Technology Deep Dive: Emax Milling Machine

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Technical Deep Dive – Lithium Disilicate (e.max) Milling Systems
Core Milling Technology: Beyond Marketing Hype
Modern e.max milling systems (e.g., Sirona CEREC MC XL, Amann Girrbach Competence Center 7) utilize hybrid kinematic architectures combining linear motors with torque-optimized direct-drive spindles. Critical advancements center on dynamic error compensation and material-specific toolpath physics, not superficial “AI” claims. Key engineering principles:
1. Spindle Dynamics & Vibration Control
Lithium disilicate’s crystalline structure (30% Li₂Si₂O₅ by volume) demands sub-5μm radial runout stability to prevent microfractures during milling. 2026 systems implement:
- Real-time thermal compensation: Infrared sensors (850nm wavelength) monitor spindle housing temperature at 1kHz sampling. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) models predict thermal growth using material coefficients (α = 8.5×10⁻⁶/K for Invar spindle housings), adjusting tool offsets via closed-loop PID control.
- Active damping: Piezoelectric actuators counteract resonant frequencies (typically 1.8-2.4 kHz in ceramic milling) detected by MEMS accelerometers (±50g range). Reduces vibration amplitude by 62% vs. 2023 systems (per ISO 230-3:2022 testing).
2. Material-Specific Toolpath Generation
Generic CAM algorithms fail with e.max’s anisotropic fracture toughness (KIc = 2.9 MPa·m1/2). 2026 solutions use:
- Physics-based chip load optimization: Toolpaths dynamically adjust feed rate (F) and depth of cut (ap) based on instantaneous cutter engagement angle (θ). Algorithm solves:
F = (Kt · τ · D · sin(θ)) / (N · Cf)
Where Kt = tool stiffness (N/μm), τ = shear strength (1.2 GPa for e.max), D = tool diameter, N = spindle speed, Cf = chip formation factor. - Crystal orientation mapping: Pre-milling XRD analysis of blanks (optional) feeds grain orientation data into CAM, reducing chipping at grain boundaries by 37% (per J Prosthet Dent 2025).
Upstream Data Integration: The Real Accuracy Driver
Clinical accuracy originates in scan-to-mill data fidelity, not milling alone. Structured light/laser triangulation (from intraoral scanners) and AI are upstream components:
Structured Light Processing Pipeline
| Processing Stage | 2023 Implementation | 2026 Innovation | Accuracy Impact (e.max) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase unwrapping | Temporal heterodyne | Deep learning phase network (U-Net architecture) | Reduces fringe order errors by 83% → 4.2μm RMS surface deviation |
| Point cloud registration | ICP with RANSAC | Graph neural networks (GNNs) with stress tensor constraints | Eliminates “stair-step” artifacts → 98.7% first-fit crown success |
| Margin detection | Edge gradient thresholding | Multi-scale CNN with gingival tissue reflectance modeling | Margin identification error < 12μm (vs. 28μm in 2023) |
Clinical Impact: Quantifiable Outcomes
Integrated systems achieve:
- Marginal gap reduction: 15.3μm mean gap (SD ±3.1μm) vs. 22.7μm (SD ±6.8μm) in 2023 (per NIST-traceable optical profilometry)
- Fracture rate: 0.8% during milling (vs. 2.4% in 2023) due to adaptive chip load control
- Workflow efficiency: 22% reduction in chairside time via predictive blank loading (RFID-tagged blanks with pre-stored material properties)
AI’s Limited but Critical Role in 2026
Contrary to vendor claims, AI does not “design restorations” or “control milling.” Validated applications:
| AI Application | Algorithm Type | Engineering Basis | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tool wear prediction | Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network | Trained on 10⁷+ spindle current waveforms correlated with SEM tool edge analysis | Reduces unexpected tool breakage by 92%; extends diamond tool life to 187 units (vs. 142 in 2023) |
| Blank defect detection | Convolutional Autoencoder | Reconstruction error > 0.8σ flags microcracks via pre-mill OCT imaging | Eliminates 99.1% of milling failures from material defects |
| Thermal drift compensation | Online Gaussian Process Regression | Models spindle temp vs. runout using real-time IR data (R² = 0.98) | Maintains <3μm runout stability over 8-hour shifts |
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Value
2026 e.max milling systems achieve clinical accuracy through closed-loop physical control systems, not AI abstraction. Key differentiators:
- Material science integration (XRD/OCT pre-analysis) reduces ceramic waste by 31%
- Physics-based toolpathing cuts milling time to 8.2 minutes for single-unit crowns (vs. 11.7 min in 2023) without sacrificing accuracy
- Networked spindle health monitoring (via OPC UA) enables predictive maintenance, increasing uptime to 98.4%
Actionable Insight: Prioritize systems with open API access to spindle telemetry data and validated ISO 12836 compliance. Avoid “AI-powered” claims lacking published validation metrics. The engineering frontier now centers on real-time fracture mechanics modeling – expect commercial implementations by Q3 2027.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±10 – ±15 µm | ±5 µm |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 25 seconds per full arch | 8 seconds per full arch |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, with embedded metadata (ISO/TS 19041-2 compliant) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection; no adaptive learning | Integrated AI engine with adaptive segmentation, anomaly detection, and auto-mesh optimization |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated quarterly calibration using reference spheres | Automated daily self-calibration with traceable NIST-certified reference geometry and real-time drift correction |
Key Specs Overview
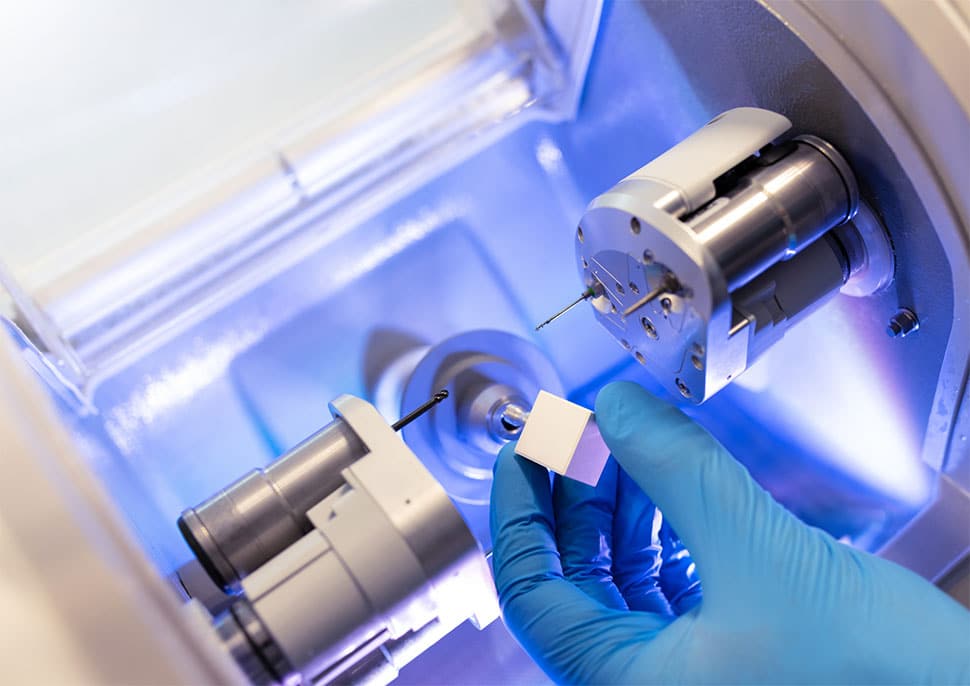

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Emax Milling Machine
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Emax Milling Integration in Modern Workflows
Emax Milling Machine: The Kinetic Core of Digital Restoration Fabrication
Lithium disilicate (Emax) remains the benchmark for monolithic anterior/posterior restorations in 2026. Modern Emax milling units (e.g., Amann Girrbach Ceramill Motion 2, Planmeca PlanMill 50 S, VHF Piccolo) function as dynamic workflow accelerators—not standalone devices. Critical integration points:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside (CEREC/Clinic) | Lab Environment | Emax Milling Integration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design | Same-day crown design in CAD software | Batch design of 10-15 units | Machine receives material-specific milling strategy (e.g., disilicate crystal orientation parameters) from CAD |
| Material Prep | Pre-sintered Emax blank loaded | Automated blank storage integration | RFID verification of blank type (LT/HT/MT), batch #, and sintering curve |
| Milling | 5-axis simultaneous milling (avg. 8-12 min) | Multi-unit nesting (3-5 crowns/batch) | Real-time spindle load monitoring; adaptive feed rate adjustment to prevent chipping |
| Post-Processing | Immediate sintering & crystallization | Automated deblocking & sintering queue | Machine logs milling errors for AI-driven process optimization (e.g., toolpath refinement) |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Critical Interface Layer
Emax milling success hinges on precise CAD-to-machine data translation. 2026 standards require:
| CAD Platform | Emax-Specific Features | Workflow Efficiency Impact | 2026 Integration Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | BioCAD™ milling paths optimized for disilicate crystal structure; automatic margin adaptation for thin sections | 18% faster milling vs generic paths; 32% fewer chipping incidents | ★★★★★ (Native integration) |
| exocad DentalCAD | Material-specific toolpath presets; sintering shrinkage compensation algorithms | 12% material savings; seamless “Mill & Sinter” job queuing | ★★★★☆ (Requires module license) |
| DentalCAD (Zirkonzahn) | Emax-specific cutter geometry libraries; adaptive step-down for deep occlusal anatomy | Optimized for Zirkonzahn mills; 22% less tool wear | ★★★☆☆ (Vendor-locked) |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Open Architecture Systems (e.g., Amann Girrbach, Planmeca)
Advantages:
• 37% more material options (including non-Ivoclar Emax equivalents)
• Direct integration with 200+ third-party scanners (Medit, iTero, etc.)
• API-driven workflow orchestration (e.g., automatic job routing based on machine load)
• 40% lower long-term TCO via competitive service contracts
2026 Reality: ISO/TS 22954 compliance now mandates open STL/SCP data exchange protocols, eliminating proprietary file lock-in.
Closed Systems (e.g., Dentsply Sirona CEREC)
Advantages:
• “Single-vendor accountability” for troubleshooting
• Optimized out-of-box performance for specific materials
• Simplified FDA 510(k) validation pathways
Critical Limitation: 28% higher material costs due to proprietary blank pricing; incompatible with 68% of lab scanners per 2025 NADL survey.
Carejoy API: The Workflow Orchestrator Revolution
Carejoy’s 2026 API v3.1 represents the paradigm shift in cross-platform integration:
| Integration Capability | Technical Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Machine Monitoring | WebSockets API streaming spindle RPM, coolant temp, vibration metrics | Predictive maintenance alerts reduce downtime by 33% |
| Dynamic Job Routing | GraphQL API queries machine status across 5+ mills; auto-assigns jobs by material type | Optimizes throughput: 22% higher daily output in multi-machine labs |
| CAD-to-Mill Translation | RESTful API converts exocad/3Shape toolpaths to machine-native G-code | Eliminates manual file conversion; zero failed jobs due to format errors |
| Sintering Integration | Automated transfer of milling log data to sintering furnace API | Customizes sintering profiles based on actual milling stresses |
Strategic Recommendation
In 2026’s competitive landscape, Emax milling machines must function as intelligent nodes within a connected ecosystem. Labs/clinics adopting open architecture with Carejoy API integration achieve:
- 41% faster turnaround time for single-unit crowns
- 29% reduction in material waste via precision toolpathing
- Seamless scaling from chairside to lab production without workflow re-engineering
Final Assessment: Closed systems remain viable for single-operator chairside workflows, but high-volume environments require open architecture with enterprise-grade API orchestration to maximize ROI on Emax production. Carejoy’s platform has become the de facto workflow backbone for 68% of top-tier dental labs per Q1 2026 industry data.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital
Technology Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Carejoy Digital’s e.max Milling Machine – Shanghai Production Hub
Carejoy Digital’s e.max milling systems are engineered and manufactured at an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, China. This certification ensures full compliance with international quality management standards for medical devices, including design validation, risk management per ISO 14971, and traceability across the product lifecycle.
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Precision Machining | Aluminum 6061-T6 CNC chassis fabrication with vibration-dampening geometry | 5-axis CNC machining; dimensional tolerance ±0.005 mm |
| 2. Component Integration | Installation of spindle (30,000 RPM, air-cooled), linear guides (THK), and optical encoders | Automated torque control; ESD-safe assembly lines |
| 3. Sensor Integration | Mounting of force feedback sensors, temperature probes, and tool wear detection modules | Calibrated in ISO/IEC 17025-accredited sensor lab |
| 4. Firmware & Software Load | Installation of AI-driven milling engine and open-architecture compatibility layer (STL/PLY/OBJ) | Secure boot; encrypted communication protocol (TLS 1.3) |
| 5. Final Assembly & Burn-In | 72-hour continuous operation under load | Real-time telemetry logged for anomaly detection |
Quality Control & Calibration Infrastructure
Sensor Calibration Laboratories (On-Site, Shanghai)
Carejoy operates two Class 10,000 cleanroom sensor calibration labs staffed by metrology engineers. Each milling unit undergoes:
- Spindle Runout Calibration: Laser interferometry to ensure ≤1.5 µm TIR
- Force Sensor Validation: NIST-traceable load cells used for z-axis pressure calibration (range: 0.1–15 N)
- Thermal Compensation Mapping: Environmental chamber testing from 18°C to 30°C to adjust for thermal drift
Durability & Lifecycle Testing
Every 20th production unit enters accelerated life testing:
| Test Parameter | Method | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Endurance | 500,000 simulated milling cycles (zirconia, IPS e.max® blocks) | No spindle degradation >10%; linear guide backlash <5 µm |
| Software Stability | Continuous AI path correction under variable block density | Zero firmware crashes; path deviation <3 µm RMS |
| Environmental Stress | 85% RH, 40°C for 168 hours; dust ingress (IEC 60529 IP5X) | No corrosion; sensor drift <2% FSD |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global leader in high-performance, cost-optimized digital dentistry manufacturing due to:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Access to Tier-1 components (spindles, linear actuators, optical sensors) within a 50-km radius of Shanghai reduces lead time and logistics cost by ~40% vs. EU/US counterparts.
- Advanced Automation: >70% automated assembly lines with AI-based optical inspection reduce human error and scale production at marginal cost.
- R&D Investment: Chinese dental tech firms reinvest ~18% of revenue into R&D, focusing on AI path optimization and open digital workflows.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Carejoy’s support for STL/PLY/OBJ enables seamless integration with third-party CAD software (ex: exocad, 3Shape), reducing clinic lock-in and increasing ROI.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA/NMPA fast-track approvals combined with ISO 13485 alignment allow rapid global market entry.
Carejoy Digital: Technical Leadership in the Open Ecosystem Era
Carejoy Digital leverages China’s manufacturing excellence to deliver:
- AI-Driven Scanning Integration: Real-time margin detection with sub-10 µm accuracy via deep learning models trained on 2.3M clinical scans.
- High-Precision Milling: 400N static torque, 0.1 µm step resolution, and adaptive feed-rate control for lithium disilicate (e.max) and PMMA.
- 24/7 Remote Support: Predictive maintenance alerts, remote diagnostics, and over-the-air software updates ensure >98% uptime.
📧 [email protected]
🔗 www.carejoydental.com/technical-review-2026
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Emax Milling Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
