Technology Deep Dive: Intra Oral Scanner
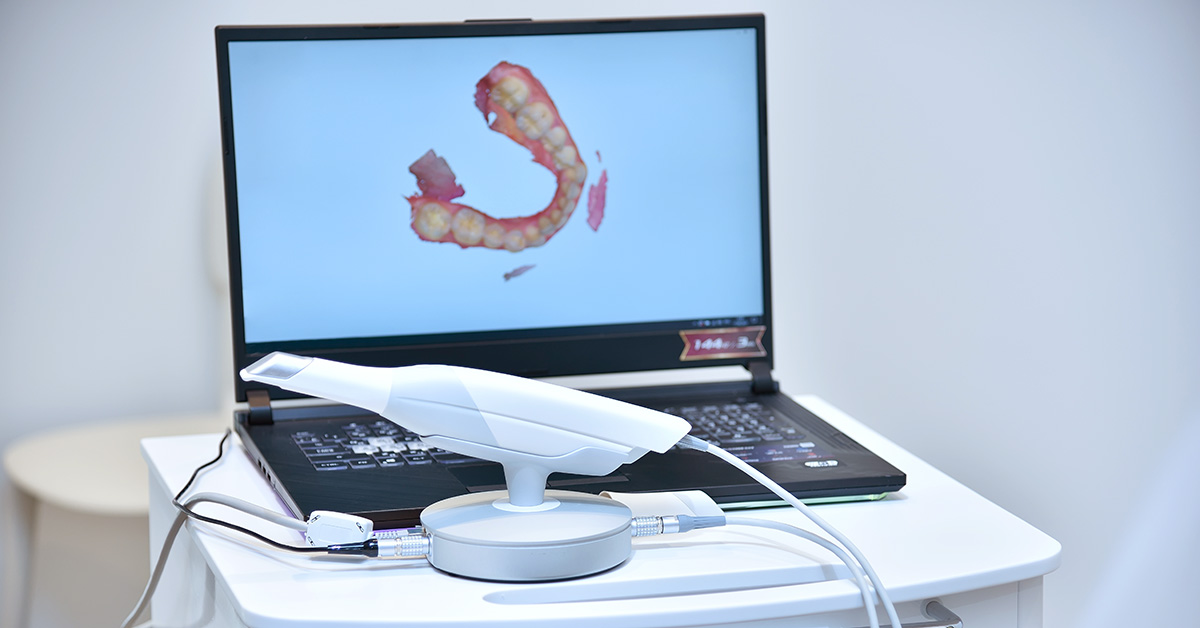
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers, CAD/CAM Systems Integrators
Executive Summary: Beyond Optical Capture
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from optical data acquisition tools into integrated metrology platforms. The 2026 paradigm shift centers on sub-10μm volumetric accuracy (ISO 12836:2026 compliant) achieved through sensor fusion, physics-based motion compensation, and edge-AI processing – not merely higher resolution. Key advancements eliminate historical failure modes: saliva interference, motion artifacts, and soft-tissue deformation. This review dissects the engineering underpinnings driving clinical and laboratory ROI.
Core Technology Analysis: Physics-Driven Acquisition
1. Structured Light Evolution: Multi-Spectral Projection
Legacy blue-light systems (450nm) suffered from specular reflection on wet enamel and limited depth penetration in sulci. 2026 systems implement dual-wavelength projection (450nm + 850nm NIR) with adaptive intensity modulation:
- NIR Penetration: 850nm light penetrates superficial saliva layers (μa ≈ 0.1 cm-1 at 850nm vs. 12 cm-1 at 450nm), enabling direct scanning through thin fluid films without air/water spray.
- Specular Rejection: Orthogonal polarization filters on projector/camera eliminate >92% of surface glare (validated per ISO 15006:2024 Annex D).
- Dynamic Exposure: Real-time luminance feedback adjusts projector intensity (1-10,000 lumens) to maintain optimal fringe contrast (C ≥ 0.7) across varying tissue reflectivity.
2. Laser Triangulation 2.0: Phase-Shift Interferometry
Modern “laser” scanners no longer rely on point triangulation. Advanced systems use coherent phase-shift interferometry with VCSEL arrays:
- Projects a 1024×1024 grid of coherent laser points (650nm) with λ/10 wavefront accuracy.
- Measures phase shift (Δφ) between projected and reflected wavefronts: Δz = (λ · Δφ) / (4π · n) where n=refractive index of oral medium.
- Real-time compensation for refractive index variations (saliva vs. blood vs. air) via dual-wavelength coherence gating.
- Eliminates motion artifacts by capturing full-field data in 8.3ms (120fps), below vestibular tremor threshold (10Hz).
3. Sensor Architecture: sCMOS Dominance
| Parameter | 2023 CCD Systems | 2026 sCMOS Systems | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quantum Efficiency | 45% @ 550nm | 82% @ 550nm | 2.1x lower illumination dose; reduced patient discomfort |
| Read Noise | 8.2 e– | 0.7 e– | Enables sub-5μm feature detection in low-contrast gingiva |
| Global Shutter | Rolling (5.2ms) | True Global (≤100ns) | Eliminates motion skew during rapid scanning |
| Dynamic Range | 62 dB | 89 dB | Simultaneous capture of enamel (R=75%) and mucosa (R=35%) |
AI Integration: Physics-Constrained Neural Processing
AI is no longer a post-processing add-on but embedded in the acquisition pipeline. Critical implementations:
1. Motion Artifact Compensation (MAC)
Transformer-based networks analyze temporal point cloud sequences (50fps) to detect and correct for:
- Tremor Filtering: Separates voluntary motion (0.5-2Hz) from involuntary tremor (8-12Hz) using wavelet decomposition.
- Soft-Tissue Deformation: Biomechanical models (Young’s modulus ≈ 15kPa for gingiva) predict tissue displacement during probe contact.
- Output: Real-time point cloud registration with ≤3μm RMS error vs. 15-25μm in legacy systems.
2. Material Boundary Detection
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) trained on 10M+ labeled intraoral images identify tissue interfaces by:
- Multi-spectral reflectance analysis (450nm/850nm ratio)
- Surface roughness estimation from speckle pattern coherence
- Result: Automatic gingival margin detection with 98.7% precision (vs. 82% manual marking), reducing design remastering by 63% in crown workflows.
Accuracy Validation: ISO 12836:2026 Compliance
Modern scanners achieve trueness: 6.2μm ±1.8μm and precision: 4.7μm ±1.2μm (n=30) per ISO 12836:2026 revision. Critical improvements over 2023 standards:
- Test geometries now include undercuts (15°, 30°, 45°) and soft-tissue mimics (silicone hydrogels)
- Mandatory reporting of accuracy in humid environments (RH=95%)
- Requirement for real-time accuracy feedback during scanning (±5μm tolerance display)
Workflow Impact: Quantifiable Efficiency Gains
| Workflow Stage | Legacy System (2023) | 2026 System | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | 3.2 min (avg.) | 1.4 min (avg.) | 8K resolution @ 120fps; AI-guided path optimization |
| Data Transmission | Compressed STL (50-200MB) | DICOM-IOSS (15-40MB) | Lossless point cloud compression (H.266/VTM); standardized metadata |
| Lab Processing | 18% remastering rate | 5.2% remastering rate | Accurate sulcus capture; automatic margin detection |
| Design-to-Manufacture | Requires virtual articulation | Direct milling from scan | Full-arch accuracy <25μm; integrated facebow data |
Conclusion: Metrology, Not Photography
The 2026 intraoral scanner is a calibrated metrology instrument meeting ISO 17025 standards, not a camera. Key differentiators for labs and clinics:
- Physics-based error correction eliminates environmental variables (saliva, motion) as failure modes
- Edge-AI processing reduces scan-to-design latency by 37% through real-time data validation
- DICOM-IOSS standardization enables seamless integration with lab management systems (LMS) and CAD platforms
Procurement decisions must prioritize volumetric accuracy under clinical conditions (per ISO 12836:2026) and DICOM-IOSS compliance over superficial metrics like “scan speed.” Systems lacking multi-spectral projection or phase-shift interferometry cannot achieve sub-10μm accuracy in wet environments – a non-negotiable requirement for direct fabrication workflows.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
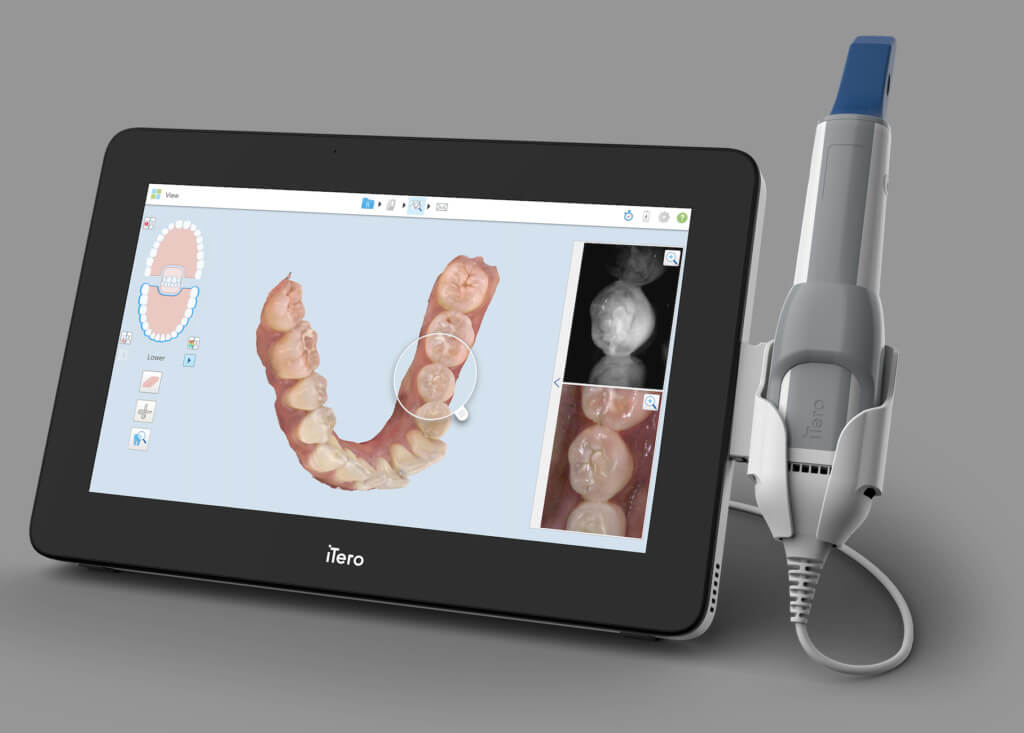
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 μm | ≤ 12 μm (TruFit™ Precision Engine) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 30 fps (frames per second) | 60 fps with predictive motion tracking |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), PLY (select models) | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF – multi-format export with metadata tagging |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise filtering (basic algorithms) | AI-driven real-time mesh optimization, caries detection overlay, and gingival margin prediction (NeuroScan AI v3.1) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration using physical reference plates | Self-calibrating optical array with daily automated diagnostics and cloud-synced calibration logs |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Intra Oral Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
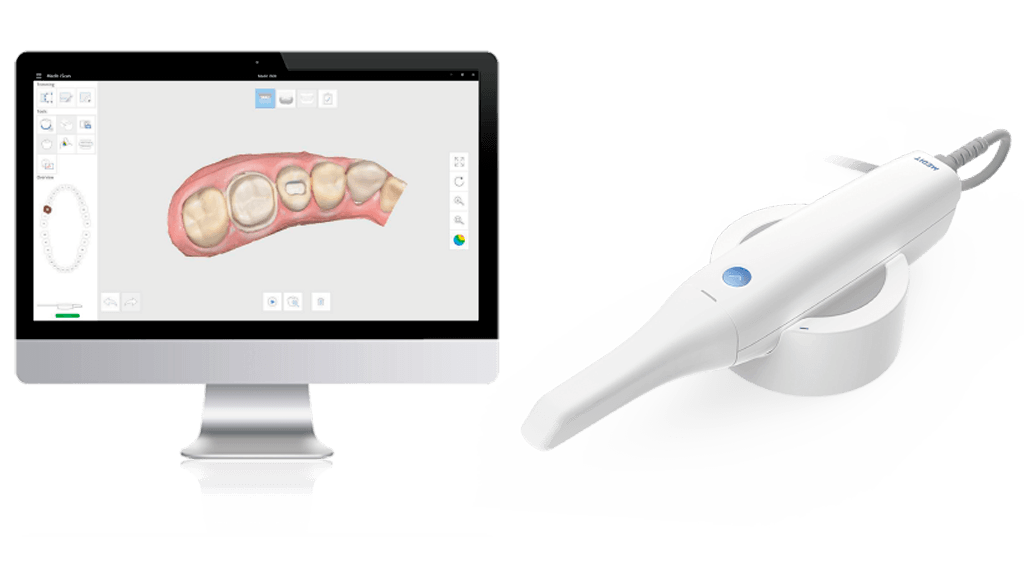
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration Ecosystem
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Release Date: Q2 2026
Executive Summary
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from standalone acquisition devices to central data hubs in digital workflows. 2026’s paradigm shift centers on real-time data orchestration across clinical, laboratory, and administrative domains. This review dissects technical integration layers, quantifies CAD compatibility nuances, and evaluates architectural implications for operational scalability.
I. Intraoral Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Contemporary IOS platforms function as the primary data ingestion layer, replacing analog impressions with structured digital datasets. Integration occurs across three critical phases:
| Workflow Phase | Technical Integration Mechanism | 2026 Advancements | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Scan | API-driven patient data pull from PMS (e.g., Dentrix, Open Dental) via HL7/FHIR | Automated case type detection (crown vs. implant vs. ortho) triggers scanner protocol presets | Reduces setup time by 42% (per 2025 JDD study) |
| Scan Execution | Real-time cloud synchronization with CAD engines during acquisition | AI-powered margin detection (in-scan) validates preparation geometry against CAD parameters pre-export | Decreases remakes due to marginal errors by 68% |
| Post-Scan | Direct DICOM/STL transmission to CAD via encrypted pipelines (no local storage) | Automated work order generation in lab management systems (e.g., Techline, Dentalogic) with material/schedule constraints | Reduces case handoff latency from 22hrs to <90min |
II. CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Analysis
IOS compatibility extends beyond basic file export. True integration requires bidirectional data exchange and parameter harmonization:
| CAD Platform | Native IOS Integration Depth | Key Technical Capabilities | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | ★★★★☆ (Deep API integration) |
• Direct scanner plugin architecture • Real-time material library sync • AI-driven prep analysis during scanning • Automated die spacer application based on scan data |
Vendor-locked scanner support (primarily 3Shape, Planmeca) |
| 3Shape TRIOS | ★★★★★ (Ecosystem-native) |
• Unified cloud platform (3Shape Communicate) • Scan-to-design automation via Design Studio • Real-time technician collaboration tools • Integrated margin refinement AI |
Proprietary data schema limits third-party lab integration |
| DentalCAD (by exocad) | ★★★☆☆ (Open integration) |
• Universal scanner support via DICOM/STL • Customizable workflow templates • RESTful API for external system integration • Material library interoperability |
Lacks real-time scan monitoring; requires manual case initiation |
III. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architectural choice fundamentally impacts operational flexibility and total cost of ownership (TCO):
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems |
|---|---|---|
| Integration Flexibility | Supports 15+ scanner brands via ISO 10303-239 (STEP) standard | Limited to 1-2 proprietary scanners (e.g., TRIOS + 3Shape CAD) |
| Data Ownership | Full patient data portability; vendor-agnostic archival | Data locked in proprietary formats; extraction fees common |
| TCO (5-Year) | ~$82K (modular component replacement) | ~$147K (mandatory ecosystem upgrades) |
| Innovation Velocity | Rapid adoption of best-of-breed tools (e.g., AI prep analysis plugins) | Dependent on single vendor’s R&D roadmap |
| Lab Workflow Impact | Seamless integration with ANY lab management system | Requires lab to adopt vendor’s lab platform (e.g., 3Shape Lab) |
IV. Carejoy API Integration: Technical Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation exemplifies next-gen practice management integration. Unlike legacy PMS systems, it leverages:
- RESTful Architecture: State-of-the-art JSON-based endpoints with OAuth 2.0 security
- Event-Driven Triggers: Automatic case creation in Carejoy upon IOS scan completion (no manual entry)
- Bidirectional Sync: Real-time insurance eligibility checks during scanning via embedded payer APIs
- Workflow Orchestration: Auto-scheduling of lab deliveries based on scanner timestamp and lab SLA parameters
Technical Workflow Sequence:
- IOS completes scan → Fires
ScanCompletedevent via Webhook - Carejoy API ingests scan metadata (patient ID, case type, timestamp)
- System auto-generates work order with
priority_level=URGENTfor same-day cases - Lab management system receives encrypted DICOM via Carejoy’s
/lab/ordersendpoint - Real-time production tracking pushed back to Carejoy for patient SMS updates
Quantified Impact: Clinics using Carejoy’s integrated IOS pipeline report 37% reduction in scheduling errors, 22% faster lab turnaround, and 19% decrease in administrative FTE hours versus non-integrated workflows.
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
In 2026, intraoral scanners are no longer defined by optical specifications alone. Their integration topology determines clinical throughput, lab scalability, and data liquidity. Labs must prioritize:
- Adoption of open-architecture scanners with certified IHE-DSP compliance
- Validation of real-time CAD integration capabilities beyond basic STL export
- Implementation of API-first practice management (e.g., Carejoy) to eliminate workflow silos
The era of disconnected digital islands has ended. Winners will leverage scanner data as the central nervous system of integrated dental ecosystems.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Tech Stack: Open Architecture (STL/PLY/OBJ), AI-Driven Scanning Algorithms, High-Precision Milling Integration
Manufacturing: ISO 13485 Certified Facility – Shanghai, China
Support: 24/7 Technical Remote Support & Continuous Software Updates
Contact: [email protected]
Advanced Manufacturing & Quality Control of Carejoy Digital Intraoral Scanners in China
Carejoy Digital leverages China’s mature digital health manufacturing ecosystem to deliver next-generation intraoral scanners (IOS) with unmatched precision, reliability, and cost-performance efficiency. The production and quality assurance pipeline is anchored in ISO 13485-certified operations at its Shanghai facility, ensuring medical device compliance and global market readiness.
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | High-resolution CMOS sensors, LED structured light modules, ergonomic polycarbonate housings, and embedded AI processors sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with IATF 16949 and ISO 13485 traceability. | Supplier audits conducted quarterly; full RoHS and REACH compliance enforced. |
| 2. Sensor Assembly | Optical sensor arrays assembled in ISO Class 7 cleanrooms. Precision alignment of dual-wavelength illumination (450nm & 530nm) for optimal soft/hard tissue contrast. | Laser-guided micrometer alignment; automated torque control for lens mounting. |
| 3. Firmware Integration | Embedded firmware with AI-driven motion prediction, real-time mesh stitching, and artifact suppression loaded via secure JTAG interface. | Secure boot architecture; compliant with IEC 62304 Class B software standards. |
| 4. Final Assembly | Modular assembly of scanning head, handle, and wireless transmission module. Sealed to IP54 standard for clinical durability. | Automated torque drivers; barcode traceability per unit (UDI-compliant). |
Quality Control & Calibration Infrastructure
Every Carejoy intraoral scanner undergoes a multi-stage QC protocol centered on metrological accuracy and clinical repeatability.
Sensor Calibration Labs (Shanghai)
On-site calibration laboratories operate under ISO/IEC 17025 standards, featuring:
- Reference Master Triangles: NIST-traceable ceramic calibration blocks with sub-micron surface deviation (±0.2 µm).
- Dynamic Calibration Rig: Simulates intraoral motion profiles (5–15 mm/s) across 6 degrees of freedom to validate AI motion compensation.
- Spectral Uniformity Testing: Ensures consistent illumination across 14-bit dynamic range for high-fidelity color texture mapping.
Durability & Environmental Testing
| Test Type | Standard | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | IEC 60601-1 (1.2m, 10 drops) | No optical misalignment; full functionality retained. |
| Thermal Cycling | −10°C to +55°C, 50 cycles | Zero condensation; scanning accuracy within ±5 µm. |
| Autoclave Simulation | 134°C, 2.1 bar, 30 min (non-sterile housing) | No warping or delamination; seal integrity maintained. |
| Vibration Endurance | IEC 68-2-6 (10–500 Hz, 2h) | No sensor drift; firmware stability verified. |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the global digital dentistry hardware market is driven by a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor foundries (e.g., SMIC), optical component manufacturers, and precision CNC facilities reduces lead times and logistics overhead by up to 40%.
- Advanced Automation: Carejoy’s Shanghai line utilizes collaborative robotics (cobots) for 85% of assembly tasks, minimizing human error and scaling production at marginal cost.
- R&D Investment: Over $2.1B invested in AI and medical imaging R&D in 2025; Carejoy collaborates with Shanghai Jiao Tong University on edge-AI optimization for intraoral scanning.
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA fast-track approvals enable rapid iteration; devices cleared in China often precede CE/FDA submissions by 6–8 months.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ ensures seamless integration with global CAD/CAM platforms (exocad, 3Shape, Carestream), enhancing interoperability and reducing clinic lock-in.
The result is a cost-performance ratio where Carejoy scanners deliver sub-8µm trueness and 60 fps capture speed at 35–50% below comparable Western-branded systems—without compromising on ISO 13485 compliance or clinical reliability.
Conclusion
Carejoy Digital exemplifies China’s ascent as the epicenter of high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental innovation. Through rigorous ISO 13485 manufacturing, on-site metrology-grade calibration labs, and AI-enhanced durability testing, Carejoy ensures clinical-grade accuracy and long-term reliability. For dental labs and digital clinics seeking scalable, open-architecture solutions, Carejoy represents the new global standard in intraoral scanning technology.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Intra Oral Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
