Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dental implant lateral incisor
In the evolving landscape of dental restoration, the lateral incisor implant stands out as a critical component in providing functional and aesthetic solutions for patients. For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of the lateral incisor implant market is essential for successful procurement. These implants not only restore the natural appearance of a smile but also enhance the overall dental functionality, making them a sought-after option in both clinical and cosmetic dentistry.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various dimensions of the dental implant lateral incisor market, providing invaluable insights tailored for discerning buyers. From the types and materials used in manufacturing to the stringent quality control measures implemented by suppliers, we explore each facet that influences purchasing decisions. Additionally, we analyze the cost structures and market dynamics, enabling buyers to make informed financial decisions.
By addressing frequently asked questions and offering practical advice, this guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing dental implants effectively. Whether you are a dental clinic, distributor, or supplier, understanding these key elements will enhance your strategic positioning in a competitive global marketplace. Equip yourself with the knowledge to secure the best products and partnerships, ensuring that your offerings meet the high standards expected by patients and practitioners alike.
Understanding dental implant lateral incisor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Lateral Incisor | Traditional design, typically cylindrical, compatible with most systems | General dental practices, restorative dentistry | Pros: Widely available, cost-effective. Cons: May not suit all anatomical conditions. |
| Mini Dental Implant | Smaller diameter, minimally invasive placement | Prosthodontics, orthodontics, cosmetic dentistry | Pros: Less bone required, quicker healing. Cons: Limited load-bearing capacity. |
| Zirconia Implant | Metal-free, aesthetic appeal, biocompatible | Aesthetic-focused practices, holistic dentistry | Pros: Excellent aesthetics, reduced risk of allergic reactions. Cons: Higher cost, less long-term data. |
| Platform-Switching Implant | Offset connection design to reduce bone loss | Advanced restorative dentistry, implantology | Pros: Enhanced stability, better aesthetics. Cons: Requires specialized training for placement. |
| Immediate Load Implant | Designed for immediate function after placement | Immediate restoration practices, urgent care | Pros: Reduced treatment time, immediate patient satisfaction. Cons: Higher risk of failure if not placed correctly. |
Standard Lateral Incisor
The Standard Lateral Incisor implant is the most commonly used type, featuring a traditional cylindrical design. Its compatibility with various implant systems makes it a go-to choice for many dental practices. B2B buyers should consider the availability and cost-effectiveness of this implant, as it is widely produced and recognized. However, it may not be suitable for patients with specific anatomical conditions that require a more tailored approach.
Mini Dental Implant
Mini Dental Implants are characterized by their smaller diameter, which allows for a less invasive placement procedure. This type is particularly beneficial in cases where there is limited bone volume. For B2B buyers, the quick healing time and reduced surgical requirements make mini implants attractive, especially in prosthodontics and orthodontics. However, they come with a trade-off in load-bearing capacity, which should be evaluated based on the intended application.
Zirconia Implant
Zirconia Implants offer a metal-free option that is highly aesthetic and biocompatible. This type is especially appealing to practices focusing on aesthetics and holistic dentistry. B2B purchasers should weigh the benefits of improved aesthetics and reduced allergy risks against the higher costs and limited long-term data available for zirconia implants. This implant type is ideal for patients concerned about metal sensitivity or those seeking a natural appearance.
Platform-Switching Implant
The Platform-Switching Implant features a unique offset connection design that helps minimize bone loss around the implant site. This type is particularly suitable for advanced restorative dentistry where aesthetics and stability are paramount. Buyers should consider the additional training required for placement, as well as the potential for enhanced outcomes in terms of stability and aesthetics, making it a worthwhile investment for specialized practices.
Immediate Load Implant
Designed for immediate function, the Immediate Load Implant allows for restoration to occur right after placement, greatly reducing treatment times. This type is particularly advantageous in urgent care scenarios. B2B buyers should be aware of the higher risk of implant failure if not placed with precision. Nevertheless, the potential for immediate patient satisfaction can drive demand, making these implants a valuable addition to any practice focused on efficiency and patient experience.
Key Industrial Applications of dental implant lateral incisor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of dental implant lateral incisor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Clinics | Replacement of missing lateral incisors | Enhances patient satisfaction and retention | Quality of materials, regulatory compliance, and pricing |
| Dental Laboratories | Custom fabrication of prosthetics | Improves turnaround time and accuracy | Advanced technology, skilled labor, and material sourcing |
| Orthodontic Practices | Aesthetic enhancements in conjunction with braces | Increases patient referrals and treatments | Compatibility with orthodontic systems and aesthetics |
| Dental Supply Companies | Distribution of implants and related components | Expands product offerings and market reach | Supplier reliability, logistics, and inventory management |
| Insurance Providers | Coverage for implant procedures | Increases patient base and service offerings | Understanding of regional regulations and reimbursement rates |
Dental Clinics
In dental clinics, the lateral incisor implant is crucial for replacing missing teeth, particularly in the aesthetic zone of the mouth. This application not only restores functionality but also significantly enhances the patient’s smile and overall confidence. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, the sourcing of high-quality implants that comply with local regulations is essential. Clinics must prioritize implants that offer durability and biocompatibility to ensure long-term success and patient satisfaction.
Dental Laboratories
Dental laboratories utilize lateral incisor implants for creating custom prosthetics tailored to individual patient needs. This application is vital for ensuring a precise fit and aesthetic appeal, which can lead to improved patient outcomes. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing advanced technologies and materials that enhance fabrication accuracy and reduce turnaround times. Collaborating with suppliers who prioritize innovation and quality can significantly impact the laboratory’s operational efficiency.
Orthodontic Practices
Orthodontic practices incorporate lateral incisor implants as part of comprehensive treatment plans to enhance aesthetics and functionality, particularly for patients undergoing braces treatment. This integration can lead to increased patient referrals and retention, as well as improved treatment results. For B2B buyers, understanding the compatibility of implants with various orthodontic systems is critical. Additionally, sourcing implants that meet aesthetic standards can help practices differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
Dental Supply Companies
Dental supply companies play a pivotal role in distributing lateral incisor implants and related components to clinics and laboratories. By expanding their product offerings, these suppliers can enhance their market reach and provide comprehensive solutions to their clients. Key considerations for sourcing include the reliability of suppliers and the efficiency of logistics. Buyers should seek partnerships that ensure timely deliveries and consistent product quality, which are crucial for maintaining strong customer relationships.
Insurance Providers
Insurance providers increasingly recognize the importance of covering dental implant procedures, including lateral incisor replacements. By doing so, they can attract a broader patient base and enhance their service offerings. For international buyers, particularly in regions with varying healthcare regulations, understanding local reimbursement rates and regulatory frameworks is essential. This knowledge allows insurance companies to tailor their policies effectively, ensuring they meet the needs of both patients and dental professionals.
Related Video: Step by Step Guide to Your Dental Implant Procedure
Strategic Material Selection Guide for dental implant lateral incisor
When selecting materials for dental implants, particularly for lateral incisors, it is crucial to consider the unique properties of each material in relation to performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in dental implants, providing insights relevant to international B2B buyers.
Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium is renowned for its excellent biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand the physiological conditions of the oral environment, including temperature fluctuations and mechanical stresses.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of titanium is its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for long-term implants. However, the cost of titanium can be relatively high compared to other materials, and its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Titanium implants are compatible with various bone types and are often used in patients with varying bone densities. Its excellent osseointegration properties enhance stability and longevity.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East, compliance with international standards such as ASTM F136 is essential. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding implant materials is crucial to ensure market access.
Zirconia
Key Properties:
Zirconia is a ceramic material known for its aesthetic qualities, high strength, and excellent biocompatibility. It offers good resistance to wear and corrosion, making it suitable for dental applications.
Pros & Cons:
The aesthetic advantage of zirconia is significant, as it closely resembles natural tooth color, making it ideal for visible areas like lateral incisors. However, it can be more brittle than titanium, leading to potential fracture under excessive stress.
Impact on Application:
Zirconia is particularly suitable for patients concerned with aesthetics, as it provides a more natural appearance. However, its compatibility with certain bone types may be less favorable compared to titanium.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from Europe, such as Poland, should ensure that zirconia implants meet the European Union’s CE marking requirements. Understanding the local market’s aesthetic preferences can also influence material selection.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
Key Properties:
PEEK is a high-performance polymer known for its excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and resistance to wear and chemicals. It is also biocompatible and can be processed easily.
Pros & Cons:
PEEK is lighter and less expensive than titanium, making it an attractive option for cost-sensitive markets. However, its lower strength compared to metals can limit its use in load-bearing applications.
Impact on Application:
PEEK implants can be used in cases where flexibility and shock absorption are beneficial. They are particularly suitable for patients with specific allergies to metals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like South America, where cost may be a significant factor, PEEK offers a viable alternative. Buyers should ensure that PEEK implants comply with local health regulations and standards.
Cobalt-Chromium Alloys
Key Properties:
Cobalt-chromium alloys are known for their high strength, wear resistance, and excellent corrosion resistance. They are often used in applications requiring high mechanical performance.
Pros & Cons:
These alloys provide exceptional durability and are suitable for long-term implants. However, they can be more expensive and may require complex manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application:
Cobalt-chromium alloys are ideal for patients with high functional demands, such as those involved in heavy chewing. Their mechanical properties make them suitable for posterior dental implants as well.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in the Middle East, understanding the specific alloy compositions and their compliance with standards like ISO 5832 is vital. Additionally, considering the local market’s acceptance of metal-based implants is important for successful product introduction.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for dental implant lateral incisor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | General use in dental implants | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Zirconia | Aesthetic implants for visible areas | Natural appearance | Brittle under stress | Med |
| PEEK | Flexible applications, allergy-sensitive patients | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower strength than metals | Low |
| Cobalt-Chromium Alloys | High-stress applications | Exceptional mechanical properties | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for dental implant lateral incisors, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dental implant lateral incisor
Manufacturing Processes for Dental Implant Lateral Incisors
The manufacturing of dental implant lateral incisors involves a series of meticulous stages designed to ensure the final product meets stringent quality standards. Each stage is critical to achieving the desired performance and reliability of the dental implants.
1. Material Preparation
The initial phase in the manufacturing process is material selection and preparation. Common materials used for dental implants include titanium and zirconia due to their biocompatibility and strength. The materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet the required specifications.
- Material Sourcing: Buyers should prioritize suppliers who source materials from reputable manufacturers with proven track records. This can mitigate risks related to subpar material quality.
- Pre-treatment Processes: Materials may be treated to enhance their properties, such as surface roughening to promote osseointegration, which is critical for the implant’s success.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes. This stage is essential for shaping the implants to their final dimensions and features.
- Techniques Used:
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is commonly used for precision forming. This technique allows for tight tolerances and complex geometries.
- 3D Printing: Increasingly popular, particularly for custom implants, this technology enables rapid prototyping and production while reducing material waste.
3. Assembly
After forming, the components are assembled. For lateral incisors, this may include integrating abutments and any necessary attachments.
- Automation vs. Manual Assembly: Some manufacturers utilize automated processes to enhance precision and reduce human error, while others may rely on skilled technicians for more complex assemblies.
- Traceability: Buyers should ensure that suppliers maintain a robust traceability system throughout the assembly process, which is crucial for quality assurance and recalls if necessary.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes that enhance the implant’s surface characteristics and overall aesthetics.
- Surface Treatments: Common methods include anodization and sandblasting, which improve surface roughness and promote better bonding with bone.
- Polishing and Coating: Some implants may receive additional coatings (e.g., hydroxyapatite) to further enhance biocompatibility.
Quality Assurance in Dental Implant Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of dental implants, given the critical role they play in dental health. Implementing robust quality control measures ensures that the implants are safe, effective, and compliant with international standards.
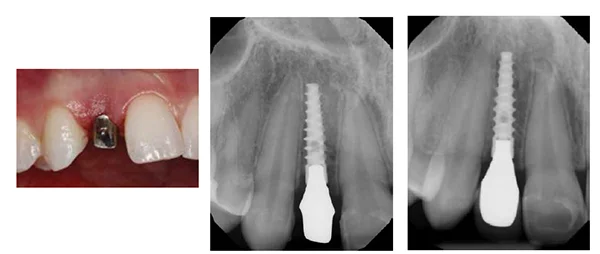
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
International Standards and Certifications
Understanding the relevant international and industry-specific standards is essential for buyers:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, it indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may also apply, particularly for materials and processes used in implant manufacturing.
Quality Control Checkpoints
A comprehensive quality control system typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase checks the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing assessments during manufacturing ensure that processes adhere to specified parameters.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough examination of the finished products guarantees they meet all specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the implants’ performance and safety:
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and wear is crucial to ensure that the implants can withstand the forces encountered in the oral environment.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Conducting cytotoxicity tests and in vivo studies to ascertain that the materials used do not provoke adverse biological responses.
- Sterilization Validation: Ensuring that the sterilization processes (e.g., autoclaving, gamma irradiation) are effective and consistent.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is vital. Here are actionable steps to achieve this:
-
Conduct Audits: Regularly auditing suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This can be done through on-site visits or third-party services.
-
Review Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports that outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC. This documentation should include any corrective actions taken for non-conformities.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors can offer unbiased evaluations of the manufacturing facilities and quality control processes.
-
Certifications Verification: Ensure that the supplier’s certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) are current and valid. This can often be verified through official channels or the certifying bodies.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
Navigating the nuances of quality control can be challenging for international buyers. Here are some considerations:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Understand the specific regulations applicable in your region. For instance, European buyers must ensure compliance with CE marking, while buyers in the Middle East may need to adhere to local health regulations.
-
Cultural Differences: Recognize that manufacturing practices and quality assurance standards may vary by region. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding expectations.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain: Consider the impact of logistics on quality. Delays and environmental factors during transport can affect the integrity of dental implants, making it crucial to work with suppliers who have robust logistics management.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing dental implant lateral incisors, ensuring they receive products that meet their quality and performance expectations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dental implant lateral incisor Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of Dental Implant Lateral Incisors
When sourcing dental implants, particularly lateral incisors, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The cost components can be categorized into several key areas:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost. Titanium and zirconia are commonly used due to their biocompatibility and strength. Sourcing high-quality materials may incur higher upfront costs but can reduce long-term complications and replacements.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in the manufacturing process. Labor costs vary by region, with countries in Europe and North America typically having higher wage standards compared to some regions in Africa and South America. Buyers should factor in the impact of labor costs on overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers with advanced technologies or cleaner production processes may have higher overheads, which can reflect in pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tooling for production can be substantial. Custom tooling for specific designs or specifications can increase initial costs but may lead to better quality and precision in the final product.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes is vital to ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards. Enhanced QC measures can increase costs, but they are necessary to prevent costly recalls or failures.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary dramatically based on the distance, shipping method, and urgency. International buyers should consider both freight costs and potential tariffs when calculating total expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on competition, market demand, and perceived value. Understanding the typical margins in your target market can aid in negotiations.
Key Price Influencers
Several factors influence the pricing of dental implant lateral incisors:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders often yield lower per-unit costs. Buyers should evaluate their needs and consider negotiating for bulk pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom implants tailored to specific patient needs or dental practices can increase costs. Clear communication with suppliers about requirements is essential to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Implants that meet international certifications (like ISO or CE) may cost more but ensure compliance and safety. Investing in certified products can mitigate risks associated with subpar materials.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, which can impact total costs. For example, opting for DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) can simplify logistics but might be more expensive upfront.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing and payment terms. Suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or larger orders.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the TCO, which includes installation, maintenance, and potential replacements. This holistic view can lead to more informed sourcing decisions.
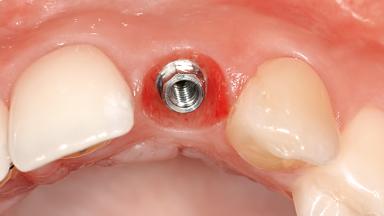
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Research Regional Pricing Nuances: Pricing can vary significantly by region. For instance, suppliers in Poland may offer competitive rates compared to those in Western Europe. Understanding regional market dynamics can yield better sourcing strategies.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Regularly review market trends and pricing changes. Economic shifts, material shortages, or regulatory changes can all impact costs.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Long-term partnerships often yield favorable terms and enhanced support.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on numerous factors, including market conditions and supplier negotiations. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers to obtain accurate quotes tailored to their specific needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dental implant lateral incisor
Key Technical Properties for Dental Implant Lateral Incisor
When selecting dental implants for lateral incisors, understanding the technical properties is crucial for ensuring quality and compatibility. Here are several critical specifications that B2B buyers should prioritize:
-
Material Grade
Dental implants are primarily made from titanium or titanium alloys due to their biocompatibility and strength. The material grade indicates the alloy composition, which affects corrosion resistance and osseointegration. For instance, Grade 4 titanium is commonly used for its superior strength, making it an excellent choice for lateral incisors that may experience significant stress during chewing. -
Surface Treatment
The surface of the implant plays a vital role in the integration with the bone. Treatments such as sandblasting or acid etching enhance the surface roughness, promoting better bone attachment. Buyers should look for implants with proven surface treatments that have been clinically validated for improved osseointegration. -
Dimensional Tolerance
Precision in manufacturing is essential for ensuring that implants fit perfectly into the prepared site. Dimensional tolerance refers to the allowable variations in the implant dimensions. High precision minimizes the risk of complications and improves the longevity of the implant. A tolerance of ±0.1 mm is often considered ideal for lateral incisors. -
Porosity
Some implants feature a porous structure, which can enhance the biological interaction with surrounding tissues. This property is significant for lateral incisors, as it can improve the stability and integration of the implant. Buyers should evaluate the porosity level and its impact on the implant’s performance. -
Length and Diameter Options
Lateral incisors often require specific implant dimensions to match the anatomical structure of the jaw. The availability of various lengths and diameters allows for customization based on patient needs. Buyers must ensure that suppliers offer a range of options to meet diverse clinical requirements.
Common Trade Terms in Dental Implant Transactions
Understanding industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the dental implant market. Here are some common terms that international B2B buyers should be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of dental implants, buyers should know whether they are dealing directly with the OEM or a distributor to ensure quality and compliance with standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For dental implants, understanding MOQ is crucial for inventory management, especially for buyers in regions with varying demand. A lower MOQ may provide flexibility for smaller clinics or practices. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and availability for specific products. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to obtain competitive pricing and ensure that all necessary specifications are included, which will help in making informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is essential for managing costs and logistics effectively. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. In the dental industry, where timely delivery can impact patient care, understanding lead times is critical for planning and operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their purchasing strategy and ensure high-quality outcomes in their dental practices.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the dental implant lateral incisor Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The dental implant sector, particularly for lateral incisors, is witnessing significant growth driven by various global factors. Increasing awareness about oral health, coupled with a rising aging population, is propelling demand for dental implants across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Notably, countries like Poland and Egypt are emerging as key players, where rising disposable incomes and improved access to dental care are leading to higher adoption rates of dental implants.
International B2B buyers should be aware of current and emerging sourcing trends, including the integration of advanced technologies such as 3D printing and digital dentistry. These innovations are not only enhancing the precision and customization of implants but also streamlining the manufacturing process, thus reducing lead times and costs. Additionally, the market is seeing a shift towards more personalized solutions, as dental professionals seek to cater to individual patient needs.
Furthermore, the competitive landscape is influenced by the consolidation of suppliers and the rise of private-label products. B2B buyers must navigate these dynamics to identify reliable partners that offer quality products and services. Establishing relationships with manufacturers who are adept at leveraging technology and market insights will be crucial for success in the evolving dental implant landscape.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the dental implant sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly regarding the use of non-biodegradable materials, is prompting buyers to seek out sustainable alternatives. Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining traction, with a focus on transparency in supply chains. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical practices, ensuring that their sourcing aligns with broader corporate social responsibility goals.
The use of ‘green’ certifications and materials is essential for compliance with increasing regulatory standards and consumer expectations. Buyers should look for implants made from biocompatible materials that have minimal environmental footprints. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or the use of recycled materials can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By prioritizing these factors, international buyers can not only meet regulatory demands but also enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Brief Evolution/History
The dental implant industry has evolved significantly since the introduction of the first modern dental implants in the 1960s. Initially, these implants were primarily made from titanium, renowned for its biocompatibility and strength. Over the decades, advancements in materials science have led to the development of more sophisticated options, including zirconia implants, which offer aesthetic advantages and reduced visibility in the mouth.
As the market matured, the focus shifted from merely providing functional solutions to offering personalized care. This evolution has been fueled by technological advancements in imaging and surgical techniques, which have improved the success rates of dental implants. Today, the emphasis on patient-centered care and sustainable practices is shaping the future of the dental implant sector, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about these trends and innovations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dental implant lateral incisor
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of dental implant lateral incisors?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their certifications, such as ISO and CE marks, which indicate compliance with international quality standards. Investigate their manufacturing processes and technologies to ensure they align with your quality expectations. Additionally, assess their reputation in the market through reviews and testimonials. Engaging in direct communication can provide insights into their reliability and customer service practices, which are crucial for long-term partnerships. -
Can I request customization for dental implant lateral incisors?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific clinical needs. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications, including dimensions, materials, and design preferences. Ensure that the supplier has the capability and experience to handle custom orders. It’s also advisable to discuss any additional costs and lead times associated with customization to avoid surprises later in the procurement process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for dental implant lateral incisors?
MOQs can vary significantly among suppliers, generally ranging from 50 to 200 units, depending on the product line and manufacturer. Lead times also fluctuate, typically between 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by factors such as production capacity and shipping logistics. It is essential to confirm these details upfront to align your purchasing strategy with your inventory needs and operational timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing dental implant lateral incisors internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common practices include upfront payments or a deposit of 30-50% with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer credit terms or letters of credit for larger orders. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that ensure both parties’ security. Always confirm the acceptable payment methods, such as wire transfers, PayPal, or credit cards, to facilitate smooth transactions. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in dental implant suppliers?
Ensure that the supplier implements rigorous quality assurance protocols, including regular product testing and compliance with international standards. Request documentation of their quality control processes, including batch testing results and inspection reports. Additionally, ask for information regarding their warranty policies and after-sales support, as these factors can significantly impact product reliability and your overall satisfaction. -
How can I handle disputes with suppliers effectively?
To mitigate disputes, establish clear terms of engagement in your contracts, including delivery timelines, quality expectations, and payment terms. If a dispute arises, maintain open communication with the supplier to address issues promptly. Consider employing mediation or arbitration as a resolution mechanism, which can be less confrontational and more cost-effective than legal action. Document all correspondence to support your case if further action is necessary. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing dental implant lateral incisors?
Logistics play a critical role in the timely delivery of dental implants. Assess the supplier’s shipping options, including freight forwarders and delivery times to your region. Familiarize yourself with import regulations, tariffs, and customs clearance procedures in your country to avoid delays. Collaborating with a local logistics partner can streamline the process and help navigate any complexities associated with international shipping. -
Are there specific certifications I should verify for dental implant products?
Yes, ensure that the dental implants come with relevant certifications such as ISO 13485 for medical devices and CE marking for products sold in Europe. These certifications indicate compliance with safety and efficacy standards. Additionally, inquire about any additional certifications relevant to your specific market, such as FDA approval for imports into the United States. Verifying these credentials will help ensure that you are sourcing safe and effective products for your customers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dental implant lateral incisor
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing for dental implant lateral incisors is essential for international B2B buyers looking to enhance their product offerings and operational efficiency. By prioritizing partnerships with reputable suppliers, conducting thorough market research, and understanding regional regulations, businesses can secure high-quality implants that meet the specific needs of their clientele.
Key Takeaways:
- Quality Assurance: Focus on sourcing implants from manufacturers that adhere to stringent quality standards and certifications.
- Cost Management: Leverage global sourcing opportunities to optimize costs without compromising on quality.
- Market Trends: Stay informed about emerging trends and technologies in dental implants to remain competitive.
As we look ahead, it is crucial for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to adopt a proactive approach in their sourcing strategies. Engaging with innovative suppliers and embracing digital tools can streamline procurement processes and improve supply chain resilience. Now is the time to act—evaluate your sourcing strategies, foster strong supplier relationships, and position your business for success in the evolving dental implant market.
