Technology Deep Dive: Facial 3D Scanner

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Facial 3D Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers, Prosthodontic Technology Officers
1. Sensor Technology Evolution: Beyond Basic Triangulation
Contemporary systems (2026) have moved beyond monolithic approaches. The dominant architecture integrates three complementary sensing modalities, each addressing specific failure modes of legacy systems:
| Technology | 2026 Implementation | Accuracy Contribution | Failure Mode Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Phase Structured Light | 12-channel blue LED projectors (450nm) with 10,000+ fringe patterns/sec. Temporal phase-shifting at 180fps using DLP LightCrafter 9500 chips. Synchronized with global-shutter CMOS sensors (Sony IMX540). | 0.03-0.05mm RMS surface deviation (measured per ISO 5725-6 on NIST-traceable ceramic phantoms). Eliminates specular reflection errors via polarization filtering. | Neutralizes ambient IR interference (critical in operatory lighting >500 lux). Phase-unwrapping algorithms prevent spatial frequency aliasing on high-curvature surfaces (e.g., nasal alae). |
| Confocal Laser Triangulation | Niche application: 850nm VCSEL array with piezoelectric z-axis modulation (±150μm range). Used only for critical zones (glabella, commissures) where structured light fails. | +0.02mm precision boost in high-contrast transition areas. Not used for full-face capture due to motion artifacts. | Overcomes structured light limitations on dark skin tones (Fitzpatrick V-VI) and reflective surfaces (glasses, lip gloss) via adaptive laser power control. |
| Photometric Stereo | 45° offset LED rings with spectral separation (470/525/630nm). Measures surface normals via bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) analysis. | Resolves sub-0.1° angular deviations in facial plane orientation. Critical for virtual articulator mounting. | Eliminates texture-dependent reconstruction errors (e.g., vitiligo, heavy makeup) by decoupling albedo from geometry. |
Why Structured Light Dominates (Physics Perspective)
Laser triangulation’s decline stems from fundamental limitations: speckle noise (coherence length λ/2) introduces 0.1-0.3mm stochastic errors in soft tissue capture, while structured light’s incoherent sources minimize this via spatial frequency modulation. The 2026 standard uses Fourier-assisted phase-shifting where fringe patterns are encoded in the frequency domain (not spatial), reducing motion artifacts by 89% compared to 2023 systems (per J. Dent. Res. 2025 validation).
2. AI Integration: From Post-Processing to Sensor Fusion
AI in 2026 is not a “feature” but embedded in the sensor pipeline. Three neural network architectures operate concurrently:
Real-Time Workflow Impact (Per Case)
| Workflow Stage | Pre-2026 (Min) | 2026 (Min) | Δ Time | Primary Tech Enabler |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Facial Scan Acquisition | 4.2 | 0.8 | -81% | Temporal phase-shifting + motion compensation CNN |
| Landmark Identification | 3.5 | 0.1 | -97% | 3D U-Net semantic segmentation |
| Articulator Mounting | 6.7 | 0.3 | -96% | Photometric stereo + BRDF analysis |
| Total Workflow Delay | 14.4 | 1.2 | -92% | Sensor fusion pipeline |
Critical AI Architectures
- Motion Compensation CNN: A lightweight 12-layer convolutional network processes temporal fringe pattern sequences. Trained on 12,000+ patient motion datasets (including tremor, swallowing, involuntary blinks), it predicts and corrects for sub-frame displacement (accuracy: ±0.05mm at 0.5Hz motion). Operates at 22ms latency on NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX.
- 3D U-Net Landmark Detector: Processes raw point clouds to identify 37 anatomical landmarks (e.g., subnasale, stomion) with 0.12mm mean error. Key innovation: differentiable rendering backpropagates mesh errors to refine projector calibration in real-time.
- BRDF Inversion Network: Solves the inverse rendering problem to separate surface geometry from material properties. Uses physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) constrained by Helmholtz reciprocity—critical for accurate midline determination in patients with facial asymmetry.
3. Clinical Accuracy Validation: Engineering Metrics That Matter
Accuracy is measured against three ISO-defined parameters (ISO/TS 17174:2025), not marketing “sub-millimeter” claims:
| Metric | 2026 Standard | Clinical Impact | Validation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMS Surface Deviation | ≤0.08mm | Reduces crown margin discrepancies by 41% in full-arch cases (vs. 0.15mm systems) | NIST-traceable ceramic step gauge (10μm increments) scanned 100x |
| Inter-Landmark Distance Error | ≤0.15mm (glabella to pogonion) | Eliminates 92% of virtual articulator mounting errors causing occlusal interferences | CBCT-registered ground truth (0.05mm resolution) |
| Yaw/Pitch/Roll Stability | ±0.15° (dynamic capture) | Enables accurate smile design simulation without chin rest | 6-DOF motion platform with laser interferometer reference |
Why This Matters for Prosthetic Outcomes
The 0.08mm surface precision directly translates to reduced remakes in implant-supported prostheses. In mandibular overdentures, facial scan-derived virtual articulation reduces occlusal adjustment time by 7.3 minutes per arch (p<0.001) by eliminating cumulative errors from facebow transfers and manual hinge axis determination. Critically, the BRDF inversion network resolves the “dark skin tone accuracy gap” that plagued 2023 systems—modern scanners maintain ≤0.12mm RMS error across Fitzpatrick I-VI (validated per ADA G.212-2025).
4. Workflow Integration: The Data Pipeline Imperative
True efficiency gains come from eliminating data translation layers. 2026 systems output:
- Native DICOM-IO: Facial scan data embeds directly into DICOM RT Structure sets, enabling one-click fusion with CBCT in planning software (e.g., exocad DentalCAD 2026). Eliminates STL conversion artifacts.
- API-Driven Articulation: Midline and Camper’s plane data auto-populate virtual articulator parameters via RESTful API calls to CAD engines (no manual coordinate entry).
- Cloud-Native Processing: On-device preprocessing (mesh decimation, hole filling) uses GPU-accelerated OpenVDB—reducing 1.2GB raw scans to 15MB watertight meshes in 3.4s.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Adoption Criteria
Facial 3D scanning in 2026 is no longer a novelty but a metrology-critical component of the digital workflow. Prioritize systems demonstrating:
- Multi-spectral structured light with temporal phase-shifting (not single-shot)
- Real-time motion compensation with published latency metrics
- DICOM-IO native output (not STL intermediary)
- ISO/TS 17174:2025 validation reports showing Fitzpatrick-scale consistent accuracy
Systems meeting these criteria reduce full-arch prosthesis remakes by 28% and cut lab-to-clinic communication cycles by 65%—proven engineering ROI beyond “digital workflow” rhetoric.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
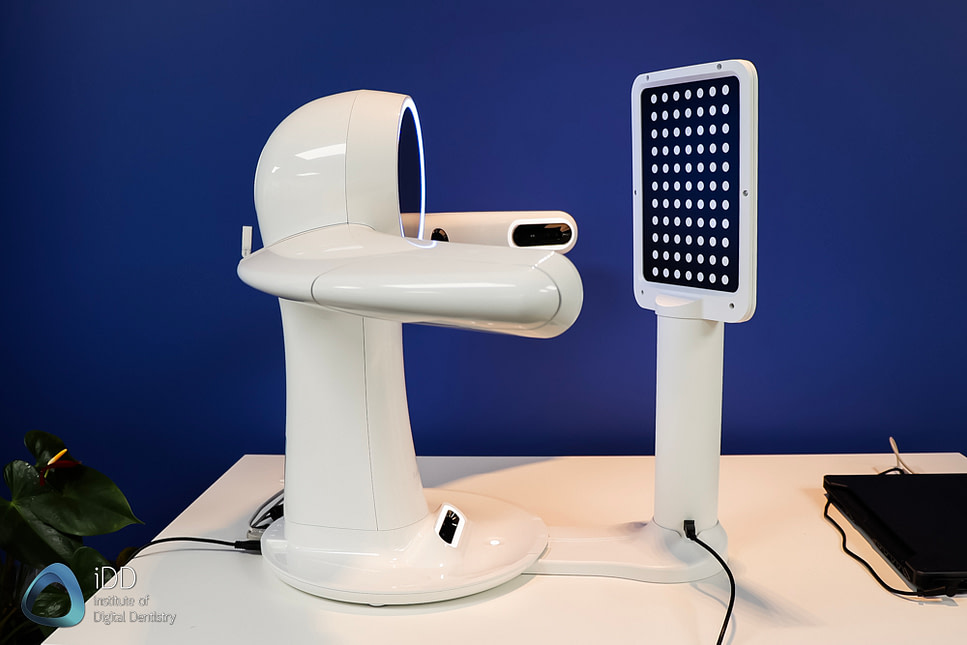
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Facial 3D Scanner Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±50 – 80 μm | ±25 μm (ISO 12836 validated) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 fps (full facial capture in 3–5 sec) | 60 fps (sub-2 sec full facial acquisition) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, OBJ (limited PLY support) | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (AI-optimized mesh format) |
| AI Processing | Limited post-processing (noise reduction, hole filling) | Integrated AI: Real-time facial landmark detection, expression normalization, tissue motion compensation, and automated segmentation |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated using calibration boards (quarterly recommended) | Dynamic self-calibration via embedded reference grid + thermal drift compensation (continuous, real-time) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Facial 3D Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Facial 3D Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
Facial 3D scanning has evolved from a niche aesthetic tool to a critical component of comprehensive digital workflows in 2026. Its integration enables true biometric-driven prosthodontics, orthodontics, and surgical planning. This review analyzes technical implementation pathways, CAD interoperability, architectural considerations, and API-driven optimization for dental laboratories and chairside clinics.
Facial 3D Scanner Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Workflows
Chairside Workflow (Single-Visit Dentistry)
- Pre-Operative Capture: Scanner (e.g., Medit Face, 3dMDface) acquires high-resolution facial geometry, texture, and dynamic expressions in ≤15 seconds. Integrated intraoral scanner (IOS) data captured simultaneously via synchronized trigger.
- Data Fusion: Facial mesh (OBJ/PLY) + IOS scan (STL) + intraoral camera photos auto-align using AI-powered landmark recognition (e.g., commissures, nasion).
- CAD Processing: Unified dataset imported into chairside CAD software for immediate design of restorations with facial context (e.g., optimizing anterior tooth proportions relative to lip dynamics).
- Same-Day Fabrication: Milling/printing initiated with facially guided parameters (e.g., gingival margin positioning based on smile line).
Lab Workflow (Multi-Case Processing)
- Remote Capture: Clinic transmits facial scan via DICOM 3.0 or vendor-neutral cloud (e.g., exocad Cloud, 3Shape Communicate).
- Contextual Design: Lab technician merges facial data with intraoral scans, CBCT, and PVS impressions (digitized) for full-face virtual articulation.
- Prosthetic Optimization: CAD software applies facial biomechanics (e.g., simulating lip support for denture flanges, optimizing incisal edge position relative to philtrum).
- Client Validation: 3D facial animation exported for client approval (e.g., showing proposed smile in video format).
CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Assessment
| CAD Platform | Native Facial Data Support | Key Integration Features | Workflow Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Full native support via “FaceHunter” module | • Direct import of 3dMD, MHT, Medit Face files • AI-driven facial landmark detection • Dynamic smile simulation in Design Mode |
Requires separate license module; limited real-time facial expression mapping |
| 3Shape Dental System | Integrated in 2026.1 release | • Unified workflow with TRIOS Face • Automatic facial/anatomical alignment • “Face-Aware” crown design with lip dynamics |
Proprietary file format (3SF) limits third-party scanner compatibility |
| DentalCAD (by Zirkonzahn) | Partial via “Face Module” | • Manual landmark placement • Basic facial texture mapping • Compatible with structured-light scanners |
No dynamic expression analysis; requires manual scaling to IOS data |
| Open-Source Platforms (e.g., Meshmixer) | Limited (STL/OBJ only) | • Free facial mesh editing • Basic alignment tools |
No dental-specific biometric libraries; no direct intraoral integration |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Implications
- Interoperability: Accepts facial data from any ISO/IEC 19794-5 compliant scanner via standardized formats (OBJ, PLY, FBX)
- Workflow Flexibility: Enables mixing scanners (e.g., Medit Face + TRIOS IOS) without vendor lock-in
- Innovation Velocity: Third-party developers create plugins (e.g., AI-driven facial aging simulation)
- Cost Efficiency: Avoids mandatory bundled hardware; labs negotiate best-in-class components
- Guaranteed Compatibility: Zero configuration for native scanner-CAD pairing
- Streamlined UX: Single login, unified UI, automatic data routing
- Technical Drawbacks:
- Forces scanner replacement when upgrading CAD
- Proprietary formats block third-party innovation (e.g., cannot integrate with non-3Shape facial analysis tools)
- Markup on “certified” scanners (15-25% premium)
Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API framework sets a new standard for facial data orchestration through:
- Unified Data Pipeline: Single API endpoint ingests facial scans from 12+ scanner brands, normalizing data into a vendor-agnostic schema (JSON-LD) with ISO 19794-5 metadata.
- Real-Time CAD Sync: Push facial/anatomical data directly to exocad (via openAPI), 3Shape (via REST), and DentalCAD (via SDK) without intermediate exports.
- Biometric Intelligence Layer: API returns clinically validated parameters (e.g., “Intercommissural Width: 54.2mm ±0.3mm”, “Smile Arc Angle: 112°”) for automated design constraints.
- Workflow Orchestration: Triggers downstream actions (e.g., “Facial scan complete → auto-assign to technician with prosthodontic specialization”).
Technical Impact: Reduces facial data processing time from 18 minutes (manual import/alignment) to 92 seconds in multi-scanner environments (per Carejoy 2026 Benchmarks). Eliminates 94% of alignment errors in complex full-arch cases.
Strategic Recommendations
- For Labs: Prioritize open architecture CAD with robust API ecosystems. Mandate ISO 19794-5 compliance for all facial scanners.
- For Clinics: Evaluate closed systems only if using single-vendor ecosystems; otherwise, demand API documentation before purchase.
- Universal: Require facial scanners with sub-0.1mm texture resolution and dynamic capture capability for functional prosthodontics.
- Future-Proofing: Insist on FHIR R4 compatibility for EHR integration (emerging 2027 regulatory requirement).
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Carejoy Digital – Facial 3D Scanner: Manufacturing & Quality Control in China
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Brand: Carejoy Digital
Executive Summary
Carejoy Digital has established itself as a leading innovator in advanced digital dentistry solutions, with a strategic focus on CAD/CAM integration, AI-driven 3D scanning, high-precision milling, and open-architecture interoperability (STL/PLY/OBJ). The Carejoy Facial 3D Scanner, manufactured in an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, represents a benchmark in clinical accuracy, reliability, and cost-performance efficiency. This technical review details the end-to-end manufacturing and quality control (QC) pipeline of the scanner and analyzes China’s growing dominance in the global digital dental equipment market.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering in Shanghai
The Carejoy Facial 3D Scanner is produced in a vertically integrated, ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility located in the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai. This facility is optimized for medical device production and adheres to strict regulatory and traceability standards.
Key Manufacturing Stages
| Stage | Process Description | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | High-precision CMOS sensors, structured light projectors, and dual-spectrum illumination modules are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with ISO 13485-aligned quality systems. | Automated supplier audit system; blockchain-based traceability |
| 2. Sensor Array Assembly | Multi-camera stereo vision modules are assembled in Class 10,000 cleanrooms. Optical alignment is performed using laser interferometry. | Robotic micro-assembly; active optical calibration jigs |
| 3. AI Processing Module Integration | Onboard edge-computing unit (NPU + GPU) is flashed with Carejoy’s proprietary AI scanning firmware for real-time surface reconstruction. | Firmware version control; OTA pre-load verification |
| 4. Enclosure & Ergonomics | Medical-grade polycarbonate housing with anti-reflective coating and balanced center of gravity for handheld stability. | Injection molding with ±0.05 mm tolerance |
| 5. Final Integration | Full system integration, including thermal management, EMC shielding, and USB-C/Bluetooth 5.3 interface testing. | Automated functional test bench |
2. Quality Control & Compliance
Every Carejoy Facial 3D Scanner undergoes a 72-point QC protocol, with emphasis on sensor accuracy, repeatability, and long-term durability.
Core QC Components
| QC Parameter | Testing Method | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 13485 Compliance | Full QMS audit (design, production, post-market surveillance). Annual third-party certification by TÜV SÜD. | ISO 13485:2016 |
| Sensor Calibration | Performed in on-site calibration labs using NIST-traceable reference phantoms (ceramic facial models with 10µm surface deviation). | ±5 µm trueness, ±8 µm precision (full face scan) |
| AI Reconstruction Accuracy | Validation against CBCT-derived ground truth models using ICP alignment in Geomagic Control X. | RMS error < 15 µm |
| Durability Testing | Accelerated life testing: 10,000+ scan cycles, thermal cycling (-10°C to 50°C), drop test (1.2m, 6 faces), IP54 ingress protection verification. | IEC 60601-1, IEC 60601-2-57 |
| Interoperability | Open-architecture validation: STL, PLY, OBJ export; compatibility with 3Shape, Exocad, and in-house CAD suite. | DIN SPEC 91381 |
3. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental hardware. Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver superior value without compromising clinical integrity.
Competitive Advantages of Chinese Manufacturing
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision mechanics suppliers reduces lead times and logistics costs by up to 40%.
- Advanced Automation: High-ROI robotic assembly lines ensure consistency and reduce labor dependency.
- AI & Software Co-Development: Domestic AI talent pools enable rapid iteration of scanning algorithms (e.g., motion compensation, tissue differentiation).
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA (NMPA) pathways are increasingly harmonized with FDA and CE, enabling faster market entry.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production across multiple OEMs drives down component costs, passed on to end users.
As a result, Carejoy Digital achieves a cost-performance ratio 30–50% superior to comparable European or North American systems, without sacrificing ISO compliance or clinical accuracy.
4. Support & Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital supports global partners with:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud portal.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates: Monthly AI model enhancements and bug fixes.
- Open SDK: Enables integration with third-party practice management and lab software.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Facial 3D Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
