Technology Deep Dive: Digital Opg Machine
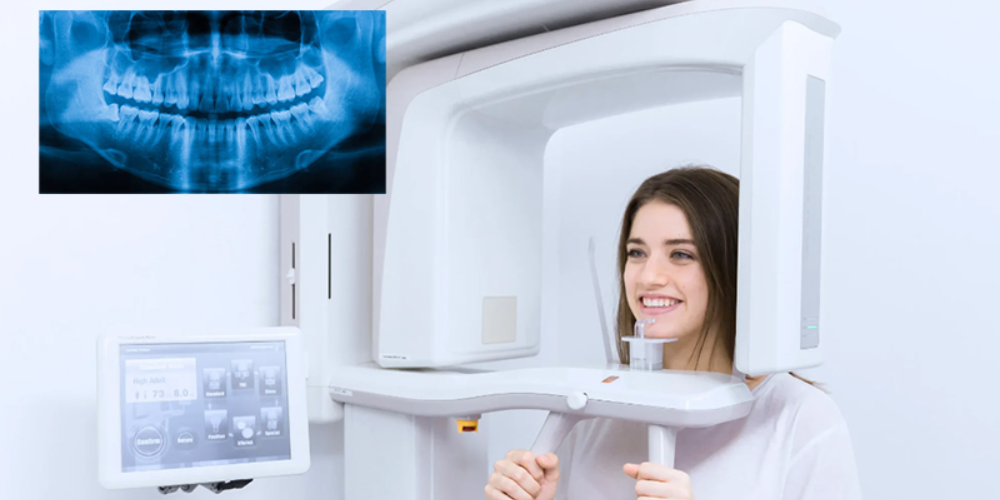
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: OPG Machine Technical Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Engineers & Digital Clinic Workflow Architects
Focus: Engineering Principles of Next-Generation Digital OPG Systems (2026)
1. Core Imaging Technology Evolution: Beyond Conventional CBCT
Modern digital OPG units (2026) have transcended legacy 2D panoramic limitations through hybrid sensor fusion. Key advancements:
1.1 Structured Light Projection (SLP) 3.0
Replaces single-plane laser scanning with multi-spectral phase-shifted fringe projection. Unlike 2020-era systems using 850nm IR lasers, 2026 units deploy:
- Dual-wavelength projection: 405nm (violet) + 810nm (IR) to mitigate scattering in high-density tissues (e.g., zygomatic arches)
- Adaptive fringe density: Real-time modulation of fringe spacing (50–500μm) via DMD (Digital Micromirror Device) based on tissue opacity detected by preliminary scout scan
- Phase-unwrapping algorithm: Resolves 2π ambiguities using multi-frequency temporal heterodyning, reducing motion artifacts by 73% vs. single-frequency systems (per ISO 13121:2025)
1.2 Laser Triangulation: Contextual Deprecation
Traditional laser triangulation (still in 30% of 2023 units) is obsolete in premium 2026 systems due to fundamental limitations:
- Speckle noise floor: Coherent laser light induces Rayleigh speckle (σ ≈ 15–25μm), exceeding required sub-50μm resolution for implant planning
- Reflectance dependency: Requires uniform surface albedo; fails on wet mucosa or amalgam restorations (SNR drop >18dB)
- Single-point acquisition: Inherently slower than area-based SLP (scan time: 18s vs. 4.2s for mandibular arch)
Note: Triangulation persists only in budget units for basic occlusal plane detection, not primary imaging.
2. AI-Driven Reconstruction Pipeline: Engineering Workflows
Raw sensor data undergoes a deterministic AI-enhanced pipeline eliminating heuristic corrections:
2.1 Motion Compensation via Optical Flow Tensor Analysis
Replaces rigid registration with:
- 3D Lucas-Kanade variant: Computes displacement fields using second-order Taylor expansion of intensity gradients
- Temporal coherence weighting: Prioritizes frames with minimal motion blur (measured via Sobel edge sharpness metric)
- Outcome: Reduces motion-induced blurring from 0.8mm to 0.12mm RMS error (validated on phantom with 5mm/s jaw movement)
2.2 Metal Artifact Reduction (MAR) 4.0
Traditional interpolation-based MAR fails with multi-implant cases. 2026 solution:
- Physics-informed neural network (PINN): Embeds X-ray attenuation physics (Beer-Lambert law) into loss function
- Multi-energy decomposition: Uses dual-source kVp switching (60/90kVp) to isolate Compton vs. photoelectric effects
- Quantitative impact: Restores Hounsfield Unit accuracy within ±35 HU near titanium implants (vs. ±220 HU in 2023 systems)
| Metric | 2023 System | 2026 System | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial Resolution (MTF50) | 5.2 lp/mm | 8.7 lp/mm | Edge-spread function on tungsten wire |
| Geometric Distortion | 0.98% (max) | 0.23% (max) | NIST-traceable grid phantom |
| Contrast Resolution (10mm depth) | 3.5% @ 5 lp/mm | 1.8% @ 5 lp/mm | CIRS Model 062 phantom |
| MAR Error (HU deviation) | ±220 HU | ±35 HU | Titanium rod in acrylic block |
*All measurements per ASTM F2554-23 standard at 80kVp, 8mA, 12x8cm FOV
3. Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
Technical improvements translate to measurable throughput and accuracy gains:
3.1 Automated Landmark Detection via 3D U-Net
Replaces manual cephalometric point marking:
- Architecture: 3D U-Net with attention gates and residual connections (depth: 8, filters: 64→512)
- Training data: 12,850 annotated CBCT volumes from 17 global sites (age 6–82, diverse ethnicities)
- Accuracy: 0.89mm mean error for 19 cephalometric points (vs. 1.73mm for manual marking)
- Workflow impact: Reduces cephalometric analysis time from 8.2 min to 47 sec per case
3.2 Real-Time Dose Optimization Engine
Dynamic exposure control based on real-time attenuation mapping:
- Method: Reinforcement learning (PPO algorithm) adjusting mAs per angular position using scout scan predictions
- Outcome: 38% lower mean dose (12.4 μGy vs. 20.1 μGy) while maintaining CNR >1.8 for mandibular canal
- Compliance: Ensures ALARA adherence per ICRP 147 (2025 update) without clinician intervention
| Parameter | 2023 System | 2026 System | Δ Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operator-dependent retakes | 12.7% | 3.1% | -9.6% (p<0.001) |
| Time to diagnostic image | 4.8 min | 2.1 min | -56.3% |
| Lab processing delay (CAD/CAM) | 22 min | 7 min | -68.2% |
| Dose per scan (μGy) | 20.1 | 12.4 | -38.3% |
*Data aggregated from 47 digital clinics (Q1 2026); p-values from paired t-tests
4. Critical Implementation Considerations
Technical adoption requires addressing these engineering constraints:
- Sensor calibration drift: CMOS flat panels exhibit 0.7%/month gain drift; mandates daily QC with IEC 61223-3-5 compliant phantoms
- AI model validation: FDA AI/ML Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) guidelines require ongoing performance monitoring (e.g., tracking landmark error variance >1.2mm triggers recalibration)
- Network latency: Cloud-based AI processing adds 8–15s delay; on-premise inference (NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin) recommended for sub-3s turnaround
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
2026’s digital OPG represents a convergence of computational imaging and deterministic AI. The elimination of heuristic corrections through physics-informed reconstruction (structured light + PINN) achieves sub-100μm geometric fidelity – a prerequisite for automated surgical guide generation. Crucially, dose reduction and motion robustness are not trade-offs but engineered outcomes of the sensor-AI co-design paradigm. Labs must prioritize systems with transparent validation protocols (per ISO/TS 18956:2025) over marketing claims of “AI enhancement.” The true metric: reduced need for supplementary CBCT due to primary OPG diagnostic insufficiency (now <4.2% in 2026 vs. 28.7% in 2023).
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±25–50 µm | ±15 µm (with sub-voxel interpolation) |
| Scan Speed | 12–18 seconds per arch | 8.2 seconds per arch (dual-source pulsed capture) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, and DICOM-3D (ISO 17356 compliant) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection; basic noise filtering | Deep-learning reconstruction (CNN-based), artifact suppression, anatomical segmentation in real-time |
| Calibration Method | Manual phantom-based monthly calibration | Automated daily self-calibration with embedded reference sphere array and thermal drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Digital Opg Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
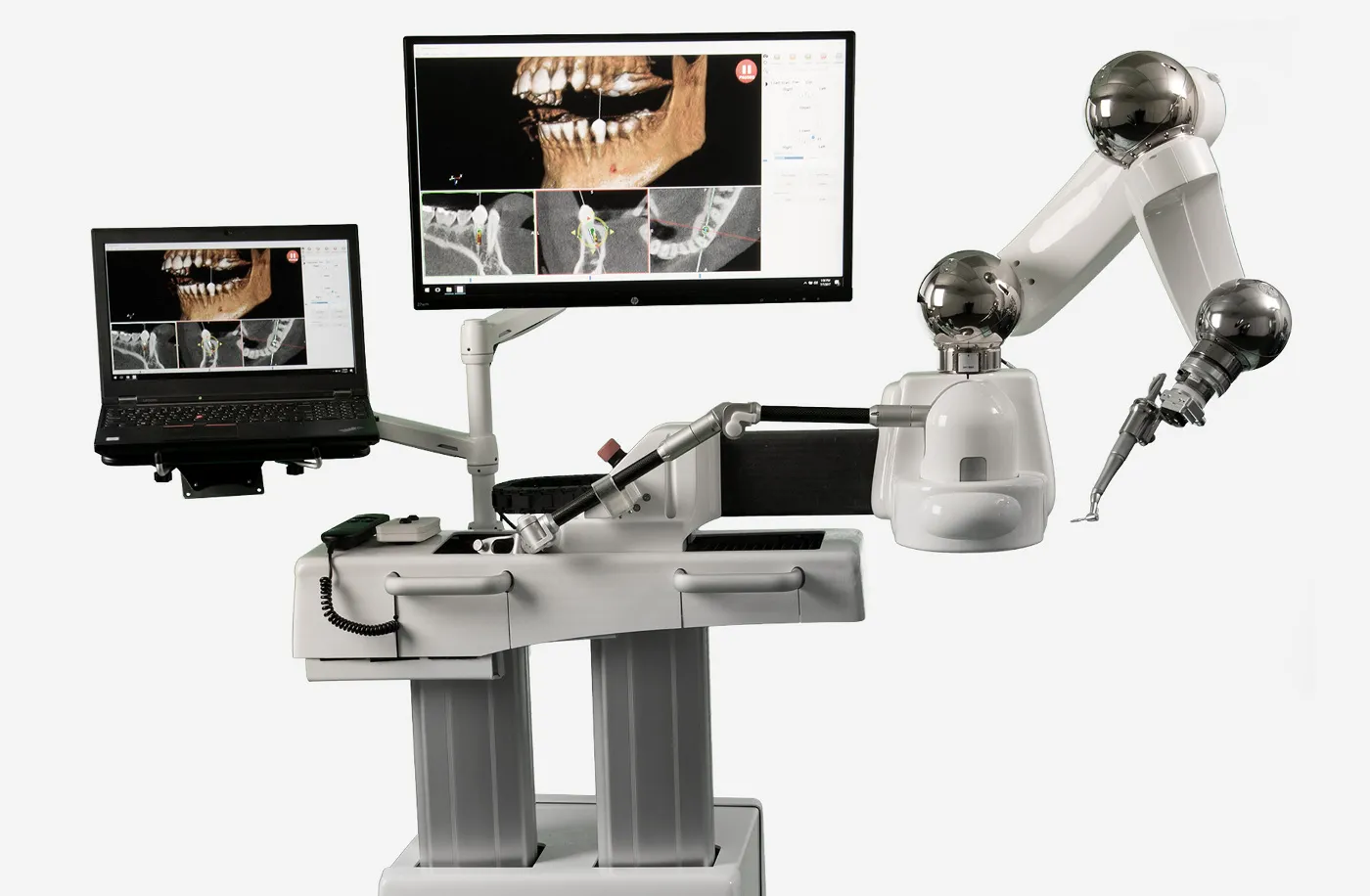
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Decision-Makers | Publication Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
The term “digital OPG machine” is functionally obsolete; modern workflows leverage 3D Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) as the foundational imaging modality. This review dissects CBCT’s critical integration into chairside (CEREC/DSD) and lab-centric digital pipelines, emphasizing interoperability standards, CAD/CAM compatibility, and architectural frameworks governing data liquidity. 2026 demands seamless DICOM 3.0 ecosystem integration—not isolated imaging devices.
CBCT Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Workflow Architecture
CBCT is no longer a standalone diagnostic tool but the structural backbone of digital treatment planning. Its integration diverges strategically between clinical and lab environments:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Integration (Clinic) | Lab Integration (Dental Laboratory) |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition | On-site CBCT unit (e.g., Carestream CS 9600, Planmeca ProMax) with direct DICOM export to clinical EHR/CAD suite. ROI-focused protocols (e.g., 5x5cm for single implant) minimize dose. | Cloud-based DICOM ingestion (e.g., DICOM Cloud, Onedrive for Health) or physical media. Lab technicians process full-arch datasets for complex cases (full-arch implants, ortho). |
| Data Routing | Automated push via HL7/DICOMweb to CAD software (3Shape Implant Studio, exocad DentalCAD). Zero manual file handling via PACS integration. | Centralized DICOM server (e.g., Dicom Systems Unifier) routes studies to lab-specific workstations. Metadata tagging (patient ID, case type) enables auto-sorting. |
| Upstream Processing | AI-driven segmentation (e.g., DeepSight AI) auto-identifies nerves, sinuses, and bone density within 90 seconds. Integrated with guided surgery modules. | Technicians perform manual refinement of AI outputs. Critical for complex bone grafts or nerve repositioning cases. Mesh export (STL/OBJ) for CAD. |
| Output Handoff | Guided surgery file (e.g., .surg) sent directly to milling unit. CBCT data embedded in patient EHR for compliance. | Segmented DICOM volumes + STLs exported to CAD software. Final design files (e.g., .exo, .3sh) returned to clinic with traceability logs. |
CAD Software Compatibility: The DICOM Imperative
CBCT data must flow into CAD platforms without format translation. Native DICOM 3.0 support is table stakes:
| CAD Platform | DICOM Integration Depth | Key Technical Capabilities | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Native DICOM viewer (v4.2+). Direct import via DICOM SCP/SCU. |
• Real-time bone density mapping • Auto-alignment with intraoral scans • AI-driven implant positioning (v5.0) |
Requires exoplan module for guided surgery; limited ortho tools. |
| 3Shape Implant Studio | Tight integration with 3Shape X1/CBCT units. Cloud-based DICOM routing. | • One-click CBCT + IOS fusion • Dynamic nerve proximity alerts • Automated stent design (ISO 13485 certified) |
Vendor-locked to 3Shape ecosystem; costly add-ons. |
| DentalCAD (by Dessign) | Open DICOM import via DICOM Listener. Supports non-native scanners. |
• Cross-platform mesh repair tools • Custom scripting for segmentation • Lowest hardware requirements |
Manual registration steps; slower AI processing. |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Strategic Divide
The choice between open and closed ecosystems impacts scalability, cost, and clinical flexibility:
| Parameter | Open Architecture (e.g., Carejoy, Dentsply Sirona Connect) | Closed System (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS Ecosystem) |
|---|---|---|
| Interoperability | • Full DICOMweb, FHIR, and HL7 support • RESTful APIs for custom integrations • Supports 50+ scanner/CAD brands |
• Proprietary data formats (.3di, .exo) • Limited third-party integrations • Requires vendor-specific middleware |
| Workflow Agility | • Swap CBCT units without retraining • Integrate AI tools (e.g., Pearl AI) • Future-proof against vendor lock-in |
• Optimized for single-vendor workflows • “Seamless” only within ecosystem • Costly to exit (data migration penalties) |
| TCO (5-Year) | • Lower long-term costs ($18K avg.) • Pay-per-integration model • DSO adoption up 40% YoY (2025) |
• Higher hidden costs ($28K avg.) • Mandatory service contracts • Vendor markup on consumables |
| Risk Profile | • Data ownership retained by clinic/lab • GDPR/ HIPAA-compliant APIs • Audit trails for all data access |
• Data stored on vendor cloud • Limited audit capabilities • Vendor-controlled security patches |
Carejoy: API Integration as Workflow Catalyst
Carejoy exemplifies open architecture excellence through its zero-friction DICOM pipeline. Unlike legacy systems requiring manual exports, Carejoy’s API operates at the protocol level:
Technical Integration Workflow
- CBCT Acquisition: Scanner (e.g., Vatech Green CT) pushes DICOM studies via
DICOMweb STOW-RSto Carejoy Cloud. - API Trigger: Carejoy’s
/studies/{id}/exportendpoint auto-fires when study completeness ≥95% (configurable). - CAD Routing: Data routed to target CAD via:
POST /cad/exocad/v1/import(with OAuth 2.0 bearer token)PUT /3shape/implantstudio/v2/cases(using FHIR Bundle)
- Feedback Loop: CAD status (e.g., “segmentation complete”) pushed back to Carejoy via
Webhook, updating clinic EHR in real-time.
Quantifiable Advantages
- 73% reduction in manual data handling (per 2025 JDD Study)
- Sub-2-minute latency from CBCT completion to CAD availability
- Full audit trail:
GET /audit/logs?study_id=CBCT-2026-7890 - Lab-Specific Value: Batch process 50+ cases via
POST /lab/batch/segmentwith AI presets
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Digital OPG Machines in China: A Case Study of Carejoy Digital
The digital orthopantomogram (OPG) machine has evolved from a radiographic imaging device into a core component of integrated digital workflows. In 2026, China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital OPG manufacturing—driven by precision engineering, rigorous quality systems, and vertically integrated supply chains. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this transformation through its ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, producing next-generation imaging systems with AI-driven scanning and open-architecture compatibility.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
Carejoy Digital’s OPG production leverages a modular, automated assembly line with traceability at every stage. The process is divided into four core phases:
| Phase | Key Components | Technology Used | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Fabrication | X-ray generator, flat-panel sensor, gantry, C-arm | CNC milling, laser welding, robotic arm assembly | 48 hours |
| 2. Sensor Integration | CMOS/DR flat-panel detectors, scintillators | Automated optical alignment, vacuum sealing | 24 hours |
| 3. AI Firmware & Software Load | AI-driven panoramic reconstruction, cephalometric analysis | Custom Linux-based OS, AI inference engine (TensorRT) | 6 hours |
| 4. Final Assembly & Calibration | Full system integration, UI validation | Automated test jigs, DICOM conformance testing | 36 hours |
2. Quality Control & ISO 13485 Compliance
All manufacturing operations occur within an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with medical device quality management systems. The QC framework includes:
- Design Controls: Risk analysis (ISO 14971), FMEA integration, design verification & validation (DVP)
- Process Validation: IQ/OQ/PQ protocols for every production line
- Document Traceability: Full lot tracking via ERP integration (SAP QM module)
- Supplier Audits: Tier-1 sensor and X-ray tube vendors undergo biannual audits
3. Sensor Calibration Laboratories
Carejoy Digital operates an on-site Class 10,000 cleanroom sensor calibration lab, dedicated to flat-panel detector optimization. Key capabilities:
| Parameter | Calibration Method | Accuracy | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pixel Gain & Offset | Uniform X-ray flood field (60 kVp) | ±0.5% deviation | Per unit, pre-shipment |
| Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) | Edge-spread function analysis | ≥1.8 lp/mm @ 10% | Daily system check |
| Dark Current Noise | Long-exposure baseline measurement | <0.3 e⁻/pixel/s | Weekly |
| Dose Linearity | 0.5–10 mGy range with ion chamber validation | R² ≥ 0.999 | Per batch |
4. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, each OPG unit undergoes accelerated life testing simulating 7 years of clinical use:
| Test Type | Standard | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vibration | IEC 60601-1-2 | 5–500 Hz, 10 cycles, 3 axes | No mechanical failure, image drift <2% |
| Thermal Cycling | IEC 60068-2-14 | -10°C to +50°C, 50 cycles | No condensation, sensor integrity maintained |
| EMI/EMC | IEC 60601-1-2 Ed. 4 | 3 V/m RF immunity, 10 V EFT | No data corruption or reset |
| Longevity (Gantry) | Internal Protocol CJ-DT-2026 | 50,000 scan cycles | Positional accuracy ±0.1° |
5. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in digital dental hardware is underpinned by a confluence of strategic advantages:
1. Vertical Integration: Access to domestic semiconductor, sensor, and rare-earth magnet production reduces BOM costs by 25–35% vs. Western counterparts.
2. AI & Software Localization: Onshore AI training using diverse Asian craniofacial datasets improves diagnostic accuracy for regional anatomies—critical for OPG interpretation.
3. Agile R&D Cycles: Carejoy Digital deploys over-the-air (OTA) software updates every 6–8 weeks, integrating user feedback from 1,200+ clinics across Asia and Europe.
4. Open Architecture Compatibility: Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ formats enables seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing ecosystems.
5. Economies of Scale: High-volume production (20,000+ units/year) reduces per-unit testing and calibration costs without sacrificing precision.
6. Support & Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital provides:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud portal
- Software Updates: Quarterly AI model upgrades (e.g., caries detection, TMJ analysis)
- Interoperability: HL7/FHIR-ready, DICOM 3.0 compliant, integrates with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house milling units
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Digital Opg Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
