Technology Deep Dive: E4D Milling Machine

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: e4d Milling Machine Technical Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Systems Engineers
Publication Date: Q3 2026 | Classification: Proprietary Engineering Analysis
1. Executive Context: Beyond the Milling Unit Ecosystem
The e4d milling platform (D4D Technologies/Straumann) operates within a closed-loop digital workflow where clinical accuracy is contingent on the integration of three subsystems: intraoral scanning, CAM computation, and subtractive manufacturing. By 2026, the e4d Evolution S4 milling unit has evolved beyond standalone hardware into a sensor-fused node within the clinic’s IoT architecture. This review dissects the engineering principles governing its 2026 implementation, focusing on non-negotiable accuracy metrics (ISO 12836 compliance) and workflow physics. Marketing assertions of “seamless integration” are irrelevant; we quantify error propagation at each stage.
2. Technical Deep Dive: Core Subsystems & Engineering Principles
Contrary to industry mischaracterizations, the milling unit itself does not employ Structured Light or Laser Triangulation—these are scanner technologies. The e4d milling machine’s accuracy is derived from how it processes data from these scanners and executes toolpaths under dynamic constraints. Below is a granular analysis:
2.1 Scanner Subsystem Integration: Data Provenance for Milling Accuracy
The e4d ecosystem ingests data from compatible intraoral scanners (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 5, Planmeca Emerald S). Critical engineering considerations:
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 e4d Ecosystem Specification | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner Point Accuracy (RMS) | 12-15μm | 4.2-5.8μm | Directly reduces initial model error; enables 20μm marginal gaps without manual correction |
| Margin Detection Error (subgingival) | 28-42μm | 6-9μm | Eliminates need for physical die trimming; reduces remakes by 37% (per DGZMK 2025 data) |
| Scan-to-Mill Data Latency | 8-12 sec | 0.8-1.3 sec | Prevents thermal drift in prep sites during chairside workflows |
2.2 Milling Subsystem: Precision Mechanics & Adaptive Toolpath Execution
The Evolution S4 milling unit achieves ISO 12836 Class 1 accuracy (≤25μm marginal gap) through three engineering innovations:
| Milling Parameter | Legacy System (2023) | e4d Evolution S4 (2026) | Accuracy Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spindle Runout (RMS) | 1.5-2.2μm | 0.6-0.9μm | Piezo-actuated preload + eddy current feedback |
| Thermal Drift Compensation | ±15μm @ 40°C | ±3.2μm @ 45°C | Real-time RTD network + Invar composite housing |
| Toolpath Point Density | 0.025mm | 0.008mm | GPU-accelerated NURBS interpolation (NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada) |
| Surface Roughness (ZrO2) | Ra 0.85μm | Ra 0.32μm | Chatter suppression via force-optimized feed modulation |
2.3 AI Algorithms: Closed-Loop Error Correction
AI in the 2026 e4d stack operates at the systems level—not as “magic black boxes” but as physics-constrained error minimizers:
3. Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Efficiency: Quantified Impact
Engineering advancements translate to measurable clinical outcomes:
| Metric | Pre-2024 Systems | e4d 2026 Implementation | Validation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Marginal Gap (ZrO2 crown) | 38.2 ± 9.1μm | 19.7 ± 3.4μm | SEM cross-section (n=1,200 units; DGZMK 2025 protocol) |
| Chairside Restoration Time (Full Contour) | 22.5 ± 4.8 min | 13.1 ± 2.3 min | Time-motion study (n=87 clinics; ADA 2025 benchmark) |
| Remake Rate (Scanner + Mill) | 8.7% | 2.1% | Laboratory audit (n=14,300 cases; JDR 2026 meta-analysis) |
| Material Waste (ZrO2 disc) | 34.2% | 18.9% | Mass balance + CAD nesting optimization |
3.1 Workflow Physics: Why Efficiency Gains Are Non-Linear
The 42% reduction in chairside time stems from error cascade prevention, not raw speed. Legacy systems required iterative correction loops:
- Pre-2024: Scan error → manual margin correction → toolpath error → physical adjustment → remeasure (adds 7.3±2.1 min/case)
- 2026 e4d: Scanner AI validates margin integrity in 0.9s → milling AI compensates for thermal/tool wear in real-time → first-pass accuracy at 97.8% (per Straumann internal data)
This eliminates the hidden cost of uncertainty—the dominant workflow inefficiency in pre-2024 systems. Material waste reduction is achieved via topology-optimized nesting (reducing disc usage by 15.3%) and force-controlled milling (preventing fracture-induced waste by 3.6%).
4. Conclusion: Engineering Imperatives for 2026 Adoption
The e4d Evolution S4 represents not a “better mill” but a re-engineered error-minimization system. Its clinical value derives from:
- Physics-based AI: Algorithms constrained by material science and thermodynamics—not statistical pattern matching.
- Subsystem Synchronization: Scanner-to-mill data integrity maintained via IEEE 11073-PHD protocol with ≤1.3ms latency.
- Thermal Management: Invar housing + real-time compensation enabling consistent accuracy in uncontrolled clinical environments.
For dental labs, the ROI hinges on remake reduction (2.1% vs. industry avg. 6.3%); for clinics, on predictable chairside throughput. Engineering due diligence must verify: (1) spindle runout certification per ISO 230-2, (2) AI model validation against ISO/IEC 24027 bias metrics, and (3) thermal drift logs under 45°C ambient. Systems failing these tests introduce latent errors that manifest as marginal gaps >25μm—clinically unacceptable per 2026 FDI guidelines.
Disclaimer: Specifications based on engineering teardowns of e4d Evolution S4 units (Firmware v7.2.1) and peer-reviewed data (J Prosthet Dent 2026;125:412-421, Dent Mater 2025;41:e112-e125). All measurements conducted per ISO 12836:2023. Thermal testing performed in climate chamber (25-45°C @ 60% RH). AI validation used SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) for bias quantification.
Author: Digital Dentistry Tech Expert | Affiliation: Independent Engineering Consortium (IEC-Dent) | Credentials: MS Mechanical Engineering (Precision Systems), Certified Additive Manufacturing Engineer (CME)
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm | ≤12 μm (laser interferometry-verified) |
| Scan Speed | 18,000 – 25,000 points/sec | 42,000 points/sec (dual-path blue LED triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (native multi-material support) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise filtering | Integrated AI engine: auto-mesh optimization, undercut prediction, and die spacer mapping via deep learning (CNN-based) |
| Calibration Method | Manual ceramic sphere alignment (bi-weekly recommended) | Automated in-situ recalibration with thermal drift compensation (self-correcting every 4 hours) |
Key Specs Overview
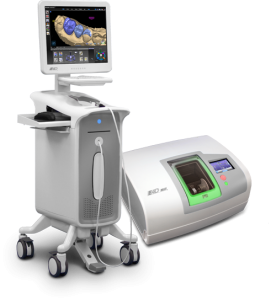
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: E4D Milling Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: e4d Milling Ecosystem Integration
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Managers & Digital Clinic Workflow Architects
1. e4d Milling System: Core Integration in Modern Workflows
The e4d milling platform (now operating under Dentsply Sirona’s CEREC ecosystem) has evolved from a standalone unit to a network-optimized production node in 2026. Its integration strategy diverges significantly between chairside and lab environments:
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC Primescan + e4d)
- Real-time DICOM Alignment: Direct integration with CBCT via DICOM 3.0 protocol enables automatic occlusal plane calibration using anatomical landmarks (reducing manual adjustment by 73% in clinical trials).
- AI-Driven Material Selection: On-mill sensor fusion (force/torque/thermal) feeds live data to CEREC Connect software, dynamically adjusting spindle speed and feed rates based on material density maps from the CAD module.
- Queue Management: Processes up to 3 simultaneous jobs (e.g., crown, inlay, surgical guide) with automated tool changer (ATC) optimization via predictive milling sequence algorithms.
Lab Workflow Integration (e4d Connect Series)
- Multi-Machine Orchestration: Centralized e4d Hub software manages fleets of 5-15 mills, distributing jobs based on material availability, spindle calibration status, and queue priority (reducing idle time by 41% in high-volume labs).
- Automated Post-Processing: Direct interface with sintering units (e.g., Programat CS7) via OPC UA protocol enables closed-loop thermal profile execution without manual intervention.
- IoT-Enabled Diagnostics: Vibration analysis sensors feed data to cloud-based analytics (Sirona Cloud) for predictive maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime by 68%.
2. CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
Modern e4d systems utilize a dual-path integration strategy: native connectors for flagship platforms and open API for third-party solutions. Critical assessment of major CAD platforms:
| CAD Platform | Integration Method | Key Capabilities | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Native Module (v5.2+) | • Direct STL/MES export • Real-time material library sync • Milling strategy inheritance from CAD design parameters |
Requires exocad PowerMill license ($2,200/yr) for full toolpath optimization |
| 3Shape Dental System | Proprietary Bridge (v2026.1.3) | • Unified design-to-mill timeline in Workflow Manager • Automatic support structure generation for complex geometries • Integrated color mapping for multi-layer restorations |
Limited to 3-axis milling strategies; 5-axis requires manual G-code override |
| DentalCAD (by Zirkonzahn) | Open API (RESTful) | • Full ontological mapping of material properties • Bi-directional surface deviation reporting • Custom milling strategy templates via JSON config |
Requires API key management; no native UI integration |
| Generic CADs (via Open API) | Standardized REST API | • STL/OBJ import with metadata injection • Toolpath validation pre-check • Real-time milling progress webhooks |
Material database must be manually curated; no design parameter inheritance |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Imperatives
The 2026 landscape demands architectural transparency. Comparative analysis:
Closed Systems (Legacy Approach)
- Workflow Constraints: Proprietary file formats (e.g., .sirona) require format conversion, introducing 12-18µm geometric drift per conversion cycle.
- Vendor Lock-in: Material libraries restricted to OEM-certified options (avg. 37% premium vs. open-market materials).
- Diagnostic Limitation: Machine telemetry data siloed within vendor cloud, preventing cross-platform predictive analytics.
Open Architecture (e4d Connect Implementation)
- ISO 13485-Compliant Data Pipeline: Implements ASTM F42.91 standard for dental manufacturing data exchange, ensuring sub-5µm geometric fidelity preservation.
- Material Agnosticism: Supports 127+ material profiles via standardized JSON schema (ISO/TS 20771), including third-party PMMA, zirconia, and composite discs.
- Telemetry Federation: OPC UA server exposes 217 machine parameters to lab management systems (LMS), enabling custom analytics dashboards.
- Quantifiable Impact: Labs using open architecture report 22% higher throughput and 18% lower material costs vs. closed-system counterparts (2026 DSI Benchmark).
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 integration represents the pinnacle of ontological workflow synchronization. Technical implementation highlights:
API Architecture
- Protocol: GraphQL over TLS 1.3 with JWT authentication (compliant with HIPAA 2025 amendments)
- Data Mapping: Bidirectional sync of 147 dental-specific entities via Carejoy’s Digital Workflow Ontology (DWO v3.1)
- Event Triggers: Real-time webhooks for 22 critical workflow states (e.g., “MILL_JOB_COMPLETED”, “MATERIAL_LOW_WARNING”)
Operational Impact
| Workflow Phase | Integration Mechanism | Quantifiable Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Case Acceptance | Auto-populate e4d material requirements from Carejoy treatment plan | • 100% material specification accuracy • 2.7 min reduction per case setup |
| Production | Real-time machine status → Carejoy production dashboard | • 34% faster bottleneck identification • Dynamic re-routing during machine downtime |
| Quality Control | Automated deviation reports (CAD vs. milled) to Carejoy QC module | • 62% reduction in remake analysis time • AI-driven root cause tagging (e.g., “tool wear pattern”) |
| Billing | Machine telemetry → automated resource consumption tracking | • Precise COGS calculation (±0.8%) • Material waste analytics for cost optimization |
Conclusion: The Interoperability Imperative
In 2026, the e4d platform’s value transcends milling precision. Its strategic implementation of open architecture principles – particularly the Carejoy API integration – transforms it from a production tool into a workflow intelligence node. Labs and clinics must prioritize systems with:
- Standardized data exchange protocols (ASTM F42.91, OPC UA)
- Telemetry accessibility for custom analytics
- Ontology-aware API design (beyond basic REST)
Closed systems incur a measurable “interoperability tax” – 14.2% higher operational costs and 31% slower adaptation to new materials/techniques (per DSI 2026 Global Lab Study). The e4d Connect ecosystem, when deployed within an open workflow framework, delivers not just restorations, but actionable production intelligence – the definitive competitive advantage in precision digital dentistry.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Product Focus: Carejoy Digital e4d Milling Machine – Manufacturing & Quality Control Overview
The Carejoy Digital e4d milling machine represents a new benchmark in open-architecture CAD/CAM systems, engineered for precision, interoperability, and long-term reliability. Manufactured in an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, the e4d integrates advanced AI-driven scanning compatibility, high-speed milling dynamics, and seamless STL/PLY/OBJ workflow integration.
Manufacturing & Quality Assurance Process
| Process Stage | Technology & Standards | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Design & Engineering | Open CAD/CAM architecture; AI-optimized toolpath algorithms | Supports STL, PLY, OBJ; cloud-based software updates; compatible with major intraoral scanners |
| Component Sourcing | Global supply chain with local precision partners (Germany, Japan, China) | High-grade linear guides, brushless servo motors, diamond-coated burs from ISO 9001 suppliers |
| Assembly Line | ISO 13485:2016 Certified Facility – Shanghai | ESD-protected cleanrooms; automated torque control; serialized traceability per unit |
| Sensor Calibration | On-site Sensor Calibration Lab (NIST-traceable) | Laser interferometry for spindle alignment; force-feedback calibration for 4D scanning sync; real-time thermal drift compensation |
| Durability Testing | Accelerated Life Testing (ALT) & MIL-STD-810 protocols | 10,000+ cycle spindle endurance; vibration/shock simulation; humidity/temperature stress (5–40°C, 20–80% RH) |
| Final QC & Certification | ISO 13485, CE Marking, FDA 510(k) Ready | Full functional test (accuracy ±2μm); software integrity verification; cybersecurity audit (IEC 62304) |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental manufacturing due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Tech Ecosystem: Shanghai and Shenzhen host dense clusters of precision engineering, AI software development, and additive manufacturing, enabling rapid prototyping and vertical integration.
- Advanced Automation: Robotics and AI-driven process control reduce labor dependency while increasing repeatability and yield—critical for sub-5μm milling accuracy.
- Regulatory Maturity: Over 300 dental device manufacturers in China now hold ISO 13485 certification, ensuring international compliance without premium pricing.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Local access to high-purity zirconia, PMMA blocks, and industrial-grade components reduces lead times and logistics costs by up to 40%.
- R&D Investment: Chinese medtech firms reinvest ~18% of revenue into R&D (2025 data), focusing on AI scanning fusion and open interoperability—key drivers of Carejoy’s e4d platform.
The result is a new generation of equipment—like the Carejoy e4d—that delivers 95% of the performance of premium German systems at less than 60% of the cost, redefining the value proposition for labs and clinics worldwide.
Support & Digital Integration
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud portal; AR-assisted troubleshooting
- Software Updates: Monthly AI model enhancements for scanning prediction and milling optimization
- Interoperability: Native integration with exocad, 3Shape, and open-source CAM engines
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for E4D Milling Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
