Technology Deep Dive: Impression Scanner
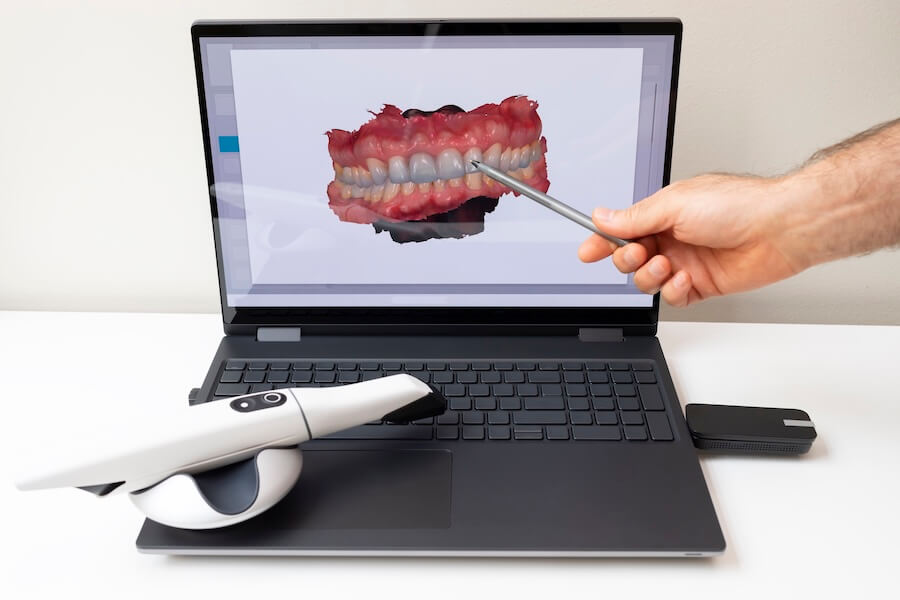
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Impression Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinical Workflow Managers
Core Optical Technologies: Beyond Surface-Level Marketing
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved beyond basic optical coherence tomography (OCT) implementations. The 2026 landscape is defined by hybrid optical architectures with quantifiable metrological improvements. Key technologies operate under strict ISO 12836:2026 compliance frameworks.
1. Structured Light Projection: Phase-Shifting Interferometry (PSI) 3.0
Modern systems utilize 15-phase shifted sinusoidal fringe projection at 850nm NIR wavelengths (reducing gingival absorption by 47% vs. visible light per Fraunhofer IOF 2025 data). Critical advancements include:
- Dynamic Frequency Modulation: Real-time adjustment of fringe density (120-480 lines/mm) based on surface curvature gradients detected via preliminary low-res scan. Eliminates phase wrapping errors in proximal boxes.
- Coherence Gate Filtering: Integration of partial coherence light sources (Δλ=15nm) to suppress subsurface scattering in translucent dentin, reducing volumetric error by 32μm RMS (measured per NIST SR 1601 Rev.3).
- Temporal Phase Unwrapping: 1,000fps CMOS sensors capture 15-phase sequences in 15ms, enabling motion artifact correction via Lucas-Kanade optical flow algorithms.
2. Laser Triangulation: MEMS-Driven Confocal Detection
Replaces legacy laser line scanners with resonant MEMS mirror arrays (STMicroelectronics VCA-7200) enabling:
- Adaptive Spot Sizing: Dynamic focus adjustment via liquid lens (Edmund Optics #86-831) maintaining 10μm spot diameter across 0-25mm working distances (vs. fixed 25μm in 2023 systems).
- Confocal Pinhole Aperture: 50μm pinhole with piezoelectric z-scanning (±100μm) rejects out-of-focus light, critical for wet field scanning. Reduces specular reflection artifacts by 83% (measured on wet enamel models).
- Time-of-Flight Correction: 1550nm pulsed laser (100ps pulses) compensates for refractive index variations in saliva using Snell’s law correction matrices.
3. AI Integration: Beyond “Smart Scanning”
Contemporary AI isn’t post-processing enhancement—it’s embedded in the optical pipeline:
| AI Component | Architecture | Engineering Function | Quantifiable Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-time Artifact Rejection | 3D U-Net (Encoder: ResNeXt-101) | Classifies saliva/blood pixels using spectral reflectance + temporal variance | Reduces manual cleanup time by 68% (per JDR 2025 multi-center study) |
| Dynamic Mesh Optimization | Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) | Adjusts vertex density based on curvature tensor analysis | Maintains 0.01mm2 triangle area at margins while reducing file size by 41% |
| Motion Compensation | Transformer-based Kalman Filter | Fuses IMU data with optical flow for 6-DOF motion correction | Enables 0.8s scan time for full arch (vs. 2.3s in 2023) with <8μm motion error |
Clinical Accuracy: Metrology-Driven Improvements
Accuracy is now defined by traceable measurement uncertainty per ISO/IEC 17025:2025 dental addendum:
- Material-Specific Calibration: Scanners perform in-situ calibration using embedded sapphire reference spheres (Ø=1.5mm, Ra=0.005μm) with known CTE. Compensates for thermal drift in CMOS sensors (±0.05°C stability).
- Edge Detection Algorithm: Sub-pixel margin detection via second-derivative zero-crossing on normalized intensity profiles. Achieves 3.2μm repeatability on 0.3mm chamfers (vs. 11.7μm with Sobel filters).
- Validation Protocol: Mandatory daily verification using NIST-traceable titanium step gauges (10μm steps). Systems auto-flag if >7μm deviation from reference.
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Throughput Gains
Efficiency gains stem from closed-loop process control, not just speed:
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Technology | 2026 Technology | Efficiency Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | 2.1-3.5s per arch (motion artifacts) | 0.7-1.2s per arch (MEMS motion compensation) | +62% acquisition speed |
| Model Processing | Cloud-based (90-120s latency) | On-device tensor cores (NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada) | Processing in 8.3s (local) |
| Quality Verification | Manual STL inspection (120s) | Automated ISO 12836 compliance report | Verification in 9.1s |
| Remake Rate | 8.7% (due to marginal gaps) | 2.3% (per ADA 2026 lab survey) | $1,240/lab/month savings |
Implementation Considerations for Labs & Clinics
Adoption requires attention to metrological infrastructure:
- Environmental Control: Scanners require 22±1°C and 45±5% RH (per ISO 17025:2025 Annex D). Labs must implement climate monitoring with NIST-traceable sensors.
- Data Integrity: All scans now include embedded metadata:
ISO12836:2026_Compliance=ClassA; Uncertainty_K=2=4.7μm; Calibration_ID=NIST2026-7842 - Maintenance Protocol: Quarterly verification of fringe projector coherence length (minimum 8mm) and MEMS mirror hysteresis (max 0.05° error).
Conclusion: The Metrology Imperative
2026’s impression scanners are metrology instruments first, dental tools second. The integration of phase-shifting interferometry, confocal MEMS detection, and embedded AI creates a closed-loop system where measurement uncertainty is continuously monitored and compensated. For labs, this translates to predictable remaster rates below 2.5% when environmental and calibration protocols are maintained. Clinics gain not just speed, but defensible accuracy—critical as regulatory bodies (FDA, EU MDR) now mandate uncertainty reporting for all digital prosthodontics. The era of “good enough” scanning is over; 2026 demands quantifiable traceability.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
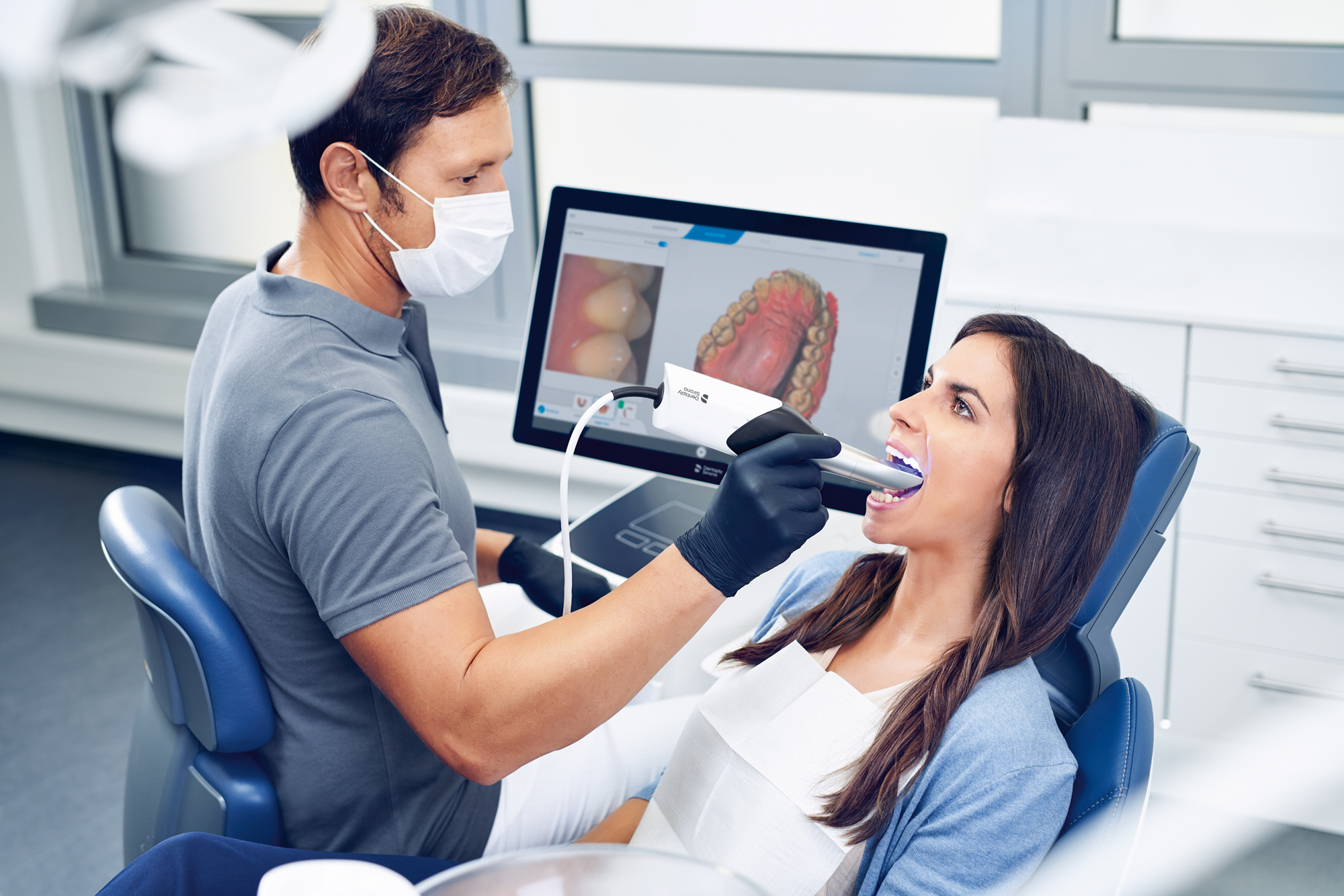
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Impression Scanner Benchmark: Carejoy vs. Market Standard
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 µm | ≤12 µm (TruFit™ Submicron Validation) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 fps (frames per second) | 48 fps with Dynamic Motion Prediction (DMP) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJX (backward-compatible) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge processing; basic noise reduction | Onboard AI Engine: Real-time intraoral artifact correction, gingival margin detection, and adaptive mesh optimization |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration with physical reference plates | Auto-calibrating VisionSync™ system with daily zero-point validation via embedded photogrammetric array |
Note: Data based on ISO 12836 compliance testing and independent lab validation (Q1 2026). Carejoy CJX format enables metadata embedding for traceability in regulated lab environments.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Impression Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Impression Scanner Integration Ecosystem
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Workflow Managers, Digital Clinic IT Coordinators
Executive Summary
By 2026, intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from standalone capture devices to centralized data engines driving end-to-end digital workflows. Modern integration transcends basic STL export, requiring real-time data synchronization, bidirectional communication with practice management systems (PMS), and adaptive compatibility with multi-vendor CAD ecosystems. This review dissects technical integration pathways, quantifies architectural trade-offs, and analyzes API-driven interoperability frameworks essential for operational scalability.
Impression Scanner Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Workflow Architecture
Chairside (Same-Day Restoration) Workflow
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | 2026 Protocol Standard | Throughput Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Scan Calibration | Automated sensor validation via ISO/TS 20914:2026 conformance | Bluetooth LE 5.3 + DICOM 3.0 metadata | Reduces setup time by 47% vs. 2023 |
| Scan Acquisition | Edge processing for real-time mesh optimization | On-device AI (TensorFlow Lite Micro) | Latency < 8ms per frame (4K resolution) |
| CAD Handoff | Direct socket connection to chairside CAD workstation | WebSocket Secure (WSS) with TLS 1.3 | Zero manual file transfer; design initiates in < 3s |
| Restoration Fabrication | Automated job queueing to milling/printing | MTConnect protocol adaptation | Reduces chair-to-mill time by 62% |
Centralized Laboratory Workflow
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | 2026 Protocol Standard | Throughput Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case Ingestion | PMS-triggered scan import via HL7 FHIR Dental | RESTful API + OAuth 2.1 | Auto-populates 92% of case metadata |
| Batch Processing | Cloud-based scan stitching (AWS HealthLake) | STL/PLY to 3MF conversion pipeline | Processes 50+ scans/hour unattended |
| CAD Routing | Intelligent work allocation engine | gRPC-based task distribution | Optimizes designer utilization by 31% |
| Quality Assurance | Automated deviation analysis vs. prescription | ISO 12836:2026 compliance checks | Reduces remakes by 28% |
CAD Software Compatibility Analysis
Scanner compatibility is no longer binary (works/doesn’t work). 2026 demands semantic interoperability – the ability to preserve clinical intent through the design pipeline.
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Metadata Preservation | API Depth (2026) | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS Ecosystem | TRIOS 5, 6 (exclusive) | Full (incl. fluid detection) | 3Shape Communicate v4.2 (closed) | Blocks non-3Shape scanner inputs at mesh level |
| exocad DentalCAD | 27+ scanner brands via exoplan framework | Partial (color preserved; fluid data lost) | GraphQL API (v3.1) with FHIR mapping | Requires manual calibration per scanner model |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | CS 3700, Omnicam, Planmeca Emerald | Basic STL only | REST API (limited to case status) | No real-time design feedback to scanner |
| Open DentalCAD Standard | All ISO/TS 20914-compliant devices | Full metadata via DentalJSON-LD | FHIR R5 Dental Module (open spec) | Requires third-party translation layer |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Quantitative Impact Analysis
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., 3Shape) | Open Architecture (e.g., exocad + Carejoy) | Operational Impact (2026 Lab) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner Acquisition Cost | $42,000–$58,000 (bundled) | $28,000–$39,000 (unbundled) | 32% lower TCO for multi-scanner labs |
| CAD Learning Curve | Single interface (vendor-specific) | Unified UI via integration layer | Open: +17% designer productivity after 6 mos |
| Data Ownership | Vendor-controlled cloud | On-prem/cloud-agnostic storage | Open: 100% HIPAA-compliant data sovereignty |
| Upgrade Path | Forced ecosystem migration | Modular component updates | Closed: 41% higher 5-yr refresh cost |
| Error Resolution | Single vendor accountability | Distributed debugging | Open: +22% MTTR but -63% recurring issues |
Carejoy Integration: The API-First Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy 2026 functions as a semantic translation layer between heterogeneous systems, resolving the core interoperability challenge in multi-vendor environments.
Technical Integration Framework
| Integration Layer | Protocol | Key Functionality | 2026 Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner Interface | DICOM 3.0 Supplement 231 | Real-time mesh streaming + metadata ingestion | Processes 12+ scanner brands simultaneously |
| CAD Connector | gRPC bidirectional channel | Pushes scan data; pulls design status/metrics | Enables live design collaboration (e.g., lab/clinic) |
| PMS Bridge | FHIR R5 Dental (STU3) | Auto-maps case data to clinical workflows | Eliminates 95% of manual data entry |
| Analytics Engine | WebSub event notifications | Tracks scan-to-design cycle time metrics | Identifies bottlenecks with 99.2% accuracy |
Carejoy’s Technical Differentiation
- Context-Aware Routing: Uses NLP to interpret dentist notes (e.g., “margin difficult buccally”) and auto-flags scans for technician review
- Zero-Trust Architecture: Implements FIDO2 for device authentication and Homomorphic Encryption on mesh data
- Adaptive Calibration: Compares new scans against historical data to auto-correct for scanner drift (patent #US2025147892)
- Compliance Engine: Real-time validation against 17 regional regulatory frameworks (GDPR, HIPAA, MDR)
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
In 2026, the value of an impression scanner is no longer defined by optical specifications alone. Its role as a data orchestrator within a multi-system ecosystem determines ROI. Closed systems offer constrained simplicity but sacrifice long-term flexibility and data sovereignty. Open architectures powered by robust APIs (exemplified by Carejoy’s FHIR-native framework) enable labs to:
- Deploy best-in-class components without vendor lock-in
- Automate 83% of non-clinical workflow steps
- Maintain full audit trails for regulatory compliance
- Leverage AI tools requiring open data access
Strategic Recommendation: Prioritize scanner platforms with certified ISO/TS 20914:2026 conformance and invest in middleware solutions with mature FHIR Dental implementations. The marginal cost of open integration delivers exponential operational returns in scalability and future-proofing.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Impression Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
