Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for zirconium dental implants side effects
Zirconium dental implants have emerged as a leading choice in the global dental market, praised for their aesthetic appeal and biocompatibility. However, like any medical device, they come with potential side effects that can significantly impact patient satisfaction and treatment outcomes. Understanding these side effects is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing dental solutions in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of zirconium dental implants, covering essential aspects such as types of implants, material composition, manufacturing and quality control processes, reputable suppliers, and cost considerations. By providing a thorough analysis of the potential side effects—including gum inflammation and sensitivity—this resource empowers buyers to make informed sourcing decisions.
Furthermore, the guide addresses frequently asked questions, helping stakeholders understand the nuances of zirconium implants in various markets. By equipping buyers with actionable insights, this guide not only enhances their purchasing strategies but also ensures they are prepared to meet the evolving demands of their clientele. In a competitive landscape, being knowledgeable about zirconium dental implants and their side effects can set businesses apart, fostering trust and long-term relationships with healthcare providers and patients alike.
Understanding zirconium dental implants side effects Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gum Inflammation | Redness, swelling, and pain around the implant site. | Dental clinics, oral surgery centers | Pros: Identifying early can prevent serious issues. Cons: May require additional treatments. |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Discomfort when consuming hot or cold foods and beverages. | Dental practices, patient management | Pros: Patient comfort can improve with the right materials. Cons: Can affect patient satisfaction. |
| Allergic Reactions | Uncommon but possible reactions to zirconium materials. | Dental suppliers, implant manufacturers | Pros: Biocompatibility reduces risks. Cons: Potential for unexpected complications. |
| Bone Integration Issues | Failure of the implant to properly fuse with jawbone. | Oral health clinics, dental implant firms | Pros: Understanding risks can improve success rates. Cons: May lead to implant failure and additional costs. |
| Aesthetic Complications | Discoloration or visibility of the implant through gum tissue. | Aesthetic dental practices, cosmetic clinics | Pros: High aesthetic value with proper selection. Cons: Poor choice can lead to patient dissatisfaction. |
Gum Inflammation
Gum inflammation is one of the most common side effects associated with zirconium dental implants. It typically presents as redness, swelling, and discomfort around the implant site. For B2B buyers, understanding this side effect is critical, as early detection and management can prevent further complications. Dental clinics must ensure that they have protocols in place for monitoring and treating inflammation to maintain patient satisfaction and avoid additional costs related to extended treatments.
Temperature Sensitivity
Temperature sensitivity can occur in patients with zirconium implants, leading to discomfort when consuming hot or cold foods. This side effect can significantly impact patient experience and satisfaction. B2B buyers in the dental industry should consider this when selecting materials and implants, as certain formulations may reduce sensitivity. Providing products that address this issue can enhance the reputation of dental suppliers and improve patient outcomes.
Allergic Reactions
While rare, allergic reactions to zirconium materials can occur, leading to discomfort or complications for the patient. Understanding the biocompatibility of zirconium is vital for B2B buyers, particularly implant manufacturers and suppliers. Offering products with proven safety profiles can minimize risks and enhance customer trust. It’s essential for dental professionals to be aware of the signs of allergic reactions to ensure timely intervention.
Bone Integration Issues
Bone integration issues can arise when the implant fails to properly fuse with the jawbone, a critical aspect of implant success. For B2B buyers, particularly in the oral health sector, understanding the factors that contribute to integration failure is essential. This knowledge can guide purchasing decisions, ensuring that only high-quality, proven products are used. Providing education to dental professionals about proper placement techniques can also mitigate these risks.
Aesthetic Complications
Aesthetic complications, such as discoloration or visibility of the implant through the gum tissue, can impact patient satisfaction. B2B buyers in aesthetic dental practices should prioritize products that guarantee a natural appearance. Understanding the aesthetic properties of zirconium implants is crucial for meeting patient expectations. Offering a range of options that cater to aesthetic preferences can enhance the value proposition for dental suppliers and practices alike.
Related Video: No One Told Me About THESE Dental Implant Side Effects…
Key Industrial Applications of zirconium dental implants side effects
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of zirconium dental implants side effects | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Manufacturing | Use of zirconium dental implants in product lines | Enhanced product offerings, appealing to aesthetic-conscious clients | Quality certifications, supplier reliability, and material sourcing integrity |
| Dental Clinics | Treatment planning and patient management | Improved patient outcomes and satisfaction rates | Training for staff on managing side effects and patient communication strategies |
| Cosmetic Dentistry | Aesthetic restorations and smile makeovers | Increased client retention through superior results | Availability of various implant sizes and shades for customization |
| Medical Equipment Supply | Distribution of zirconium dental implants and components | Expanded market reach and revenue streams | Compliance with international regulations and standards for dental products |
| Research Institutions | Clinical studies on the effects and efficacy of zirconium implants | Contribution to dental science and innovation | Collaboration with dental professionals for practical insights and data collection |
Industry Applications of Zirconium Dental Implants Side Effects
Dental Manufacturing
In the dental manufacturing sector, companies incorporate zirconium dental implants into their product lines to meet the growing demand for aesthetic and biocompatible solutions. The side effects associated with these implants, such as gum inflammation and sensitivity, are critical for manufacturers to address in their product design and marketing. By ensuring that their products minimize these side effects, manufacturers can enhance their offerings and attract clients who prioritize both functionality and aesthetics.
Dental Clinics
Dental clinics utilize zirconium dental implants to provide patients with durable and visually appealing tooth replacement options. Understanding the potential side effects, such as temperature sensitivity, allows clinics to tailor their treatment plans and improve patient management. By effectively communicating these side effects to patients, clinics can enhance satisfaction and trust, leading to higher retention rates and positive referrals.
Cosmetic Dentistry
In cosmetic dentistry, zirconium dental implants are often employed for smile makeovers and aesthetic restorations. The side effects of these implants must be considered to ensure optimal outcomes for clients. By addressing issues like gum sensitivity and inflammation, cosmetic dentists can provide a more comfortable experience, thereby increasing client loyalty and satisfaction. The ability to customize implants according to individual needs further enhances their appeal.
Medical Equipment Supply
Medical equipment suppliers play a vital role in distributing zirconium dental implants and their components. Understanding the side effects associated with these implants allows suppliers to better inform dental professionals about product features and benefits. Compliance with international regulations is essential for suppliers to maintain credibility and market access. By focusing on high-quality products that address potential side effects, suppliers can expand their market reach and revenue opportunities.
Research Institutions
Research institutions engage in clinical studies examining the effects and efficacy of zirconium dental implants. By investigating the side effects, these institutions contribute valuable insights to the field of dental science. Collaborations with dental professionals can enhance the quality of research and provide practical data that can inform future product development. This research not only advances knowledge but also positions institutions as leaders in dental innovation.
Related Video: Titanium vs Ceramic (Zirconia): Choosing The Right Dental Implants For You
Strategic Material Selection Guide for zirconium dental implants side effects
When selecting materials for zirconium dental implants, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials is crucial for international B2B buyers. This guide analyzes key materials commonly associated with zirconium dental implants, focusing on their performance characteristics, application impacts, and considerations for buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
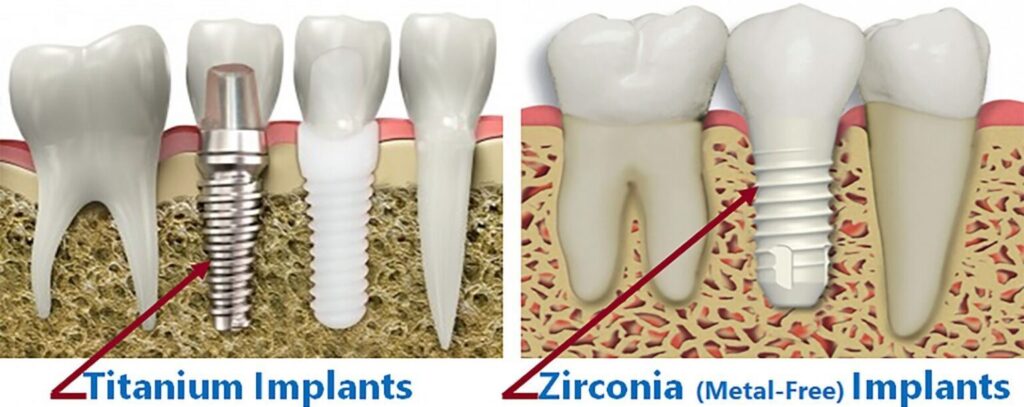
Zirconium Oxide (Zirconia)
Key Properties:
Zirconium oxide, or zirconia, is known for its exceptional strength and toughness, making it an ideal choice for dental implants. It exhibits low thermal conductivity, which minimizes sensitivity to temperature changes. Additionally, zirconia is highly resistant to corrosion and wear, ensuring longevity in oral applications.
Pros & Cons:
Zirconia implants provide excellent aesthetic results due to their tooth-like color and translucency. They are biocompatible, reducing the risk of allergic reactions. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly, which may affect the overall price of the implants.
Impact on Application:
Zirconia’s compatibility with oral media is excellent, as it does not corrode or degrade in the presence of saliva or other oral fluids. This stability ensures that the implants maintain their integrity over time, promoting better oral health.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that zirconia implants comply with international standards such as ISO 13485 for medical devices. In regions like the UAE and Spain, adherence to local regulations and certifications is essential for market entry.
Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium is renowned for its strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications, including dental implants.
Pros & Cons:
Titanium implants have a long history of success in dental applications, with high osseointegration rates. However, they can cause allergic reactions in some patients, which may necessitate alternative materials like zirconia for sensitive individuals. Additionally, titanium’s metallic appearance may not be as aesthetically pleasing as zirconia.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is compatible with oral environments, but its metallic nature can sometimes lead to issues with thermal conductivity, causing discomfort for some patients when consuming hot or cold foods.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with ASTM F136 for titanium alloys is crucial. Buyers from regions with stringent health regulations, such as Europe, should ensure that titanium implants meet the necessary safety and efficacy standards.
Alumina
Key Properties:
Alumina, or aluminum oxide, is a ceramic material known for its hardness and wear resistance. It has a high melting point and excellent chemical stability, making it suitable for dental applications.
Pros & Cons:
Alumina implants offer good aesthetics and are biocompatible. However, they are more brittle than zirconia and titanium, which can lead to fracture under stress. The cost of alumina can also be higher due to its specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Alumina’s chemical stability ensures compatibility with oral environments, but its brittleness limits its use in load-bearing applications compared to zirconia and titanium.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the need for compliance with standards such as ISO 6872 for dental ceramics. In regions like South America, where dental health regulations may vary, understanding local compliance requirements is essential.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for zirconium dental implants side effects | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zirconium Oxide (Zirconia) | Dental implants requiring aesthetic appeal and biocompatibility | Excellent aesthetics and biocompatibility | High manufacturing complexity and cost | High |
| Titanium | Traditional dental implants with a long history of use | Proven success and high osseointegration | Potential for allergic reactions and metallic appearance | Medium |
| Alumina | Non-load bearing dental applications with aesthetic needs | Good aesthetics and chemical stability | Brittle nature and higher cost | High |
This guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers considering zirconium dental implants. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific market needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for zirconium dental implants side effects
Zirconium dental implants have become a popular choice in the dental industry due to their aesthetic qualities and biocompatibility. However, to ensure these implants meet the highest standards of quality and safety, it is crucial to understand the manufacturing processes involved, as well as the quality assurance protocols that govern them. This guide provides an in-depth look at these processes, aimed specifically at international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of zirconium dental implants involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product’s quality and performance.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing zirconium dental implants is the preparation of zirconium oxide powder. This high-purity material is sourced from reputable suppliers who adhere to strict quality standards. The powder undergoes various processes to ensure its homogeneity and particle size distribution, which are crucial for the subsequent forming stage.
2. Forming
In this stage, the prepared zirconium powder is subjected to a forming process, which can include:
- Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP): This technique ensures uniform density and strength across the implant by applying pressure uniformly from all directions.
- Sintering: The formed implants are then sintered in a controlled atmosphere furnace. This process involves heating the zirconium to high temperatures, allowing the particles to bond together, thus enhancing strength and durability.
These techniques are essential to produce implants that can withstand the forces exerted during chewing and provide long-term stability.
3. Assembly
Once the individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final implant structure. This may involve the integration of additional components, such as abutments or screws, which are also made from zirconium or other compatible materials.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage includes several processes aimed at enhancing the implant’s surface properties:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as sandblasting or acid etching are used to modify the surface texture, improving osseointegration and reducing the risk of bacterial colonization.
- Polishing: The final surface finish is achieved through polishing, which enhances the aesthetic appeal of the implant and ensures smooth interactions with surrounding tissues.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of zirconium dental implants. Adherence to international standards and rigorous quality control measures ensures that the implants are safe, effective, and reliable.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the following standards:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system and is essential for ensuring consistent quality across manufacturing processes.
- ISO 13485: Specifically relevant to medical devices, this standard emphasizes the importance of a quality management system that meets regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For European markets, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For markets in Africa and the Middle East, understanding the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards can also be beneficial, especially in the context of biocompatibility and material safety.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing and inspection of the finished products to ensure they meet all specifications and standards before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
To verify the quality and performance of zirconium dental implants, various testing methods are employed, including:
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing the strength, durability, and fatigue resistance of the implants.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Evaluating the implants’ compatibility with human tissues to ensure safety.
- Sterilization Validation: Ensuring that the sterilization process effectively eliminates pathogens without compromising implant integrity.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for documentation that demonstrates compliance with relevant standards and testing results.
- Utilize Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party organizations to conduct inspections can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers, particularly from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local regulations and cultural expectations regarding dental products can influence quality standards and practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Each region may have specific regulations governing dental implants. Familiarity with these regulations is essential to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
- Supply Chain Considerations: Buyers should assess the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final delivery, to ensure consistent quality across all stages.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures related to zirconium dental implants, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs. This knowledge not only enhances buyer confidence but also supports the overall goal of providing safe and effective dental solutions to patients.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for zirconium dental implants side effects Sourcing
When sourcing zirconium dental implants, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. The costs associated with these implants can vary significantly based on several components, including materials, labor, and overhead, as well as external factors that influence pricing.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary material for zirconium dental implants is zirconium oxide, which is known for its strength and biocompatibility. Prices for raw zirconium can fluctuate based on market demand and supply chain conditions. Buyers should be aware of the quality of materials, as higher-quality zirconium may incur higher costs but can lead to better patient outcomes.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required to manufacture zirconium dental implants, involving processes such as milling and sintering. Labor costs can vary by region, with countries in Europe typically having higher labor costs compared to those in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead costs, impacting the final pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized machinery and tools can be significant. As production scales, these costs can be amortized over a larger volume of implants, potentially lowering per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality assurance processes are critical to ensure the safety and efficacy of dental implants. QC costs can add to the overall expense but are essential for compliance with health regulations and achieving certification.
-
Logistics: Transportation and storage costs should be considered, particularly for international shipments. These costs can fluctuate based on fuel prices and shipping routes.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their risks and investments. Understanding the margin expectations in different regions can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of zirconium dental implants:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders can lead to discounts. Establishing long-term contracts may also yield better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized implants will generally incur higher costs due to the additional manufacturing processes required.
-
Quality/Certifications: Implants that meet stringent quality standards or have specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE marking) may command higher prices due to the added assurance of safety and effectiveness.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality might charge a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial, as these can impact the total landed cost of the implants.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume purchasing and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing. Be prepared to discuss quality and delivery timelines to gain favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, potential returns, and warranty considerations.
-
International Pricing Nuances: When sourcing from different regions, consider currency fluctuations and import tariffs that could impact the overall cost. For buyers in Africa and South America, understanding local regulations is also critical.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Quality Assurance: Always prioritize quality over cost. A cheaper implant may lead to higher costs down the line due to complications or failures.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and changes in material costs. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations and help anticipate price changes.
Disclaimer
Pricing for zirconium dental implants can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. The information provided here is indicative and should be validated with suppliers to ensure accuracy in specific purchasing contexts.
Spotlight on Potential zirconium dental implants side effects Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘zirconium dental implants side effects’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for zirconium dental implants side effects
Zirconium dental implants are a popular choice in the dental industry due to their aesthetic appeal and biocompatibility. However, understanding their technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This knowledge not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also ensures compliance with industry standards and customer satisfaction.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Composition
– Definition: Zirconium dental implants are primarily composed of zirconium oxide (ZrO2), known for its high strength and biocompatibility.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the material composition is essential for assessing the implant’s performance, longevity, and potential for allergic reactions. Buyers should ensure that the material meets international safety and quality standards. -
Mechanical Strength
– Definition: This property refers to the implant’s ability to withstand biting forces without fracturing. Zirconium implants typically have a flexural strength of around 900 MPa.
– B2B Importance: High mechanical strength is crucial for ensuring the durability and effectiveness of the implant, which directly influences patient satisfaction and reduces the risk of replacements or repairs. -
Corrosion Resistance
– Definition: The ability of zirconium implants to resist degradation when exposed to bodily fluids and environmental conditions.
– B2B Importance: Corrosion resistance is vital for maintaining the integrity and longevity of the implant. Buyers should inquire about the corrosion testing methods used by manufacturers to ensure product reliability. -
Thermal Conductivity
– Definition: Zirconium implants have low thermal conductivity, meaning they are less affected by temperature changes.
– B2B Importance: This property enhances patient comfort, as it minimizes sensitivity to hot and cold foods, making zirconium implants a preferred choice for many patients. -
Surface Treatment
– Definition: Various techniques (e.g., sandblasting, acid etching) are used to enhance the implant’s surface for better osseointegration.
– B2B Importance: A well-treated surface promotes faster and more secure bonding with the jawbone, which is critical for the success of the implant. Buyers should look for suppliers who provide detailed information on their surface treatment processes.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality suppliers and ensure they are sourcing products from reputable manufacturers. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and budget effectively. It is especially relevant for smaller businesses that may have limited storage or financial resources.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ is essential for comparing costs and negotiating favorable terms with suppliers. Buyers should provide detailed specifications to receive accurate quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total cost of procurement. -
Biocompatibility
– Definition: The property of a material to be compatible with living tissue without causing adverse reactions.
– Importance: Biocompatibility is a critical factor in dental implants, as it affects patient safety and implant acceptance. Buyers should ensure that the products they source have been tested for biocompatibility according to international standards.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing zirconium dental implants, ensuring they choose the best products for their needs while also fostering strong relationships with suppliers.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the zirconium dental implants side effects Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for zirconium dental implants has witnessed substantial growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for aesthetic dental solutions and advancements in dental technology. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of several key trends shaping this sector.
-
Technological Advancements: Innovations in 3D printing and CAD/CAM technologies have streamlined the production of zirconium implants, allowing for customized solutions that enhance patient outcomes. Buyers should explore partnerships with manufacturers utilizing these technologies to gain a competitive edge.
-
Rising Consumer Awareness: As more information about the benefits and side effects of zirconium implants becomes available, patient education is increasing. This trend is driving demand for high-quality, biocompatible products, which are essential for maintaining oral health and minimizing side effects.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Market Diversification: The zirconium dental implant market is expanding beyond traditional healthcare settings. New players from emerging markets are entering the field, offering competitive pricing and innovative products. B2B buyers should assess the offerings from these new entrants to ensure they are sourcing the best value.
-
Regulatory Compliance: International buyers must navigate complex regulatory landscapes that vary by region. Understanding local regulations regarding dental products is crucial to avoid compliance issues and ensure product quality.
By staying attuned to these trends, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with market dynamics and consumer expectations.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical focus in the dental implant sector, with implications for both environmental impact and ethical sourcing. For B2B buyers, integrating sustainable practices into sourcing strategies is not only a moral imperative but also a competitive advantage.
-
Environmental Impact: The production of zirconium implants can generate waste and emissions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adopt eco-friendly manufacturing practices, such as reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste. Look for companies that implement sustainable practices throughout their supply chain.
-
Ethical Supply Chains: Ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly is vital. Buyers should seek out manufacturers that are transparent about their sourcing practices and can provide certifications that demonstrate ethical material procurement. This includes verifying that zirconium is mined and processed under fair labor conditions.
-
Green Certifications: B2B buyers should consider working with suppliers that possess recognized sustainability certifications. These certifications can provide assurance that the products meet environmental standards and ethical sourcing guidelines. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management can be a valuable indicator of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
By focusing on sustainability and ethical sourcing, international B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing demand for environmentally responsible products in the dental sector.
Brief Evolution/History
Zirconium dental implants emerged as a viable alternative to traditional titanium implants in the early 2000s. Initially developed to address aesthetic concerns associated with metal implants, zirconium’s biocompatibility and natural appearance quickly gained traction among both dental professionals and patients. Over the years, improvements in manufacturing techniques and material science have led to enhanced durability and reduced side effects, solidifying zirconium implants as a preferred choice in restorative dentistry. As the market continues to evolve, the focus on minimizing side effects and improving patient satisfaction remains paramount, driving ongoing innovation in the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of zirconium dental implants side effects
-
What are the common side effects associated with zirconium dental implants?
Zirconium dental implants are generally well-tolerated, but they can lead to side effects such as gum inflammation, sensitivity to temperature changes, and, in rare cases, allergic reactions. Understanding these potential issues is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Suppliers should provide detailed information about the side effects and any clinical studies backing their claims to ensure transparency and trust. -
How can I vet suppliers of zirconium dental implants?
When sourcing zirconium dental implants, it’s crucial to conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers. Look for certifications such as ISO 13485 or CE marking, which indicate compliance with international quality standards. Request references from other B2B buyers and consider suppliers’ track records in customer service and product quality. Engaging in direct communication about their production processes can also provide insights into their reliability and trustworthiness. -
Can zirconium dental implants be customized for specific markets?
Many suppliers offer customization options for zirconium dental implants to meet specific market needs, such as varying sizes or shapes for different demographics. Discussing customization possibilities with suppliers can enhance your product offering and cater to local preferences. Ensure that any customization adheres to quality standards and that the supplier can provide adequate documentation to support these changes. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for zirconium dental implants?
MOQs for zirconium dental implants can vary significantly between suppliers, often ranging from 50 to 500 units. Lead times may also differ based on the supplier’s production capacity, ranging from a few weeks to several months. It is advisable to negotiate these terms upfront to align your purchasing strategy with inventory management and customer demand in your target markets. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
Quality assurance is vital when sourcing zirconium dental implants. Suppliers should provide documentation related to their quality control processes, including batch testing, sterilization methods, and clinical trial results. Inquire about their quality management systems and whether they conduct regular audits and inspections to maintain high product standards. Establishing clear QA expectations can help mitigate risks associated with product defects. -
Are there specific certifications I should look for when sourcing zirconium dental implants?
Yes, when sourcing zirconium dental implants, look for certifications such as CE marking for compliance with European safety standards and FDA approval for the U.S. market. Additionally, ISO certifications, particularly ISO 13485 for medical devices, indicate adherence to quality management systems. These certifications ensure that the products meet rigorous safety and efficacy standards, which is critical for your business reputation. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding product quality or delivery issues?
To effectively manage disputes, establish clear terms and conditions in your purchase agreements, including quality expectations and delivery timelines. In the event of a dispute, maintain open communication with the supplier to address concerns promptly. If necessary, refer to contractual obligations and seek mediation or arbitration to resolve issues amicably. Document all communications and agreements to support your position during disputes. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing zirconium dental implants?
Importing zirconium dental implants involves several logistics considerations, including customs clearance, import duties, and compliance with local regulations. Work closely with your supplier to ensure all necessary documentation, such as certificates of origin and compliance, is prepared. Additionally, consider partnering with a freight forwarder experienced in medical device logistics to streamline the shipping process and mitigate delays.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for zirconium dental implants side effects
In summary, understanding the side effects of zirconium dental implants is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key considerations include potential issues such as gum inflammation and sensitivity, which can impact patient satisfaction and the overall success of dental procedures.
Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in mitigating these risks. By partnering with reputable suppliers who prioritize quality and biocompatibility, buyers can ensure that they are offering products that enhance patient outcomes and maintain high standards of care. Additionally, staying informed about the latest advancements in implant technology and patient management strategies can further empower dental practices to deliver superior services.
Looking ahead, the demand for zirconium dental implants is expected to grow, driven by their aesthetic appeal and biocompatibility. B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships that align with these trends, fostering innovation and improving patient care. Investing in education and support for dental professionals will enhance their ability to manage any side effects effectively, ultimately leading to improved patient trust and satisfaction. Engage with industry leaders today to explore the best sourcing strategies for zirconium dental implants and position your business for future success.
