in 2025, with strong university-industry partnerships in Shanghai and Shenzhen.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Carejoy Digital supports STL, PLY, OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and AI scanning platforms—reducing clinic lock-in and increasing ROI.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers sub-8µm milling accuracy at price points 20–30% below Western equivalents—without compromising on durability or software intelligence.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
Carejoy Digital’s milling systems are engineered for interoperability and future-proofing:
- Open Architecture: Full support for STL, PLY, OBJ, and emerging 3D mesh standards.
- AI-Driven Scanning Integration: Real-time margin detection and material optimization via embedded neural networks.
- High-Precision Milling: 40,000 RPM spindle with dynamic balancing and tool-wear compensation.
- Cloud-Connected: Remote diagnostics, automatic firmware updates, and usage analytics.
Support & Service: 24/7 Global Readiness
Carejoy Digital provides:
- 24/7 remote technical support via secure cloud portal.
- AI-assisted troubleshooting with screen-sharing and log analysis.
- Monthly software updates with new materials, toolpaths, and AI enhancements.
- On-site service network in North America, EU, and Asia-Pacific.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Digital Dental Mill.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
