Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for zirconium dental implants
In the evolving landscape of dental restoration, zirconium dental implants stand out as a pivotal innovation, offering exceptional strength, aesthetic appeal, and biocompatibility. As the demand for durable and visually appealing dental solutions increases globally, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of zirconium implants becomes critical for B2B buyers. These implants not only provide superior performance but also foster patient satisfaction, making them a preferred choice among dental professionals.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international B2B buyers with essential insights into zirconium dental implants. We will explore various types of implants, including monolithic, layered, and hybrid zirconia, each tailored for specific clinical applications. Additionally, we will delve into the manufacturing processes and quality control measures that ensure the reliability and safety of these products, highlighting the importance of regulatory compliance in different markets.
Buyers will gain valuable information on supplier options, cost considerations, and market trends that can influence purchasing decisions. Furthermore, a dedicated FAQ section will address common queries, aiding buyers in navigating the complexities of sourcing zirconium dental implants. By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers will be equipped to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and enhance their offerings in the competitive dental market.
Understanding zirconium dental implants Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monolithic Zirconia | Solid structure, high strength, and durability | Posterior crowns and high-stress restorations | Pros: Excellent wear resistance, cost-effective. Cons: Limited aesthetic options compared to layered types. |
| Layered Zirconia | Combination of zirconia core and porcelain outer layer | Anterior crowns and aesthetic restorations | Pros: Superior aesthetics, natural appearance. Cons: More expensive due to layering process. |
| Hybrid Zirconia | Composite material enhancing durability and thermal resistance | Versatile applications in dental restorations | Pros: High performance, adaptable for various restorations. Cons: Requires careful handling during manufacturing. |
| Zirconia Implants | Root form implants made of zirconia for osseointegration | Implant dentistry and tooth replacement | Pros: Biocompatible, reduced risk of allergic reactions. Cons: Limited availability in some regions. |
| Customized Zirconia | Tailored zirconia solutions based on specific clinical needs | Tailor-made restorations for unique cases | Pros: Personalized solutions, optimal fit. Cons: Longer lead times and potentially higher costs. |
Monolithic Zirconia
Monolithic zirconia implants are crafted from a single block of zirconia, providing exceptional strength and durability. They are particularly suitable for posterior crowns where chewing forces are significant. B2B buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of this type, as it requires no additional layering, making it an economical choice for high-stress applications. However, aesthetic options may be limited compared to layered variations, which could be a deciding factor for clients prioritizing visual appeal.
Layered Zirconia
Layered zirconia combines the robust properties of zirconia with the aesthetic advantages of porcelain. This type is ideal for anterior crowns, where appearance is critical. B2B buyers can leverage its realistic translucency and customizable color to meet patient demands. However, the increased complexity in manufacturing and higher costs could be a concern for practices focused on budget constraints. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced aesthetics against the investment required.
Hybrid Zirconia
Hybrid zirconia represents a blend of zirconia with other advanced materials, enhancing its performance in demanding applications. This type is particularly valuable in versatile dental restorations that require both strength and adaptability. B2B buyers should note its excellent thermal resistance and mechanical properties, making it suitable for a wide range of clinical scenarios. However, careful handling during manufacturing is essential, as the composite nature may complicate production processes.
Zirconia Implants
Zirconia implants are designed for osseointegration, offering a biocompatible solution for tooth replacement. Their non-reactive nature significantly reduces the risk of allergic reactions, making them an attractive option for many patients. For B2B buyers, the growing demand for biocompatible materials in dental practices underscores the importance of sourcing high-quality zirconia implants. However, availability may vary by region, necessitating careful supplier selection to ensure consistent access.
Customized Zirconia
Customized zirconia solutions are tailored to meet specific clinical requirements, providing optimal fit and function. This type is particularly beneficial for unique cases that necessitate personalized approaches. B2B buyers should consider the added value of bespoke restorations, as they can enhance patient satisfaction and clinical outcomes. However, the trade-off includes longer lead times and potentially higher costs, which may not align with all buyers’ operational frameworks.
Related Video: Zirconia All on 4 dental implants; is it right for you?
Key Industrial Applications of zirconium dental implants
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of zirconium dental implants | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Clinics | Use of zirconium implants for single-tooth replacements | Enhanced patient satisfaction due to aesthetics and durability | Compliance with local regulations, biocompatibility testing |
| Dental Laboratories | Fabrication of custom dental prosthetics | Streamlined production processes and reduced failure rates | Access to advanced CAD/CAM technology, quality of materials |
| Orthodontics | Integration in orthodontic treatment plans | Improved treatment outcomes and patient comfort | Availability of support for alignment and fitting procedures |
| Cosmetic Dentistry | Application in smile makeovers | High aesthetic appeal leading to increased patient referrals | Expertise in aesthetics, customization options |
| Dental Equipment Suppliers | Supply of zirconium implants to dental practices | Competitive pricing and reliable supply chain | Supplier certifications, quality assurance measures |
Dental Clinics
Zirconium dental implants are increasingly used in dental clinics for single-tooth replacements. Their aesthetic appeal and durability make them a preferred choice for patients seeking natural-looking restorations. For international buyers, it is crucial to ensure that the implants meet local regulatory standards and undergo biocompatibility testing to minimize the risk of allergic reactions. Sourcing from manufacturers with a proven track record in quality assurance will enhance patient satisfaction and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Dental Laboratories
In dental laboratories, zirconium implants are essential for the fabrication of custom dental prosthetics, such as crowns and bridges. The use of zirconium not only improves the strength and longevity of these restorations but also reduces the failure rates associated with inferior materials. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer advanced CAD/CAM technology for precise manufacturing and ensure that the raw materials used are of high quality. This will result in a more efficient production process and superior outcomes for patients.
Orthodontics
Zirconium dental implants play a significant role in orthodontic treatment plans, where they are used to anchor orthodontic devices. Their strength and biocompatibility contribute to improved treatment outcomes and enhanced patient comfort. International buyers should seek suppliers that provide comprehensive support for alignment and fitting procedures, ensuring that the implants integrate seamlessly into the overall orthodontic strategy. This collaboration can lead to better patient experiences and higher retention rates.
Cosmetic Dentistry
In the realm of cosmetic dentistry, zirconium implants are pivotal for achieving stunning smile makeovers. Their high aesthetic value, mimicking the translucency and color of natural teeth, allows dental professionals to create visually appealing results that boost patient confidence. B2B buyers must consider suppliers with expertise in aesthetics and the ability to provide customization options to meet diverse patient needs. This focus on aesthetics can lead to increased referrals and a stronger reputation in the market.
Dental Equipment Suppliers
Dental equipment suppliers are vital in the distribution of zirconium implants to dental practices. By ensuring a reliable supply chain and competitive pricing, these suppliers can significantly enhance the operational efficiency of dental clinics. Buyers should evaluate potential suppliers based on their certifications and quality assurance measures to guarantee that the implants meet the necessary standards. A solid partnership with a reputable supplier can lead to sustained business growth and improved service delivery.
Related Video: Titanium vs Ceramic (Zirconia): Choosing The Right Dental Implants For You
Strategic Material Selection Guide for zirconium dental implants
When selecting materials for zirconium dental implants, it is essential to evaluate various options based on their properties, performance, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the production of zirconium dental implants, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Monolithic Zirconia
Monolithic zirconia is a single solid block of zirconia used primarily for dental crowns and bridges.
- Key Properties: It exhibits exceptional hardness, making it highly resistant to wear and fracture. Monolithic zirconia can withstand significant chewing forces and is thermally stable, which is crucial for oral applications.
- Pros & Cons: Its durability and wear resistance make it ideal for posterior crowns where stress is high. However, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring advanced techniques and equipment, which may increase production costs.
- Impact on Application: Monolithic zirconia is compatible with various dental restoration procedures and provides excellent aesthetics due to its tooth-like appearance.
- Considerations for Buyers: International buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ISO 13485 for medical devices. Understanding regional preferences for aesthetics and strength is also vital.
2. Layered Zirconia
Layered zirconia combines a zirconia core with an outer layer of porcelain, offering both strength and aesthetic appeal.
- Key Properties: The zirconia core provides strength, while the porcelain layer enhances aesthetics, mimicking the translucency of natural teeth.
- Pros & Cons: This material is versatile and suitable for anterior crowns where appearance is paramount. However, the layering process can complicate manufacturing and increase costs due to the need for additional materials and labor.
- Impact on Application: Layered zirconia is particularly effective in visible restorations, providing a natural look while maintaining durability.
- Considerations for Buyers: Buyers must consider the regulatory requirements for layered materials in their respective countries, such as CE marking in Europe or FDA approval in the U.S.
3. Hybrid Zirconia
Hybrid zirconia is a composite material that blends zirconia with other advanced ceramics, enhancing its performance characteristics.
- Key Properties: This material offers improved thermodynamic properties and mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-stress applications.
- Pros & Cons: The adaptability of hybrid zirconia allows for innovative dental solutions, but its complexity can lead to higher manufacturing costs and longer production times.
- Impact on Application: Hybrid zirconia is ideal for demanding dental applications, including implants that require both strength and aesthetic quality.
- Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should assess the compatibility of hybrid zirconia with local dental practices and regulations, ensuring that the material meets international standards.
4. Zirconium Alloy
Zirconium alloys, often combined with other metals, are used to enhance the mechanical properties of dental implants.
- Key Properties: These alloys typically exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for long-term use in the oral environment.
- Pros & Cons: The primary advantage is their enhanced durability and resistance to wear. However, the cost of alloying elements can make these materials more expensive than pure zirconia.
- Impact on Application: Zirconium alloys are particularly effective in environments where corrosion resistance is critical, such as in patients with high acidity in their saliva.
- Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific alloy compositions and their compliance with international standards, as well as the potential need for additional certifications.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for zirconium dental implants | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monolithic Zirconia | Posterior crowns and bridges | Exceptional durability and wear resistance | Complex manufacturing process | High |
| Layered Zirconia | Anterior crowns for aesthetics | Natural appearance with strong core | Higher production costs due to layering | Medium |
| Hybrid Zirconia | High-stress dental applications | Enhanced mechanical and thermal properties | More expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Zirconium Alloy | Long-term implants in corrosive environments | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost due to alloying elements | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions when sourcing zirconium dental implants tailored to specific market needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for zirconium dental implants
Zirconium dental implants are increasingly favored in the dental industry due to their strength, aesthetic appeal, and biocompatibility. Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in producing these implants is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section delves into the essential stages of manufacturing, quality control (QC) standards, and practical insights for verifying supplier quality.
Manufacturing Processes for Zirconium Dental Implants
The manufacturing of zirconium dental implants involves several critical stages:
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of high-purity zirconia powder. This powder is typically derived from zirconium oxide (ZrO2) and is processed to achieve the desired properties. Key techniques include:
- Milling: The zirconia powder is milled to achieve the necessary particle size, which is crucial for subsequent forming processes.
- Sintering: The milled powder is then compacted and subjected to high temperatures in a sintering process, which enhances its density and strength.
2. Forming
Once the material is prepared, it moves to the forming stage. This involves shaping the zirconia into the desired implant form. Common methods include:
- Injection Molding: This technique allows for precise shaping of complex geometries. It is essential for creating implants that fit well within the dental arch.
- Pressing: Cold isostatic pressing can also be used to form the implants, providing uniform density and reducing defects.
3. Assembly
After forming, the components may require assembly, especially if they are designed to work in conjunction with other dental devices. This stage may include:
- Component Integration: For implants that involve multiple parts, such as abutments, precise alignment and integration are critical.
- Surface Treatments: Surface modifications, such as sandblasting or coating, enhance osseointegration and improve the implant’s success rate.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing processes that ensure the implants are ready for clinical use. This includes:
- Polishing: The implants are polished to achieve a smooth surface, which is vital for both aesthetics and biocompatibility.
- Quality Inspection: Final inspections are conducted to ensure that the implants meet all specifications and standards.
Quality Assurance in Zirconium Dental Implants
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that each implant meets stringent international standards. Key aspects of QC include:
International Standards
B2B buyers should be familiar with the following standards that govern the quality of dental implants:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS), ensuring consistent quality across all manufacturing processes.
- ISO 13485: Specifically tailored for medical devices, this standard focuses on regulatory compliance and risk management throughout the product lifecycle.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- FDA Approval: In the United States, FDA approval is necessary for dental implants, ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Quality Control Checkpoints
To ensure the quality of zirconium dental implants, manufacturers typically implement several quality control checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials, including zirconia powder, are inspected upon receipt to verify their quality and compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are performed to monitor processes and detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished implants undergo rigorous testing and inspections to ensure they meet all specifications before being released to the market.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods play a vital role in quality assurance. Some of the most common include:
- Mechanical Testing: Includes tensile strength, fatigue, and wear tests to assess the durability of the implants.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Evaluates how the implant interacts with biological tissues, ensuring safety for patients.
- Surface Roughness Measurement: Assesses the surface texture, which is critical for osseointegration.
Verifying Supplier Quality
For international B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to quality standards is paramount. Here are actionable strategies to verify supplier QC:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify compliance with international standards and internal quality processes.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances
When sourcing zirconium dental implants, buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances:
- Regional Regulations: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements. For example, the South African Health Products Regulatory Authority (SAHPRA) oversees medical devices in South Africa, while in Turkey, the Turkish Medicines and Medical Devices Agency (TITCK) governs the market.
- Documentation Requirements: Ensure that suppliers can provide all necessary documentation, including certificates of compliance with ISO standards and any local regulatory approvals.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding the local market’s expectations and cultural nuances can aid in building strong relationships with suppliers.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for zirconium dental implants, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality products that meet the needs of their dental practices and patients.
Related Video: Full arch dental implant supported zirconia with titanium bar
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for zirconium dental implants Sourcing
When sourcing zirconium dental implants, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the key cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips for negotiating favorable terms.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in zirconium dental implants is the raw material itself. Zirconia, known for its strength and biocompatibility, can vary significantly in price based on purity and source. Buyers should consider sourcing from reputable suppliers to ensure quality, which can affect overall pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect expenses related to the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is essential for precision machining and finishing of zirconium implants. Regions with higher labor costs may see increased pricing, so evaluating supplier locations can help in cost management.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead, making it vital to assess the operational efficiency of potential suppliers.
-
Tooling: The cost of molds and tooling necessary for producing zirconium implants can be substantial, particularly for custom designs. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs, especially for specialized or low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Given the medical nature of dental implants, rigorous QC processes are crucial. This includes testing for durability, biocompatibility, and compliance with international standards. QC costs can be significant and should be factored into the overall price.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the geographic location of the supplier and the buyer. For international transactions, understanding Incoterms is crucial to determining who bears the cost and risk during transit.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the specific buyer-supplier relationship.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can influence pricing. Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing capabilities.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom implants designed for specific clinical needs may incur additional costs. Clear communication of specifications can help manage expectations and pricing.
-
Materials: The choice of zirconium grade (e.g., monolithic vs. layered) significantly impacts pricing. Buyers should evaluate the performance characteristics necessary for their applications to make informed material choices.
-
Quality/Certifications: Implants that meet stringent international standards (e.g., ISO 13485, CE marking) may come at a premium due to the associated compliance costs. Buyers must weigh the importance of certifications against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Building strong relationships with reputable suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers to clarify responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can all influence final costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Buyers should approach negotiations with a clear understanding of their needs and the supplier’s capabilities. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can lead to favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, maintenance, and potential rework costs. This holistic view helps in making informed sourcing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of regional pricing differences and currency fluctuations that may affect costs. Conducting market research can provide insights into fair pricing benchmarks.
Disclaimer
Prices for zirconium dental implants can vary widely based on the factors discussed. This analysis serves as a guideline; actual costs should be confirmed with suppliers to account for real-time market conditions and specific buyer requirements.
Spotlight on Potential zirconium dental implants Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘zirconium dental implants’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for zirconium dental implants
Zirconium dental implants are at the forefront of modern dentistry due to their superior properties and aesthetic appeal. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the technical specifications and trade terminology is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The classification of zirconium based on its purity and composition, often denoted as ZrO2.
– B2B Importance: Higher-grade zirconium provides better strength and biocompatibility, which directly impacts the longevity and success rate of implants. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee high material grades to ensure product quality. -
Tensile Strength
– Definition: The maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking, typically measured in megapascals (MPa).
– B2B Importance: Zirconium implants need high tensile strength to endure the forces exerted during chewing. Understanding tensile strength helps buyers assess the durability of implants in different applications, especially in high-stress environments. -
Fracture Toughness
– Definition: A measure of a material’s ability to resist crack propagation, often expressed in MPa√m.
– B2B Importance: High fracture toughness indicates that the implant will remain intact under stress, reducing the risk of failure. This is critical for buyers looking for reliable, long-lasting solutions. -
Surface Roughness
– Definition: The texture of the implant surface, which can influence osseointegration—the process by which the implant bonds with the jawbone.
– B2B Importance: A rougher surface generally promotes better bone integration, leading to improved stability and longevity. Buyers should inquire about surface treatments and their impact on performance. -
Thermal Stability
– Definition: The ability of zirconium to maintain its properties under varying temperature conditions.
– B2B Importance: Thermal stability is crucial for implants exposed to the heat generated in the mouth. Buyers should ensure that the implants can withstand these conditions without compromising structural integrity.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance for Buyers: Understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers evaluate the authenticity and quality of the products offered. OEMs often have rigorous quality controls in place. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance for Buyers: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and manage costs effectively. Suppliers with lower MOQs may provide more flexibility for smaller practices or emerging markets. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products.
– Importance for Buyers: An RFQ allows buyers to compare offers from different suppliers, ensuring they receive competitive pricing and favorable terms. -
Incoterms
– Definition: International commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade.
– Importance for Buyers: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations, which is crucial for effective supply chain management.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- CE Marking
– Definition: A certification mark that indicates a product’s compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– Importance for Buyers: For those sourcing products in Europe, ensuring that zirconium dental implants carry CE marking is essential for regulatory compliance and market acceptance.
By grasping these essential properties and terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the complex landscape of zirconium dental implants more effectively, ensuring quality, compliance, and satisfaction in their procurement processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the zirconium dental implants Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The zirconium dental implants market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for aesthetic and durable dental solutions. Globally, the trend towards minimally invasive procedures and advancements in dental technology are reshaping the landscape. B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of several emerging trends:
-
Technological Innovations: The rise of CAD/CAM technology is streamlining the design and manufacturing processes of zirconium dental implants, enhancing precision and reducing lead times. Buyers should seek suppliers who leverage these technologies for improved product consistency.
-
Customization and Personalization: There is a growing demand for customized dental implants tailored to individual patient needs. Suppliers that offer bespoke solutions can provide a competitive edge and foster stronger partnerships with dental practices.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory standards for dental implants. Understanding these regulations is crucial for international buyers. For instance, CE marking in Europe and FDA approval in the US are essential for market entry. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with local regulations to avoid legal complications.
- Rising Demand in Emerging Markets: Countries in Africa and South America are witnessing increased dental healthcare investments, leading to higher demand for quality dental implants. Buyers in these regions should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers who can support the growing market with affordable yet high-quality solutions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern in the zirconium dental implants sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the sourcing of raw materials is under scrutiny. B2B buyers should consider the following aspects:
-
Environmental Impact: The production of zirconium dental implants involves energy-intensive processes. Buyers should seek suppliers who utilize renewable energy sources and implement waste reduction strategies in their manufacturing practices.
-
Ethical Supply Chains: Ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical sourcing practices is critical. This includes verifying that raw materials are sourced responsibly and that labor practices meet international standards. Buyers should engage with suppliers who are transparent about their supply chain and have robust ethical policies in place.
-
‘Green’ Certifications: Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other sustainability credentials can help buyers identify suppliers committed to minimizing their environmental footprint. Collaborating with certified suppliers not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products.
Brief Evolution/History
Zirconium dental implants have evolved significantly since their introduction in the late 20th century. Initially, titanium was the dominant material; however, zirconium gained popularity due to its superior aesthetic properties and biocompatibility. Over the years, advancements in material science have led to the development of various zirconium forms, such as monolithic and layered zirconia, which cater to different clinical requirements. This evolution has positioned zirconium as a leading choice for dental professionals seeking durable and aesthetically pleasing solutions for their patients. As the market continues to grow, international B2B buyers must stay informed about these advancements to make strategic sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of zirconium dental implants
-
How can I vet suppliers of zirconium dental implants?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by checking their certifications such as ISO 13485 for quality management systems and CE marking for compliance with European standards. Request references and case studies from previous clients in your region. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities or conducting virtual audits to assess their production capabilities. Look for suppliers who have a proven track record in international trade, especially in regions similar to yours, such as Africa or South America, to ensure they understand local market dynamics. -
Can zirconium dental implants be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for zirconium dental implants. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, including dimensions, aesthetics, and mechanical properties. Customization can also extend to packaging and labeling to suit local regulations or branding requirements. Ensure that the supplier has the technical capability and experience in producing tailored solutions, as this can significantly enhance the product’s acceptance in your target market. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for zirconium dental implants?
MOQs for zirconium dental implants can vary widely depending on the supplier and product specifications, typically ranging from 50 to 500 units. Lead times also differ based on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production capacity, often ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. When negotiating, clarify these terms upfront and consider your inventory needs to avoid excess stock or shortages. Suppliers who are flexible with MOQs can be beneficial for smaller businesses or those entering new markets. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should implement rigorous quality assurance processes that include raw material testing, in-process inspections, and final product evaluations. Ask for documentation of their quality control protocols, such as statistical process control (SPC) and validation reports. Certifications like ISO 13485 and compliance with local regulations are essential indicators of their commitment to quality. Additionally, inquire about their ability to provide post-market surveillance data to ensure long-term product performance. -
What certifications should zirconium dental implants have for international trade?
For international trade, the most crucial certifications include CE marking for the European market, FDA approval for the U.S. market, and local certifications such as CDSCO in India or ANVISA in Brazil. These certifications demonstrate compliance with safety and efficacy standards. Suppliers should be able to provide documentation proving their products meet these regulatory requirements. Ensure you understand the certification process in your specific region to avoid delays in importing. -
How can I manage logistics and shipping for zirconium dental implants?
Effective logistics management involves selecting reliable shipping partners who specialize in medical device transportation. Consider factors such as shipping times, costs, and customs clearance processes in your region. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and understand the regulatory requirements for medical devices. Additionally, establish a clear communication channel for tracking shipments and managing any unexpected delays or issues during transit. -
What steps should I take if a dispute arises with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, begin by reviewing the contract terms related to quality, delivery, and payment. Engage in open communication with the supplier to resolve the issue amicably. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as outlined in your agreement. Document all communications and decisions made during the dispute process for reference. Establishing clear terms and conditions upfront can help mitigate potential disputes and provide a framework for resolution. -
What payment options are typically available for international purchases of zirconium dental implants?
Payment options for international purchases often include wire transfers, letters of credit, and payment platforms like PayPal or Escrow services. Wire transfers are common for larger transactions, while letters of credit provide security for both parties. Discuss payment terms with your supplier, considering factors like advance payment, payment upon delivery, or installment plans. Be aware of any currency exchange considerations and transaction fees that may apply, particularly when dealing with suppliers in different regions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for zirconium dental implants
The strategic sourcing of zirconium dental implants presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As the demand for durable, aesthetically pleasing, and biocompatible dental solutions continues to rise, leveraging the unique properties of zirconia can provide a competitive edge. Key takeaways include:
- Quality Assurance: Ensure suppliers adhere to global regulatory standards, such as ISO 13485 and CE marking, to guarantee product reliability.
- Material Advantages: Focus on sourcing monolithic and layered zirconia for their exceptional strength, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal, catering to diverse clinical needs.
- Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the lifecycle costs of zirconium implants, as their durability can lead to lower long-term expenses compared to traditional materials.
In conclusion, fostering strategic partnerships with reliable manufacturers can enhance your product offerings and patient satisfaction. Embrace the growing trend towards zirconium dental implants to position your business at the forefront of the dental restoration market. Take action now—explore sourcing opportunities that align with your business goals and tap into the potential of zirconium technology to drive your success in the competitive dental industry.
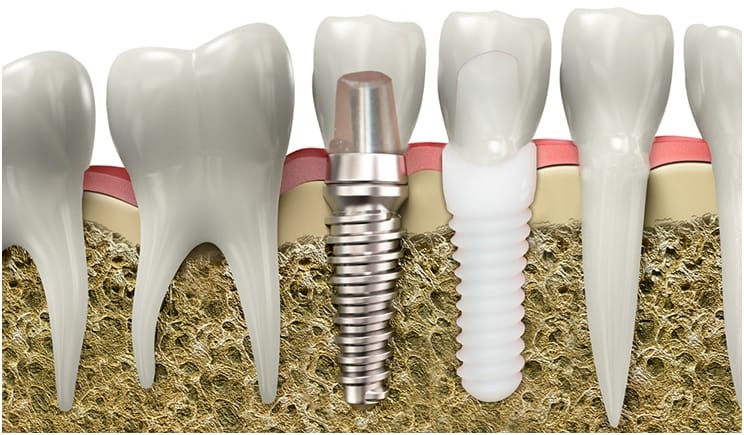
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
