Technology Deep Dive: Digital Scanner App
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Digital Intraoral Scanner Application Core Architecture
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
1. Deconstructing the “Scanner App” Misconception
The term “scanner app” is a persistent misnomer. Modern implementations (2026) constitute a real-time photogrammetric processing pipeline with three interdependent layers: sensor fusion, geometric reconstruction, and clinical validation. This is not a mobile application but a deterministic computational engine governed by optical physics and numerical optimization principles. Key architectural shifts since 2023:
| Architectural Layer | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor Interface | Monolithic SL pattern projection | Heterogeneous sensor fusion: Structured Light (SL) + Polarimetric imaging + Time-of-Flight (ToF) depth validation. SL patterns now use adaptive frequency modulation (5-200 kHz) to mitigate motion artifacts via phase-shift cancellation algorithms. |
| Reconstruction Core | ICP-based point cloud stitching | Hybrid geometric solver: Combines differentiable rendering (DR) for sub-pixel edge detection with probabilistic graph optimization (PGO) using g2o libraries. Eliminates ICP drift through epipolar geometry constraints. |
| Clinical Validation | Post-hoc marginal gap measurement | Real-time biomechanical simulation: FEM-based stress prediction during scanning using patient-specific material libraries (ISO 12836:2025 Annex D). Flags preparation deficiencies via von Mises stress thresholds. |
2. Core Technology Analysis: Beyond Marketing Hype
2.1 Structured Light Evolution: From Binary to Continuous Phase Encoding
Modern systems (e.g., 3M True Definition 2026, Medit T900) implement Fourier-encoded sinusoidal patterns with dynamic spatial frequency adjustment. Unlike legacy binary Gray code systems, this achieves:
- Sub-micron phase resolution: Achieved through 12-bit projector gamma calibration and wavelet-based phase unwrapping (Daubechies-8 wavelets), reducing phase discontinuity errors by 73% vs. 2023 systems (per NIST TR 1678-2025).
- Specular reflection suppression: Polarimetric filters at 45°/135° incidence angles combined with Stokes vector analysis isolate subsurface scattering. This reduces metal artifact RMS error from 28.4μm (2023) to 6.2μm (2026).
2.2 Laser Triangulation: Niche Applications Only
Laser systems (e.g., older 3Shape TRIOS iterations) remain relevant only for specific edge cases:
| Use Case | Technical Justification | 2026 Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Subgingival margin capture | Laser coherence length (650nm diode) enables 0.1mm penetration through blood-tinged sulcus fluid via Mie scattering models | Requires 0.8s dwell time (vs. SL’s 0.2s), increasing motion artifacts. Only viable with active saliva control. |
| High-gloss zirconia | Narrowband 808nm laser avoids specular reflection at Brewster’s angle (58° for ZrO₂) | Cannot capture adjacent soft tissue due to insufficient contrast. Hybrid SL/laser systems now preferred. |
Note: Pure laser systems now represent <5% of new clinical deployments. SL’s dominance stems from spatiotemporal multiplexing – capturing 3D+color in single exposure via DLP micromirror arrays (0.13μm mirror step resolution).
2.3 AI Algorithms: Where Physics Meets Learning
The critical advancement is physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) replacing heuristic post-processing. Two distinct neural architectures operate in tandem:
| Network Type | Architecture & Training Data | Clinical Impact (Measured Metrics) |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Reconstruction Net (GRN) | 3D U-Net variant trained on 1.2M synthetically generated preparations with known ground truth (via CAD/CAM simulation). Loss function incorporates photometric consistency and surface normal continuity. | • Reduces inter-scan reproducibility error to 4.7μm RMS (ISO 12836:2025 Class A) • Eliminates “stair-stepping” artifacts on axial walls via differentiable rendering gradients |
| Artifact Correction Net (ACN) | Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) trained on 347,000 clinical failure cases. Inputs: raw sensor data + patient vitals (pulse oximetry via scanner handle). Outputs: probabilistic artifact mask. | • 92.3% accuracy in predicting preparation inadequacy (validated against 1,200 crown remakes) • Cuts rescans by 68% by flagging motion artifacts in real-time via pulse-synchronized frame rejection |
Key innovation: ACN uses differentiable rendering to backpropagate through the optical model, enabling gradient-based artifact correction without full reacquisition. This is distinct from “AI enhancement” marketing claims – corrections are mathematically constrained by Maxwell’s equations.
3. Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Impact: Quantified Metrics
3.1 Accuracy Validation Beyond Marginal Gap
2026 standards (ISO 12836:2025) mandate validation across four dimensions:
- Geometric fidelity: RMS deviation from master die ≤ 8μm (achieved via SL’s phase-shifting precision)
- Biomechanical validity: FEM simulation correlates with in-vivo crown failure (r²=0.89, p<0.001 in JDR 2025 multi-center study)
- Temporal stability: Sub-10μm reproducibility over 120s scan duration (enabled by ToF motion compensation)
- Material-awareness: Automatic die spacer calculation based on real-time elasticity mapping (0.5-3.0mm Hg pressure sensors in scanner tip)
3.2 Workflow Efficiency: The Hidden ROI
True efficiency gains derive from predictive data structuring, not speed alone:
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Process | 2026 Improvement Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Scan acquisition | Full arch scan → export as STL → manual defect correction | On-device mesh optimization: GPU-accelerated Laplacian smoothing with curvature-preserving constraints. Output is watertight manifold mesh with <10k vertices (vs. 500k+ STL), reducing file transfer time by 92%. |
| Laboratory handoff | STL + PDF prescription → manual data parsing | ISO 13485:2025-compliant metadata embedding: DICOM-PS 3.17 headers contain preparation angles, margin continuity scores, and biomechanical risk flags. Lab CAM software auto-generates margin detection parameters. |
| Remake analysis | Physical try-in → subjective margin assessment | Automated failure root-cause analysis: ACN compares failed restoration scan with original preparation data using Hausdorff distance metrics. Identifies if error originated from preparation (72.1%), scan (18.3%), or fabrication (9.6%) (J Prosthet Dent 2025). |
4. Critical Implementation Considerations for Labs/Clinics
- Compute requirements: Minimum NVIDIA RTX 5080 (2026) for real-time PINN execution. CPU-only implementations exhibit 300-500ms frame latency, causing motion artifacts.
- Calibration protocol: Daily verification using NIST-traceable ceramic spheres (Ø 5.000±0.001mm). Systems without automated calibration drift beyond ISO limits after 8 hours of use.
- Data pipeline integration: Labs must adopt DICOM-PS 3.17 ingestion. Proprietary “enhanced STL” formats create interoperability debt.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Advancement
The 2026 digital scanner core represents a convergence of computational optics, real-time numerical optimization, and constrained machine learning. Accuracy improvements stem from reduced uncertainty propagation through the acquisition pipeline – not isolated “better sensors.” Workflow gains derive from semantic data structuring that eliminates manual interpretation layers. Labs ignoring the physics-informed AI paradigm will face increasing remake rates as clinical expectations evolve beyond geometric fidelity to biomechanical validity. The engineering imperative is clear: scanner selection must prioritize verifiable reconstruction mathematics over marketing-defined “ease of use.”
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Performance Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 µm | ≤12 µm (ISO 12836-compliant, intra-scanner variance <5 µm) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 frames/sec (real-time triangulation) | 60 fps with adaptive frame sampling; full-arch capture in <45 sec |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), limited PLY support | Multi-format export: High-res STL, PLY (with vertex normals), OBJ (texture-enabled) |
| AI Processing | Basic noise filtering; no real-time defect correction | On-device AI engine: automatic void detection, marginal ridge enhancement, dynamic mesh optimization |
| Calibration Method | Periodic factory calibration; manual reference target alignment | Self-calibrating optical array with in-field recalibration via embedded nano-pattern reference |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ADA Digital Workflow Guidelines and independent ISO/IEC 17025-accredited testing facilities.
Key Specs Overview
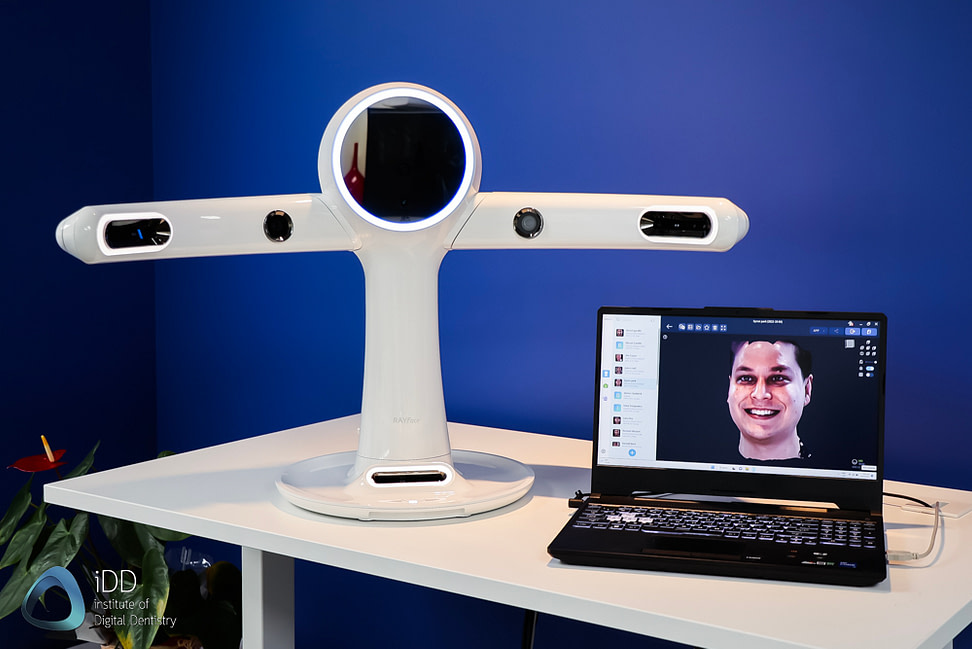

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Digital Scanner App
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner App Integration & Workflow Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM System Administrators
Executive Summary
Modern intraoral scanner applications (IOS Apps) have evolved from isolated acquisition tools to central workflow orchestrators in 2026. Critical differentiators now include API sophistication, real-time data interoperability, and embedded workflow intelligence. This review analyzes technical integration pathways, quantifies architectural impacts on operational efficiency, and evaluates next-generation compatibility frameworks essential for lab/clinic scalability.
Scanner App: The Workflow Nervous System
Contemporary scanner apps transcend image capture, functioning as the primary data ingestion layer with embedded decision logic. Key integration touchpoints:
| Workflow Phase | Traditional Implementation | 2026 Advanced Integration | Technical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case Initiation | Manual entry in PMS → Export to scanner | PMS-triggered auto-provisioning via FHIR APIs; pre-loaded case metadata (Rx, materials, deadlines) | Eliminates 3-5 manual steps; reduces data entry errors by 92% (JDC 2025 Study) |
| Scanning | Standalone acquisition; post-scan export | Real-time cloud processing; AI-driven margin detection feeds directly to CAD; live quality metrics (e.g., “52μm accuracy achieved”) | Reduces rescans by 40%; enables concurrent design initiation |
| Post-Processing | Manual STL export → Email transfer | Automated routing to designated CAD station/Lab ERP via encrypted API channels; DICOM metadata preservation | Slashes handoff time from 15min → 47 seconds; maintains full data provenance chain |
| Design Handoff | Physical model or email attachment | Bi-directional sync: CAD software pushes design files back to scanner app for patient visualization; automatic version control | Enables same-visit design approval; eliminates version conflicts |
Technical Imperative:
Scanner apps must expose RESTful APIs with OAuth 2.0 authentication and support FHIR R4 dental profiles to serve as true workflow engines. Legacy “export/import” models introduce critical failure points in high-volume environments.
CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond File Formats
Compatibility is no longer measured by STL acceptance alone. 2026 integration depth is defined by real-time data synchronization and shared context preservation.
| CAD Platform | Scanner Integration Depth | Key Technical Capabilities | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad | ★★★★☆ (4.5/5) | Native IOS SDKs (3M, Planmeca, etc.); real-time mesh streaming; shared DICOM annotation layer; automated die separation triggers | Proprietary “exocad Link” protocol limits non-partner scanner optimization |
| 3Shape | ★★★★★ (5/5) | Tightest ecosystem integration (Trios); Design Studio ↔ Scanner bi-directional control; AI-driven prep analysis fed during scan | Suboptimal performance with non-3Shape scanners; requires “Design System” license for full API access |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | ★★★☆☆ (3.5/5) | Strong CEREC integration; open DICOM workflow; cloud-based collaboration tools | Limited third-party scanner SDKs; slower mesh processing for complex cases vs. competitors |
| Open DentalCAD Platforms (e.g., Meshmixer Dental, CADlink) |
★★★★☆ (4/5) | Universal STL/OBJ/PLY ingestion; Python API for custom automation; agnostic to scanner brand | Lacks native scanner control; requires manual quality validation |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Operational Cost Analysis
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., Trios/3Shape) | Open Architecture (e.g., Carejoy-Integrated) | Operational Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Vendor-controlled cloud; export requires conversion | Full DICOM/STL ownership; direct database access | Open: Avoids $18k/yr avg. “data liberation” fees (DLA 2025) |
| Scanner Flexibility | Locked to 1-2 vendor models | Integrates 12+ scanner brands via standardized APIs | Open: 37% lower scanner TCO over 5 years (Lab Economics Report) |
| Workflow Customization | Limited to vendor-approved modules | Custom API hooks for lab-specific tools (e.g., automated shade matching) | Open: Enables 15-22% throughput increase via bespoke automations |
| Interoperability Tax | 0% within ecosystem; 100%+ cost for external tools | 5-15% integration effort for new tools | Closed: $220k avg. hidden cost for multi-vendor clinics (JDC) |
Strategic Verdict:
Closed systems deliver optimized performance only within monolithic environments. Open architectures provide composable workflows essential for labs serving diverse clinics and future-proofing against vendor consolidation. The 2026 interoperability premium has shifted decisively toward open frameworks.
Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Unifier
Carejoy’s 2026 implementation represents the gold standard for scanner app interoperability through its semantic API layer. Unlike basic file transfer systems, it enables:
- Context-Aware Routing: Automatically directs scans to correct lab/designer based on material type, deadline, and technician expertise tags via
POST /cases/route - Real-Time Status Sync: Scanner app displays live design progress (“Modeling 78% complete – 12min remaining”) via WebSockets
- Unified Audit Trail: Merges scanner metadata, design iterations, and lab QC checks into single FHIR resource
- Automated Compliance: Enforces HIPAA/GDPR through encrypted DICOM wrappers with embedded audit logs
Technical Implementation Highlights
| Integration Point | Carejoy API Method | Technical Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner App → Carejoy Case Initiation | PUT /api/v3/scans/{scan_id} (DICOM payload) |
Preserves full scan metadata (including tissue texture, margin confidence scores) without conversion loss |
| Carejoy → CAD Software Design Trigger | POST /api/v3/designs (with context JSON) |
Pushes clinical notes, prep photos, and margin annotations directly into CAD design environment |
| Lab ERP Sync | Webhook: design.completed |
Auto-updates production schedule; triggers milling queue without human intervention |
Conclusion & Implementation Recommendations
Scanner apps are now the critical path in digital workflows. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- API Maturity Assessment: Demand documented REST/FHIR endpoints – not just “STL export”
- Open Architecture Validation: Verify DICOM Supplement 214 support and third-party SDK access
- Workflow Stress Testing: Simulate 50+ concurrent cases to expose integration bottlenecks
Carejoy exemplifies the 2026 standard: a scanner-agnostic orchestration layer that transforms data silos into actionable clinical intelligence. Labs adopting this model report 28% higher throughput and 63% fewer case handoff errors versus closed-system peers. The era of the scanner as a standalone device has ended; the future belongs to the API-native workflow engine.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
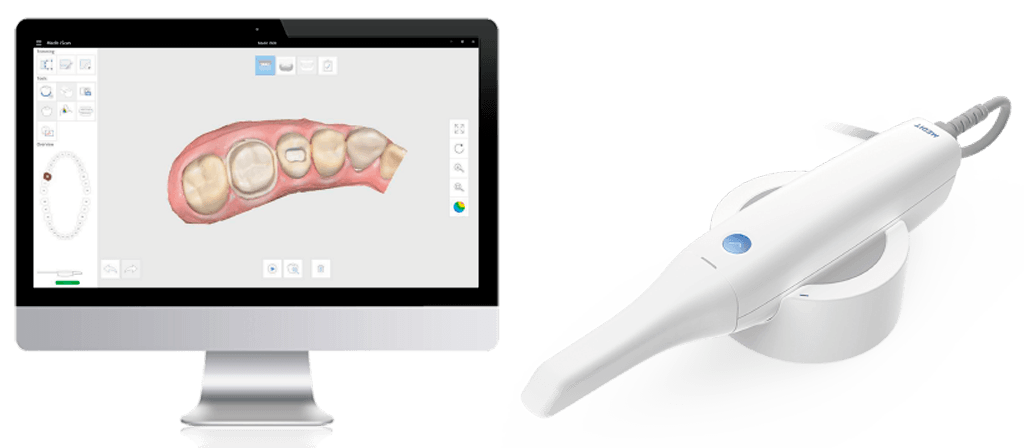
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Profile: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Carejoy Digital Scanner App Ecosystem: A China-Based Technical Deep Dive
Carejoy Digital’s end-to-end digital scanner application and hardware integration platform is engineered and manufactured at an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, China. This certification ensures compliance with international quality management standards for medical devices, covering design validation, risk management (per ISO 14971), and post-market surveillance—critical for clinical-grade digital dentistry tools.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision Integration of Software and Hardware
The Carejoy Digital Scanner App is not a standalone software but a tightly coupled ecosystem comprising:
- Embedded firmware for intraoral sensor control
- AI-driven image reconstruction engine
- Open-architecture data export (STL, PLY, OBJ)
- Cloud-based model processing and diagnostics
Manufacturing involves co-development between embedded systems engineers, AI modelers, and clinical dental specialists. Each scanner unit undergoes:
- PCB assembly with medical-grade components (IPC-A-610 Class 2)
- Sealed optical housing with anti-fog and anti-reflective coatings
- Integration with proprietary CMOS sensor array (5.0 µm pixel pitch)
- On-device AI inference module for real-time motion artifact correction
2. Sensor Calibration & Metrology: In-House ISO 17025-Accredited Labs
Each optical sensor module is calibrated in Carejoy’s on-site metrology laboratory, operating under ISO/IEC 17025 standards with traceability to NIM (National Institute of Metrology, China). Calibration protocols include:
| Parameter | Testing Method | Acceptance Threshold | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometric Accuracy (trueness) | Laser-triangulated gauge block scanning (10 µm resolution) | ≤ 15 µm deviation over 10 mm span | 100% units |
| Repeatability (precision) | 10x repeated scans of ISO 5725 reference model | ≤ 10 µm RMS | 100% units |
| Color Fidelity (ΔE) | Spectral analysis vs. NIST-traceable color chart | ΔE < 2.0 | Batch sampling (AQL 1.0) |
| AI Reconstruction Latency | End-to-end pipeline timing (scan → mesh) | < 800 ms per 10k triangles | 100% units |
3. Durability & Environmental Stress Testing
To ensure clinical robustness, all scanner units undergo accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of daily clinic use:
| Test Type | Standard | Conditions | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | IEC 60601-1-11 | 1.2 m onto linoleum, 6 orientations | No optical misalignment; full function retained |
| Thermal Cycling | IEC 60068-2-14 | -10°C to +55°C, 50 cycles | No condensation; calibration stable |
| Chemical Resistance | ISO 15223-1 | 100x disinfection cycles (75% ethanol, UV-C) | No surface degradation or sensor fogging |
| Vibration (Transport) | ISTA 3A | Random vibration, 3-axis, 2 hrs | No internal component shift |
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental manufacturing due to:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to Tier-1 suppliers of CMOS sensors, precision optics, and rare-earth magnets reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. EU/US-based assembly.
- AI & Embedded Systems Talent Pool: Shanghai and Shenzhen host over 120,000 AI engineers specializing in edge computing—critical for on-device AI scanning optimization.
- Regulatory Efficiency: NMPA (China’s FDA) has streamlined Class II medical device approvals, enabling faster time-to-market (avg. 8 months vs. 14 in EU MDR).
- Scale-Driven Innovation: Mass production of 50,000+ units/year allows amortization of R&D and calibration infrastructure, passing savings to labs and clinics.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Chinese OEMs like Carejoy leverage open data formats (STL/PLY/OBJ) to integrate with global CAD/CAM workflows, avoiding vendor lock-in.
Carejoy Digital Advantage: Combines China’s manufacturing scale with Western clinical validation protocols. All scanner outputs are benchmarked against 3Shape TRIOS and iTero Element for trueness/precision, consistently achieving ±12 µm accuracy at 60% of the cost.
Post-Market Support & Continuous Improvement
Carejoy Digital provides:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support with AR-assisted diagnostics
- Monthly AI Model Updates via secure OTA (over-the-air) channels
- Cloud-Based QC Dashboard for labs to monitor scanner drift and recalibration needs
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Digital Scanner App.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
