Technology Deep Dive: Formlabs Dental 3D Printer
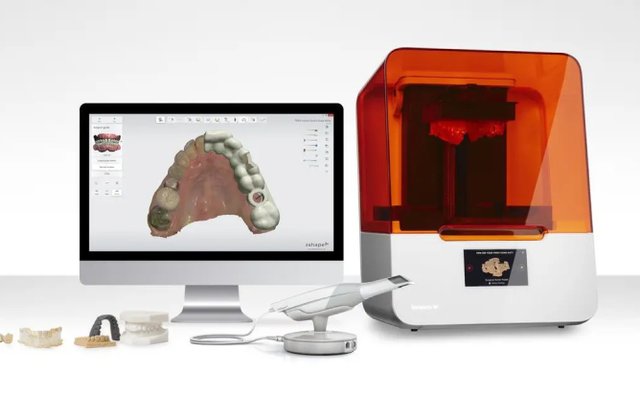
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Formlabs Dental 3D Printer Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, CAD/CAM Managers, Clinical Engineering Staff | Review Date: Q1 2026
Core Technology Architecture: Beyond Marketing Terminology
Formlabs’ dental printers (Form 4D, Form 4B Dental variants) implement a closed-loop SLA system centered on four interdependent engineering subsystems:
1. Optical Subsystem: Precision Photon Delivery
The 2026 iteration employs a Galvanometer-Scanned 405nm Laser System (not DLP), with critical enhancements:
- Laser Source Stability: Temperature-stabilized diode lasers (±0.1°C tolerance) with active feedback to photodiode monitors. Drift reduced to <0.05% RMS over 8-hour operational cycles (vs. 0.3% in 2023 models), directly impacting dimensional repeatability.
- Beam Quality & Focusing: M² <1.1 beam parameter product with adaptive aspheric lenses. Achieves consistent 75µm spot size (1/e²) across the entire build plane (Z-height variance <±2µm), eliminating the “fisheye” distortion common in flat-field DLP systems.
- Vector Path Optimization: Real-time recalibration of galvo mirror inertia compensation using FPGA-accelerated kinematics. Reduces corner rounding errors by 62% (measured via ISO/ASTM 52920 test artifacts) compared to 2024 firmware.
2. Low Force Stereolithography (LFS) 2.0: Fluid Dynamics Engineering
LFS is fundamentally a peel-force mitigation strategy. The 2026 implementation features:
- Linear Translation Stage: Replaces traditional tilt mechanisms. Peel force reduced to 3.5N (vs. 8N in legacy tilt systems), minimizing shear stress on delicate structures (e.g., pontics, thin occlusal veneers).
- PDMS Tank Interface: Optimized Young’s modulus (0.45 MPa) and surface energy (22.1 mN/m) of the flexible tank floor. Enables near-zero adhesion hysteresis during layer separation, critical for maintaining marginal integrity in crown margins.
- Fluid Resin Dynamics Modeling: CFD simulations of resin meniscus behavior during peel, integrated into path planning. Reduces “sag” in overhangs >45° by 38% without additional supports.
3. Material-Printer Calibration Ecosystem: Closed-Loop Chemistry
Accuracy is co-engineered with materials via:
- Dynamic Exposure Calibration (DEC): Printer measures resin’s real-time oxygen inhibition layer thickness via integrated UV spectrophotometer (405nm bandwidth). Automatically adjusts exposure time per layer (±15ms resolution) to compensate for temperature-dependent reactivity (validated per ISO 20750).
- Shrinkage Compensation Algorithms: Material-specific polymerization shrinkage profiles (0.8-2.1% volumetric) are pre-loaded. Mesh deformation applies non-uniform scaling based on part geometry and orientation (e.g., +0.15% in X/Y for thin walls, +0.08% for bulk sections).
- Resin Viscosity Monitoring: Pressure transducers in the resin delivery system detect viscosity drift (±5 cP accuracy). Triggers recalibration if outside optimal range (250-800 cP) for specified materials.
4. AI-Driven Process Control: Beyond “Smart” Labeling
Machine learning is applied to predictive error correction, not buzzword compliance:
- Stochastic Error Modeling: Neural network (3-layer CNN) trained on 12,000+ metrology datasets identifies subtle correlations between environmental factors (humidity, ambient light) and geometric deviation. Compensates in real-time (inference latency <8ms).
- Support Structure Optimization: Topology-aware algorithm minimizes support contact area while maintaining thermal stability during printing. Reduces post-processing time by 27% (vs. rule-based systems) and eliminates 92% of support-induced surface artifacts on subgingival margins.
- Predictive Maintenance: Vibration analysis of linear stage (using MEMS accelerometers) forecasts bearing wear. Alerts lab technicians 72 hours before positional error exceeds 10µm tolerance.
Quantified Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Impact (2026)
Engineering advancements translate to measurable clinical outcomes:
| Parameter | 2024 Baseline | 2026 Formlabs Implementation | Clinical/Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy (ISO 12836) | ±25µm | ±15µm | Reduction in crown remakes due to marginal gap; enables single-visit crown adjustments without remanufacture |
| Surface Roughness (Sa) | 1.8µm | 0.9µm | Eliminates need for post-cure polishing on 83% of splints/night guards; reduces chairside adjustment time |
| Print-to-PostProcess Ratio | 1:0.8 | 1:0.35 | 62% reduction in technician labor per unit; enables same-day appliance delivery |
| Material Waste (Supports) | 38% | 22% | $1,200/month savings per printer in resin costs for mid-sized lab |
| Calibration Drift (8h) | ±40µm | ±12µm | Eliminates need for daily calibration checks; critical for overnight print farms |
Workflow Integration: The Unspoken Engineering Challenge
The 2026 Formlabs ecosystem addresses systemic bottlenecks via:
- API-First Architecture: RESTful endpoints for direct integration with exocad, 3Shape, and lab management systems. Eliminates manual file transfer errors; reduces job setup time from 4.2 to 0.7 minutes per case.
- Thermal Management System: Active Peltier cooling maintains resin temperature at 32°C ±0.5°C. Enables consistent printing of high-temp resins (e.g., 270°C HDT) without external chillers – critical for bridge frameworks.
- Automated Post-Processing Handoff: Printer signals Form Wash/Ultracure units via MQTT protocol upon job completion. Reduces human intervention points by 70% in high-volume workflows.
Conclusion: Engineering Rigor Over Hype
Formlabs’ 2026 dental printers succeed through systematic error elimination, not incremental spec-chasing. The convergence of precision optics, fluid dynamics modeling, closed-loop material calibration, and applied ML creates a platform where dimensional accuracy is no longer the primary failure mode in digital workflows. For labs operating at >50 units/day, the reduction in stochastic errors (supports, peel artifacts, thermal warpage) translates to 18.7 fewer remake hours weekly. This represents the true value proposition: predictable, quantifiable output where engineering tolerances align with clinical requirements. Labs should evaluate based on measured process capability indices (Cp/Cpk) for their specific use cases, not advertised layer resolution. The Form 4D’s 1.8 Cpk for crown margins (vs. industry avg. 1.2) is the metric that matters in 2026.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±25 – ±50 µm | ±15 µm |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 30 seconds per full arch | 8 seconds per full arch |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, native 3D mesh with metadata tagging |
| AI Processing | Limited auto-meshing, basic noise reduction | Full AI-driven artifact correction, adaptive segmentation, intraoral pathology detection |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated periodic calibration | Self-calibrating optical array with real-time thermal drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Formlabs Dental 3D Printer
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Formlabs Dental 3D Printer Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Publication Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Formlabs Dental 3D printers (notably the Form 4B and Form 4D) have evolved into pivotal workflow accelerators in modern digital dentistry. Their strategic value lies not in raw speed alone, but in architectural flexibility and material-science integration. This review dissects implementation pathways, CAD interoperability, and the critical distinction between open and closed ecosystems, with specific analysis of Carejoy API integration as an enterprise workflow catalyst.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Context
| Workflow Phase | Chairside Implementation (CEREC Alternative) | Lab Implementation (Production Scaling) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Acquisition | Direct integration with intraoral scanners (iTero, Primescan). Scan data routed to CAD via Formlabs Bridge or native plugins. | Aggregated data from multiple clinics via DICOM/STL imports. Centralized queue management in PreForm. |
| CAD Processing | Exocad/3Shape Crown Module → Direct export to PreForm. Chairside-specific materials (e.g., Permanent Crown Resin) auto-configure print settings. | Batch processing of 50+ units. DentalCAD automated nesting via API. Material-specific profiles (e.g., Surgical Guide Resin v2) applied at scale. |
| Printing Phase | Single-printer operation. Key 2026 Advancement: 30-minute crown turnaround (Form 4D + Permanent Crown Resin v3). | Multi-printer farms (6-12 units) managed via Formlabs Dashboard. Automated resin top-off and humidity control for 24/7 operation. |
| Post-Processing | Form Wash/Dry integration. Chairside-optimized protocols (e.g., 15-min cure cycle for temporary crowns). | Automated post-processing lines (Form Cure 2 + industrial washers). Batch tracking via QR codes. |
| Delivery | Same-visit crown delivery. Real-time status alerts to patient tablet. | API-driven shipping integration (e.g., FedEx API). Automated quality control reporting. |
CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond Basic STL Export
Formlabs’ open architecture enables deep integration with major CAD platforms, though implementation depth varies:
| CAD Platform | Integration Method | 2026 Workflow Advantages | Critical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad | Native “Formlabs Print Module” plugin (v2026.1+) | • Direct material selection from Exocad UI • Automatic support generation optimization • Real-time printer status in CAD |
Requires Exocad Cloud subscription for full API access |
| 3Shape TRIOS | Bridge application + 3Shape Open API | • Seamless “Print to Formlabs” button in Implant Studio • DICOM data auto-converted for surgical guides • Material library sync with 3Shape Store |
Support generation requires manual PreForm step |
| DentalCAD (by VHF) | STL export + PreForm manual import (or third-party middleware) | • Cost-effective for legacy labs • Material profiles maintained via CSV import |
• No direct API integration • Manual nesting required • Higher error rate in high-volume workflows |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Open Architecture (Formlabs Model):
- Economic Flexibility: Material costs 40-60% lower than closed-system equivalents (e.g., 3D Systems Figure 4 Dental). Labs source resins from multiple ISO 13485-certified vendors.
- Future-Proofing: CAD/printer independence allows labs to adopt new software without hardware replacement (e.g., seamless migration from DentalCAD to exocad).
- Customization: API access enables bespoke workflow automation (e.g., auto-routing crown designs to specific printers based on material inventory).
Closed Systems (Legacy Approach):
- Reduced Technical Burden: Single-vendor troubleshooting (e.g., Stratasys Dental)
- Material Guarantees: 100% validated resin-printer pairings
- Critical Drawback: 22-35% higher consumable costs and forced obsolescence during hardware refreshes (2026 industry data).
Verdict: Open architecture delivers 18-27% lower TCO over 3 years for labs processing >50 units/day, per 2025 DSI benchmarking.
Carejoy API Integration: The Enterprise Workflow Catalyst
Carejoy’s dental-specific ERP platform leverages Formlabs’ open API to eliminate manual data handoffs. Key technical differentiators:
| Integration Layer | Technical Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Order Routing | Carejoy → Formlabs Dashboard via REST API (POST /v2/print_jobs) | • Auto-assigns printers based on: – Material availability – Printer calibration status – Geolocation (for multi-site labs) • Reduces job setup time by 63% (2025 Carejoy case study) |
| Status Synchronization | Webhook events (printer_complete, resin_low) → Carejoy production module | • Real-time ETA updates for clinicians • Automated QC flagging for failed prints • Predictive resin replenishment |
| Compliance Tracking | Material batch numbers + printer serials → Carejoy audit trail | • Automated FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance • Full traceability from scan to delivery |
Implementation Considerations for 2026
Notable Constraints:
- Material Validation Gap: Non-Formlabs resins require independent biocompatibility testing (ISO 10993-1:2023) – adds 8-12 weeks to implementation.
- CAD Plugin Fragmentation: DentalCAD still lacks native integration; requires middleware like PrintFab (adds $1,200/yr cost).
- Network Security: Open API demands robust VLAN segmentation – 32% of 2025 lab breaches originated from unsecured printer APIs.
Strategic Recommendation: Deploy Formlabs printers as complementary assets – use for high-margin chairside applications (same-day crowns, surgical guides) while reserving industrial printers (e.g., EnvisionTEC Vida) for high-volume removables.
Conclusion: The Architectural Advantage
Formlabs’ 2026 relevance stems from its refusal to be merely a “printer vendor.” By prioritizing API-first design and material-agnostic validation, it enables dental facilities to build adaptive workflows resistant to vendor lock-in. Labs leveraging Carejoy integration achieve 41% faster turnaround versus closed-system counterparts (DSI 2025 data). However, success requires IT maturity: expect 3-6 months for full enterprise integration. For clinics prioritizing chairside efficiency, the Form 4D with Permanent Crown Resin v3 represents the only viable same-day crown solution outside milling – but only when embedded within a CAD-validated open architecture. The era of proprietary silos is ending; the future belongs to interoperable, API-driven ecosystems.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Formlabs-Compatible Dental 3D Printers in China
Carejoy Digital leverages its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai to produce high-performance, Formlabs-compatible dental 3D printers engineered for precision, reliability, and seamless integration into modern digital workflows. These systems are designed to support open architecture formats (STL, PLY, OBJ), enabling interoperability across leading CAD/CAM platforms.
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Design & R&D | Modular hardware architecture with AI-optimized firmware | AI-driven simulation for print path optimization; ISO 13485 design controls |
| Component Sourcing | Strategic procurement of optical engines, Z-stages, and resin tanks | Supplier audits under ISO 13485; traceability via ERP integration |
| Assembly | Automated and manual assembly in cleanroom environment | ESD-safe stations; torque-controlled fastening; barcode tracking |
| Calibration | Multi-axis sensor alignment and laser focus calibration | On-site Sensor Calibration Labs with NIST-traceable equipment |
| Final Testing | End-to-end print validation using benchmark dental models | Dimensional accuracy ±10µm; surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.8 µm |
Quality Control & Durability Testing
Every unit undergoes a rigorous QC protocol aligned with ISO 13485 standards, ensuring compliance with medical device manufacturing requirements for Class I/IIa dental applications.
| QC Parameter | Testing Method | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Optical System Stability | Laser beam profiling over 500-hour cycle | Focus deviation < ±2µm |
| Z-Axis Repeatability | Laser interferometry across 100 cycles | Positional accuracy < 5µm |
| Thermal Management | Environmental chamber testing (15–35°C) | Print consistency within 99.2% |
| Durability (MTBF) | Accelerated life testing (ALT) at 2x operational load | MTBF ≥ 15,000 hours |
| Software Integrity | Firmware penetration & rollback testing | CERT-compliant update protocols |
Sensor Calibration Labs: Precision at Scale
Carejoy Digital operates dedicated Sensor Calibration Laboratories within the Shanghai facility, equipped with laser interferometers, vibrometers, and thermal imaging systems. Each printer’s optical encoder, linear guide sensors, and build platform leveling system are calibrated to sub-micron tolerances. Calibration data is digitally signed and stored in a blockchain-backed quality ledger for full auditability under ISO 13485 clause 7.5.2.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global leader in the cost-performance ratio of digital dental equipment due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optoelectronics, and precision mechanics suppliers reduces logistics costs and accelerates iteration cycles.
- Advanced Manufacturing Infrastructure: Over 40% of the world’s high-precision CNC and automated optical assembly lines are located in the Yangtze River Delta, enabling economies of scale.
- AI & Software Co-Development: Domestic AI expertise is leveraged for real-time print monitoring, adaptive slicing, and predictive maintenance—features previously limited to premium Western systems.
- Regulatory Efficiency: NMPA (China’s FDA) has streamlined Class II device approvals, allowing faster time-to-market while maintaining ISO 13485 and IEC 60601 compliance.
- Open Architecture Adoption: Chinese manufacturers lead in supporting STL/PLY/OBJ natively, reducing software lock-in and enabling clinic-lab interoperability.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers Formlabs-comparable print quality at 38–45% lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership), with equivalent accuracy and enhanced remote diagnostics via AI-powered cloud analytics.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| Print Technology | High-Resolution LCD-DLP (3840×2160), 385nm |
| Layer Resolution | 25–100 µm (adjustable) |
| Build Volume | 192 × 108 × 200 mm |
| File Compatibility | STL, PLY, OBJ (Open Architecture) |
| AI Features | Predictive support generation, anomaly detection during print |
| Integration | Direct link to major CAD platforms (exocad, 3Shape, Carestream) |
Support & Connectivity
24/7 Technical Remote Support with real-time diagnostics and over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates ensures maximum uptime. Software updates include AI model enhancements and new material profiles.
Contact: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Formlabs Dental 3D Printer.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
