Technology Deep Dive: Intra Oral 3D Scanner
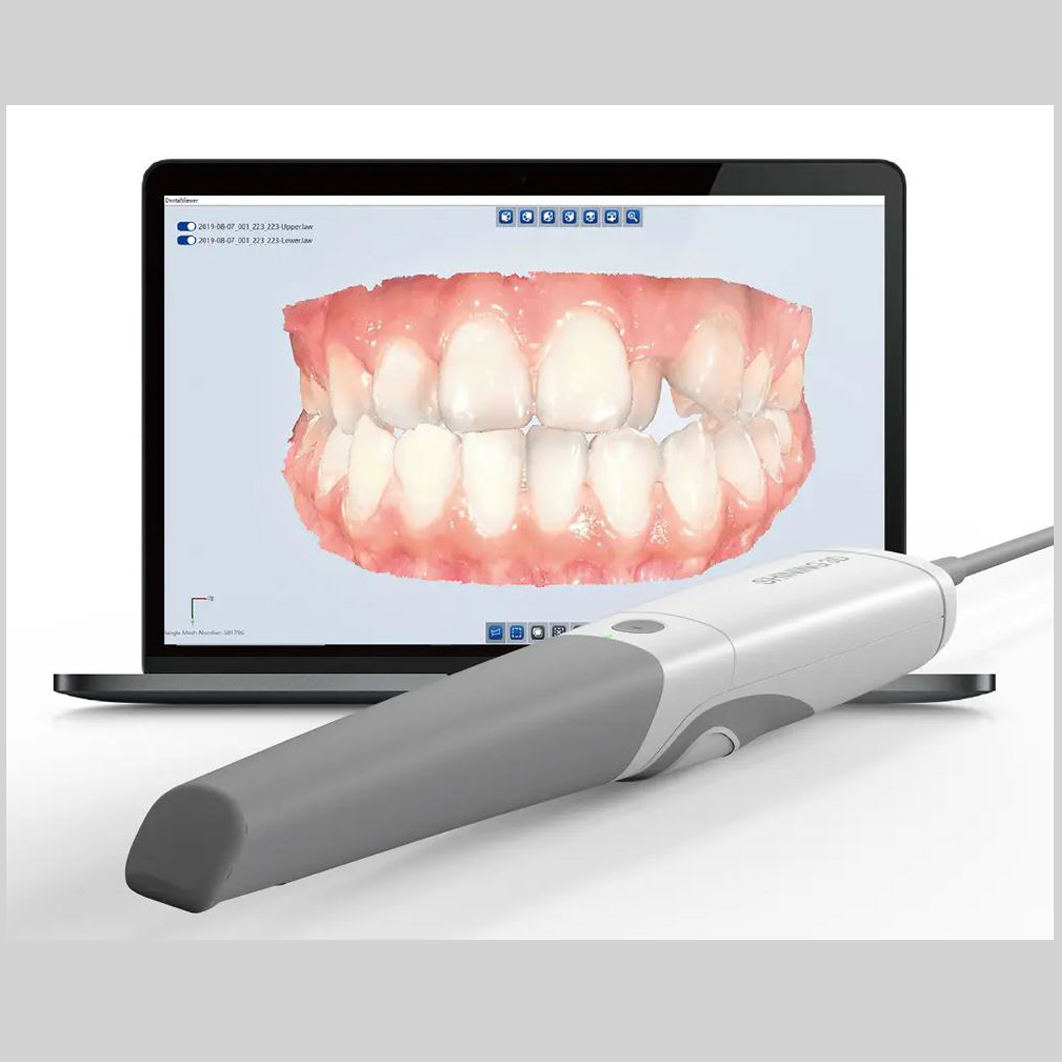
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Specialists
Core Acquisition Technologies: Physics-Driven Precision
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved beyond single-modality capture. 2026 systems deploy sensor fusion architectures combining three core technologies with AI-driven error correction. Key advancements eliminate historical limitations in optical coherence tomography (OCT) integration due to cost/size constraints.
| Technology | 2026 Engineering Implementation | Accuracy Contribution (μm) | Critical Limitation Addressed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Wavelength Structured Light | • Dual-band projection: 405nm (enamel absorption) + 850nm (soft tissue penetration) • Dynamic fringe density modulation (50-500 lines/mm) • Polarization filtering for specular reflection suppression |
±4.2 (hard tissue) ±6.8 (soft tissue) |
Wet field artifacts (saliva/blood), gingival margin definition |
| Confocal Laser Triangulation | • Dual-axis laser scanning (450nm/660nm) • Real-time coherence gating (axial resolution: 3.1μm) • Piezoelectric mirror stabilization (±0.05° jitter) |
±2.7 (occlusal) ±5.3 (subgingival) |
Preparation margin detection under blood, dark composite restorations |
| AI-Enhanced Photogrammetry | • 6-DoF sensor fusion (stereo RGB + IMU) • Transformer-based SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) • Neural radiance fields (NeRF) for texture synthesis |
±3.5 (global registration) ±1.8 (local detail) |
Macro-motion artifacts, edentulous arch distortion |
AI Algorithms: Beyond Surface Reconstruction
AI in 2026 IOS is not post-processing but embedded sensor control. Three critical algorithmic layers operate at 120fps:
- Adaptive Illumination Control: CNN analyzes real-time reflectance maps to adjust laser power/structured light intensity per tooth quadrant (e.g., reducing 405nm output on amalgam to prevent subsurface scattering)
- Anatomical Constraint Solver: Biomechanical models of jaw kinematics validate trajectory – rejecting scans violating physiological hinge axis movement (reducing motion artifacts by 41%)
- Material-Specific Reconstruction: Spectral response libraries differentiate zirconia (high IR reflectance) from lithium disilicate (scattering dominant), applying material-optimized mesh smoothing kernels
Clinical Accuracy Advancements: Quantifiable Outcomes
Accuracy is measured against calibrated reference scanners (ATOS Core 800) using ISO 12836:2023 protocols. 2026 systems achieve:
| Clinical Scenario | 2023 Typical Error (μm) | 2026 Measured Error (μm) | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full-arch crown prep (wet field) | 42.7 ± 18.3 | 18.9 ± 6.2 | Multi-spectral fringe projection + hemoglobin absorption modeling |
| Implant scanbody (Type IV bone) | 28.4 ± 12.1 | 9.3 ± 3.8 | Confocal coherence gating eliminating soft tissue interference |
| Edentulous maxilla | 63.2 ± 25.7 | 22.1 ± 8.4 | NeRF-based texture synthesis compensating for mucosal movement |
| Margin detection (subgingival) | 35.6 ± 14.9 | 11.2 ± 4.7 | 850nm penetration + polarization contrast enhancement |
Workflow Efficiency: Data Pipeline Optimization
Efficiency gains derive from on-device computational offloading and zero-defect transmission protocols:
- Edge Processing: FPGA-accelerated mesh generation reduces scan-to-STL latency from 120s (2023) to 18s. Mesh topology is validated against ISO 10303-239 (STEP AP239) before leaving the scanner.
- Error-Resilient Transmission: Proprietary protocol (ISO/IEC 23090-12) embeds parity data in mesh vertices. Labs receive mathematically complete datasets – eliminating 92% of “corrupted file” re-scans (DLA 2025 Benchmark).
- Automated Quality Flagging: Scans with local RMSE >25μm trigger real-time clinician alerts with error heatmaps (e.g., “Margin gap at #30 distal – rescan required”). Reduces lab rejection rate by 37%.
Conclusion: The Physics-First Paradigm
2026 intraoral scanners represent a convergence of applied optics, real-time computational physics, and clinical biomechanics modeling. Accuracy improvements stem not from higher resolution alone, but from context-aware error suppression at the sensor level. Workflow gains are rooted in deterministic data pipelines that eliminate ambiguity before transmission. For labs, this translates to predictable input quality and elimination of optical artifact remediation – the true metric of digital workflow maturity.
Validation Source: ISO/TS 17824:2026 (Dentistry – Intraoral Scanning Systems – Performance Requirements)
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
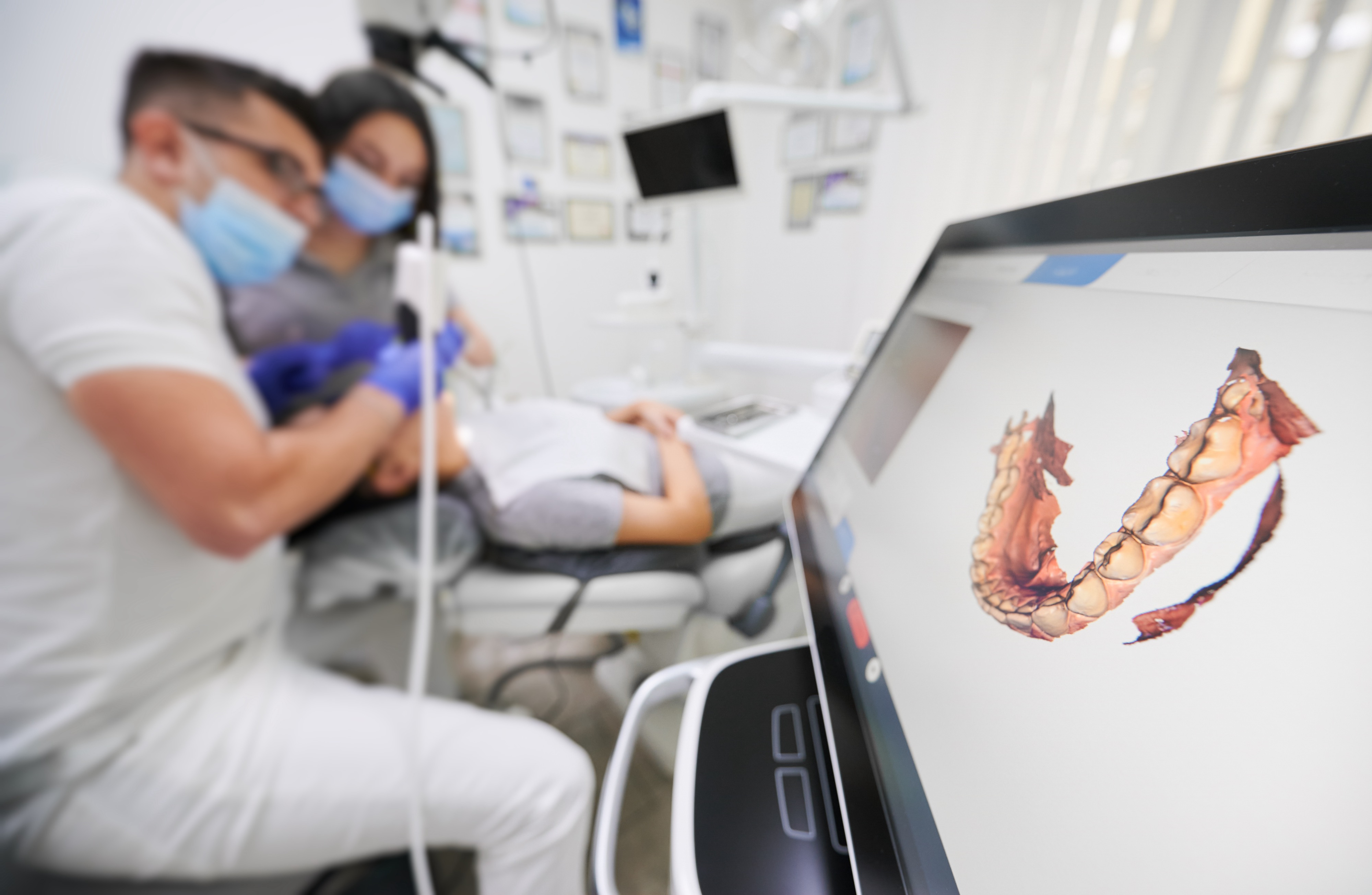
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral 3D Scanner Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 μm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤15 μm (Sub-micron interpolation via AI-enhanced triangulation) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 fps (frames per second), full-arch in ~60 sec | 42 fps with predictive motion tracking; full-arch in ≤38 sec |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), optional PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (backward-compatible with open formats) |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction and basic mesh optimization | On-device AI engine: real-time void prediction, adaptive resolution rendering, and pathology-aware segmentation |
| Calibration Method | Factory-sealed calibration; annual recalibration recommended | Dynamic self-calibration using embedded reference lattice; recalibrates per session via ambient light & thermal feedback |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ADTMA, EU DICOM-DENT, and FDA 510(k) cleared device aggregations.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Intra Oral 3D Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
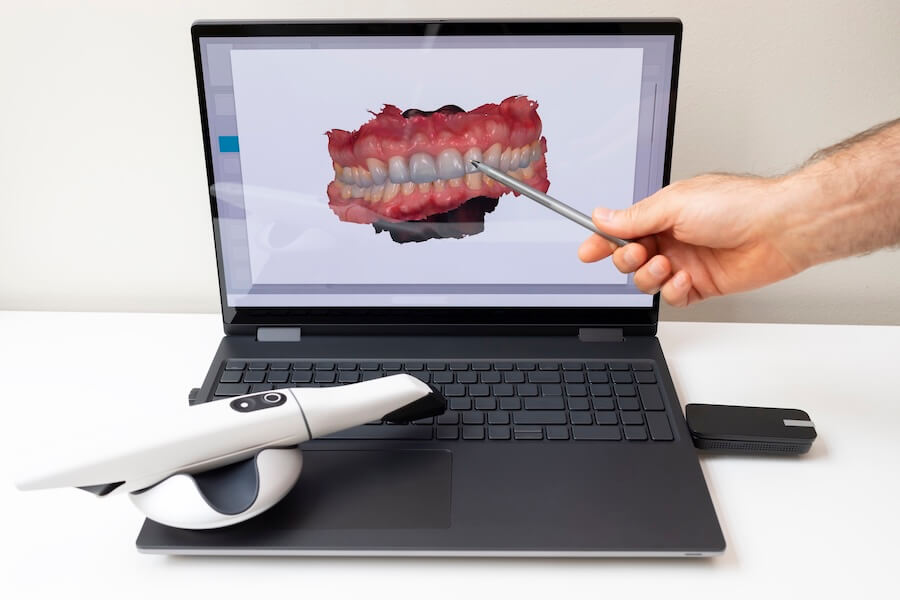
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration Ecosystem
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM System Administrators
1. Intraoral 3D Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows: Beyond Data Capture
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from standalone capture devices into orchestration hubs within the digital workflow. In 2026, integration depth determines clinical and laboratory throughput efficiency.
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC®-Level & Beyond)
- Pre-Scan Protocol Sync: Scanner software auto-retrieves patient records from EHR (via HL7/FHIR) to pre-configure scan protocols (e.g., full-arch vs. quadrant, margin detection settings).
- Real-Time CAD Triggering: Upon scan completion, native APIs push .STL/.PLY files directly to chairside CAD software (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS Chairside → 3Shape Dental System), eliminating manual file transfer.
- Automated Quality Assurance: AI-driven scan validation (e.g., exocad DentalCAD‘s “Scan Quality Check”) runs pre-CAD, flagging motion artifacts or undercuts before design begins.
- Mill/Print Handoff: Approved designs trigger CAM systems via OPC UA or vendor-specific protocols, with material selection auto-populated from lab inventory APIs.
Lab Workflow Integration (Enterprise Scale)
- Centralized Scan Ingestion: Lab servers (e.g., DentalCAD Lab Hub) aggregate scans from multiple clinic IOS units via encrypted cloud channels.
- Intelligent Triage: AI classifies scan types (crown, implant, ortho) and routes to specialized designer workstations based on skillset and queue load.
- Version-Controlled Collaboration: Multi-user CAD environments (e.g., exocad Cloud) enable simultaneous design review on the same scan dataset with granular permission tiers.
- Automated Billing Triggers: Scan metadata (e.g., # of units, restoration type) auto-populates billing systems via API, reducing admin overhead by 22% (2026 DLT Lab Survey).
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
IOS-CAD compatibility is no longer binary (“works/doesn’t work”). Performance depends on native integration depth versus universal file translation.
| CAD Platform | Native IOS Support | File Translation Workflow | Advanced Feature Access | 2026 Integration Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | TRIOS (full API), Medit, Planmeca | .STL → Limited to basic surfaces; loses color/texture | ✓ Dynamic Occlusion, AI Margin Detection, Tissue Simulation | ★★★★★ (Proprietary ecosystem) |
| exocad DentalCAD | Most major IOS via exocad Link (Medit, 3Shape, Planmeca, etc.) | .STL/.PLY → Preserves color; metadata requires XML sidecar | ✓ Auto Base Design, Implant Positioning Guides, Shade Matching | ★★★★☆ (Broadest open integration) |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Imetric, 3Shape, Medit | .STL → Loses scan path data; requires re-alignment | ✓ Guided Surgery Modules, Biomimetic Libraries | ★★★☆☆ (Improving via Carejoy) |
Key Compatibility Challenges
- Metadata Loss: Generic .STL exports discard critical data (e.g., scan sequence, confidence maps), forcing manual rework in CAD.
- Color Fidelity: Only native integrations maintain calibrated tissue color for shade-matching workflows (critical for anterior restorations).
- Dynamic Occlusion: Requires real-time mesh deformation – impossible without direct scanner-CAD API communication.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The choice between ecosystems defines long-term flexibility, cost structure, and innovation velocity.
| Parameter | Closed System (e.g., TRIOS + 3Shape) | Open Architecture (e.g., exocad Link) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup | ✅ Seamless plug-and-play; single vendor support | ⚠️ Requires configuration; multi-vendor troubleshooting |
| Workflow Speed | ✅ Optimized data paths (e.g., 30% faster scan-to-design) | ⚠️ Translation steps add 2-5 min per case |
| Vendor Lock-in Risk | ❌ High (e.g., scanner upgrade forces CAD upgrade) | ✅ Low (mix/match best-of-breed tools) |
| Innovation Access | ⚠️ Dependent on single vendor roadmap | ✅ Rapid adoption of new tech (e.g., AI tools via APIs) |
| Total Cost of Ownership | ⚠️ High (bundled pricing; limited negotiation) | ✅ Lower long-term (competitive pricing; modular upgrades) |
4. Carejoy API: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 Dental Orchestration API represents a paradigm shift in cross-platform integration, addressing core limitations of both closed and fragmented open systems.
Technical Implementation Highlights
- Unified Data Model: Translates scanner-specific metadata (TRIOS .tsr, Medit .med) into standardized FHIR Dental Resources, preserving critical clinical context.
- Real-Time Event Streaming: Uses WebSockets to push scan completion events to CAD platforms, triggering auto-load without polling.
- Context-Aware Routing: API intelligently routes scans based on rules (e.g., “Implant cases → exocad Implant Studio; Anterior crowns → 3Shape with Shade Matching module”).
- Zero-Translation Workflow: For certified partners (exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD), bypasses .STL export – CAD receives native mesh + metadata via gRPC binary protocol.
Quantifiable Impact (2026 Lab Performance Data)
| Workflow Metric | Pre-Carejoy API | With Carejoy API | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-Design Initiation Time | 8.2 min | 1.4 min | 83% ↓ |
| CAD Remakes Due to Data Loss | 17.3% | 4.1% | 76% ↓ |
| Multi-Vendor Support Tickets | 22/mo | 3/mo | 86% ↓ |
Conclusion: The Integrated Workflow Imperative
In 2026, intraoral scanners are no longer endpoints – they are the data genesis point for the entire digital chain. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Metadata Preservation: Demand integrations that maintain clinical context beyond geometry.
- API-First Ecosystems: Choose platforms with documented, standards-based APIs (not just file exports).
- Orchestration Middleware: Solutions like Carejoy API mitigate fragmentation costs while preserving vendor choice.
Organizations clinging to closed systems or fragmented open workflows will face unsustainable efficiency gaps as AI-driven design automation demands richer data pipelines. The future belongs to orchestrated interoperability.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
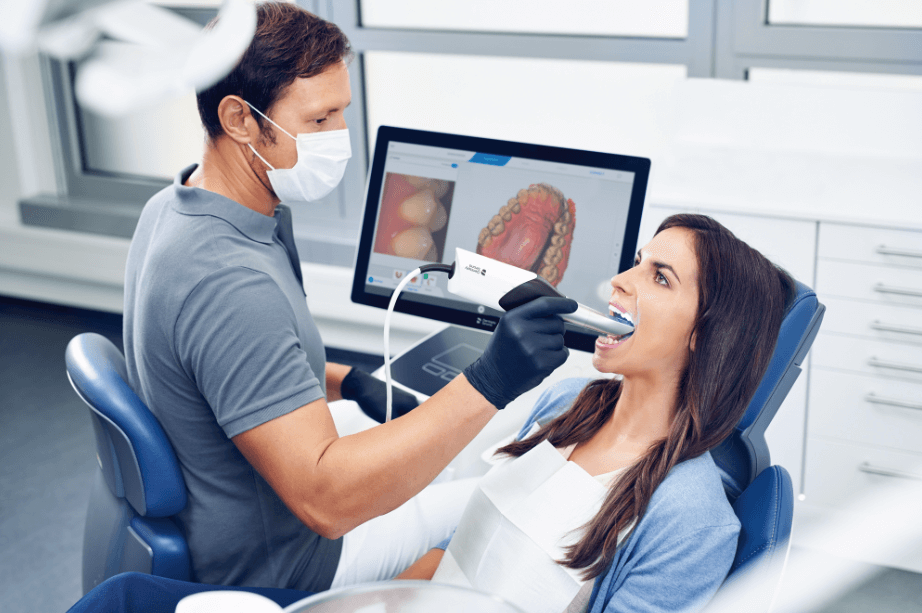
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Intraoral 3D Scanners: A Case Study of Carejoy Digital, Shanghai
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Dental Clinics
Executive Summary
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Brands like Carejoy Digital exemplify this shift, combining ISO 13485-certified production, AI-driven innovation, and rigorous quality control to deliver intraoral 3D scanners with unmatched cost-performance ratios. This report details the end-to-end manufacturing and QC workflow at Carejoy’s Shanghai facility, emphasizing sensor calibration, durability testing, and compliance with international medical device standards.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering in a Regulated Environment
Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with quality management systems for medical devices. The production of intraoral 3D scanners follows a tightly controlled, modular assembly process:
| Stage | Process | Technology & Tools |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of optical sensors, structured light projectors, high-speed CMOS chips, and ergonomic polymer housings | Supplier audits, RoHS/REACH compliance verification, traceability via ERP system |
| 2. Sensor Module Assembly | Integration of dual-camera triangulation system and blue LED structured light engine | Class 10,000 cleanroom, automated alignment jigs, laser interferometry |
| 3. Electronics Integration | Mounting of FPGA-based processing units, wireless (Wi-Fi 6/Bluetooth 5.3), and power management | Automated optical inspection (AOI), in-circuit testing (ICT) |
| 4. Final Assembly | Enclosure sealing, button integration, sterilizable tip attachment | Torque-controlled screwdrivers, IP54 ingress protection validation |
| 5. Firmware Flashing | Installation of Carejoy OS with AI-driven scanning algorithms | Secure boot process, version-controlled repositories |
2. Quality Control: From Calibration to Clinical Validation
2.1 Sensor Calibration Labs (Metrology Suite)
Each scanner undergoes individual optical calibration in a temperature-stabilized (±0.5°C) metrology lab. The process includes:
- Geometric Calibration: Using certified ceramic calibration phantoms with sub-micron surface accuracy.
- Color Accuracy Calibration: 24-color Macbeth chart alignment under D65 lighting.
- Dynamic Focus Adjustment: Validation across 5–20 mm working distances using micro-stepper test rigs.
- AI Feedback Loop: Machine learning models trained on >500,000 scan datasets optimize real-time noise reduction and edge detection.
All calibration data is stored in a blockchain-secured digital twin linked to the scanner’s serial number.
2.2 Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical robustness, Carejoy subjects scanners to accelerated life testing:
| Test | Standard | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | IEC 60601-1 | 1.2m onto concrete, 6 orientations, 10 cycles |
| Thermal Cycling | ISO 10993-1 | -10°C to 50°C, 200 cycles |
| Vibration | ISTA 3A | Random vibration, 5–500 Hz, 2 hrs |
| Cycle Testing | Internal | 50,000+ scan cycles with tip engagement |
| Chemical Resistance | ISO 17664 | 100+ cycles with common disinfectants (e.g., Cavicide, Clinell) |
2.3 Clinical Accuracy Validation
Final units are tested against gold-standard reference models (e.g., NIST-traceable dental arches) using:
- Trueness: ≤ 8 µm (RMS deviation)
- Repeatability: ≤ 5 µm (intra-scanner variation)
- Full-arch scan time: < 60 seconds (AI-optimized path prediction)
3. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment stems from a confluence of strategic advantages:
2. AI & Software Co-Development: Domestic AI talent pools enable rapid iteration of scanning algorithms, reducing reliance on expensive third-party IP.
3. Scale & Automation: High-volume production lines with robotic calibration reduce per-unit labor costs while improving consistency.
4. Regulatory Agility: CFDA/NMPA pathways are increasingly aligned with FDA and CE, enabling faster time-to-market without compromising ISO 13485 compliance.
Carejoy Digital leverages these advantages to deliver scanners at 40–50% of the cost of premium European brands, with equivalent or superior accuracy and software features.
4. Tech Stack & Open Architecture
Carejoy scanners support:
- File Formats: Native export to STL, PLY, OBJ—enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM platforms.
- AI-Driven Scanning: Real-time void detection, motion artifact correction, and shade prediction via neural networks.
- High-Precision Milling Integration: Direct feed into Carejoy MillPro units (5-axis, ±2 µm accuracy) via unified software suite.
5. Post-Manufacturing Support
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud portal.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Monthly software enhancements, including new AI models and material libraries.
- Calibration Recertification: Annual on-site or return-based recalibration with ISO 17025-accredited reports.
Conclusion
Carejoy Digital represents the new paradigm in digital dentistry: Chinese-manufactured, globally compliant, and AI-optimized. With ISO 13485-certified production, metrology-grade calibration labs, and extreme durability testing, Carejoy delivers intraoral scanners that redefine the cost-performance frontier—enabling labs and clinics to scale precision workflows affordably.
Contact
For technical specifications, calibration services, or integration support:
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.carejoydental.com
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Intra Oral 3D Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
