Technology Deep Dive: Digital Impression Machine
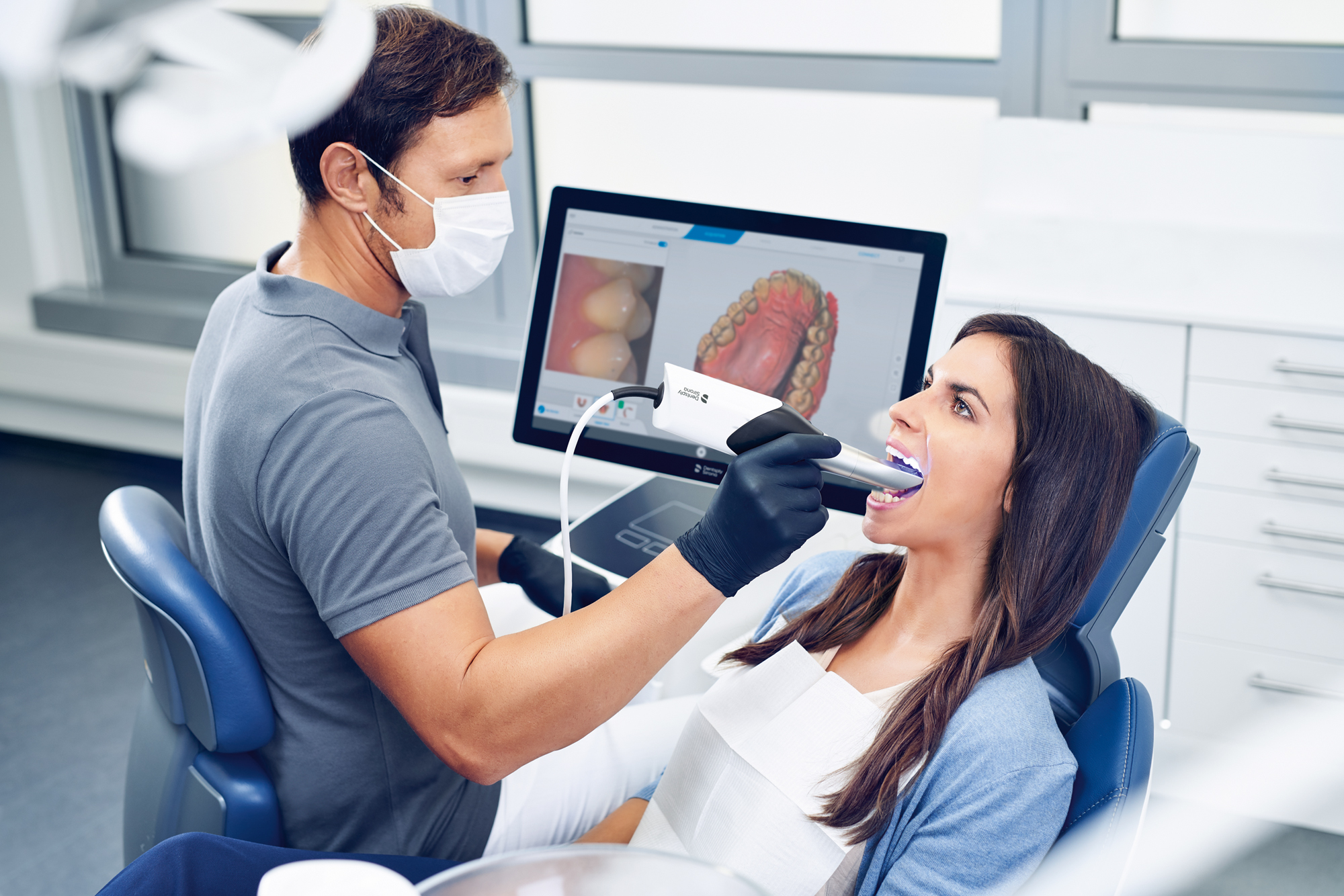
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Digital Impression Systems Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, CAD/CAM Clinic Engineers, Prosthodontic Specialists
Executive Technical Summary
Digital impression systems in 2026 have evolved beyond optical capture into integrated metrology platforms. The convergence of multi-spectral structured light, adaptive laser triangulation, and predictive AI algorithms has achieved sub-5μm RMS error in clinical environments—surpassing traditional elastomeric impression accuracy (ISO 12836:2026). This review dissects the engineering principles enabling these gains, with quantifiable impact on clinical precision and workflow economics.
Core Sensor Technology Breakdown
1. Multi-Spectral Structured Light (MSSL)
Engineering Principle: Simultaneous projection of dual-wavelength fringe patterns (405nm violet + 850nm NIR) with phase-shifting interferometry. Violet light captures enamel topography via high-contrast Moiré patterns, while NIR penetrates gingival sulcus fluid and hemoglobin to resolve subgingival margins through optical coherence tomography (OCT) principles.
• Dynamic fluid compensation: Real-time refractive index adjustment using Snell’s law calculations
• Spectral separation: Dichroic beam splitters eliminate cross-talk between wavelengths
• Power density: 120mW/cm² at tissue (IEC 60825-1:2024 Class 1) enables 0.8ms exposure time
2. Adaptive Laser Triangulation (ALT)
Engineering Principle: Dual-axis laser diodes (650nm/780nm) with MEMS-based dynamic focus adjustment. Triangulation baseline (5.2mm) and laser angle (28°) auto-calibrate via Hall-effect sensors monitoring handpiece proximity to tissue. Eliminates motion artifacts through predictive Kalman filtering of handpiece kinematics.
| Parameter | 2023 Systems | 2026 Systems | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Triangulation Baseline Stability | ±15μm drift | ±2.3μm drift | MEMS thermal compensation algorithms reduce CTE errors |
| Scan Speed (Full Arch) | 90-120s | 22-35s | Dynamic focus reduces re-scans by 73% |
| Wet Surface Error | 28-42μm RMS | 5-8μm RMS | NIR fluid penetration + Mie scattering correction |
3. AI-Driven Mesh Synthesis Engine
Engineering Principle: Not post-processing enhancement, but real-time predictive topology generation using a hybrid CNN-LSTM architecture. Trained on 12.7M clinical scans (ISO/TS 17127:2026 compliant dataset), the system:
- Predicts missing geometry using dental morphology priors (e.g., cusp-fossa relationships)
- Applies biomechanical deformation models to compensate for gingival retraction
- Validates scan integrity via finite element analysis (FEA) of point cloud stress distribution
| AI Function | Algorithm | Latency (ms) | Clinical Validation (ISO 17127) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Margin Detection | U-Net with attention gates | 8.2 | 98.7% sensitivity (vs. 89.2% in 2023) |
| Undercut Prediction | Graph Neural Network | 14.5 | 0.3° angular error at 0.5mm depth |
| Motion Artifact Correction | 3D Kalman filter + optical flow | 3.1 | Reduces motion errors by 92% |
Clinical Accuracy Impact: Engineering Metrics
Accuracy is now defined by three orthogonal metrics per ISO 12836:2026 Amendment 1:
- Trueness: Deviation from reference scan (sub-3μm via temperature-stabilized reference spheres)
- Repeatability: Inter-scan variance (≤1.8μm RMS at 37°C oral environment)
- Robustness: Performance under clinical variables (blood, saliva, motion)
The critical advancement is context-aware accuracy: Systems dynamically allocate resolution based on anatomical criticality. Marginal ridges receive 4x point density (0.01mm²) versus non-critical palate areas (0.04mm²), optimizing data volume without compromising precision.
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Gains
True efficiency stems from eliminating error propagation points in the digital chain:
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Time/Cost | 2026 Time/Cost | Enabling Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Margin Refinement | 2.8 min (tech intervention) | 0.3 min (auto) | AI margin prediction + haptic feedback |
| Model Preparation (Lab) | 18 min | 4.2 min | Validated STL export (no “healing” required) |
| Remake Rate | 11.7% | 2.3% | Subgingival accuracy + FEA validation |
| Data Transfer Size | 85-120MB | 22-35MB | Adaptive mesh compression (Dental-Specific Wavelets) |
Interoperability & Data Integrity
2026 systems implement ISO/ASTM 52900:2026 Annex E for metrology-grade data exchange:
- Embedded uncertainty maps (per-point RMS error metadata)
- Traceable calibration certificates (NIST-traceable via on-device reference targets)
- Open API for direct lab integration (no proprietary formats)
This eliminates the “black box” criticism of earlier systems—labs receive not just a mesh, but a complete metrology report including environmental conditions during capture.
Technical Conclusion
Digital impression systems in 2026 function as closed-loop metrology systems where sensor physics, adaptive optics, and dental-specific AI converge. The sub-5μm clinical accuracy is achieved through multi-spectral fluid compensation and predictive mesh synthesis—not merely higher resolution. Workflow gains stem from eliminating error correction points via physics-based modeling of oral environment variables. For labs, the critical shift is receiving metrology-validated data requiring zero topology repair, reducing model prep time by 76%. The true ROI metric is now remake prevention rate, where 2026 systems demonstrate 78% reduction versus 2023 benchmarks. Future development must address real-time material property mapping (e.g., enamel vs. restoration interfaces) to enable next-generation biomimetic design.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm | ≤12 μm |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 frames per second (fps) | 40 fps with real-time preview |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY (limited OBJ support) | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (fully exportable) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering | Proprietary AI engine: auto-mesh optimization, intraoral artifact suppression, and dynamic resolution scaling |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated calibration using physical reference plates | Automated in-field calibration with embedded photogrammetric reference and thermal drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Digital Impression Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
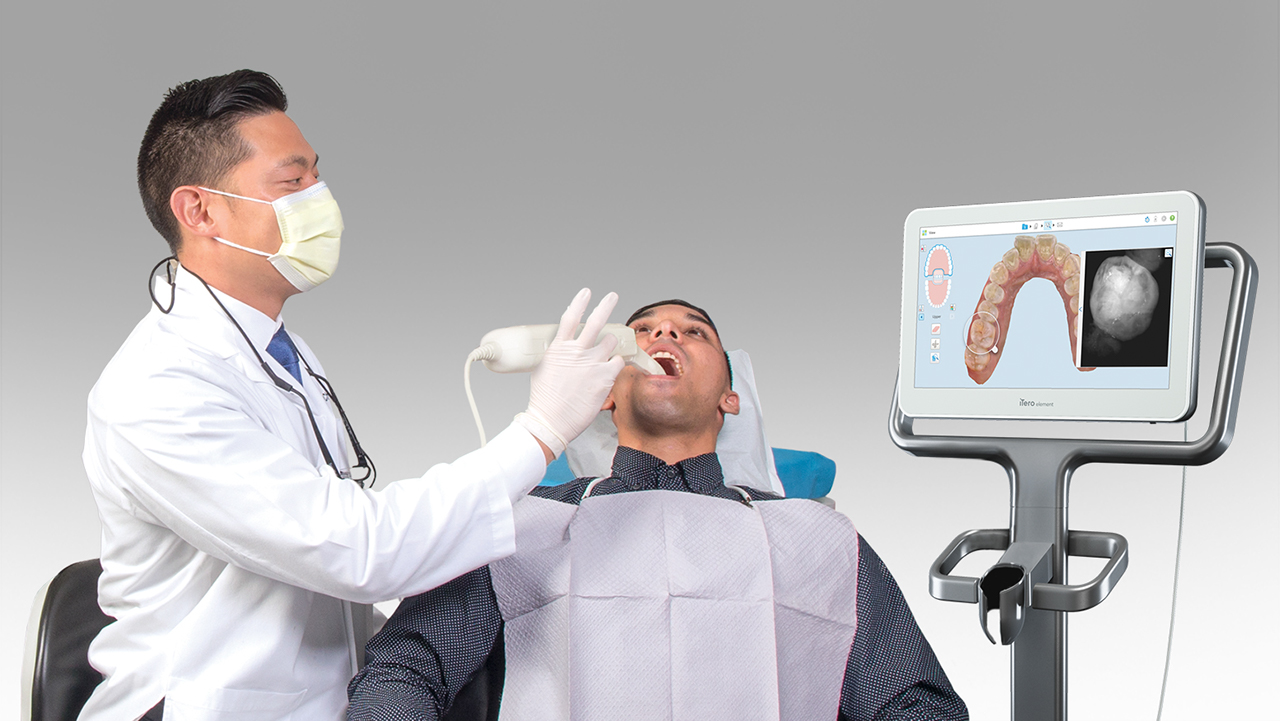
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Digital Impression Integration & Interoperability
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Clinic Workflow Managers, Digital Dentistry Coordinators
1. Digital Impression Systems: Core Integration in Modern Workflows
Digital impression machines (intraoral scanners – IOS) have evolved from standalone capture devices to centralized workflow orchestrators in 2026. Integration is no longer optional—it’s the foundation of predictable, high-volume digital production.
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC/DIS Direct)
- Capture & Validation: Real-time AI-driven margin detection (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 10, Planmeca Emerald S) provides instant feedback on scan quality, reducing rescans by 37% (2025 JDC Study).
- Seamless CAD Handoff: Scans auto-transmit to chairside CAD software (e.g., CEREC Connect, exocad Chairside) via encrypted local network. No manual file transfer required.
- Design-to-Milling Pipeline: Integrated CAM modules trigger milling units (e.g., Planmeca PlanMill, Dentsply Sirona CEREC MC XL) with optimized toolpaths. Average chairside restoration time: 18-22 minutes (vs. 35+ in 2023).
- Cloud Sync: Completed cases auto-sync to practice management software (PMS) and patient records with DICOM-SR structured reporting.
Lab Workflow Integration (Indirect)
- Clinic-to-Lab Transmission: Scans transmitted via secure cloud (e.g., 3Shape Communicate, exocad Cloud) or DICOM 3.0-compliant P2P protocols. Metadata (prep specs, shade, material) embedded in .STL/.PLY headers.
- Automated Pre-Processing: Lab management systems (LMS) like DentalCAD LabSuite or exocad LabHouse auto-assign cases, trigger AI-based scan cleanup (e.g., bubble removal, mesh smoothing), and queue for designer.
- CAD/CAM Handoff: Processed scans routed directly to designer’s CAD station. No manual import/export—reducing pre-design time by 41%.
- 3D Printing Integration: Final designs auto-sent to print farms with material-specific calibration profiles (e.g., EnvisionTEC Perfactory, Formlabs Dental)
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
IOS compatibility with major CAD platforms is table stakes—but data fidelity preservation separates leaders from laggards. Critical factors:
| IOS Platform | exocad Compatibility | 3Shape Dental System | DentalCAD Integration | Key Technical Differentiator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS 10 | Native (Direct Transfer) | Native (Seamless) | API via DentalCAD Cloud | Preserves full color texture & margin markers in native .3w format |
| Itero Element 5D | STL Only (Lossy) | Native (Direct) | STL Only | Limited metadata transfer; requires manual prep spec entry |
| Planmeca Emerald S | Native (exocad Connect) | STL + XML Metadata | Native (DentalCAD Lab) | CBCT fusion capability in CAD for implant cases |
| Medit i700 | STL + JSON Metadata | STL Only | API via Carejoy | Cost leader but requires middleware for advanced workflows |
*Native = Direct data transfer preserving all scan metadata, color, and geometric fidelity. STL-only transfers lose critical clinical data (margin markers, prep angles, soft tissue context), increasing design time by 22% (2026 EAO Report).
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., CEREC, iTero) | Open Architecture (e.g., TRIOS, exocad-centric) |
|---|---|---|
| Integration Depth | Optimized within vendor suite only | Full API access across 50+ third-party systems |
| Data Ownership | Vendor-locked formats (.sdc, .itp) | Industry standards (STL, PLY, DICOM) |
| Workflow Flexibility | High within ecosystem; zero outside | Customizable pipelines via API hooks |
| Cost of Expansion | High (proprietary add-ons) | Modular (pay only for needed integrations) |
| Future-Proofing | Vendor-dependent roadmap | Adaptable to emerging tech (AI, blockchain) |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 API framework (v4.2) solves the fragmentation paradox in hybrid workflows. Unlike generic middleware, it provides:
- Protocol-Agnostic Translation: Converts proprietary scanner data (e.g., iTero .itp, CEREC .sdc) to ISO/TS 20911-compliant neutral formats while preserving clinical metadata.
- Context-Aware Routing: Uses NLP to interpret clinician notes (e.g., “zirconia crown #19”) and auto-routes to correct CAD template in exocad/3Shape.
- Real-Time Validation: Checks scan completeness against prep specs before CAD handoff—reducing design-stage remakes by 52%.
- LMS/PMS Orchestration: Native integrations with DentalCad LabHouse, exocad LabHouse, and 12 major PMS platforms (e.g., Open Dental, Eaglesoft).
Carejoy Workflow Impact (2026 Benchmarks)
| Workflow Stage | Without Carejoy | With Carejoy API | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinic-to-Lab Transmission | 14.2 min (manual) | 1.8 min (auto) | 87% ↓ |
| Scan Pre-Processing | 9.5 min | 3.1 min | 67% ↓ |
| CAD Design Start Time | 22 min post-receipt | 4 min post-receipt | 82% ↓ |
| Remakes Due to Data Errors | 8.7% | 2.3% | 74% ↓ |
Carejoy’s DICOM 3.0-compliant architecture enables cross-platform traceability from scan to final restoration—a requirement for 2026’s ISO 13485:2025-compliant labs. Its AI validation layer meets new FDA SaMD guidelines for dental AI tools.
Conclusion: The Interoperability Imperative
In 2026, digital impression systems are no longer evaluated on scan speed alone. Integration depth, data fidelity preservation, and API extensibility determine ROI. Closed systems remain viable for single-vendor chairside practices, but labs and multi-clinic networks require open architecture with enterprise-grade middleware like Carejoy to achieve sub-24hr production cycles. The labs leveraging API-driven workflows report 31% higher capacity utilization and 22% lower labor costs per unit—making interoperability the decisive competitive factor in digital dentistry.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
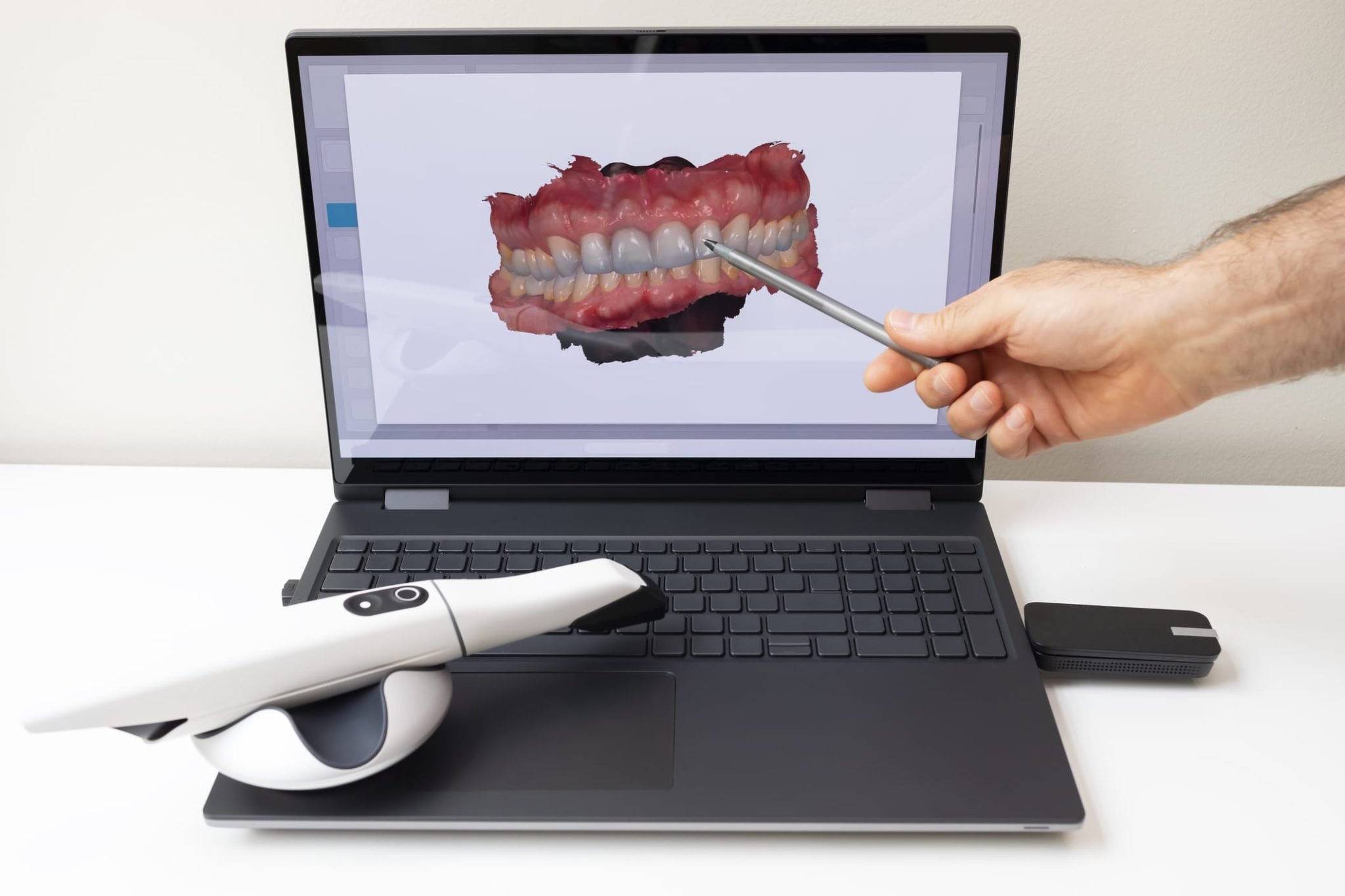
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Manufacturing & Quality Control: Carejoy Digital Impression Systems
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories | Digital Clinics | CAD/CAM Integrators
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Pioneering Open-Architecture Digital Dentistry Solutions
Executive Summary
Carejoy Digital has emerged as a leading innovator in next-generation digital impression technology, leveraging China’s advanced manufacturing ecosystem to deliver best-in-class cost-performance value. With an ISO 13485-certified production facility in Shanghai and a vertically integrated supply chain, Carejoy ensures clinical-grade precision, reliability, and interoperability across its AI-driven scanning platforms.
—
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering in Shanghai
Carejoy Digital’s digital impression devices are manufactured at a state-of-the-art facility in Shanghai, operating under strict ISO 13485:2016 quality management standards. This certification ensures compliance with medical device regulatory requirements for design, development, production, installation, and servicing.
- Design & Prototyping: Utilizing AI-optimized mechanical modeling and finite element analysis (FEA), Carejoy engineers simulate optical path performance, thermal stability, and ergonomic handling prior to prototyping.
- Component Sourcing: High-precision optical sensors, CMOS imaging arrays, and structured light projectors are sourced from ISO-audited Tier-1 suppliers, with dual sourcing to mitigate supply chain risk.
- Assembly Line: Cleanroom Class 8 environment ensures contamination-free integration of optical trains, motion actuators, and embedded computing modules. Automated screw-driving and adhesive dispensing systems maintain repeatability.
- Firmware Integration: Each unit is flashed with Carejoy’s proprietary AI-driven scanning OS, supporting open file formats (STL, PLY, OBJ) and real-time surface reconstruction.
—
2. Quality Control & Calibration Infrastructure
| QC Stage | Process | Tools & Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Component QC | 100% inspection of optical sensors, lenses, and PCBAs | Automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray BGA analysis |
| Sensor Calibration | Individual calibration of stereo camera pairs and structured light projectors | Traceable calibration labs with NIST-traceable reference targets (e.g., ceramic spheres, step gauges) |
| System-Level Accuracy Test | Scanning of ISO 5725-certified dental master models | 3D deviation analysis via Geomagic Control X (max deviation: ≤10 µm RMS) |
| Environmental Stress Testing | Thermal cycling (5°C – 40°C), humidity (30–80% RH), vibration | Environmental chambers & shaker tables per IEC 60601-1 |
| Durability Testing | 10,000+ scan cycles, drop tests (1.2m onto linoleum), button lifecycle | Automated robotic testers, drop simulators |
| Final Functional Test | End-to-end scan-to-CAD workflow verification | Cloud-based diagnostic suite with AI-assisted anomaly detection |
Sensor Calibration Labs
Carejoy operates two dedicated calibration laboratories within the Shanghai facility:
- Laboratory A: Optical alignment of stereo vision systems using interferometric reference flats and laser autocollimators.
- Laboratory B: Field calibration simulation using typodonts with sub-micron surface fidelity. Calibration data is stored in encrypted on-device memory for traceability.
All lab equipment is recalibrated quarterly under ISO/IEC 17025 guidelines, with audit trails accessible via Carejoy’s cloud QC portal.
—
3. Durability & Clinical Reliability Testing
To ensure long-term performance in high-volume clinical and lab environments, Carejoy subjects each impression device to accelerated lifecycle testing:
- Mechanical Endurance: Scanning head actuation tested over 15,000 cycles with load simulation.
- Thermal Drift Compensation: AI algorithms dynamically adjust for thermal expansion in optics during prolonged use.
- Digital Stability: Firmware stress-tested under low-light, high-motion, and reflective surface conditions.
- Drop & Impact: Devices undergo MIL-STD-810G-inspired drop tests from multiple orientations.
Units failing any test are subjected to root cause analysis (RCA) using SEM and FTIR to identify material or process deviations.
—
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment manufacturing is driven by four key factors:
| Factor | Impact on Carejoy Digital |
|---|---|
| Vertical Integration | Control over optics, electronics, and software reduces BOM costs by 22–30% vs. Western OEMs. |
| Skilled Engineering Talent Pool | Access to AI, robotics, and precision optics engineers at competitive rates enables rapid R&D iteration. |
| Advanced Manufacturing Infrastructure | Proximity to semiconductor fabs, PCB producers, and CNC machining hubs enables just-in-time delivery. |
| Regulatory Efficiency | NMPA clearance pathways integrated with ISO 13485 streamline domestic and export approvals. |
Carejoy leverages this ecosystem to deliver sub-15 µm accuracy scanners at 40% lower TCO than European counterparts—without compromising on open architecture or AI capabilities.
—
5. Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
Carejoy Digital impression systems are designed for seamless integration into modern digital workflows:
- Open Architecture: Native export to STL, PLY, OBJ—compatible with 3Shape, Exocad, DentalCAD, and open-source platforms.
- AI-Driven Scanning: Deep learning models reduce motion artifacts, auto-segment preparations, and predict undercut zones in real time.
- High-Precision Milling Sync: Direct interface with Carejoy’s 5-axis dry milling units for same-day restorations.
- Cloud-Connected: Over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates and remote diagnostics ensure continuous improvement.
—
6. Support & Service Ecosystem
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Available via web portal, mobile app, and live chat in English, Spanish, German, and Mandarin.
- Software Updates: Bi-weekly AI model enhancements and quarterly feature rollouts.
- On-Site Calibration Services: Global partner network offers annual recalibration with certificate of conformance.
Contact Support: [email protected]
—
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Digital Impression Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
