Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for titanium vs ceramic dental implants
As the global dental implant market evolves, the choice between titanium and ceramic implants has emerged as a pivotal consideration for dental professionals and international B2B buyers. Understanding the nuances between these two materials is essential, as they offer distinct advantages and limitations that can impact patient outcomes and practice profitability. Titanium implants, with their long-standing history and robust clinical data, continue to be a reliable choice, whereas ceramic implants, particularly those crafted from zirconia, are gaining traction due to their aesthetic benefits and biocompatibility.
This guide provides a comprehensive analysis of the titanium versus ceramic dental implant landscape, covering various aspects crucial for informed sourcing decisions. Key topics include material properties, manufacturing and quality control standards, supplier profiles, and cost considerations. Additionally, we will address common FAQs, ensuring that buyers from diverse regions—including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—are equipped with the knowledge necessary to navigate this competitive market landscape.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that align with their business goals and patient needs, ultimately fostering trust and satisfaction in their dental offerings. This exploration into the world of dental implants empowers buyers to identify high-quality products that meet the evolving demands of dental practices and patients alike.
Understanding titanium vs ceramic dental implants Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Screw Implants | Traditional design, high durability, excellent osseointegration. | General dental practices, oral surgery | Pros: Proven longevity, cost-effective. Cons: Aesthetic concerns due to metallic color. |
| Zirconia Screw Implants | Made from zirconia, tooth-colored, excellent biocompatibility. | Aesthetic-focused dental practices | Pros: Superior aesthetics, hypoallergenic. Cons: Higher cost, limited long-term data. |
| Titanium Root Form Implants | Root-like structure, designed for immediate loading. | Implantology, restorative dentistry | Pros: High success rates, strong integration. Cons: Requires sufficient bone density. |
| Zirconia One-Piece Implants | Monoblock design, no abutment required, enhanced aesthetics. | Cosmetic dentistry, holistic practices | Pros: Simplified procedure, natural appearance. Cons: Technique-sensitive, potential fracture risk. |
| Titanium Mini Implants | Smaller diameter, less invasive, used for stabilization. | Orthodontics, denture stabilization | Pros: Minimal surgical intervention, cost-effective. Cons: Limited load-bearing capacity. |
Titanium Screw Implants
Titanium screw implants are the standard in dental implantology, favored for their robust mechanical properties and high success rates. They are well-suited for a wide range of applications, including general dental practices and oral surgery. When considering B2B purchasing, buyers should note their cost-effectiveness and proven longevity. However, the metallic appearance can be a concern for patients prioritizing aesthetics, particularly in visible areas.
Zirconia Screw Implants
Zirconia screw implants are gaining traction due to their aesthetic appeal and biocompatibility. These implants are ideal for dental practices focused on cosmetic outcomes, as their tooth-like color blends seamlessly with natural teeth. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of superior aesthetics against the higher costs and the relatively limited long-term data available. The hypoallergenic nature of zirconia makes it an attractive option for patients with metal sensitivities.
Titanium Root Form Implants
These implants mimic the natural root structure of teeth and are designed for immediate loading, making them suitable for implantology and restorative dentistry. Their high success rates and strong osseointegration capabilities are significant selling points for B2B buyers. However, the need for sufficient bone density can limit their applicability in certain cases, which is a critical consideration for purchasing decisions.
Zirconia One-Piece Implants
Zirconia one-piece implants eliminate the need for an abutment, simplifying the surgical procedure and enhancing aesthetics. They are particularly appealing to cosmetic dentists and holistic practices. B2B buyers should consider the advantages of a streamlined process and natural appearance, while also being aware of the technique sensitivity and potential fracture risks associated with these implants.
Titanium Mini Implants
Titanium mini implants offer a less invasive alternative for stabilizing dentures and orthodontic appliances. They are particularly useful in cases where traditional implants may not be feasible. B2B buyers will appreciate their minimal surgical intervention and cost-effectiveness, but should also take into account their limited load-bearing capacity, which may restrict their use in more demanding applications.
Related Video: Titanium vs Ceramic (Zirconia): Choosing The Right Dental Implants For You
Key Industrial Applications of titanium vs ceramic dental implants
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of titanium vs ceramic dental implants | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Clinics | Use of titanium implants for high-volume restorations | Proven durability and cost-effectiveness | Supplier reliability, certification, and material quality |
| Cosmetic Dentistry | Ceramic implants for aesthetic restorations | Enhanced patient satisfaction with natural appearance | Availability of various designs and sizes |
| Orthodontics | Titanium for anchorage devices in orthodontic treatments | Strong support for dental movements | Compliance with health regulations and biocompatibility |
| Dental Laboratories | Production of custom ceramic implants | Ability to meet specific patient needs | Advanced manufacturing capabilities and technology |
| Medical Device Companies | Research and development of hybrid implants | Innovation in dental solutions and market differentiation | Access to the latest materials and clinical data |
Dental Clinics
In dental clinics, titanium implants are widely used for high-volume restorations due to their proven durability and cost-effectiveness. These implants have a long history of success, making them a reliable choice for dental professionals. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing titanium implants requires ensuring that suppliers are certified and maintain high material quality to meet local health regulations.
Cosmetic Dentistry
Ceramic implants have gained popularity in cosmetic dentistry for aesthetic restorations. Their natural appearance is ideal for patients seeking a seamless blend with existing teeth, enhancing overall satisfaction. Buyers in Europe, particularly in markets like Italy, should prioritize suppliers that offer a range of designs and sizes to cater to diverse patient needs, ensuring that the implants meet both aesthetic and functional requirements.
Orthodontics
In orthodontics, titanium implants serve as anchorage devices that provide strong support for dental movements. Their durability is crucial for effective treatment outcomes. B2B buyers in the Middle East must consider the compliance of these implants with health regulations and their biocompatibility, as this is vital for patient safety and successful orthodontic procedures.
Dental Laboratories
Dental laboratories utilize ceramic implants for the production of custom solutions tailored to specific patient needs. The ability to create personalized implants enhances the service offering of these labs, leading to improved patient outcomes. When sourcing ceramic materials, businesses must focus on suppliers with advanced manufacturing capabilities and technology to ensure precision and quality in their products.
Medical Device Companies
Medical device companies are increasingly researching and developing hybrid implants that combine the benefits of both titanium and ceramic materials. This innovation aims to address specific patient needs while differentiating products in a competitive market. Buyers need to access the latest materials and clinical data to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving dental implant sector, ensuring that their offerings meet the highest standards of safety and efficacy.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for titanium vs ceramic dental implants
When selecting dental implants, the choice between titanium and ceramic materials is pivotal for ensuring optimal performance, patient satisfaction, and compliance with international standards. This analysis delves into the key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers regarding titanium and ceramic dental implants.
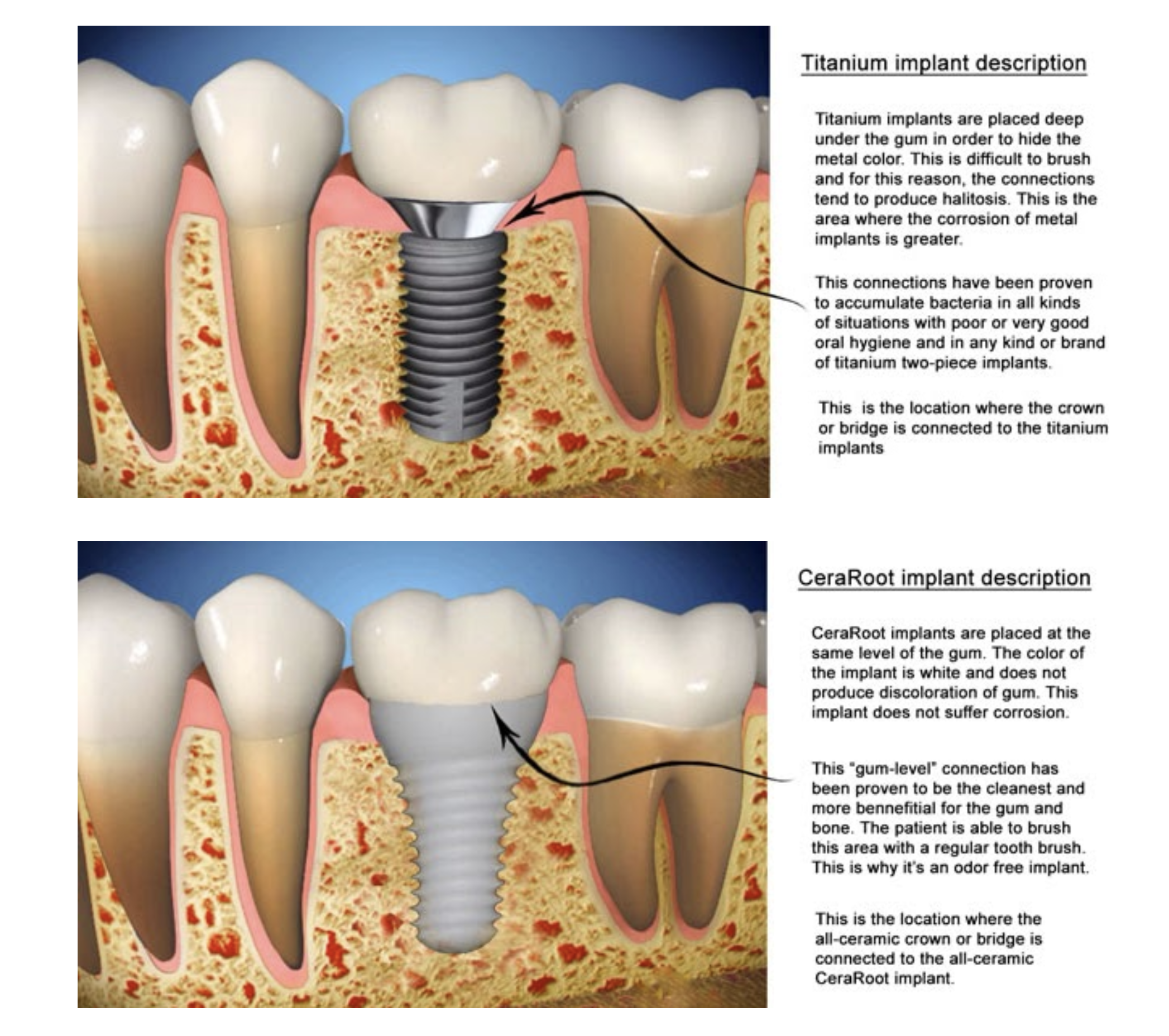
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Titanium Implants
Key Properties: Titanium implants are known for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and high resistance to corrosion. They can withstand significant pressure and are biocompatible, integrating well with bone tissue through a process called osseointegration. Titanium also has a thermal conductivity that can affect patient comfort with temperature-sensitive foods.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium implants is their proven durability and long-term success rates, often exceeding 95% after ten years. They are generally more affordable than ceramic implants, making them a cost-effective option for dental practices. However, titanium’s metallic appearance can be a drawback in aesthetic applications, particularly in the anterior region. Additionally, there is a risk of allergic reactions in a small percentage of patients.
Impact on Application: Titanium implants are suitable for a wide range of dental applications, including both anterior and posterior placements. Their robustness makes them ideal for patients with high biting forces or those who grind their teeth.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO for titanium implants. The availability of titanium implants is generally high, but variations in quality and manufacturing standards may exist across regions.
Ceramic (Zirconia) Implants
Key Properties: Ceramic implants, primarily made from zirconia, offer excellent biocompatibility and a natural tooth-like appearance. They have lower thermal conductivity than titanium, which can enhance patient comfort. However, they may have lower fracture resistance compared to titanium under extreme conditions.
Pros & Cons: The aesthetic advantage of ceramic implants is significant; they blend seamlessly with natural teeth, making them ideal for anterior placements. They are hypoallergenic, appealing to patients with metal sensitivities. However, ceramic implants are generally more expensive due to their complex manufacturing processes and may have limited long-term data compared to titanium. Additionally, they are more susceptible to fractures in high-stress situations.
Impact on Application: Ceramic implants are particularly suitable for aesthetic applications where visibility is a concern. They are also compatible with MRI scans, making them a preferred choice for patients who may require future imaging.
Considerations for International Buyers: B2B buyers in regions like Europe, particularly in countries like Italy, should ensure that ceramic implants meet the required EU standards and certifications. The higher cost and limited availability of various designs may influence purchasing decisions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for titanium vs ceramic dental implants | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Suitable for both anterior and posterior applications, especially in high-stress areas | Proven durability and long-term success | Metallic appearance may affect aesthetics | Medium |
| Ceramic (Zirconia) | Ideal for aesthetic applications, particularly in the anterior region | Natural tooth-like appearance and hypoallergenic | Higher cost and limited long-term data | High |
In conclusion, the choice between titanium and ceramic dental implants hinges on various factors, including aesthetic requirements, patient sensitivities, and long-term performance expectations. International B2B buyers must consider regional standards, material properties, and cost implications to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their market’s needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for titanium vs ceramic dental implants
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for titanium and ceramic dental implants are critical factors for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding these processes can help buyers make informed decisions about their suppliers and ensure that the products meet the required standards for quality and safety.
Manufacturing Processes
Titanium Dental Implants
1. Material Preparation
– Raw Material Sourcing: Titanium implants are primarily made from commercially pure titanium (CP Ti) or titanium alloys. Suppliers must ensure that the titanium meets international standards, such as ASTM F136 for CP Ti.
– Cleaning and Treatment: The raw titanium is subjected to cleaning processes to remove any contaminants. This may include acid etching or sandblasting to enhance surface properties.
2. Forming
– Machining: The titanium is machined into the desired shape using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology, which allows for precise dimensions and geometries.
– Forging: In some cases, titanium is forged to improve its mechanical properties. This involves shaping the metal under heat and pressure to enhance its strength.
3. Assembly
– Component Integration: For multi-part implants, components such as abutments are assembled with the implant body. This requires precise fitting to ensure proper function.
– Welding/Soldering: If necessary, welding techniques may be used to join parts, ensuring a durable assembly.
4. Finishing
– Surface Treatment: The surface of titanium implants often undergoes additional treatments, such as anodization or coating with bioactive materials, to promote osseointegration.
– Final Inspection: Each implant is inspected for defects and dimensional accuracy before packaging.
Ceramic Dental Implants
1. Material Preparation
– Zirconia Sourcing: Ceramic implants are primarily made from zirconia, a biocompatible ceramic material. Suppliers should ensure that the zirconia complies with standards like ISO 6872.
– Powder Preparation: Zirconia powder is processed to achieve the desired grain size and purity, critical for the mechanical properties of the final product.
2. Forming
– Injection Molding: The zirconia powder is often shaped using injection molding, allowing for complex geometries that mimic natural tooth roots.
– Sintering: The molded parts are then subjected to high-temperature sintering, which densifies the zirconia and gives it strength. This process is crucial for achieving the desired mechanical properties.
3. Assembly
– Component Integration: Similar to titanium implants, ceramic implants may have components like abutments. The assembly requires precision to ensure compatibility.
– Cementing or Bonding: Specialized adhesives may be used for joining components, particularly in one-piece designs.
4. Finishing
– Polishing and Glazing: The surface of ceramic implants is polished to enhance aesthetics and reduce bacterial adhesion. Glazing may also be applied for additional protection.
– Final Quality Check: A thorough inspection ensures that the final product meets aesthetic and functional standards.
Quality Assurance
International Standards
Both titanium and ceramic dental implants are subject to rigorous international standards to ensure safety and efficacy. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: General quality management systems applicable to all manufacturing processes.
- ISO 13485: Specific to medical devices, ensuring quality management systems are in place for design, development, production, and distribution.
- CE Marking: Required in Europe, indicating that the implant meets health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: For titanium implants, the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may apply if the titanium is sourced from oil and gas applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is vital throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the implants meet the necessary standards. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials upon receipt, ensuring compliance with specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process, including dimensional checks and material property assessments.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product, including functionality, aesthetics, and compliance with standards.
Common Testing Methods
To verify the quality of dental implants, several testing methods are employed, including:
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluating tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and fracture toughness.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Ensuring the materials do not elicit adverse reactions in biological environments.
- Surface Analysis: Techniques like scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to assess surface roughness and treatment efficacy.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are several strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing practices, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports that outline testing methods, results, and adherence to standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to conduct evaluations of the manufacturing process and final products.
Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers
When sourcing dental implants from international suppliers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances must be considered:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are compliant with local and international regulations specific to dental products.
- Cultural and Regional Variations: Be aware of regional preferences and standards, as these may influence the types of implants offered and their acceptance in local markets.
- Communication and Support: Establish clear lines of communication with suppliers to address any quality concerns promptly and effectively.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for titanium and ceramic dental implants, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and customer needs.
Related Video: Ceramic tiles manufacturing process by Ceratec – How it’s made?
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for titanium vs ceramic dental implants Sourcing
When considering the sourcing of dental implants, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics between titanium and ceramic implants is crucial for B2B buyers. This analysis will delve into the various cost components, price influencers, and provide strategic tips for negotiating the best deals in international markets, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials:
– Titanium: Generally more cost-effective due to its widespread availability and established supply chains. The cost of titanium can fluctuate based on global metal prices.
– Ceramic (Zirconia): Often more expensive, primarily due to the high manufacturing costs associated with zirconia and the specialized processes required to produce it. -
Labor:
– Labor costs can vary significantly by region. In high-wage countries, the labor component may represent a larger portion of the total cost, particularly for ceramic implants, which require skilled technicians for precise placement.
-
Manufacturing Overhead:
– This includes costs associated with running the manufacturing facility, which can be higher for ceramic implants due to the advanced technology and processes involved. -
Tooling:
– Tooling costs are generally similar for both types of implants, but custom tooling for specific designs or sizes may increase costs, especially for ceramic implants. -
Quality Control (QC):
– Rigorous QC processes are vital for both materials, but the costs can be higher for ceramic implants due to their relatively newer market presence and the need for extensive testing. -
Logistics:
– Transportation and shipping costs can vary based on the Incoterms agreed upon and the destination. These can significantly impact the overall pricing, particularly for international buyers. -
Margin:
– Manufacturers will typically set margins based on the perceived value of the product. Titanium implants might have lower margins due to their established market presence, while ceramic implants could command higher margins due to their niche appeal.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders can lead to significant discounts. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs to leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specifications can drive up costs. Buyers should assess whether customization is necessary or if standard options suffice.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly influences costs. Buyers must weigh the benefits of ceramic’s aesthetic appeal against its higher price point.
-
Quality/Certifications: Implants with higher quality certifications or those that meet specific international standards may come at a premium, reflecting their reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively. Costs can vary significantly based on whether the supplier or buyer is responsible for shipping and insurance.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate terms and prices. Building a relationship with suppliers can lead to better deals over time.
-
Cost Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and potential replacement costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, prices may vary significantly between European suppliers and those in Africa or South America due to local market dynamics.
-
Long-Term Partnerships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to more favorable pricing structures and better service.
-
Stay Informed: Regularly update your knowledge on market trends, material costs, and emerging technologies in dental implants to make informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices for dental implants can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. The insights provided here are indicative and should be used as a guideline rather than a definitive pricing framework. Always conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers for accurate pricing and terms.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for titanium vs ceramic dental implants
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology related to titanium and ceramic dental implants is crucial for B2B buyers in the dental industry. This knowledge helps in making informed procurement decisions that align with clinical requirements and patient needs.
Critical Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the specific classification of titanium or zirconia used in implants. Titanium is often categorized into grades (e.g., Grade 4, Grade 5), indicating its purity and mechanical properties.
– B2B Importance: Higher-grade materials typically offer better biocompatibility and strength, which are essential for long-term implant success. Buyers must ensure they source implants made from appropriate grades to meet clinical standards. -
Osseointegration
– Definition: The process by which a dental implant becomes anchored to the jawbone, forming a stable and functional interface.
– B2B Importance: Implants with superior osseointegration properties enhance the longevity of the implant and reduce the risk of failure. Buyers should inquire about clinical studies demonstrating osseointegration rates for specific products. -
Fracture Toughness
– Definition: A measure of a material’s ability to resist crack propagation. For dental implants, this is particularly relevant for ceramic materials, which may be more brittle than titanium.
– B2B Importance: Understanding fracture toughness is critical, especially for high-stress applications. Buyers should evaluate the fracture resistance of implants to avoid potential complications in patients with bruxism or high bite forces. -
Thermal Conductivity
– Definition: The ability of a material to conduct heat. Titanium has higher thermal conductivity than ceramic.
– B2B Importance: This property can influence patient comfort, particularly regarding sensitivity to temperature changes. Buyers should consider thermal properties when selecting implants for patients with heightened sensitivity. -
Corrosion Resistance
– Definition: The ability of a material to withstand degradation due to environmental factors, such as saliva and oral bacteria. Titanium is generally corrosion-resistant, but certain conditions can lead to corrosion over time.
– B2B Importance: A product’s corrosion resistance affects its lifespan and reliability. Buyers should assess the long-term performance of titanium implants under varying conditions to ensure product durability.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers to ensure they are sourcing high-quality implants from reputable manufacturers. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and budget effectively, ensuring they can meet demand without overstocking. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A standard business process where a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods under sales contracts.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk, and responsibilities associated with international transactions, which is vital for smooth logistics. -
CE Marking
– Definition: A certification mark indicating that a product meets European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– Importance: For buyers in Europe, ensuring that dental implants carry the CE mark is essential for compliance and marketability.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make better procurement decisions, ensuring they select the most suitable dental implants for their needs and those of their clients.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the titanium vs ceramic dental implants Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The dental implant market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, increasing consumer awareness, and a growing demand for aesthetic and biocompatible solutions. Titanium implants have long been the standard due to their proven durability and cost-effectiveness, but ceramic implants, particularly those made from zirconia, are gaining traction as a viable alternative, particularly in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key trends include a shift towards minimally invasive procedures and a rise in digital dentistry technologies, such as 3D printing and computer-aided design/manufacturing (CAD/CAM). These technologies are streamlining the production and customization of implants, making it easier for dental professionals to meet diverse patient needs. Moreover, the increasing acceptance of ceramic implants among dental practitioners is notable, particularly in regions with a high demand for aesthetic solutions. For B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for sourcing decisions, as they indicate a potential shift in market preferences that could affect supply chain strategies.
Additionally, the globalization of the dental implant market presents opportunities for partnerships and collaborations. Buyers should consider engaging with manufacturers that not only offer competitive pricing but also demonstrate innovation in product development and responsiveness to market changes. Staying informed about emerging players in the ceramic implant segment, especially those focusing on aesthetics and biocompatibility, can provide a competitive edge in sourcing strategies.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming an essential consideration for B2B buyers in the dental implant sector. The environmental impact of materials used in dental implants, particularly titanium mining and processing, raises concerns about resource depletion and ecological degradation. Conversely, ceramic implants, often produced from more sustainable materials, offer a more environmentally friendly option. This shift is attracting attention from buyers looking to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles.
Ethical sourcing is paramount in this context. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to ethical practices, including responsible material sourcing, fair labor practices, and compliance with environmental regulations. Green certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and materials that have undergone eco-labeling can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, as regulatory frameworks tighten globally, B2B buyers must ensure that their supply chains are transparent and accountable. This includes verifying that suppliers are not only compliant with local regulations but also align with international sustainability standards. Engaging with manufacturers who prioritize eco-friendly practices not only mitigates risk but also enhances brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
Brief Evolution/History
The use of dental implants dates back to ancient civilizations, but the modern era began in the 1960s with the introduction of titanium implants. Titanium’s biocompatibility and strength made it the preferred material for dental restoration. Over the decades, extensive research has confirmed its efficacy, leading to widespread adoption across the globe.
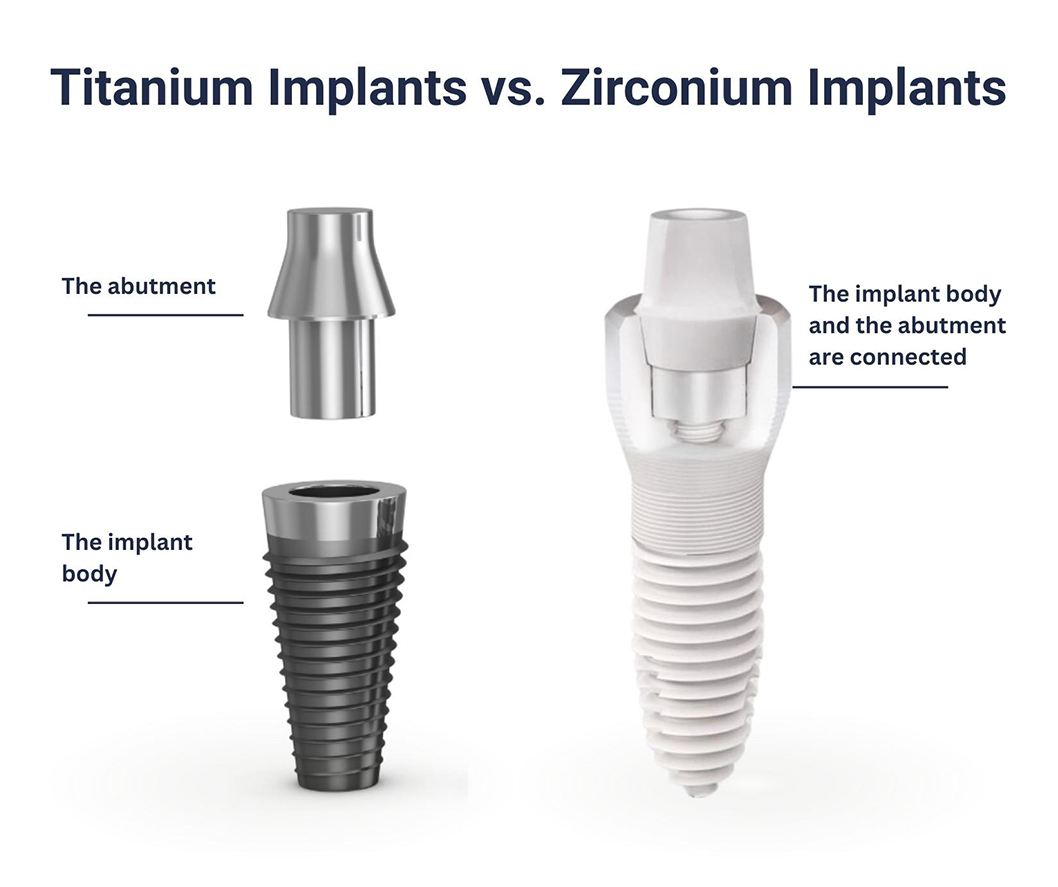
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In recent years, however, advancements in material science have propelled ceramic implants into the spotlight. Zirconia, introduced as a metal-free alternative, has gained popularity due to its aesthetic appeal and reduced risk of allergic reactions. This evolution reflects a broader trend in dentistry towards materials that not only meet functional requirements but also cater to patient preferences for aesthetics and health-conscious solutions. As such, the landscape of dental implants continues to shift, encouraging B2B buyers to stay abreast of these developments for informed sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of titanium vs ceramic dental implants
-
What criteria should I consider when vetting suppliers of titanium and ceramic dental implants?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their certifications, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices, and check for compliance with local regulations in your target markets. Evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures, including adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Request references from other international buyers, and assess their capacity to meet your specific needs, including customization options. Additionally, consider their experience in exporting to regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, as this can affect logistics and support. -
Can titanium and ceramic dental implants be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for both titanium and ceramic implants, including various sizes, shapes, and surface treatments. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities. Customization can be particularly beneficial for addressing unique patient needs or aesthetic preferences. However, be aware that customized products may have longer lead times and could require a minimum order quantity (MOQ), so clarify these details upfront.
-
What are the typical lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQ) for titanium and ceramic dental implants?
Lead times can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of your order. Standard titanium implants may have lead times ranging from 4 to 8 weeks, while customized ceramic implants can take longer, sometimes up to 12 weeks. MOQs also differ; titanium implants often have lower MOQs (e.g., 10-50 units), while ceramic implants might require higher quantities due to their manufacturing processes. Always confirm these details during your initial discussions to align expectations. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of dental implants?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from 30% upfront and 70% upon delivery to net 30 or net 60 days. Some suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders or early payment. It’s essential to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow needs and ensure there are clear agreements in place to avoid disputes later. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods or letters of credit for higher-value transactions to mitigate risk. -
What quality assurance measures and certifications should I look for in dental implants?
Look for suppliers that hold relevant quality certifications, such as ISO 13485, which indicates compliance with international standards for medical devices. Inquire about their quality assurance processes, including routine testing for biocompatibility and mechanical properties. Request documentation of their quality control procedures, including batch records and inspection reports. This information helps ensure the implants meet safety and performance standards essential for successful patient outcomes. -
How do logistics and shipping affect the procurement of dental implants?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of dental implants. Evaluate potential suppliers based on their shipping capabilities and experience in international trade, particularly with customs clearance and import regulations in your target markets. Consider their ability to manage inventory and handle potential delays. It’s advisable to discuss shipping options, including express delivery for urgent orders, and to clarify who bears the shipping costs and any associated risks. -
What steps should I take if I encounter a dispute with a supplier regarding dental implants?
In the event of a dispute, refer to the terms outlined in your purchase agreement, which should specify the process for resolution, including timelines for addressing issues. Maintain clear communication with the supplier to understand their perspective and seek a mutually beneficial solution. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods. Document all communications and agreements to protect your interests and provide evidence if the situation escalates. -
How can I ensure compliance with local regulations when importing dental implants?
To ensure compliance, familiarize yourself with the regulatory requirements for medical devices in your country and any countries you plan to distribute to. This may include obtaining necessary import licenses, registering the products with health authorities, and ensuring that the implants meet specific safety and efficacy standards. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience navigating these regulations, and consider consulting legal experts or regulatory affairs professionals to assist with compliance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for titanium vs ceramic dental implants
In conclusion, the choice between titanium and ceramic dental implants is pivotal for B2B buyers navigating the evolving landscape of dental solutions. Titanium implants have a long-standing reputation for their durability, cost-effectiveness, and high success rates, making them a reliable option. Conversely, ceramic implants, particularly zirconia, are gaining traction due to their aesthetic appeal and biocompatibility, appealing to a segment of patients seeking a more holistic approach to dental care.
For international B2B buyers, strategic sourcing is essential. It involves evaluating not just the cost but also the long-term benefits and patient outcomes associated with each implant type. By understanding regional preferences and patient demographics, buyers can tailor their offerings to meet market demands more effectively.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to stay informed about ongoing advancements in dental implant technology. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize research and innovation will ensure a competitive edge in providing quality dental solutions. Explore partnerships that align with your strategic goals, and position your business to thrive in this dynamic market.
