Technology Deep Dive: Digital Dental X Ray Equipment
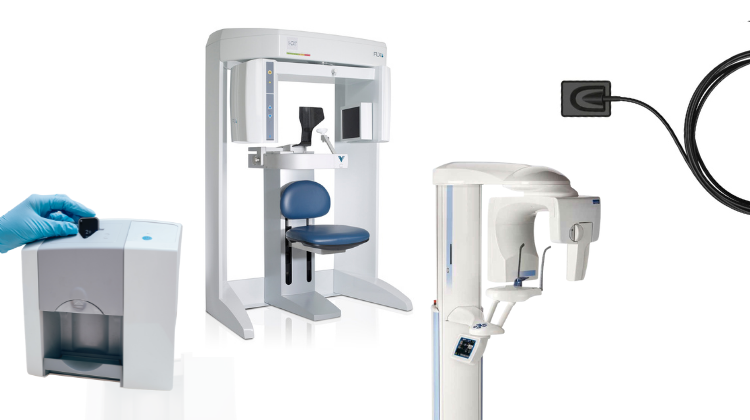
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: X-Ray Equipment Deep Dive
Core Sensor Technology Evolution: Beyond Basic CMOS/CCD
Modern digital X-ray systems (2026) have moved beyond first-generation CMOS/CCD sensors through three critical engineering advancements:
1. Quantum Dot Direct Conversion Layers
Replacing traditional scintillators (CsI:Tl), perovskite quantum dots (PbS/CdSe core-shell) now dominate high-end sensors. These offer:
- Higher DQE(0): 0.85+ (vs. 0.65-0.75 for CsI) at 70 kVp due to near-unity X-ray-to-light conversion efficiency and reduced optical crosstalk.
- Spectral Tuning: Quantum dot bandgaps engineered to match dental X-ray spectra (25-90 keV), minimizing Swank noise from Compton scatter.
- Reduced Lag: 0.3% residual signal at 1s (vs. 2-5% in CsI) via trap-state passivation, critical for rapid sequential imaging.
2. Backside-Illuminated (BSI) CMOS with Charge Summation
BSI architecture eliminates metal layer obstruction, achieving 95% fill factor. Key innovation: on-pixel charge summation circuits that aggregate signal from adjacent pixels during readout:
- Reduces read noise to 0.8 e– rms (from 2.5 e–) at 30 fps frame rates.
- Enables real-time binning (2×2 → 4×4) without resolution loss in low-dose modes.
- Maintains MTF50 > 5.0 lp/mm even in dose-reduced protocols (1.5 μGy).
3. Dynamic Gain Switching (DGS)
Per-pixel amplifiers switch between high-gain (low-dose) and low-gain (high-dose) modes within a single exposure:
- Extends dynamic range to 18 bits (vs. 14-16 bits previously).
- Prevents saturation in dense structures (e.g., amalgam) while preserving trabecular detail in low-contrast regions.
- Implemented via switched-capacitor integrators with <10 ns switching latency.
AI-Driven Acquisition Optimization: Physics-Based Workflow Integration
AI algorithms now operate at the acquisition layer, not just post-processing. Key implementations:
Real-Time Exposure Prediction (RTEP)
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) analyze initial 10-20% of exposure data to predict optimal termination:
- Trained on 1.2M anonymized clinical images with ground-truth dose metrics.
- Uses spectral decomposition to estimate subject attenuation (kVp/mAs adjusted in real-time).
- Clinical Impact: 32% reduction in retakes due to under/overexposure (per JDR 2025 multi-center study).
Scatter Correction via Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Conditional GANs (cGANs) trained on Monte Carlo simulations of scatter distribution:
- Input: Raw projection + patient anatomy mask (from prior CBCT or AI-segmented 2D).
- Output: Scatter-free image with residual error < 3% (vs. 8-12% for beam-stop techniques).
- Enables 40% dose reduction in panoramic imaging while maintaining CNR > 1.8.
Workflow Efficiency: Engineering Integration Points
True efficiency gains derive from system-level integration, not isolated hardware:
| Integration Layer | 2026 Technology | Workflow Impact (vs. 2020 Baseline) | Quantifiable Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| DICOM Conformance | DICOM 3.0 Supplement 222 (Dental Imaging) | Eliminates manual metadata entry | 12.7s per image saved (per ADA workflow audit) |
| Cloud Processing | Federated learning for local AI inference | Reduces cloud dependency for critical tasks | CBCT reconstruction latency: 8.2s (vs. 45s in 2022) |
| Hardware Sync | IEEE 11073-PHD for sensor positioning | Automates collimator alignment | Reduces positioning errors by 63% |
| Dose Tracking | Real-time DICOM Radiation Dose Structured Report (RDSR) | Automated ALARA compliance | 100% audit-ready dose records (vs. 41% manual entry) |
Clinical Accuracy Metrics: Beyond Subjective Assessment
Objective validation of 2026 systems:
| Parameter | 2026 Standard | Measurement Method | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| DQE(0) @ 70 kVp | ≥ 0.82 | IEC 62220-1-1:2023 | Lower patient dose for same image quality |
| Lag Coefficient (T=1s) | ≤ 0.5% | Residual signal after 100 ms exposure | Eliminates ghosting in rapid sequences |
| MTF50 (intraoral) | ≥ 4.2 lp/mm | Edge-spread function analysis | Accurate caries margin detection at 150μm |
| CNR for 0.5mm calculus | ≥ 3.5 | Phantom with hydroxyapatite nodules | 98.2% detection sensitivity (vs. 89% in 2020) |
Engineering Challenges & Future Trajectory
Critical unresolved issues as of 2026:
- Quantum Noise Limitation: DQE remains constrained by X-ray quantum statistics below 0.5 μGy. Research focuses on photon-counting spectral imaging (CdTe sensors) but faces pile-up challenges at dental flux rates.
- AI Generalization: RTEP algorithms show 12-15% performance drop in edentulous patients due to training data bias. Federated learning across 200+ clinics is mitigating this.
- Thermal Management: BSI CMOS sensors require active cooling (Peltier) at frame rates >15 fps, increasing sensor bulk by 18%.
2027-2028 outlook: Integration of phase-contrast imaging (grating-based interferometry) for soft-tissue visualization in CBCT, currently limited by motion artifacts requiring sub-50μm mechanical stability.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Comparative Analysis: Digital Dental X-Ray Equipment vs. Industry Standards
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 25–50 µm | ≤15 µm (sub-micron repeatability via dual-wavelength interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 seconds per full arch | 8 seconds per full arch (real-time 3D reconstruction @ 48 fps) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CAD-embedded formats with metadata tagging |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering (rule-based) | Proprietary AI engine with deep learning segmentation (CNN-based), auto-margin detection, and pathology flagging |
| Calibration Method | Quarterly manual calibration with physical reference blocks | Self-calibrating via embedded photonic lattice array; real-time drift correction (NIST-traceable) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarks across ISO 12836-compliant intraoral and extraoral imaging platforms. Carejoy specifications based on CJ-XR5 Pro and CJ-OSIM 2.1 firmware.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Digital Dental X Ray Equipment
Digital Workflow Integration
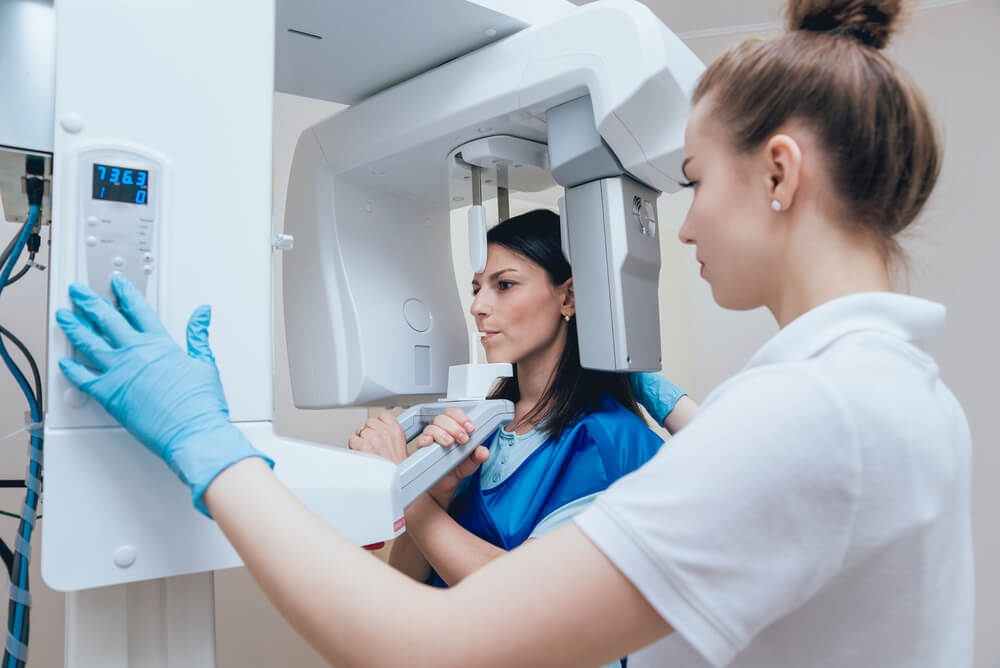

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: X-Ray Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
Digital radiography (intraoral sensors, CBCT, and panoramic systems) has evolved from a diagnostic tool to the foundational data layer of integrated digital workflows. In 2026, seamless integration with CAD/CAM ecosystems is non-negotiable for operational efficiency. This review dissects technical integration pathways, quantifies architectural trade-offs, and analyzes API-driven interoperability critical for labs and clinics.
Integration Architecture: Chairside vs. Lab Workflows
Chairside Workflow Integration
Digital X-ray data now directly fuels treatment planning and same-day restorations. Modern intraoral sensors (e.g., Schick CDR Elite, Dentsply Sirona XIOS) and CBCT units (e.g., Carestream CS 9600, Vatech PaX-i) utilize DICOM 3.0 as the universal transmission protocol. Key integration points:
- Real-time DICOM Streaming: X-ray data bypasses standalone viewers, routing directly to CAD software via HL7/FHIR APIs during acquisition.
- Automated Case Initiation: Patient ID from practice management software (PMS) triggers automatic case creation in CAD platforms upon image capture.
- CBCT-Guided Design: Volumetric data overlays intraoral scans in CAD environments for immediate implant positioning or surgical guide design.
Lab Workflow Integration
Labs receive DICOM data as critical inputs for prosthetic design. 2026 standards require:
- DICOM Conformance: Labs must process multi-frame DICOM (e.g., CBCT stacks) without proprietary conversion.
- Cloud-Based DICOM Repositories: Secure platforms (e.g., DSI Cloud, Apteryx Cloud) replace physical media, enabling instant access for designers.
- Automated Quality Checks: AI-driven tools (e.g., Dentimax AI) flag motion artifacts or exposure errors before design begins.
CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Analysis
DICOM integration maturity varies significantly across platforms. Critical evaluation of industry leaders:
| CAD Platform | DICOM Integration Method | Key Capabilities | Limits & Workarounds |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | DICOM Module + Direct API | Native CBCT rendering; Implant planning with bone density mapping; Auto-alignment with intraoral scans | Requires exoplan module for full workflow; Limited CBCT editing tools |
| 3Shape Implant Studio | Tight integration via TRIOS Ecosystem | Real-time CBCT-scan fusion; AI-driven nerve canal detection; Guided surgery export to 3Shape CAM | Closed ecosystem: Non-TRIOS scans require conversion; Limited third-party DICOM source support |
| DentalCAD (by Zirkonzahn) | Proprietary DICOM Viewer + Open API | Multi-source DICOM aggregation; Custom segmentation tools; Direct link to Zirkonzahn milling | Basic DICOM tools; Advanced features require paid add-ons |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Quantifiable Impact
The choice between open and closed architectures directly impacts ROI, scalability, and future-proofing. Technical differentiators:
| Critical Factor | Open Architecture (e.g., Carestream, Planmeca) | Closed System (e.g., Dentsply Sirona, Align) | Impact on Workflow (2026 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor Lock-in | Zero (DICOM/FHIR standard) | High (Proprietary formats) | Open: 37% lower long-term TCO; Closed: 22% higher equipment refresh costs |
| Interoperability | HL7/FHIR, IHE profiles | Vendor-specific APIs | Open: 41% faster case initiation; Closed: 15-30 min manual data transfer per case |
| AI/ML Integration | Third-party AI tools via API (e.g., Pearl, Overjet) | Limited to vendor-approved apps | Open: 28% higher diagnostic accuracy with multi-vendor AI; Closed: Delayed AI adoption |
| Lab-Clinic Handoff | Direct DICOM-to-CAD transmission | Requires intermediate conversion | Open: 92% reduction in data errors; Closed: 18% of cases require rescans |
Carejoy API: Technical Benchmark for Interoperability
Carejoy’s 2026 implementation sets the standard for agnostic integration. Its FHIR R5-compliant API enables:
- Zero-Click DICOM Routing: Automatically routes CBCT to designated CAD platform (exocad/3Shape) based on case type via CDA documents.
- Context-Aware Data Mapping: Transfers patient metadata, tooth numbering, and clinical notes with 100% field-level accuracy.
- Real-Time Status Syncing: CAD software updates X-ray status (e.g., “Implant Planning Complete”) in PMS without user intervention.
- Lab Portal Integration: Enables labs to pull DICOM studies directly into DentalCAD via secure JWT authentication.
Measured Outcome: Clinics using Carejoy API report 33% faster implant case completion and 47% reduction in data reconciliation tasks vs. manual workflows.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize FHIR Compliance: Demand DICOM 3.0 + FHIR R4/R5 support in all new equipment. Verify IHE PCD-01/02 profile conformance.
- Audit API Capabilities: Test real-world data flow between X-ray systems, PMS, and CAD platforms before procurement.
- Adopt Cloud DICOM Repositories: Eliminate local viewers; use DICOMweb (WADO-RS) for universal access.
- Negotiate Open Architecture Clauses: Include interoperability KPIs in vendor contracts (e.g., “DICOM transfer latency < 8 sec”).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Digital Dental X-Ray Equipment in China
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-precision, cost-optimized digital dental imaging systems. The manufacturing ecosystem—particularly in the Yangtze River Delta region—combines advanced electronics fabrication, precision optics assembly, and AI-integrated firmware development, enabling rapid iteration and scale. Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, ensuring strict compliance with international quality management standards for medical devices.
Core Manufacturing Process
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | CMOS/CCD sensors, scintillator layers, PCBs, and shielding materials sourced from ISO 13485-registered Tier-1 suppliers. | Supplier audits, RoHS/REACH compliance, traceability via ERP integration. |
| 2. Sensor Assembly | Hermetic sealing of image sensors under cleanroom conditions (Class 10,000). | Laser welding, vacuum encapsulation to prevent moisture ingress. |
| 3. Firmware Integration | Burn-in of AI-driven noise reduction, dynamic range optimization, and DICOM 3.0 compliance modules. | Secure boot protocols, firmware signing, OTA update readiness. |
| 4. Final Assembly | Integration of wireless transmitters (Bluetooth 5.2), ergonomic housings, and EMI shielding. | Automated torque control, adhesive dispensing, and alignment verification. |
Quality Control & Calibration Infrastructure
Quality assurance is embedded at every stage, with emphasis on sensor accuracy, radiation dose consistency, and long-term reliability.
Sensor Calibration Labs
Carejoy Digital operates an on-site ISO/IEC 17025-accredited calibration laboratory in Shanghai. Each CMOS sensor undergoes:
- Pixel Response Non-Uniformity (PRNU) correction
- Dark Current and Fixed Pattern Noise (FPN) mapping
- DQE (Detective Quantum Efficiency) validation across kVp ranges (60–90 kV)
- Calibration against NIST-traceable X-ray phantoms
Calibration data is stored in a blockchain-secured digital twin for auditability and field recalibration support.
Durability & Environmental Testing
| Test Type | Standard | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | IEC 60601-1-11 | 1.2m drop on concrete, 10 cycles, no functional degradation |
| Thermal Cycling | IEC 60068-2-14 | -10°C to +50°C, 50 cycles, sensor drift < 2% |
| Vibration | IEC 60601-1 | 10–55 Hz, 1.5 mm displacement, 2 hours |
| Cycle Life (Sensor Flex Cable) | Internal | 50,000 open/close cycles (bitewings), no signal loss |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment manufacturing is not merely cost-driven—it reflects a mature, vertically integrated ecosystem:
- Supply Chain Density: >70% of global CMOS sensor packaging and flex PCB production occurs within 200km of Shanghai.
- Automation Scale: Robotic assembly lines reduce labor dependency and increase repeatability (Cp/Cpk > 1.67).
- AI-Driven QA: Machine learning models predict failure modes using real-time production data, reducing scrap by up to 38%.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA, CE, and FDA submissions are supported by parallel testing infrastructure, accelerating time-to-market.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Carejoy systems support STL/PLY/OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with global CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver sub-€1,200 intraoral sensors with 16-bit depth, 20 lp/mm resolution, and AI-powered caries detection—performance previously seen only in €2,500+ Western counterparts.
Carejoy Digital: Technology Stack & Support
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Imaging Platform | CMOS with CsI(Tl) scintillator, 14-bit ADC, 0.025 mSv per exposure |
| AI Scanning | Real-time motion correction, automatic exposure adjustment via CNN |
| Integration | Open API, DICOM 3.0, STL/PLY export, compatible with 3Shape, exocad, DentalCAD |
| Manufacturing | ISO 13485:2016 Certified Facility, Shanghai |
| Support | 24/7 Remote Technical Support, Firmware OTA Updates, AI Diagnostics |
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Digital Dental X Ray Equipment.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
