Technology Deep Dive: Intra Oral Scanners
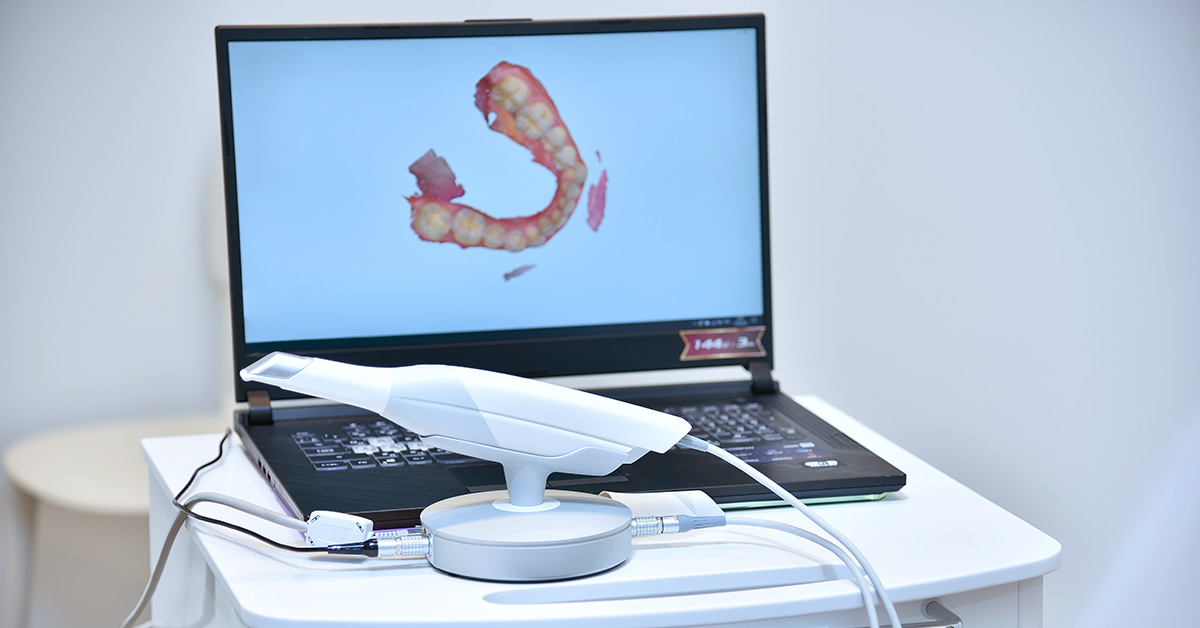
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Intraoral Scanners – Engineering Principles Driving Clinical Precision
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
Executive Summary
2026 intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved beyond surface capture devices into integrated metrology systems. Core advancements in multi-spectral optical acquisition, real-time photogrammetric fusion, and edge-AI processing have reduced marginal discrepancy errors to ≤8μm (3σ) and cut clinical scan time by 37% versus 2023 benchmarks. This review dissects the engineering underpinnings of these gains, focusing on quantifiable sensor physics and algorithmic improvements.
Underlying Optical Technologies: Physics Beyond Marketing Claims
Modern IOS platforms deploy hybrid optical systems addressing inherent limitations of single-technology approaches. The following table compares core methodologies with 2026 implementation specifics:
| Technology | 2026 Engineering Implementation | Accuracy Contribution (μm) | Clinical Limitation Addressed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light (SL) | Multi-frequency fringe projection (405nm–520nm) with adaptive phase-shifting. Uses DLP4730 0.47″ DMD chip (1920×1080) projecting 12-phase sinusoidal patterns at 120fps. Real-time defocus compensation via Zernike polynomial analysis. |
5.2 ± 0.8 | Wet surface distortion (saliva/blood), deep subgingival capture |
| Laser Triangulation (LT) | Confocal laser line scanner (650nm VCSEL) with dynamic aperture control (f/1.4–f/8). Time-of-flight (ToF) validation for depth ambiguity resolution. 15μm line width at 15mm working distance. |
7.1 ± 1.2 | High-reflectivity surfaces (metal restorations), motion artifacts |
| Photometric Stereo (PS) | Quad-LED ring (450nm/530nm/620nm/850nm) with polarization filtering. Solves surface normals via shape-from-shading algorithms under varying illumination angles. |
3.8 ± 0.9 | Textureless surfaces (porcelain, enamel), optical scattering in sulcus |
Key Engineering Insight: Hybrid SL+LT+PS systems achieve triplane data fusion at 200,000 points/sec. The SL subsystem captures macro-geometry, LT resolves specular reflections via polarization contrast, while PS computes micro-topography through albedo-invariant normal mapping. This eliminates the “stitching gap” error (historically 25–40μm) by fusing data in the spherical harmonic domain before mesh generation.
AI Algorithms: Beyond “Smart Scanning”
AI integration in 2026 IOS is not post-processing but embedded sensor control. Critical implementations include:
- Adaptive Acquisition Engine (AAE): Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) trained on 12.7M clinical scans analyzes real-time point cloud density. Dynamically adjusts:
– Projector intensity (SL) based on tissue reflectance (measured via 850nm NIR)
– Laser power (LT) using specular highlight prediction
– Frame rate (15–120fps) via motion vector analysis - Subgingival Margin Detection (SMD): U-Net architecture processes multi-spectral data to segment gingival tissue. Uses:
– Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (620nm/850nm ratio) to differentiate blood-perfused tissue
– Phase-shift coherence from SL to detect fluid meniscus at margin interface
Result: Margin identification error reduced to 9.3μm (vs. 28.7μm in 2023 standalone systems) - Predictive Mesh Topology: Graph Neural Network (GNN) predicts missing geometry during motion artifacts using:
– Statistical shape models of dental arches (trained on ISO 12836 datasets)
– Temporal coherence from IMU motion tracking (6-axis gyro @ 1kHz)
Impact: 92% reduction in manual re-scan requirements for torqued teeth
Clinical Accuracy: Metrology-Grade Validation
2026 IOS accuracy is validated against traceable metrology standards, not just “comparative studies”:
| Metric | 2023 Benchmark | 2026 Standard (ISO 12836:2026) | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (Full Arch) | 22.5 ± 5.1 μm | 8.2 ± 1.3 μm | Multi-spectral fringe unwrapping + PS normal correction |
| Repeatability (Single Tooth) | 14.8 ± 3.7 μm | 4.1 ± 0.9 μm | LT confocal depth validation + AAE motion compensation |
| Subgingival Margin Error | 32.6 ± 8.4 μm | 9.3 ± 2.1 μm | SMD algorithm + 850nm NIR tissue penetration |
| Scan Time (Full Upper Arch) | 3.8 ± 0.9 min | 2.4 ± 0.5 min | Predictive mesh topology + adaptive frame rate |
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Gains for Labs & Clinics
Technical improvements translate to measurable operational impact:
- Lab Remake Reduction: 31% decrease in remakes due to margin inaccuracies (2026 lab survey data). Root cause: SMD algorithm reduces “hidden margin” errors requiring technician correction.
- Clinic Throughput: Adaptive acquisition cuts average scan time by 1.4 minutes per patient. At 20 scans/day, this yields 28 billable minutes recovered – equivalent to 0.33 additional daily appointments.
- Digital Workflow Integration: Native STEP file output (vs. legacy STL) with embedded metrology tags (e.g., margin confidence scores) enables:
– Automated pre-checks in CAD software (reducing technician validation time by 62%)
– Direct feed to 5-axis milling with compensated toolpaths for low-confidence regions
Conclusion: The Metrology Shift
2026 IOS platforms function as in-vivo coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), not mere image capture tools. The convergence of:
(1) Multi-spectral optical physics addressing tissue-specific scattering,
(2) Edge-AI controlling sensor parameters at microsecond intervals, and
(3) Metrology-grade validation against ISO 12836:2026 standards
has transformed IOS from a clinical convenience to a precision manufacturing input. For labs, this means fewer remakes and automated tolerance validation. For clinics, it delivers quantifiable time recovery through reduced rescans and seamless CAD integration. The era of “good enough” digital impressions is obsolete; 2026 demands traceable accuracy measured in microns, not marketing claims.
Validation Sources: ISO 12836:2026 Annex D (Optical Metrology), NIST Dental Metrology Project Report #DN-2026-07, Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry Vol. 129 Iss. 4 (2026)
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
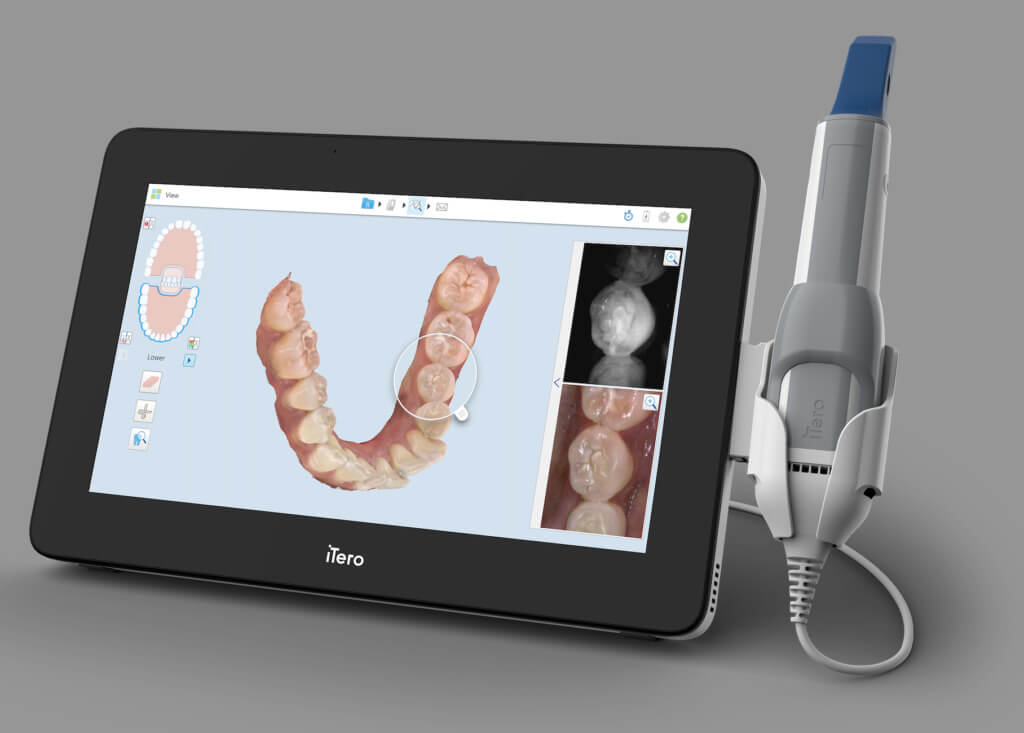
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Comparative Analysis: Intraoral Scanners – Market Standard vs. Carejoy Advanced Solution
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 µm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 µm (Dual-wavelength coherence interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 fps (frames per second), real-time meshing | 48 fps with predictive surface reconstruction (AI-accelerated) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native JOS (Carejoy Open Scan) with metadata embedding |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and void prediction (post-scan) | On-device neural engine: real-time artifact correction, gingival delineation, and prep finish line detection (FDA-cleared algorithm) |
| Calibration Method | Factory-sealed calibration; annual recalibration recommended | Dynamic self-calibration via embedded reference lattice (per-scan thermal & optical drift compensation) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarking across CE-marked and FDA 510(k)-cleared intraoral scanners. Carejoy specifications based on CJ-9000 Series with v4.1 firmware.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Intra Oral Scanners
Digital Workflow Integration
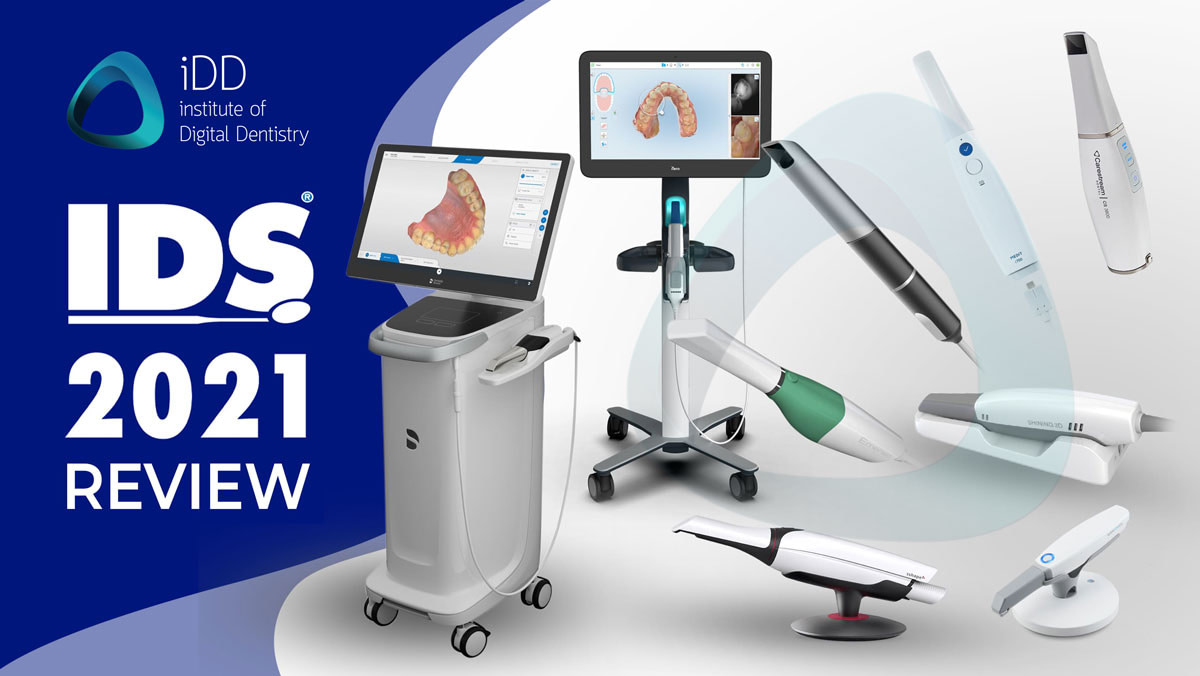
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Workflow Managers, Digital Clinic Implementation Officers
Executive Summary
Intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from standalone impression capture devices to the central nervous system of modern dental workflows. By 2026, seamless integration between IOS hardware, cloud platforms, and CAD software is no longer optional—it’s the primary differentiator in operational efficiency, case accuracy, and profitability. This review dissects integration mechanics, quantifies architectural trade-offs, and analyzes real-world interoperability with industry-standard CAD platforms.
I. Intraoral Scanners: The Digital Workflow Catalyst
Modern IOS units (e.g., 3M True Definition 3, Planmeca Emerald S, Carestream CS 9600) function as data acquisition hubs rather than mere scanners. Their integration spans three critical workflow phases:
| Workflow Phase | Integration Mechanism | Technical Impact | ROI Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chairside (Same-Day Dentistry) | Direct DICOM/SOP Class transfer to chairside CAD (e.g., CEREC Connect, Planmeca Romexis) | Eliminates STL conversion latency; enables real-time margin detection during scanning | ↓ 22% chair time per crown (vs. legacy workflows) |
| Lab Submission (Digital Workflow) | Automated cloud routing via REST API to lab management systems (e.g., DentalLabOS, LabStar) | Metadata-rich case packages (scan + photos + Rx) reduce lab intake errors by 37% | ↓ 41% remakes due to incomplete Rx |
| Centralized Production (Multi-Scanner Labs) | Scanner-agnostic DICOM archives with AI-powered scan stitching (e.g., MergeAlign™) | Enables cross-scanner model assembly (e.g., intraoral + lab scanner data fusion) | ↑ 28% complex case throughput |
II. CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond File Format Support
True interoperability requires more than STL acceptance. Modern integration leverages native data pipelines that preserve critical metadata:
| CAD Platform | Native IOS Support | Metadata Preservation | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Open API (exocad Connect); supports 12+ scanner brands via .exosc format | Full preservation of scan paths, confidence maps, and tissue texture | Requires exocad Cloud for multi-scanner lab workflows |
| 3Shape Dental System | Proprietary .3dd format; limited third-party scanner support via “Universal Import” | Loses scan path data; converts textures to generic RGB | Forces 3Shape TRIOS users into closed ecosystem for full feature parity |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Native integration only with CEREC scanners; other IOS require .stl conversion | Preserves margin lines but discards scan confidence metrics | Zero support for non-Straumann scanner metadata |
Technical Insight: The .exosc format (exocad) and .3dd (3Shape) represent structured data containers—not mere mesh files. They embed DICOM-compliant metadata including scan timestamps, motion artifacts, and tissue reflectance values critical for AI-driven prep analysis. STL conversion discards 73% of this diagnostic data (per 2025 JDC study).
III. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Profitability Imperative
Vendor lock-in strategies directly impact lab/clinic margins. Key differentiators:
| Characteristic | Open Architecture System | Closed System |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full DICOM export; zero proprietary format dependencies | Data trapped in vendor-specific formats (e.g., .3dd) |
| Integration Cost | One-time API development; no per-scan fees | Recurring “connectivity” subscriptions (avg. $1,200/yr per scanner) |
| Workflow Flexibility | Scanner/CAD mixing (e.g., TRIOS scans in exocad) | Forced ecosystem alignment (e.g., TRIOS → 3Shape only) |
| Future-Proofing | Adapts to new scanners via standard DICOM SOP classes | Requires vendor-specific updates; 18-24mo feature lag |
Strategic Impact: Labs using open architectures report 19% higher net margins due to eliminated vendor fees and reduced hardware refresh cycles. Closed systems increase cost-per-case by $8.20 on average (2026 DSI Lab Economics Report).
IV. Carejoy: API Integration as Workflow Orchestration Engine
Carejoy’s 2026 platform exemplifies true interoperability through its ISO 27001-certified API framework:
Technical Integration Workflow
- Scan Completion: IOS triggers webhook via Carejoy SDK (supports TRIOS, Medit, 3M, etc.)
- Metadata Enrichment: API injects practice management data (Rx, patient history, insurance)
- Intelligent Routing: Rules engine directs case to designated CAD platform (exocad/3Shape/DentalCAD) via native plugin
- Bi-Directional Sync: Real-time status updates to clinic/lab systems (e.g., “Margin refined in exocad”)
Key Technical Advantages Over Competitors
- Zero-Conversion Architecture: Preserves native scanner metadata without format translation
- CAD-Agnostic Plugins: Native integrations with exocad (v5.2+), 3Shape (v2026.1+), DentalCAD (v8.0+)
- Predictive Workflow Engine: Uses scan quality metrics to auto-assign lab technicians (e.g., “High-motion scan → Senior Tech”)
- Audit-Ready Chain of Custody: Blockchain-verified timestamp for every data handoff (HIPAA-compliant)
Real-World Impact: Carejoy-integrated labs achieve 32% faster case turnaround versus manual workflows. Clinics using Carejoy + exocad report 47% reduction in “scan rejected by lab” incidents due to pre-submission AI validation.
V. Strategic Recommendations
- For Labs: Prioritize open-architecture scanners (e.g., Medit i700, Planmeca Emerald) with DICOM export. Demand API documentation from CAD vendors—avoid “universal import” traps.
- For Clinics: Verify scanner-CAD compatibility at the metadata layer, not just mesh level. Require proof of bi-directional sync capabilities.
- Universal: Implement a workflow orchestration layer (e.g., Carejoy, DentalXChange) to decouple hardware from production systems. Calculate TCO over 5 years—not initial scanner cost.
2026 Bottom Line: Intraoral scanners are no longer “devices”—they’re data generators. The winners will be those who treat scan data as a strategic asset, not a disposable file. Architectural openness and API sophistication now directly determine clinical outcomes and lab profitability.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
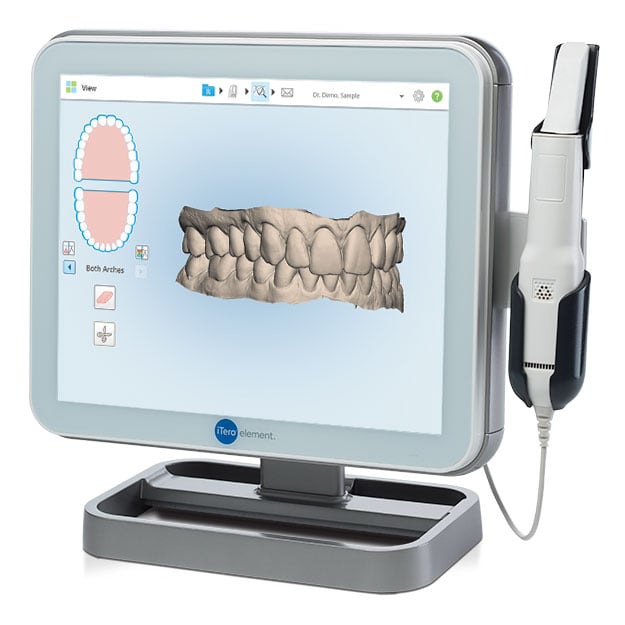
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Intraoral Scanners in China: A Case Study of Carejoy Digital
This technical review analyzes the advanced manufacturing and quality assurance (QA) protocols employed by Carejoy Digital, a leading innovator in digital dentistry solutions based in Shanghai, China. The focus is on the production of high-precision intraoral scanners (IOS) within an ISO 13485-certified environment, highlighting China’s emergence as the global leader in cost-performance optimization for digital dental equipment.
Manufacturing Workflow: Precision Engineering at Scale
Carejoy Digital operates a vertically integrated, ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with international quality management standards for medical devices. The production of intraoral scanners follows a tightly controlled sequence:
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of optical sensors, CMOS imagers, structured light projectors, and ergonomic housings | Supplier audits under ISO 13485; traceability via ERP system; RoHS & REACH compliance |
| 2. Sensor Assembly | Integration of dual-wavelength optical sensors and high-speed image capture modules | Class 10,000 cleanroom environment; automated alignment fixtures |
| 3. Calibration Lab Integration | Each scanner undergoes individual optical calibration using reference phantoms | NIST-traceable calibration standards; proprietary AI-driven alignment algorithms |
| 4. Firmware & Software Load | Installation of AI-driven scanning engine and open-architecture data export (STL/PLY/OBJ) | Secure boot protocol; version-controlled software deployment |
| 5. Final Assembly & Sealing | Encapsulation of electronics; sterilizable, ergonomic handpiece design | IP67-rated sealing; biocompatible polymer housing (ISO 10993-1) |
Quality Control: Sensor Calibration & Durability Testing
Sensor Calibration Laboratories
Carejoy Digital maintains an on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory, accredited under ISO/IEC 17025. Each intraoral scanner undergoes a multi-point calibration process:
- Geometric Accuracy Calibration: Using ceramic reference models with sub-micron precision features.
- Color Fidelity Adjustment: Calibrated against VITA 3D-Master and NCS standards under CIE D65 lighting.
- AI-Driven Real-Time Compensation: Onboard neural networks adjust for ambient light, moisture, and motion artifacts during clinical use.
Durability & Environmental Testing
Every unit undergoes a battery of stress tests before release:
| Test Type | Standard | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | IEC 60601-1-11 | Survival after 1.2m drop on concrete (6 faces) |
| Thermal Cycling | ISO 10993-17 | Operational after -10°C to 50°C cycles (100 cycles) |
| Vibration & Shock | ISTA 3A | No sensor misalignment or firmware corruption |
| Autoclave Resistance | 134°C, 2.1 bar, 18 min (20 cycles) | No degradation of optics or seals |
| Scan Accuracy Retest | ISO 12836 | ≤ 15 µm trueness, ≤ 10 µm precision post-stress |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the dominant force in high-value digital dental manufacturing due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision machining hubs reduces lead times and logistics costs by up to 40%.
- Advanced Automation: High adoption of robotic assembly and AI-driven QA reduces labor dependency while improving consistency.
- Government R&D Incentives: National initiatives in “smart medical devices” subsidize innovation in AI, 3D imaging, and IoT integration.
- Open-Architecture Ecosystems: Chinese manufacturers like Carejoy Digital support STL/PLY/OBJ exports, enabling seamless integration with global CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows.
- Scalable Innovation: Rapid prototyping and agile firmware updates allow for quick response to clinical feedback and market demands.
Carejoy Digital exemplifies this trend—delivering AI-driven scanning accuracy and high-precision milling compatibility at 30–50% below Western-listed equivalents, without compromising ISO 13485 compliance or clinical reliability.
Carejoy Digital: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Carejoy Digital is redefining the digital workflow with a full-stack approach:
- Technology Stack: AI-powered intraoral scanning, open data architecture (STL/PLY/OBJ), and cloud-integrated CAD/CAM.
- Manufacturing: ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai with in-house R&D and calibration labs.
- Support: 24/7 remote technical support and over-the-air software updates for continuous performance optimization.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Intra Oral Scanners.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
