Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dental implants or veneers
Navigating the global market for dental implants and veneers is an essential endeavor for B2B buyers seeking to enhance their offerings in the dental industry. With a growing demand for dental restoration solutions, understanding the nuances of this market can significantly impact business success. Dental implants and veneers not only improve aesthetic outcomes but also restore functionality, making them critical components in modern dentistry.
This guide aims to equip international buyers—particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—with comprehensive insights into dental implants and veneers. We will explore various types of implants and veneers, including single-tooth implants, implant-supported bridges, and aesthetic veneers, tailored to different patient needs. Additionally, we will delve into materials used in manufacturing, highlighting advancements such as biocompatible substances and additive manufacturing techniques.
Quality control and manufacturing processes are vital for ensuring product reliability. Therefore, this guide will outline essential manufacturing and quality assurance standards, regulatory requirements, and best practices. Furthermore, we will provide an analysis of suppliers, including key players in diverse markets, as well as insights into cost structures to enable informed purchasing decisions.
By navigating through this extensive resource, B2B buyers will gain the knowledge necessary to make strategic sourcing decisions, positioning themselves effectively in the competitive landscape of dental solutions.
Understanding dental implants or veneers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Tooth Implant | Replaces a single missing tooth; integrated into the jawbone. | Dental clinics, oral surgery centers | Pros: Aesthetic, functional, high success rate. Cons: Higher cost per unit compared to multi-tooth solutions. |
| Implant-Supported Bridge | Multiple implants support a bridge for several missing teeth. | Dental practices, prosthodontics | Pros: Restores multiple teeth, stable, improved aesthetics. Cons: More invasive, requires precise planning. |
| Implant-Retained Denture | Dentures anchored by implants; removable but more stable than traditional dentures. | Denture clinics, senior care facilities | Pros: Enhanced stability, improved chewing efficiency. Cons: May require more maintenance and adjustment. |
| Zirconia Implants | Made from zirconia ceramic; offers a metal-free option. | Cosmetic dentistry, holistic practices | Pros: Biocompatible, aesthetic, less risk of metal allergies. Cons: Limited long-term data compared to titanium. |
| Mini Implants | Smaller diameter implants; less invasive and quicker to place. | General dental practices, orthodontics | Pros: Cost-effective, less surgical time, suitable for narrow spaces. Cons: May not provide the same strength as traditional implants. |
Single Tooth Implant
Single tooth implants are designed to replace individual missing teeth by integrating directly into the jawbone. This type is ideal for patients needing a straightforward solution without affecting adjacent teeth. For B2B buyers, key considerations include the implant’s material, the surgeon’s expertise, and the associated costs. The high success rate and aesthetic benefits make them a preferred option for dental practices focusing on individual patient needs.
Implant-Supported Bridge
An implant-supported bridge involves using multiple implants to support a bridge for patients missing several teeth in a row. This solution is particularly beneficial in restoring function and appearance while minimizing the need for adjacent tooth alteration. B2B buyers should evaluate the complexity of the surgical procedure, the materials used for the bridge, and the total treatment timeline. The stability and longevity of this option often justify the initial investment for dental clinics.
Implant-Retained Denture
Implant-retained dentures offer enhanced stability for patients who require full arch restoration. These dentures are anchored by implants, providing a more secure fit compared to traditional dentures. For B2B buyers, the main considerations include the cost of implants, the potential need for additional adjustments, and the benefit of improved patient satisfaction. This option is particularly suitable for senior care facilities looking to enhance the quality of life for residents.
Zirconia Implants
Zirconia implants are crafted from a ceramic material that is metal-free, appealing to patients with metal sensitivities or aesthetic concerns. They provide a natural appearance and are biocompatible, making them suitable for cosmetic dental practices. B2B buyers should assess the availability of zirconia implants and their compatibility with existing surgical protocols. While they offer aesthetic advantages, the limited long-term data may be a concern for some dental professionals.
Mini Implants
Mini implants are smaller in diameter and require less invasive surgical procedures, making them ideal for patients with limited bone density or those seeking a quicker solution. They are often more cost-effective than traditional implants and can be placed with less surgical time. For B2B buyers, it is crucial to evaluate the strength and longevity of mini implants in comparison to standard options. This type is particularly useful for general dental practices and orthodontics focused on providing accessible solutions.
Related Video: Dental Veneers Procedure Explained
Key Industrial Applications of dental implants or veneers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of dental implants or veneers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Clinics | Restoration of missing teeth through implants | Enhances patient satisfaction and retention | Compliance with local regulations and quality certifications |
| Orthodontics | Use of veneers for aesthetic enhancements | Increases service offerings and revenue streams | Material quality and aesthetic matching |
| Dental Laboratories | Custom fabrication of implants and veneers | Streamlined workflow and reduced turnaround time | Advanced manufacturing technologies and material sourcing |
| Healthcare Institutions | Surgical applications in trauma and oncology cases | Improved patient outcomes and procedural efficiency | Supplier reliability and product traceability |
| Cosmetic Dentistry | Aesthetic corrections using veneers | Higher patient referrals and competitive advantage | Training and support for application techniques |
Dental Clinics
In dental clinics, dental implants are crucial for restoring missing teeth, providing a permanent solution that mimics natural teeth in function and appearance. This application not only enhances patient satisfaction but also boosts retention rates as patients seek comprehensive care under one roof. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing implants requires adherence to local regulatory standards, ensuring that suppliers possess the necessary certifications such as CE marking or FDA approval.
Orthodontics
Veneers serve a significant role in orthodontics by offering aesthetic enhancements to patients seeking to improve their smile. These thin shells are applied to the front of teeth to correct issues such as discoloration and misalignment. For B2B buyers in South America and Europe, selecting high-quality materials that match the aesthetic needs of diverse patient demographics is essential. Additionally, orthodontic practices should consider suppliers that provide training on veneer application techniques to ensure optimal results.
Dental Laboratories
Dental laboratories utilize advanced technologies to custom fabricate dental implants and veneers tailored to individual patient needs. This capability enhances workflow efficiency, reduces turnaround times, and allows for the production of high-quality, precise restorations. For B2B buyers, particularly those from Europe and Africa, it’s vital to assess the technological capabilities of suppliers, ensuring they employ state-of-the-art manufacturing methods and source high-grade materials that comply with international quality standards.
Healthcare Institutions
In healthcare institutions, dental implants are increasingly used in surgical applications, particularly in trauma and oncology cases where patients may require complex restorative solutions. The integration of dental implants in treatment plans can significantly improve patient outcomes and procedural efficiency. For international buyers from the Middle East and South America, key considerations include the reliability of suppliers, the traceability of materials, and the availability of support services for surgical teams.
Cosmetic Dentistry
Cosmetic dentistry heavily relies on veneers for aesthetic corrections, allowing practitioners to offer transformative solutions that enhance patients’ smiles. This application not only leads to higher patient referrals but also provides a competitive edge in the market. B2B buyers, especially in regions like Europe, should prioritize suppliers that offer comprehensive support, including training in application techniques and access to a variety of materials that cater to different aesthetic preferences and clinical requirements.
Related Video: How Dentists Insert Dental Implants
Strategic Material Selection Guide for dental implants or veneers
When selecting materials for dental implants and veneers, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the properties of the materials, their advantages and disadvantages, and regulatory compliance. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in dental implants and veneers, providing insights tailored for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is renowned for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, high corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. It can withstand significant mechanical loads and is stable under various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: Titanium implants are durable and have a long lifespan, making them suitable for permanent solutions. However, they can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes, such as precision machining.
Impact on Application: Titanium is compatible with various dental environments, including oral fluids, making it ideal for implants. Its resistance to corrosion ensures longevity, even in challenging conditions.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure that titanium implants comply with international standards such as ISO 13485 and ASTM F136. In regions like Europe, CE marking is essential, while in Africa and South America, buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding medical devices.
Zirconia
Key Properties: Zirconia is a ceramic material known for its aesthetic appeal and high strength. It offers excellent resistance to wear and is less prone to corrosion than metals.
Pros & Cons: Zirconia provides a natural tooth-like appearance, making it a preferred choice for veneers and visible implants. However, it can be more brittle than titanium, which may limit its use in load-bearing applications. Additionally, the cost can be higher due to the complex manufacturing techniques required.
Impact on Application: Zirconia is suitable for aesthetic applications and is biocompatible, reducing the risk of adverse reactions. However, its brittleness means it may not be ideal for all implant types.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should verify that zirconia products meet relevant standards such as ISO 6872 for dental ceramics. Understanding local market preferences for aesthetics versus durability is also crucial, especially in regions where cosmetic dentistry is prioritized.
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
Key Properties: PEEK is a high-performance polymer known for its excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility. It can withstand high temperatures and is stable under sterilization processes.
Pros & Cons: PEEK is lightweight and offers good flexibility, making it suitable for various dental applications. However, it may not have the same aesthetic appeal as metal or ceramic options and can be less durable under heavy loads.
Impact on Application: PEEK is particularly effective in environments where flexibility is required, such as in dental prosthetics. Its resistance to chemicals makes it compatible with various dental materials and cleaning agents.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure that PEEK implants comply with ASTM standards for polymers used in medical devices. Additionally, understanding the local acceptance of polymer-based implants versus traditional materials is essential for market success.
Glass Ceramics
Key Properties: Glass ceramics combine the properties of glass and ceramics, offering high strength and aesthetic qualities. They are known for their excellent translucency, mimicking natural teeth.
Pros & Cons: These materials provide superior aesthetics and are suitable for veneers and anterior implants. However, they can be less durable than metal options and may be prone to chipping or fracturing under stress.
Impact on Application: Glass ceramics are ideal for cosmetic applications where appearance is paramount. Their aesthetic properties make them a popular choice for veneers, but their mechanical limitations must be considered in load-bearing situations.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure that glass ceramics meet ISO standards for dental materials. In regions with high aesthetic demands, such as Europe, understanding consumer preferences for appearance versus durability is vital.
| Material | Typical Use Case for dental implants or veneers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Dental implants | High durability and biocompatibility | Higher cost and complex mfg | High |
| Zirconia | Aesthetic veneers and implants | Natural tooth-like appearance | Brittle, higher manufacturing cost | High |
| Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | Dental prosthetics | Lightweight and flexible | Less aesthetic appeal | Medium |
| Glass Ceramics | Veneers | Superior aesthetics | Prone to chipping | Medium |
This material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers in the dental industry, helping them make informed decisions based on the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. Understanding local regulatory requirements and market preferences is crucial for successful procurement and application.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dental implants or veneers
The manufacturing of dental implants and veneers involves several intricate processes and stringent quality assurance protocols. This guide outlines the typical stages of manufacturing and the quality control measures that international B2B buyers should consider when sourcing these products.
Manufacturing Processes
Material Preparation
The manufacturing journey begins with material selection. Common materials for dental implants include titanium and zirconia, chosen for their biocompatibility and strength. Key steps include:
– Material Sourcing: Ensure that materials comply with international standards, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices.
– Pre-Processing: Materials undergo cleaning and sterilization to eliminate contaminants that could affect the quality of the final product.
Forming
The forming stage involves shaping the materials into the desired configurations. Techniques can vary significantly:
– CNC Machining: Widely used for precision shaping of titanium implants. This method provides high accuracy and repeatability.
– Additive Manufacturing: Also known as 3D printing, this technique is gaining traction for its ability to create complex geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve. It allows for customization based on patient needs.
Assembly
For certain products like implant-supported bridges, assembly is a critical stage. This may involve:
– Component Integration: Combining various parts, such as abutments and fixtures, to create a complete implant system.
– Welding or Bonding: Ensuring that the components are securely attached, which is vital for long-term performance.
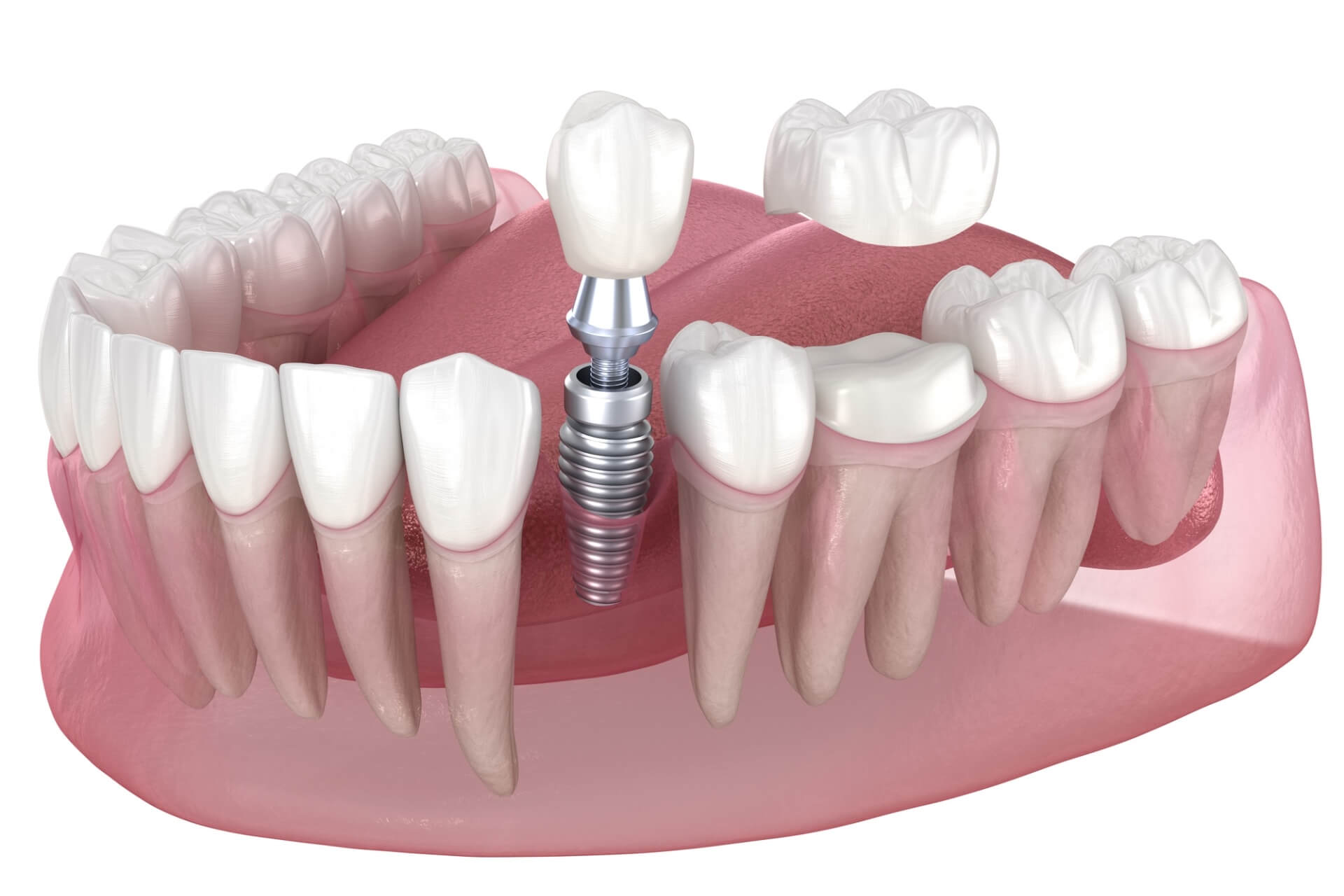
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the product’s surface characteristics, which is crucial for both aesthetic and functional purposes:
– Surface Treatment: Techniques such as sandblasting or acid etching improve osseointegration (the process by which the implant bonds with the jawbone).
– Polishing and Coating: Enhancements such as anodizing or applying a bioactive coating can further improve biocompatibility and aesthetic appeal.
Quality Assurance
International Standards
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of dental implants and veneers is governed by several international standards. Key standards include:
– ISO 9001: This standard ensures that the manufacturing processes are effective and consistently improve.
– ISO 13485: Specific to medical devices, it sets out requirements for a quality management system that demonstrates the ability to provide medical devices and related services that consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
Industry-Specific Certifications
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in Europe, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- FDA Approval: In the United States, the FDA oversees the approval of medical devices, which includes rigorous testing and documentation.
- API Certification: Relevant for those manufacturing in specific regions, ensuring adherence to local regulations.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is an ongoing process, and several checkpoints are critical:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the manufacturing process.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production helps catch defects early.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products to ensure they meet all specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Testing is vital to ensure product safety and efficacy. Common methods include:
– Mechanical Testing: Evaluates the strength and durability of implants under simulated conditions.
– Biocompatibility Testing: Ensures that materials do not provoke adverse biological responses.
– Sterility Testing: Confirms that the final product is free from viable microorganisms.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify the quality assurance practices of their suppliers. Here are actionable strategies:
– Conduct Audits: Regularly scheduled audits of suppliers can uncover potential quality issues and verify compliance with international standards.
– Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide detailed quality management documentation, including ISO certifications and quality control reports.
– Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes.
Regional Considerations for B2B Buyers
When sourcing dental implants or veneers, international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider regional nuances:
– Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulations; understanding local requirements (e.g., ANVISA in Brazil, CDSCO in India) is crucial.
– Cultural Preferences: Buyers in different markets may have unique aesthetic requirements or preferences regarding dental products.
– Supply Chain Logistics: Consideration of shipping times and costs, especially when sourcing from manufacturers in different continents, is essential for effective inventory management.
Conclusion
Manufacturing dental implants and veneers is a complex process that requires careful attention to detail and rigorous quality assurance practices. By understanding the manufacturing stages and quality control measures, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure high-quality products that meet the needs of their markets. Building relationships with compliant suppliers, verifying their quality practices, and staying informed about regional regulations will enhance the procurement process and contribute to successful business outcomes.
Related Video: SMART Quality Control for Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dental implants or veneers Sourcing
When sourcing dental implants or veneers, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the key cost components, pricing influencers, and essential tips for effective negotiation.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Titanium and zirconia are common materials for dental implants, with titanium being less expensive but zirconia offering superior aesthetics. Veneers typically use porcelain or composite resin, with porcelain being more costly due to its durability and natural appearance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in manufacturing, quality control, and logistics. Skilled labor is essential in dental implant production, often leading to higher costs, particularly in regions with stringent regulations and quality standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads, thus lowering the final product price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific implant designs can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers should consider whether standardized products can meet their needs to minimize tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Regulatory compliance and quality assurance processes add to the cost. Certifications such as ISO 13485 or FDA approvals require investment in testing and documentation, impacting the final pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary greatly depending on the destination, shipping method, and urgency. Understanding Incoterms is critical for buyers to clarify responsibilities related to transportation costs, insurance, and risk.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position, competition, and product exclusivity.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to negotiate Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) that align with their inventory strategies.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized implants or veneers may incur higher costs due to the need for specialized production techniques. Clear communication of specifications is vital to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to additional costs.
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials can significantly affect pricing. Buyers should evaluate the trade-offs between cost and quality to find the best fit for their market.
-
Quality/Certifications: Implants and veneers with higher certifications generally come at a premium. Buyers must balance the need for quality with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of suppliers can influence pricing. Engaging with established suppliers can provide assurance of quality but may come at a higher cost.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts or better terms for committed buyers or bulk orders.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. TCO includes logistics, potential warranty issues, and the cost of returns, which can significantly affect the overall expenditure.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can impact the final price. Understanding local regulations and compliance requirements is essential for smooth transactions.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Pricing for dental implants and veneers can vary widely based on the factors outlined. Buyers should seek quotes from multiple suppliers to gauge the market and ensure competitive pricing.
By carefully considering these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and market demands.
Spotlight on Potential dental implants or veneers Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘dental implants or veneers’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dental implants or veneers
Key Technical Properties of Dental Implants and Veneers
Understanding the essential technical properties of dental implants and veneers is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly for those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The following specifications are critical for making informed purchasing decisions:
-
Material Grade: Dental implants are commonly made from titanium or zirconia. Titanium (particularly grade 4) is favored for its strength and biocompatibility, while zirconia is increasingly popular for aesthetic applications. Understanding the material grade helps buyers assess durability and compatibility with patient health.
-
Surface Roughness: The surface texture of an implant can influence osseointegration, the process by which the implant anchors to the jawbone. A rougher surface (measured in micrometers) promotes better integration, which is vital for long-term success. Buyers should ensure that the products they source have optimal surface properties for enhanced performance.
-
Tolerance Levels: This refers to the permissible limits of variation in the implant dimensions. Tighter tolerances generally indicate better quality control and precision in manufacturing, which is essential for ensuring a proper fit and function. Buyers should inquire about tolerance specifications to avoid issues during installation.
-
Load-Bearing Capacity: Dental implants must withstand significant forces during chewing. The load-bearing capacity is typically measured in Newtons (N) and is essential to ensure that the implants can support the functional demands placed upon them. Buyers should ensure that selected products meet or exceed expected clinical loads.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Given that dental implants are exposed to saliva and various other bodily fluids, they must exhibit high corrosion resistance. This property is typically evaluated through tests that simulate oral conditions. Buyers should prioritize implants with proven corrosion resistance to ensure longevity and safety.
Common Trade Terminology in the Dental Implant Industry
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Below are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce products that are then marketed under another company’s brand. For dental implants, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers gauge product quality and reliability, as well as potential for customization.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management, especially for buyers in emerging markets where cash flow may be a concern.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a standard business process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products. This is particularly useful for B2B buyers to compare pricing and terms across multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive competitive offers.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and liability.
-
CE Marking: This certification indicates that a product meets European Union safety, health, and environmental protection standards. For buyers in Europe, ensuring that dental implants have CE marking is vital for compliance and marketability.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complex landscape of dental implants and veneers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions that align with industry standards and patient needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the dental implants or veneers Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global dental implants and veneers market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for aesthetic dental solutions and advancements in dental technology. As of 2023, the market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 7%, with notable contributions from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key drivers include a rising geriatric population, increased disposable income, and heightened awareness of oral health.
International B2B buyers should be aware of emerging technologies such as 3D printing and digital dentistry, which are revolutionizing the manufacturing processes. These technologies not only enhance the precision and customization of implants and veneers but also reduce production times and costs. Additionally, the shift towards minimally invasive procedures is influencing product development, as dental professionals seek solutions that offer quicker recovery times for patients.
Another important trend is the globalization of supply chains, which allows buyers from diverse regions to source high-quality products at competitive prices. However, buyers must navigate complex regulations and standards across different countries, such as CE marking in Europe, FDA approval in the U.S., and local regulations in African and Middle Eastern markets. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming increasingly vital in the dental implants and veneers sector, as environmental concerns gain traction among consumers and regulatory bodies. The production of dental implants often involves materials like titanium and zirconia, which have significant environmental footprints. International B2B buyers should consider suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly practices and materials, such as biodegradable polymers or recycled metals.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers should establish partnerships with manufacturers who demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and adhere to ethical labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 26000 for social responsibility can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, adopting ‘green’ certifications can enhance a company’s marketability. For instance, obtaining certifications that validate the use of sustainable materials in dental products not only appeals to eco-conscious consumers but can also open doors to new markets and partnerships, particularly in Europe where regulatory frameworks are increasingly stringent.
Brief Evolution/History
The dental implants and veneers sector has evolved significantly since the first modern implants were introduced in the 1960s. Initially, these implants were made from simple materials like stainless steel, which lacked biocompatibility. Over the decades, advancements in materials science led to the development of titanium implants, which are now the gold standard due to their excellent integration with bone (osseointegration).
In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) further transformed the sector, allowing for customized solutions tailored to individual patient needs. This evolution continues today with the advent of digital dentistry and 3D printing technologies, which promise to further enhance the precision, affordability, and accessibility of dental solutions worldwide.
For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential for recognizing the ongoing innovation in the market and the potential for future developments that could impact sourcing strategies and consumer preferences.
Related Video: Full Mouth Dental Implants: Everything You Need to Know and Cost
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dental implants or veneers
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of dental implants or veneers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their certifications such as ISO 13485 and CE marking, which indicate compliance with international quality standards. Research their manufacturing processes and quality management systems to ensure they can meet your specific needs. Additionally, request references or case studies from other international buyers to gauge their reliability and service quality. Consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if possible, or utilize third-party audits to confirm their credibility and operational practices. -
Can I customize dental implants or veneers to meet specific patient needs?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for dental implants and veneers, including variations in size, shape, and material. Discuss your requirements upfront, as this can affect lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs). Ensure that the supplier has a robust design and prototyping process in place to accommodate custom orders. Collaborating closely with the supplier during the design phase can enhance product functionality and patient satisfaction. -
What are the typical lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs) for dental implants or veneers?
Lead times can vary significantly based on the supplier’s capabilities, product complexity, and customization level. Generally, standard orders may take 4-6 weeks, while custom orders can extend to 8-12 weeks. MOQs are also supplier-dependent; some may allow small initial orders, especially for new business relationships, while others may require higher quantities to justify production costs. It’s advisable to negotiate these terms during initial discussions to align expectations. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing dental implants or veneers?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include partial upfront payments (30-50%), with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Some suppliers may offer credit terms based on your purchasing history and relationship. Always clarify payment terms and methods (e.g., wire transfer, letter of credit) in advance to avoid misunderstandings. Consider using escrow services for larger transactions to ensure both parties are protected. -
How can I ensure the quality of dental implants or veneers before purchase?
To ensure product quality, request comprehensive documentation from suppliers, including certificates of compliance, detailed product specifications, and test reports. Consider conducting pre-shipment inspections through third-party services to verify that the products meet your standards. It’s also beneficial to request samples before placing a large order, allowing you to assess the product firsthand. Establish clear quality assurance protocols in your purchasing agreement to safeguard your interests. -
What certifications should I verify for suppliers of dental implants or veneers?
Key certifications to look for include ISO 13485 for quality management systems in medical devices, CE marking for compliance with European safety standards, and FDA approval if sourcing from the U.S. These certifications demonstrate that the supplier adheres to stringent quality and safety regulations. In regions like Africa and the Middle East, local regulatory compliance may also be necessary, so verify any additional certifications relevant to your market. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing dental implants or veneers?
Logistics is crucial in international trade. Assess the supplier’s experience with shipping to your region, including customs clearance and regulatory compliance. Determine the shipping methods available (air, sea, or express courier) and their associated costs. It’s also important to discuss who will handle duties and taxes upon import. Establish a reliable logistics partner to minimize delays and ensure timely delivery, especially when dealing with perishable or time-sensitive products. -
How should I handle disputes or issues with suppliers of dental implants or veneers?
Establishing clear terms and conditions in your contract can help mitigate disputes. Include clauses for dispute resolution, such as mediation or arbitration, to provide structured avenues for resolution. Maintain open lines of communication with your supplier to address issues promptly as they arise. If a dispute escalates, document all communications and agreements for reference. Involvement of legal counsel specializing in international trade can be beneficial for navigating complex issues.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dental implants or veneers
Strategic sourcing in the dental implants and veneers market is pivotal for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance their competitive edge. By leveraging a robust sourcing strategy, businesses can ensure access to high-quality products while optimizing costs and compliance with regulatory standards. Understanding the diverse types of dental implants, the latest manufacturing technologies, and the materials involved is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Takeaways:
- Quality Assurance: Prioritize suppliers with proven quality management systems, such as ISO 13485 certification, to ensure product reliability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarize yourself with the regulatory requirements specific to your region, including CE marking in Europe and FDA approvals in the USA.
- Innovative Technologies: Explore advancements like additive manufacturing which can lead to customized solutions and reduced lead times.
As the dental market continues to evolve, staying informed about trends and innovations will be crucial. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively engage with suppliers and industry experts to navigate this dynamic landscape. Now is the time to strengthen your supply chain by forging strategic partnerships that will drive growth and enhance patient outcomes.
