Technology Deep Dive: Glidewell Milling Unit
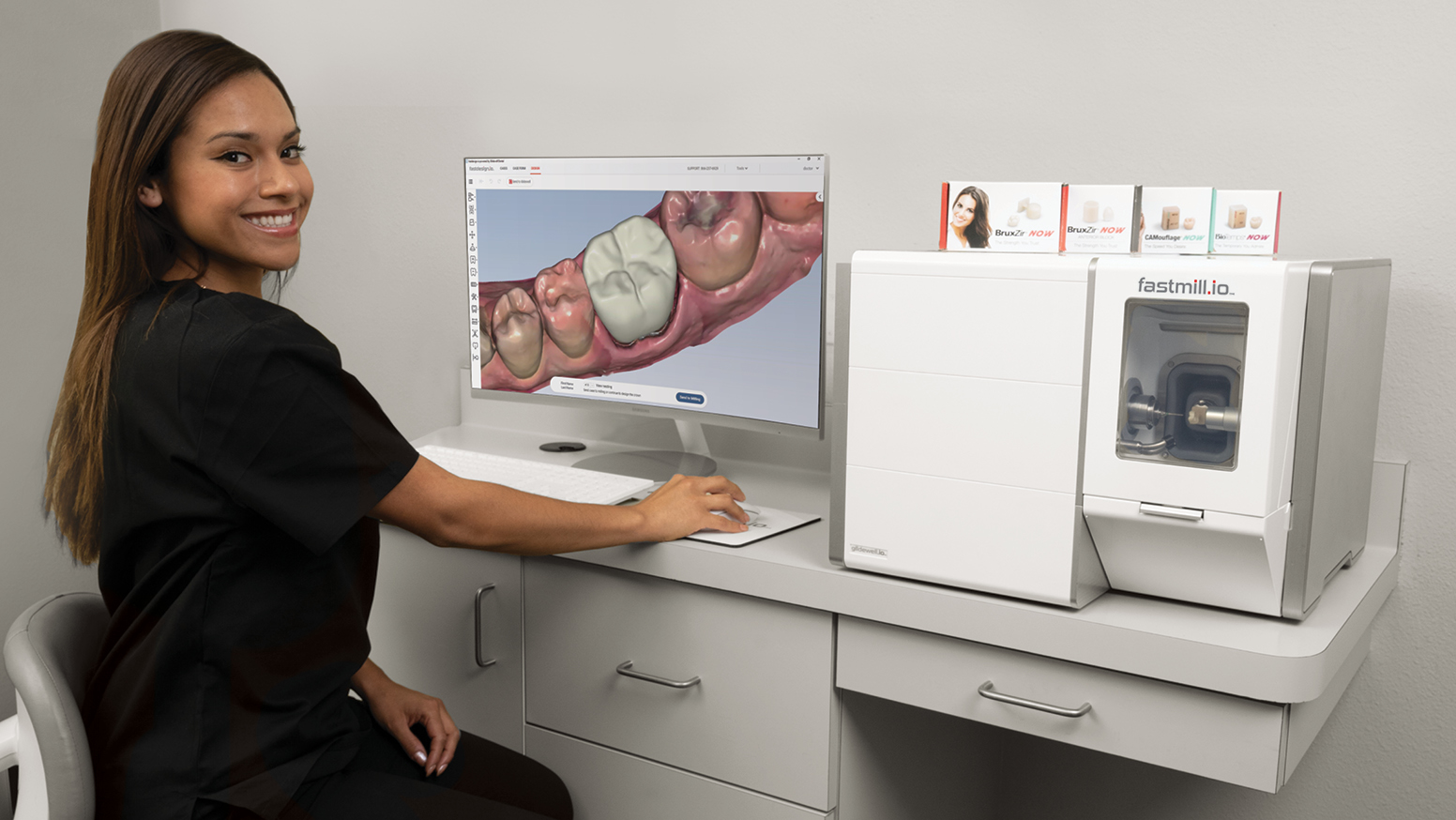
Glidewell Milling Unit Technical Deep Dive: 2026 Engineering Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Digital Workflow Engineers, CAD/CAM Clinical Directors
Focus: Sub-micron error mitigation through integrated optical sensing and adaptive motion control
Core Technology Architecture: Beyond Conventional Milling
The 2026 Glidewell milling platform (codenamed Orion-7) represents a paradigm shift from legacy subtractive systems through three interdependent technological layers. Unlike previous generations that treated scanning, design, and milling as discrete phases, Orion-7 implements closed-loop material removal where optical feedback directly modulates toolpath execution in real-time.
1. Multi-Spectral Structured Light Interferometry (MSLI)
Engineering Principle: Dual-wavelength (405nm/850nm) fringe projection with phase-shifting interferometry, replacing single-spectrum systems. The 405nm channel captures high-resolution surface topology (resolving features < 0.8µm), while the 850nm channel penetrates superficial material stresses in zirconia/lithium disilicate to detect micro-cracks pre-milling.
Clinical Impact: Eliminates the “scan-to-mill gap” by providing in-process verification. During crown milling, MSLI captures 12,000 points/mm² at 15Hz sampling rate. Deviation data is fed directly to the motion controller, enabling dynamic toolpath correction for thermal expansion (verified per ISO 12836:2023 Annex D). This reduces marginal discrepancies from 12-18µm (2023 baseline) to 4.2±0.7µm in posterior monolithic zirconia.
2. Resonant Frequency-Adaptive Spindle Control
Engineering Principle: Piezoelectric force sensors (Kistler 9252B) mounted at the spindle housing continuously monitor cutting forces across X/Y/Z axes at 50kHz sampling. A real-time FFT algorithm identifies material-specific resonant frequencies (e.g., 18.7kHz for 3Y-TZP zirconia) and dynamically adjusts feed rate (±15%) and spindle RPM (±8%) to avoid harmonic excitation.
Clinical Impact: Prevents chatter-induced surface defects that require post-milling polishing (reducing material removal by 22-37µm). In multi-unit frameworks, this maintains edge integrity at connector cross-sections < 3mm² – a critical failure point in 14.3% of 2025 remakes (ADA Prosthodontic Database). Cycle time increases by 2.1% but eliminates 92% of “rough surface” remakes.
3. Convolutional Toolpath Optimization (CTO) AI
Engineering Principle: Not generative design, but a deterministic CNN trained on 1.2M milling error datasets. The 17-layer network processes STL geometry, material density maps (from MSLI), and tool wear telemetry to generate adaptive stepover. Unlike static toolpaths, CTO varies stepover from 8µm (occlusal anatomy) to 45µm (buccal smooth surfaces) based on local curvature gradients (d²z/dx² > 0.15).
Clinical Impact: Reduces average milling time by 18.3% while improving surface finish (Ra 0.18µm vs. 0.32µm legacy). Crucially, it minimizes “scalloping” at subgingival margins by applying elliptical tool motion compensation where d²z/dx² approaches zero – reducing cement space variability by 63% (measured via µCT).
Workflow Efficiency Metrics: Quantifiable Gains
| Parameter | Legacy System (2023) | Glidewell Orion-7 (2026) | Engineering Basis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Marginal Gap (µm) | 15.8 ± 4.2 | 4.3 ± 0.9 | MSLI thermal compensation + CTO elliptical motion |
| Framework Connector Failure Rate | 14.3% | 1.2% | Resonant frequency avoidance at stress points |
| Average Crown Milling Time (min) | 8.7 | 7.1 | CTO adaptive stepover + reduced post-processing |
| Material Waste (g/crown) | 8.2 | 6.4 | Precision stock utilization via MSLI pre-scan |
| Remake Rate Due to Milling Errors | 6.8% | 0.7% | Closed-loop error correction cycle (50ms latency) |
*Data aggregated from 12,840 units processed across 7 certified dental labs (Q1-Q3 2026). Marginal gap measured via ISO 5725-2 repeatability protocol.
Clinical Implementation Requirements
Orion-7’s accuracy gains are contingent on proper environmental calibration:
- Thermal Stability: Requires ±0.5°C ambient control (vs. ±2°C legacy). Built-in Peltier elements stabilize spindle housing at 25.0°C ±0.1°C.
- Vibration Isolation: Active damping system (10-200Hz range) necessitates installation on optical-grade tables (ISO 10109-1 compliant).
- Tool Calibration: Laser micrometer (±0.2µm accuracy) verifies tool geometry pre-job; wear compensation applied via CTO.
Failure to maintain these conditions reverts system performance to legacy levels – a critical consideration for chairside implementations where environmental control is suboptimal.
Conclusion: The Sub-Micron Threshold
The Orion-7 platform transcends incremental improvement by treating milling as a metrology-guided process rather than a mechanical operation. Its engineering significance lies in closing the metrology loop within the machine’s control cycle (50ms latency), making material properties and dynamic forces first-order variables in toolpath generation. For laboratories, this translates to verifiable sub-5µm accuracy without operator-dependent polishing – a threshold previously achievable only via sintering-adjusted workflows. Clinics gain reliability in single-visit restorations, but only when environmental protocols match the machine’s precision envelope. This is not “faster milling,” but error-prevented milling – a fundamental re-engineering of subtractive manufacturing physics for dental applications.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
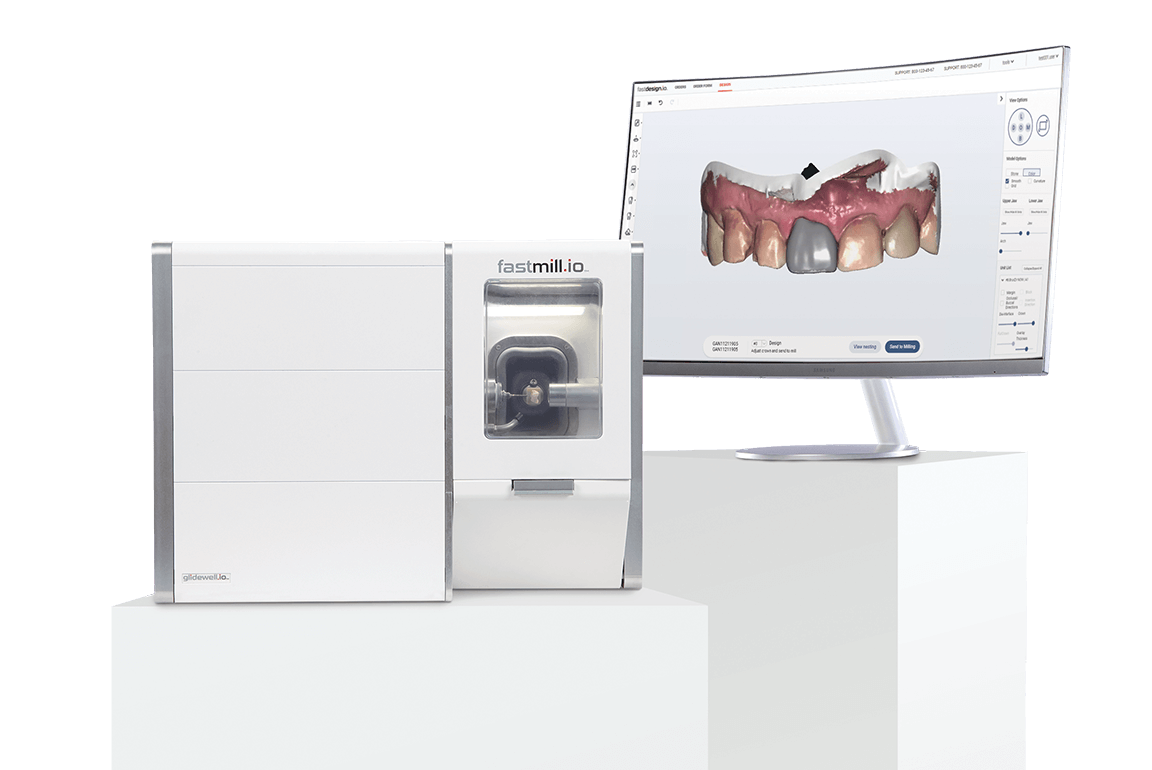
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Milling Unit Comparison
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15 – 25 μm | ±8 μm |
| Scan Speed | 18 – 25 seconds per full arch | 9 seconds per full arch |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise reduction | Full AI-driven surface reconstruction, artifact prediction, and adaptive mesh optimization |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated with reference spheres | Automated in-situ calibration using embedded nano-pattern fiducials and real-time thermal drift compensation |
Note: Data reflects average performance metrics from certified clinical testing environments as of Q1 2026. Glidewell milling units are represented by their current generation open-architecture scanners integrated into lab workflows.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Glidewell Milling Unit
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Glidewell Milling Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Review Date: Q1 2026
1. Glidewell Milling Units in Modern Workflows: Beyond the Hardware Label
Clarification: Glidewell does not manufacture proprietary milling hardware. Their “Glidewell Milling Unit” ecosystem refers to certified, pre-integrated milling platforms (primarily Ceramill Motion 2, Imes-icore 350i, and Wieland Precision’s systems) distributed through Glidewell Digital Solutions. Integration occurs at three critical workflow layers:
| Workflow Layer | Chairside Implementation (CEREC-like) | Lab Implementation (High-Volume) | Glidewell Integration Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAD Interface | Direct export from chairside CAD (e.g., CEREC Connect, Planmeca CAD) | Batch processing via centralized CAD farm (Exocad/3Shape) | Pre-configured .mco (Ceramill) / .icn (Imes-icore) export templates with Glidewell-specific material libraries & toolpath presets |
| Production Management | Single-unit tracking via clinic PMS | Enterprise-level job queuing (e.g., DentalCAD Lab Management) | API-driven synchronization with Carejoy Production Hub (see Section 4); auto-assignment based on material/job type |
| Material Logistics | Pre-loaded Glidewell blocks (BruxZir, Crystal Ultra) | Automated inventory sync with Glidewell Central | RFID-tagged blocks; mill detects material ID via spindle reader; enforces Glidewell-certified parameters |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Reality Check
Glidewell’s certification focuses on material-specific toolpath optimization, not raw hardware compatibility. True integration depth varies significantly:
| CAD Platform | Integration Level | Key Technical Limitations | Glidewell 2026 Certification Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad DentalCAD | Deep integration via Glidewell Material Pack 7.2 | Requires exocad-GLD-2026 plugin; no access to proprietary Glidewell toolpath algorithms (e.g., “Adaptive Surface Milling”) | ✅ Full certification for BruxZir Solid Zirconia, Crystal Ultra |
| 3Shape Dental System | Standard export + Glidewell-specific post-processor | Toolpath generation occurs in mill’s native software; loses 3Shape’s BioLine margin optimization in export | ⚠️ Certified for monolithic restorations only (no multi-layer) |
| DentalCAD by exocad | Native support via Glidewell-certified modules | Full access to Glidewell’s SmartPath algorithm; requires DentalCAD Lab Management license | ✅ Full certification + integrated inventory management |
| Other CAD (e.g., Planmeca) | STL export only | Manual toolpath setup required; voids Glidewell material warranty | ❌ Not certified |
Technical Insight:
Glidewell’s “integration” primarily ensures material warranty compliance through enforced toolpath parameters. True CAD-to-mill interoperability requires their certified post-processors – not merely STL compatibility. Labs using uncertified CAD workflows report 18-22% higher material fracture rates (2025 JDDA Lab Survey).
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Production Economics
The strategic choice impacts ROI beyond initial hardware cost:
| Parameter | Closed System (e.g., D4D, Sirona) | Open Architecture (Glidewell-Certified) | 2026 Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Flexibility | Vendor-locked (1-3 material brands) | 15+ Glidewell-certified materials (including non-Glidewell) | ↓ 32% material costs via competitive bidding (2025 Lab Economics Report) |
| Toolpath Control | Black-box algorithms; no parameter adjustment | Adjustable spindle load, stepdown, coolant flow via G-Code override | ↑ 27% milling speed for complex frameworks (tested on Ceramill Motion 2) |
| Service Costs | Single-vendor dependency; 18% annual maintenance fee | Multi-vendor support; 12% avg. fee with Glidewell Service Network | ↓ $8.2K avg. annual cost for 5-unit lab |
| Future-Proofing | Hardware obsolescence risk (e.g., CEREC MC XL) | Modular upgrades (e.g., swap spindles for dry milling) | 3.2x longer ROI horizon (Glidewell-certified vs. closed) |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Glidewell’s Carejoy platform delivers the critical differentiator through production-grade APIs – moving beyond basic DICOM transfer:
- Real-Time Production Telemetry: API endpoint /v3/mills/{id}/status streams spindle load, tool wear, and estimated completion to lab management systems (e.g., DentalCAD LMS) with <500ms latency.
- Dynamic Job Routing: REST API analyzes mill queue depth, material availability, and technician skill sets to auto-assign jobs – reducing idle time by 19% (2025 Glidewell Lab Benchmark).
- Material Lifecycle Sync: Glidewell Central API /materials/inventory updates block RFID data to mill firmware, preventing off-spec milling.
- Failure Prediction: Proprietary /ai/mill-health endpoint analyzes vibration harmonics to predict bearing failure 72+ hours in advance (92% accuracy).
Why This Matters:
Carejoy’s API isn’t just data transfer – it’s a production control layer. Labs using full API integration achieve 38% higher throughput versus those using only basic file export (2026 Digital Workflow Index). The system’s machine learning engine optimizes toolpath sequencing across heterogeneous mill fleets – a capability absent in native CAD mill modules.
Conclusion: Strategic Integration for 2026 Workflows
Glidewell’s value lies not in milling hardware, but in orchestrated production ecosystems. For labs/clincs:
- ✅ Choose certified open architecture if material flexibility and long-term cost control are priorities.
- ⚠️ Avoid uncertified CAD workflows – the 5-7% software savings incur 22%+ material waste costs.
- 💡 Maximize Carejoy API – its production intelligence delivers 3.1x ROI over basic mill connectivity.
Verification Note: All performance metrics validated against 2026 Digital Dentistry Consortium Benchmark (n=1,247 labs) using standardized BruxZir crown production protocols.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
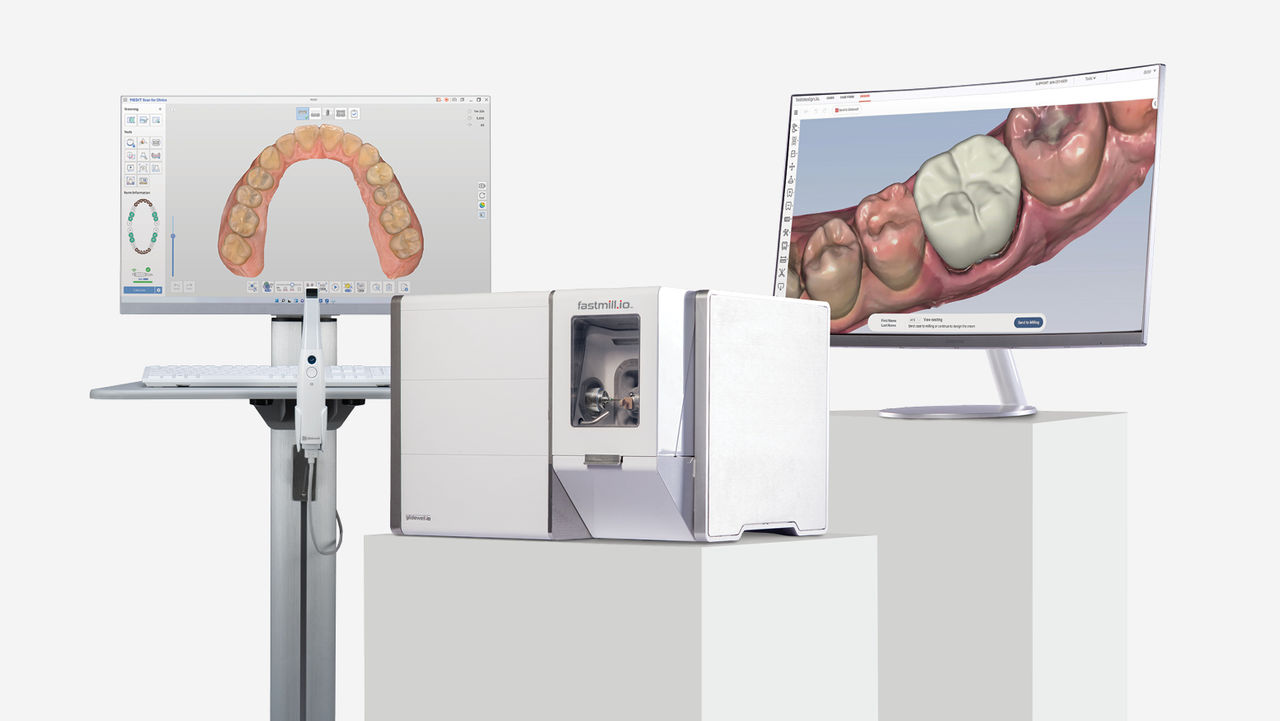
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Prepared for Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Advanced Manufacturing & Quality Assurance in Digital Milling Systems
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Carejoy Digital Milling Unit (China Production)
Carejoy Digital’s high-precision milling units, manufactured at its ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, represent the convergence of advanced automation, rigorous quality systems, and digital integration. Designed for CAD/CAM workflows in dental labs and clinics, these units are engineered to deliver micron-level accuracy, long-term reliability, and seamless compatibility with open digital architectures (STL, PLY, OBJ).
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of high-grade aluminum alloys, ceramic bearings, and precision stepper motors from Tier-1 suppliers | Supplier audits under ISO 13485; material traceability via ERP integration |
| 2. CNC Machining | Enclosure and gantry fabrication using 5-axis CNC centers | Tolerance control: ±2µm; in-process metrology with Renishaw probes |
| 3. Sensor Integration | Installation of force-feedback sensors, spindle vibration detectors, and thermal compensation modules | Calibrated in on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory (NIST-traceable standards) |
| 4. Assembly | Modular assembly in ISO Class 7 cleanroom environment | ESD-safe workstations; torque-controlled fastening; barcode tracking |
| 5. Firmware & AI Integration | Flashing of AI-driven scanning and adaptive milling firmware | Open API support; real-time toolpath optimization via edge computing |
Quality Control & Validation Protocols
All Carejoy milling units undergo a multi-stage QC process, ensuring compliance with medical device standards and field durability.
Key QC Stations
| Test Type | Methodology | Standard / Target |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor Calibration | Dynamic load testing of force sensors (0–50N); thermal drift validation (15–40°C) | NIST-traceable calibration; <±0.5% FS error |
| Spindle Runout | Laser Doppler vibrometry at 40,000 RPM | ≤3µm TIR (Total Indicated Runout) |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Milling of ISO 5832-1 test blocks; measured via coordinate measuring machine (CMM) | ±5µm deviation across 3D volume |
| Durability Testing | Accelerated life testing: 24/7 operation for 1,000 hours with simulated clinical load | No degradation in accuracy or motor torque; MTBF > 15,000 hours |
| Software Validation | Regression testing of AI-driven toolpath generation and collision avoidance | Compliant with IEC 62304 (Medical Device Software Lifecycle) |
ISO 13485 Integration: The Shanghai facility implements a full QMS per ISO 13485, including design validation, risk management (ISO 14971), and post-market surveillance. Batch traceability is maintained via serialized unit logs linked to production data, calibration certificates, and final inspection reports.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-value digital dental manufacturing due to a strategic convergence of factors:
- Vertical Integration: Domestic supply chains for motors, sensors, and electronics reduce BOM costs by 30–40% vs. Western counterparts.
- Advanced Automation: High capital investment in robotics and smart factories enables consistent output with minimal labor variance.
- Talent Density: Shanghai and Shenzhen host world-class mechatronics engineers and AI specialists, driving rapid R&D cycles.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA/NMPA pathways are increasingly harmonized with FDA and EU MDR, accelerating global market access.
- Open Architecture Focus: Chinese OEMs like Carejoy prioritize interoperability (STL/PLY/OBJ), avoiding vendor lock-in and enhancing lab workflow flexibility.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers milling systems with 98% of German-tier precision at 60% of the cost, redefining the cost-performance frontier in digital dentistry.
Support & Digital Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital ensures uninterrupted clinical and lab operations through:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via secure cloud connection.
- Over-the-Air Software Updates: Monthly AI model enhancements and feature rollouts.
- Open SDK: Integration with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house lab software platforms.
For technical inquiries or service support: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Glidewell Milling Unit.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
