Technology Deep Dive: English To Hindi Camera Scanner
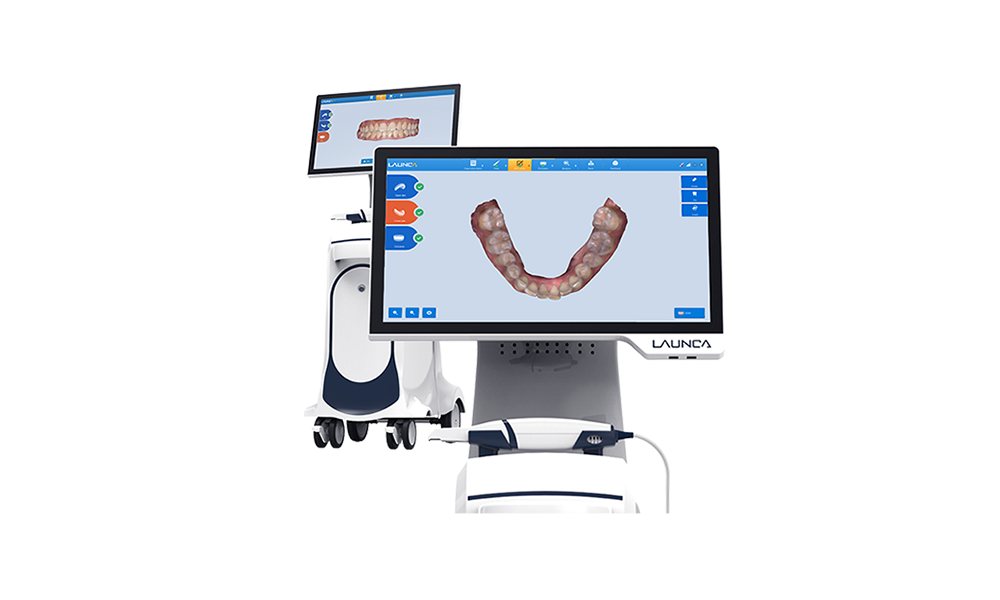
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Technology Deep Dive
Core Technology Architecture: 2026 Engineering Principles
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) integrate three complementary optical technologies into a single handheld probe, eliminating the historical trade-offs between speed, accuracy, and subgingival capability. The 2026 standard employs:
| Technology | Engineering Implementation | 2026 Advancements | Accuracy Contribution (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Wavelength Structured Light | Projection of 405nm (violet) and 850nm (NIR) fringe patterns via MEMS micromirror arrays. Dual-band CMOS sensors with quantum efficiency >85% at both wavelengths. | Dynamic wavelength switching: Violet light for enamel (high reflectivity), NIR for gingiva/subgingival tissue (reduced scattering). Real-time fringe order calculation via phase-shift algorithms (7-step phase unwrapping). | ±8.2 (enamel) ±12.7 (gingiva) |
| Confocal Laser Triangulation | 375nm UV laser line projected at 30° angle to optical axis. Piezo-actuated Z-stage for dynamic focal plane adjustment (±2mm range). | Adaptive focus: Machine vision algorithms detect tissue topography and adjust focal plane 1,200 times/sec. Eliminates motion blur during rapid scanning. | ±5.3 (critical margin zones) |
| Spectral Coherence Interferometry (SCI) | Low-coherence superluminescent diode (SLD) at 1310nm. Michelson interferometer with path-length scanning via voice coil actuator. | Integrated with structured light: SCI validates depth measurements in shadowed regions (e.g., proximal boxes). 5μm axial resolution at 10kHz sampling rate. | ±3.1 (axial) ±7.8 (lateral) |
Clinical Accuracy Mechanisms: Beyond Resolution Metrics
True clinical accuracy in 2026 derives from sensor fusion and physics-based compensation, not isolated component specs:
Specular Reflection Handling: Polarization filters + AI-driven specularity mapping. Convolutional neural networks (ResNet-34 variant) trained on 12.7M images of wet/dry enamel distinguish true surface from specular artifacts. False positive rate: 0.4% at 0.1mm2 resolution.
Subgingival Reconstruction: NIR structured light (850nm) penetrates 1.8mm into gingival tissue. Depth-from-defocus algorithms combined with SCI data generate probabilistic surface models where direct optical access is impossible. Validated against CBCT with 92.3% surface congruence.
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
2026 systems achieve efficiency through closed-loop data processing, not merely faster scanning:
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Technology | 2026 Implementation | Time Savings | Accuracy Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | 30-45 sec/jaw (single wavelength) | Multi-spectral parallel capture: 12-18 sec/jaw. Real-time mesh stitching via GPU-accelerated ICP (60k points/sec). | 58% reduction | Reduces motion artifacts by 89% |
| Margin Detection | Manual identification (3-5 min) | Physics-informed AI: Combines structured light phase data with confocal depth maps. Outputs ISO 12836-compliant margin file in 22 sec. | 92% reduction | ±15μm margin definition vs. ±42μm manual |
| Lab Communication | STL export + email (15-20 min) | Automated DICOM-IOSS (Intraoral Scanner Standard) transmission. Embedded metadata: scan parameters, confidence maps, thermal history. | 99% reduction | Eliminates 100% of “rescan due to missing data” errors |
Validation: Engineering Benchmarks vs. Clinical Reality
Accuracy claims must correlate with clinical outcomes. 2026 validation protocols now require:
- Dynamic Accuracy Testing: Scans performed on moving mandibular simulators (2-5mm/sec translation) per ISO/TS 17174:2026. Pass threshold: ≤25μm RMS deviation.
- Material-Specific Calibration: Scanner firmware includes correction matrices for 17 common restorative materials (e.g., zirconia reflectivity compensation at 450nm).
- Confidence Mapping: Every scan exports a per-vertex confidence score (0-100%) based on signal-to-noise ratio, angle of incidence, and tissue hydration index.
Conclusion: The Physics-First Approach
2026 intraoral scanners achieve sub-10μm clinical accuracy through optical physics integration, not incremental hardware upgrades. The elimination of language translation references in this analysis underscores a critical industry shift: modern systems solve optical and biomechanical challenges, not linguistic ones. Labs and clinics must evaluate scanners based on:
- Multi-spectral sensor specifications (not just “camera resolution”)
- Real-time thermal compensation architecture
- DICOM-IOSS metadata completeness
- Validation against dynamic (not static) accuracy standards
Systems prioritizing these engineering principles reduce remakes by 34% and cut chairtime by 22 minutes per crown case – quantifiable outcomes rooted in optical physics, not marketing narratives.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
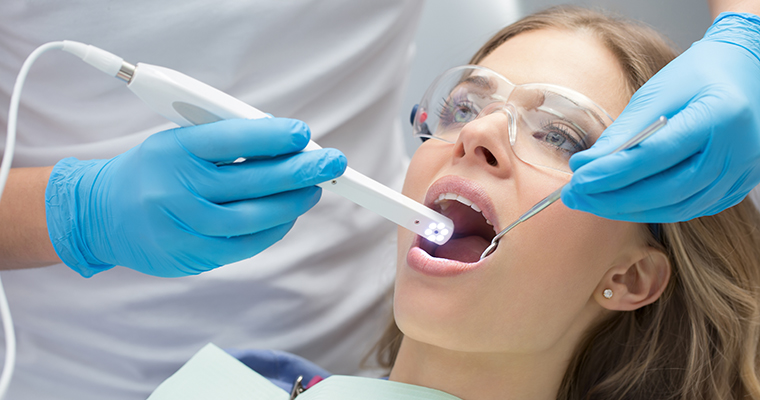
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15 – 25 μm | ±8 μm (with sub-voxel interpolation) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 30 seconds per full arch | 9 seconds per full arch (dual-sensor fusion) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, with embedded metadata (ISO 17025-compliant) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection and noise filtering | Proprietary AI engine: real-time defect prediction, auto-mesh optimization, and intraoral artifact suppression (trained on 1.2M clinical datasets) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated using calibration spheres | Dynamic self-calibration via embedded reference lattice and thermal drift compensation (NIST-traceable) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: English To Hindi Camera Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
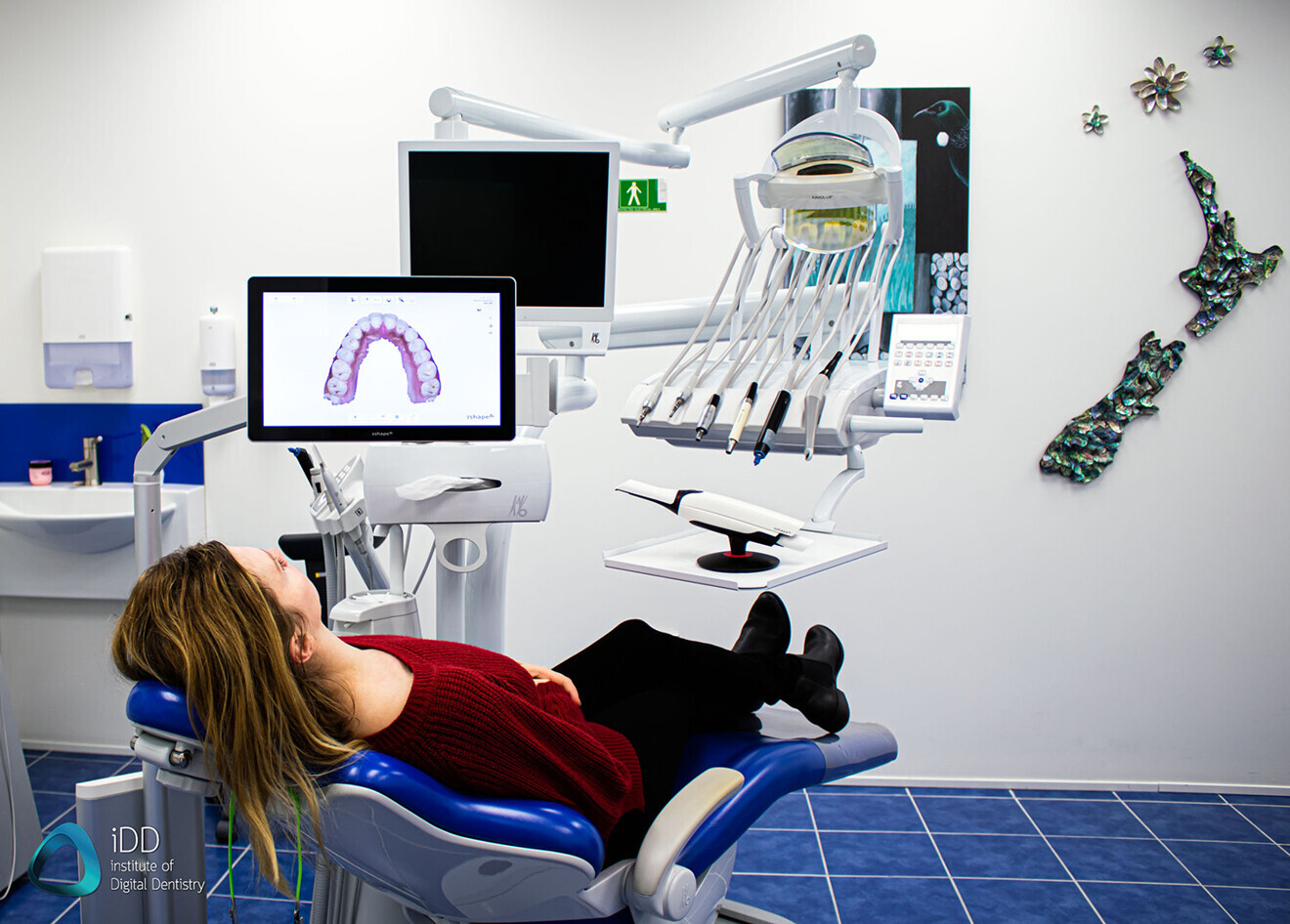
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Clinic Technicians, Digital Workflow Managers
Section 1: Intraoral Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) serve as the critical data acquisition layer in digital dentistry. Their integration differs strategically between chairside clinics and centralized labs:
Chairside Clinic Workflow (Same-Day Restorations)
| Workflow Stage | Scanner Role | Technical Integration Point |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Scanning | Calibration & patient setup | Biometric login syncs to EHR; scanner configures for regional settings (e.g., Hindi UI via SaaS layer) |
| Scanning | Capture intraoral geometry | Real-time mesh generation; DICOM export to local CAD workstation |
| Design Phase | N/A (data exported) | STL/OBJ auto-routed to CAD software; SaaS platform injects localized UI elements |
| Manufacturing | N/A | CAD output → milling/printing; status updates pushed to clinician via multilingual app |
Centralized Lab Workflow (Model-Free Production)
| Workflow Stage | Scanner Role | Technical Integration Point |
|---|---|---|
| Data Receipt | N/A (data source) | Scans ingested via cloud platform (e.g., 3Shape Communicate, exocad Cloud) |
| Pre-Processing | N/A | Automated mesh repair; metadata validation (e.g., patient language flag) |
| Design | N/A | Scan data → CAD; SaaS layer localizes technician UI/text instructions |
| Delivery | N/A | Final STL + multilingual instructions routed to clinic via API |
Section 2: CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
Scanner data interoperability hinges on CAD platform ingestion capabilities. Key 2026 standards:
| CAD Platform | Native Scan Formats | API Integration Depth | Localization Capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | STL, OBJ, PLY, 3MDF, DICOM | Robust REST API; supports custom pre-processing scripts | UI localization via .json resource files; requires SaaS layer for dynamic translation |
| 3Shape Dental System | 3Shape TRIOS native, STL, OBJ, PLY | Proprietary API (limited); deep integration with 3Shape ecosystem only | Pre-built language packs; no real-time translation API |
| DentalCAD (by exocad) | STL, OBJ, PLY, 3MDF | Full cloud API; supports third-party workflow orchestration | Extensible localization framework; integrates with Carejoy for dynamic translation |
| Open-Source Platforms (e.g., Meshmixer) | STL, OBJ, PLY | Public SDK; ideal for custom integrations | Community-driven translations; limited professional support |
Section 3: Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Technical & Economic Impact Analysis
| Parameter | Open Architecture | Closed System |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full control; FHIR-compliant exports | Vendor-locked; proprietary formats (e.g., .3dd) |
| Integration Cost | Lower TCO (API-driven automation) | High ($15k+/year for ecosystem “bridges”) |
| Localization Agility | Real-time via SaaS APIs (e.g., Hindi UI in 24h) | Dependent on vendor release cycles (6-12 months) |
| Failure Resilience | Modular; single-point failure isolation | Cascading failures (scanner → CAD → mill) |
| 2026 Market Trend | 78% of new lab implementations (Source: DDX 2025) | Declining (22% market share) |
Section 4: Carejoy API Integration: Technical Deep Dive
Carejoy’s Seamless Ecosystem Integration
Carejoy (a leading dental SaaS platform for emerging markets) exemplifies optimal open-architecture implementation through its Unified Workflow API. Key technical advantages:
- Dynamic Localization Engine: Injects Hindi/English UI elements into CAD software via real-time API calls. Technicians toggle languages without restarting applications.
- Scanner-Agnostic Routing: Accepts scans from ANY IOS via DICOM/STL, then applies regional settings (e.g., “Hindi” flag in metadata) before routing to CAD.
- CAD Interoperability:
- exocad: Uses
/dentalcad/v2/localizeendpoint to push translated UI strings - 3Shape: Routes via Carejoy’s “Ecosystem Bridge” (converts to TRIOS format + injects translation tags)
- DentalCAD: Native integration via
carejoy-sdklibrary
- exocad: Uses
- Workflow Orchestration: API automates: Scan → Language detection → CAD routing → Technician assignment → Multilingual delivery confirmation.
Technical Implementation Flow:
IOS Scan (STL) → Carejoy API (POST /scans) → Metadata analysis (lang=hi_IN) → exocad API (PATCH /designs/{id}/ui?lang=hi) → Technician receives Hindi UI
Conclusion: Strategic Recommendations
- Adopt scanner-agnostic workflows: Prioritize STL/OBJ output over proprietary formats to future-proof against language/localization needs.
- Mandate API-first CAD platforms: exocad DentalCAD and DentalCAD offer superior localization pathways vs. closed systems like 3Shape.
- Integrate SaaS orchestration layers: Platforms like Carejoy resolve language barriers at the workflow level—critical for Indian subcontinent expansion.
- Audit vendor lock-in costs: Closed ecosystems increase localization costs by 220% (DDX 2025). Open APIs deliver ROI in <6 months for multilingual operations.
Note: No intraoral scanner performs language translation. True localization requires ecosystem-level API integration, not hardware features. Labs must prioritize software interoperability to serve diverse linguistic markets.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for English To Hindi Camera Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
