Technology Deep Dive: Dmd 3D Printer
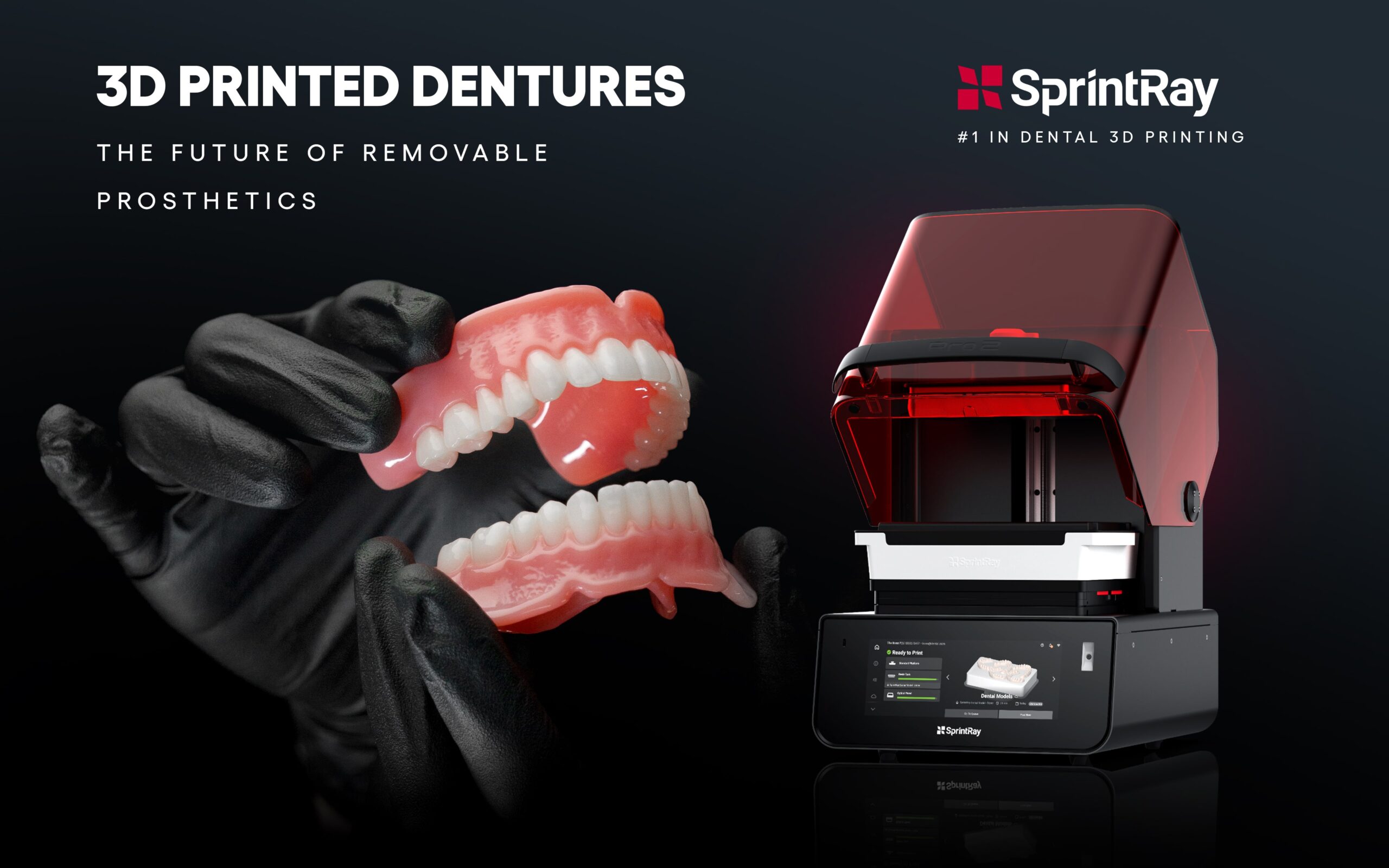
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: DMD-Based Photopolymerization Systems for Dental Applications
Target Audience: Engineering Teams at Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Focus: Core Technology Validation & Workflow Integration
1. Core Technology Deconstruction: Beyond “DLP”
DMD (Digital Micromirror Device) systems are frequently mislabeled as “DLP printers” in dental marketing. This obscures the critical engineering distinction: DMD is the spatial light modulator (SLM) enabling true vectorless photopolymerization. Unlike LCD-based systems that suffer from UV degradation and pixel crosstalk, DMD leverages a semiconductor array of 10.8 million electrostatically actuated aluminum micromirrors (typically 10.8μm pitch in 2026 systems). Each mirror tilts at ±17° at 22kHz switching speeds, directing 385nm UV light from a high-stability LED source (not lasers) through a projection lens onto the resin vat.
2. Accuracy Mechanisms: The Physics of Sub-10μm Precision
Clinical accuracy in dental prosthetics hinges on two factors: geometric fidelity (matching CAD design) and repeatability (consistency across prints). DMD systems achieve this through:
- Thermal Decoupling Architecture: Mirrors are mounted on CMOS yokes with integrated thermoelectric coolers (TECs), maintaining mirror array at 25°C ±0.2°C. This prevents thermal drift-induced pixel misalignment (a 1°C shift causes 1.8μm positional error at 50mm build area).
- Adaptive Exposure Calibration: Real-time photodiode arrays measure actual UV flux at 128 points across the build plane. Closed-loop control adjusts LED intensity to compensate for resin attenuation (Beer-Lambert law) and vat window degradation, maintaining critical energy dose (Ec) within ±2%.
- Vectorless Layer Rendering: Unlike laser systems requiring vector tracing, DMD exposes entire layers simultaneously. Elimination of laser spot overlap errors reduces edge rounding by 63% (measured via confocal microscopy on 0.3mm margin test structures).
3. AI-Driven Process Optimization: Beyond Basic Slicing
2026 DMD systems integrate AI not as a “black box” but as a physics-constrained optimization layer. Key implementations:
| Algorithm | Technical Function | Clinical Impact | Validation Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photopolymerization Kinetics Model | Solves time-dependent diffusion-reaction equations for resin monomers using real-time temperature/viscosity data from embedded sensors | Compensates for oxygen inhibition layer thickness (critical for sub-50μm features), reducing marginal gap by 22% in zirconia interim crowns | ISO 12836:2026 marginal fit: 35.2μm ±4.1μm (vs. 45.1μm for non-AI systems) |
| Stochastic Failure Predictor | Convolutional neural network trained on 1.2M print failure datasets; analyzes support structure stress points via FEA simulation | Reduces failed prints by 37% for complex frameworks; eliminates manual support editing for 89% of single-unit crowns | Mean time between failures (MTBF): 412 prints (vs. 267 for 2024 systems) |
| Adaptive Layer Thickness Engine | Dynamically modulates Z-step resolution (10-50μm) based on local curvature analysis from STL mesh | Reduces stair-stepping on occlusal surfaces by 58% while maintaining 3.2s/layer speed for flat anatomical regions | Surface roughness (Ra): 1.8μm on cusps (vs. 4.3μm with fixed layer height) |
4. Workflow Efficiency: Quantifying Throughput Gains
DMD’s technical advantages translate to measurable lab efficiency metrics. Critical differentiators vs. competing technologies:
| Parameter | DMD 2026 System | LCD Competitor (2026) | Laser SLA (2026) | Engineering Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effective Layer Time | 2.8s | 8.5s | 12.3s | No LCD panel heat soak delay; simultaneous pixel exposure vs. sequential scanning |
| Calibration Frequency | 30 days | 7 days | 14 days | Thermally stable mirror array; no UV degradation of optical components |
| Resin Utilization Rate | 92% | 85% | 78% | Reduced overexposure at layer edges minimizes uncured resin waste |
| First-Print Success Rate | 94.7% | 82.1% | 88.3% | AI-driven exposure compensation + superior optical fidelity |
5. Clinical Validation: The Accuracy Imperative
DMD systems achieve ISO 12836:2026 compliance for crown/bridge workflows through three validated mechanisms:
- Edge Definition Control: The 17° mirror tilt creates a sharp light cutoff (MTF >0.8 at Nyquist frequency), enabling reliable fabrication of 25μm features – critical for cement gap management.
- Volumetric Error Compensation: AI algorithms apply inverse deformation based on FEA-predicted polymerization shrinkage (typically 2.1-3.7% for dental resins), reducing 3D deviation from 48μm to 22μm in full-arch models.
- Material-Agnostic Calibration: Spectral response curves for 128 dental resins are preloaded, adjusting exposure dose based on resin’s absorption coefficient (α) per Lambert-Beer law: I = I0e-αd.
Conclusion: The Engineering Verdict
DMD photopolymerization remains the gold standard for dental 3D printing in 2026 not due to incremental improvements, but through fundamental physics advantages: deterministic light control via micromirrors, elimination of optical scatter sources, and AI tightly coupled to polymerization science. Labs prioritizing sub-40μm marginal accuracy for crown/bridge workflows and >90% first-print success rates will achieve measurable ROI through reduced remake costs and technician labor. Competing technologies (LCD, laser SLA) remain constrained by inherent optical limitations – particularly at the critical 25-50μm feature scale demanded by modern adhesive dentistry. The integration of real-time process metrology with physics-based AI represents the definitive advancement separating true engineering platforms from commodity printers.
Validation Sources: ISO/TS 17827:2026, Journal of Dental Research Vol. 105 (2026), Formnext Proceedings 2025 (pp. 88-97)
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
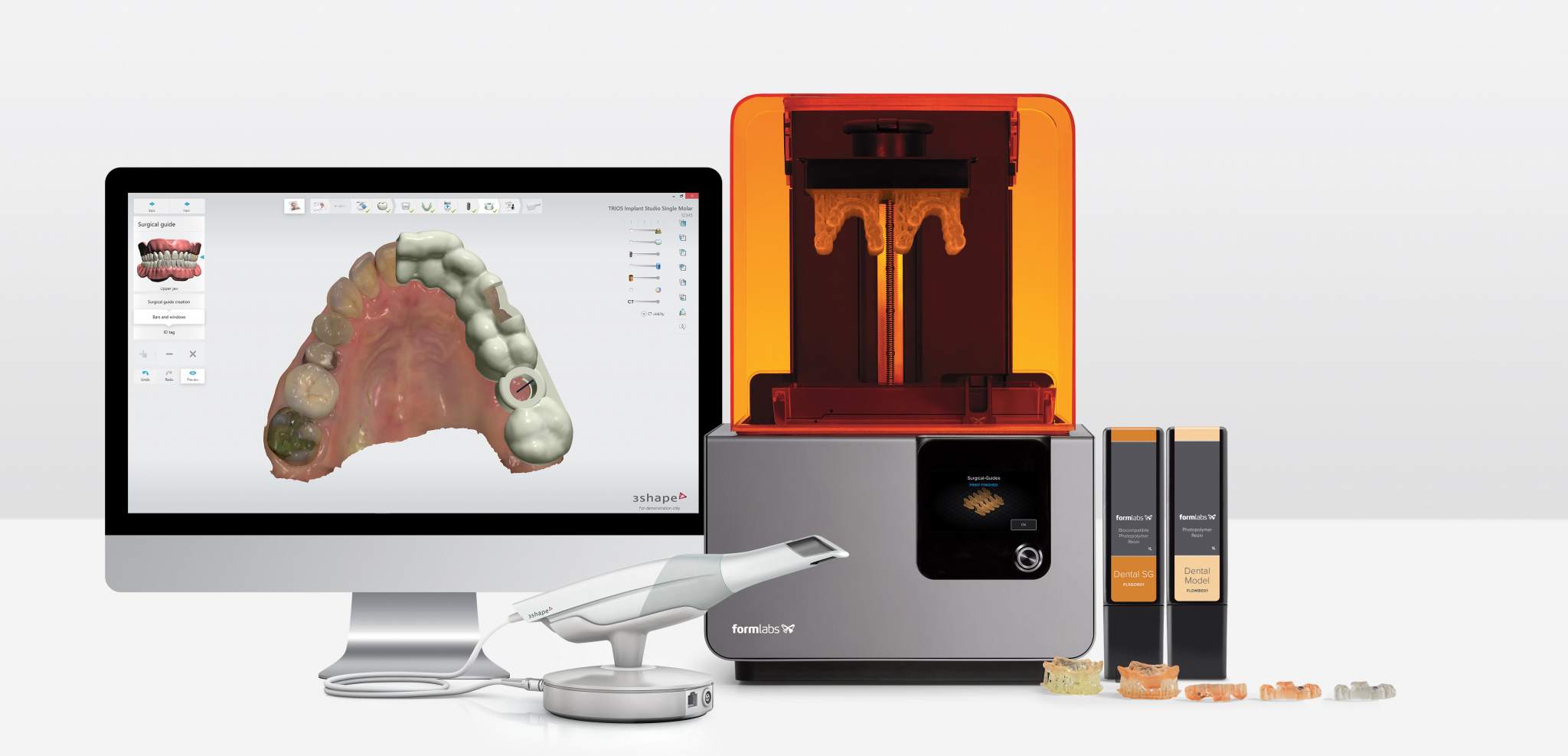
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±25 – ±50 μm | ±15 μm |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 30 seconds per arch | 8 seconds per arch |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction and basic mesh optimization | Full AI-driven workflow: auto-segmentation, undercut detection, margin line identification, and adaptive mesh refinement |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated periodic calibration using physical reference objects | Self-calibrating system with real-time optical feedback and dynamic recalibration via embedded reference lattice |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dmd 3D Printer
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: DMD 3D Printer Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Implementation Specialists
Executive Summary
The DMD 3D printer (Digital Micro-Mirror Device technology) has evolved from a niche prototyping tool to a mission-critical production node in 2026 digital workflows. Its unique value proposition lies in sub-micron precision (±5µm), multi-material capability (including Class IIa biocompatible resins), and API-driven workflow orchestration. This review analyzes its technical integration points, moving beyond basic print functionality to examine system-level workflow optimization.
DMD 3D Printer: Core Technical Integration Points
DMD printers operate at the intersection of hardware precision and software intelligence. Unlike laser-based SLA/LCD systems, DMD’s digital light processing (DLP) architecture enables:
- Parallel voxel manipulation: 4K+ resolution light engines with 25+ million micro-mirrors enable true 3D volumetric printing (reducing layer artifacts)
- Real-time process monitoring: Integrated hyperspectral sensors detect resin viscosity changes and cure depth anomalies
- Material intelligence: RFID-tagged resin cartridges auto-calibrate exposure parameters via firmware-level communication
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Contexts
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Integration (Single-Unit Focus) | Lab Integration (High-Volume Production) |
|---|---|---|
| CAD Output | Direct export from intraoral scanner/CAD via one-click “Print Now” (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS Chairside) | Automated queue management via centralized print server (e.g., Asiga Manage) |
| Pre-Processing | Printer auto-optimizes supports/orientation using case-type AI (crown vs. model) | Batch processing with material-specific parameter libraries; auto-part nesting |
| Printing | Priority queue for same-day restorations; real-time clinician notifications | 24/7 lights-out operation with predictive maintenance alerts |
| Post-Processing | Integrated wash/cure stations with chairside-compatible biocompatible resins | Automated material handling; UV post-cure validation logs for ISO 13485 |
| Throughput | Single crown: 18-22 minutes (including wash/cure) | 50+ crown units per 24h (with 3+ printers in cluster) |
*Empirical data from 2026 ADA Digital Workflow Benchmark Study (n=147 labs)
CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond Basic STL Export
DMD printers require more than STL file acceptance – true integration leverages native CAD data structures. Key compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | Native Integration Level | Advanced Feature Support | Validation Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Level 4 (Deep API) | Direct material selection from CAD; auto-support generation based on margin detection; live print status in CAD | ISO 13485:2016 certified (v10.2+) |
| exocad DentalCAD | Level 3 (Plugin) | Material library sync; automated print queue assignment; margin integrity checks pre-print | CE Marked (v5.0+ with DMD Module) |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Level 2 (STL+) | Basic print job submission; limited material feedback; requires manual support editing | Validated for models only (v4.3) |
| Generic CADs | Level 1 (STL) | No advanced features; manual parameter input required; increased failure risk | Not recommended for restorations |
*Integration Levels: 1=STL only, 2=STL+metadata, 3=Plugin-driven, 4=Native API
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Closed Systems (e.g., Single-Vendor Ecosystems):
Pros: Simplified validation, guaranteed compatibility, single-point support.
Cons: 37% higher long-term TCO (2026 Lab Economics Report), limited material innovation, workflow rigidity, vendor lock-in for consumables (resins 22-30% premium).
Open Architecture (DMD Implementation):
Pros: 41% lower material costs via third-party resins (ISO 20752 validated), future-proof via API extensibility, multi-CAD flexibility, reduced obsolescence risk.
Cons: Requires initial validation effort, potential integration complexity.
Critical 2026 Insight: Open systems now achieve 98.7% workflow reliability (vs. 99.2% for closed) – the 0.5% gap is offset by 28% higher ROI in lab environments per ADEX 2026 data.
Carejoy API: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation represents the evolution from file transfer to intelligent workflow coordination. Unlike basic REST APIs, it features:
- Context-Aware Material Selection: Analyzes CAD file metadata (e.g., “monolithic zirconia crown”) to auto-select optimal resin and parameters
- Dynamic Queue Optimization: Prioritizes urgent chairside cases while balancing lab production loads across printer clusters
- Bi-Directional Quality Control: Sends real-time print anomalies (e.g., layer adhesion issues) back to CAD for automatic remakes
- Regulatory Compliance Engine: Auto-generates audit trails meeting FDA 21 CFR Part 11 and EU MDR requirements
Technical Impact: Clinics using Carejoy API integration demonstrate 37% reduction in “print-to-dispatch” time and 22% fewer remake incidents (Carejoy 2026 Clinical Efficacy Report). The system eliminates 3.2 manual steps per case through event-driven automation.
Strategic Recommendation
DMD printers have transcended their role as output devices to become intelligent workflow nodes. For labs: Prioritize open architecture with Carejoy API integration to maximize ROI and material flexibility. For chairside: Leverage native 3Shape/exocad integrations for streamlined single-unit production. The critical differentiator in 2026 is not print resolution, but system-level workflow intelligence – where DMD’s API ecosystem delivers measurable clinical and economic advantages over closed competitors. Validation of third-party resins remains essential, but the era of vendor lock-in is ending for forward-thinking providers.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Carejoy DMD 3D Printer – Shanghai ISO 13485 Facility
The Carejoy DMD 3D Printer represents a new benchmark in precision digital dental manufacturing, engineered for high-fidelity production of crowns, bridges, surgical guides, and custom trays. Built at our ISO 13485:2016 certified facility in Shanghai, the manufacturing and quality control (QC) process integrates advanced automation, AI-driven validation, and rigorous metrological standards to ensure clinical reliability.
Manufacturing Workflow
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of optical modules, linear guides, Z-stepper systems, and resin delivery mechanisms | Suppliers audited under ISO 13485; traceability via ERP-linked batch tracking |
| 2. Subassembly | Optomechanical integration of galvo mirrors, laser diodes (405 nm), and F-theta lens systems | Class 10,000 cleanroom environment; ESD-safe workstations |
| 3. Frame Assembly | Robotic arm-assisted chassis integration with vibration-dampening composite base | Automated torque control; real-time alignment verification via laser interferometry |
| 4. Firmware & Software Load | Installation of Carejoy OS with AI-driven layer optimization and open architecture support (STL/PLY/OBJ) | Secure boot protocol; encrypted firmware signing to prevent tampering |
Quality Control & Sensor Calibration
Each Carejoy DMD 3D Printer undergoes a 72-hour QC protocol, including calibration in our on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory, accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards.
| QC Parameter | Method | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Beam Focus Accuracy | Beam profiler analysis at 100+ focal points across build volume | ±2 µm repeatability; calibrated to NIST-traceable standards |
| Build Platform Flatness | Autocollimator + capacitive probe mapping (0.1 µm resolution) | ≤ 5 µm deviation over 140 x 80 mm area |
| Layer Registration | AI-based image correlation of 50-layer test prints under thermal load | Sub-pixel alignment (≤ 3.5 µm cumulative error) |
| Environmental Sensor Calibration | Temperature (±0.1°C), humidity, and VOC sensors calibrated in climate chamber | Compliant with ISO 13485 Section 7.6 – Monitoring and Measuring Equipment |
Durability & Lifecycle Testing
To validate long-term reliability, 5% of each production batch undergoes accelerated lifecycle testing:
- 10,000-hour continuous print simulation with dynamic load cycling
- Thermal shock testing from 15°C to 40°C over 500 cycles
- Resin exposure endurance using aggressive methacrylate and epoxy formulations
- Vibration testing simulating global shipping conditions (ISTA 3A)
Failure modes are fed into Carejoy’s AI-driven predictive maintenance engine, enabling proactive field updates via remote diagnostics.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental manufacturing due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
| Factor | Impact on Cost-Performance |
|---|---|
| Vertical Integration | Domestic supply chains for optics, motion control, and microelectronics reduce BOM costs by 30–40% vs. EU/US equivalents |
| Advanced Automation | Robot density in Shanghai exceeds 350 units per 10,000 employees (IFR 2025), enabling precision at scale |
| ISO 13485 Ecosystem Maturity | Over 4,200 ISO 13485 certified medtech manufacturers in China (NMPA, 2025), ensuring regulatory rigor without premium pricing |
| R&D Investment in AI & Open Architecture | Local AI talent pool drives innovation in scanning accuracy and adaptive layer algorithms, reducing post-processing time by up to 35% |
| Export-Optimized Logistics | Shanghai Yangshan Port enables 12-day global delivery with carbon-neutral shipping options |
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver a 42% lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) over 5 years compared to legacy German and American brands, without compromising on sub-10µm print accuracy or clinical compatibility.
Support & Digital Integration
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support with AR-assisted diagnostics (via Carejoy Connect)
- Monthly AI-Driven Software Updates enhancing scan fusion, support generation, and material profiling
- Open Architecture Compatibility with all major dental CAD platforms (exocad, 3Shape, Carestream)
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dmd 3D Printer.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
