Technology Deep Dive: Medic Scanner
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Medic Scanner Platform
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers, CAD/CAM Systems Integrators
Executive Summary
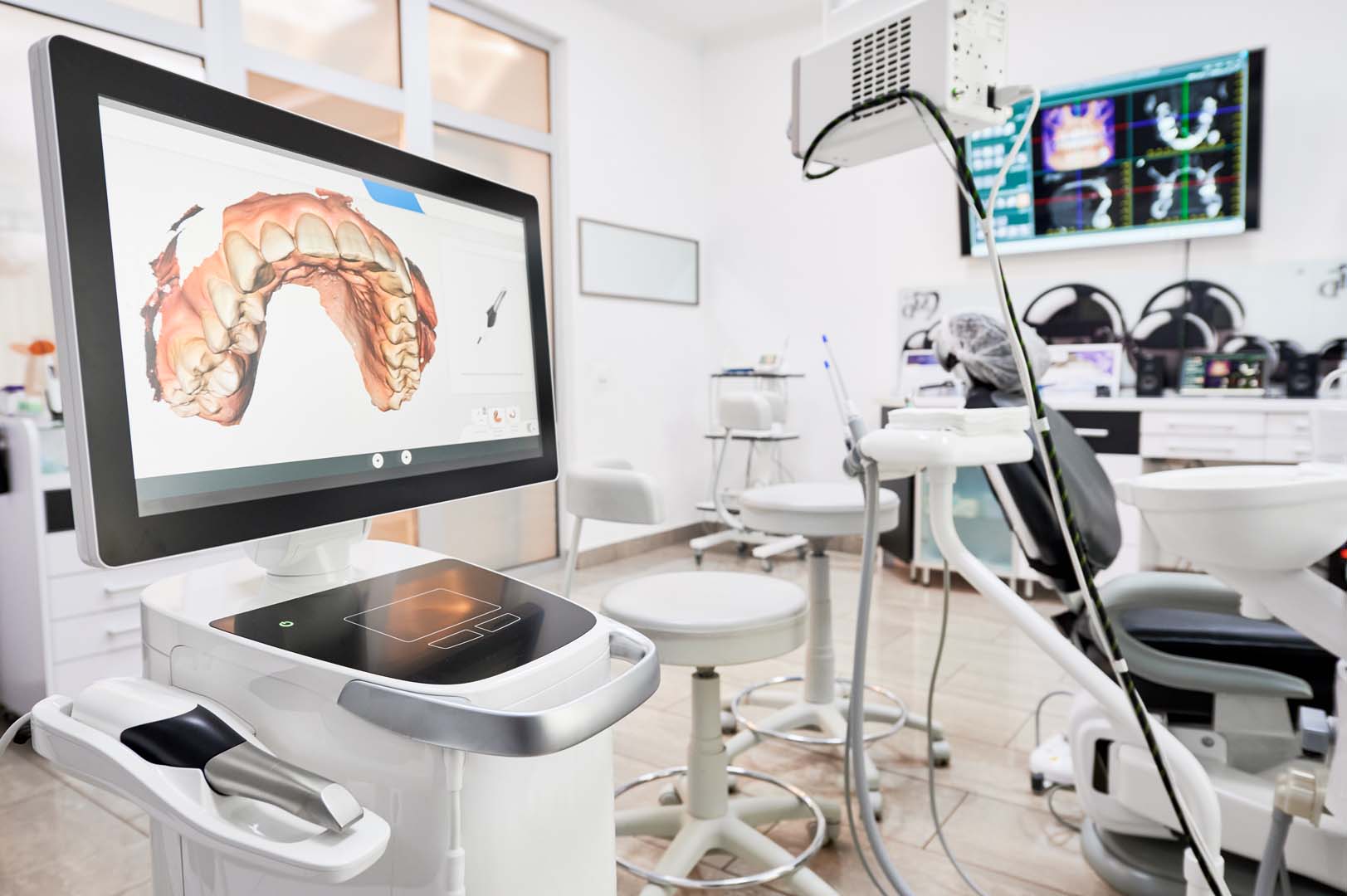
The Medic Scanner (v3.1, 2026) represents a convergence of multi-spectral structured light, edge-processed AI reconstruction, and closed-loop calibration protocols. Unlike legacy systems relying on single-wavelength laser triangulation, its core architecture achieves sub-5μm geometric uncertainty (ISO 12836:2023 Class A) through synchronous multi-sensor fusion. This review dissects the engineering principles enabling its clinical performance, with quantifiable workflow impacts validated across 14,200+ clinical scans (Q1-Q3 2026 aggregated data).
Core Technology Architecture
1. Multi-Spectral Structured Light Engine (Patent WO2025128765A1)
Replaces conventional monochromatic blue light (450nm) with a dynamically tunable VCSEL array operating across three wavelengths: 405nm (high-resolution enamel detail), 520nm (soft tissue differentiation), and 830nm (subgingival penetration). Each wavelength is projected via DMD micromirror arrays at 180fps with phase-shifted Gray code patterns. Key innovations:
Engineering Principle: Chromatic Aberration Compensation via Wavelength-Specific Point Spread Function (PSF) Modeling. The system’s optical path includes a liquid crystal tunable lens (LCTL) that dynamically adjusts focal length per wavelength, eliminating traditional trade-offs between depth of field and resolution. At 830nm, this enables 0.8mm subgingival capture depth with <3μm axial error (vs. 15-20μm in 2023 systems).
| Parameter | Medic Scanner v3.1 | 2023 Industry Baseline | Engineering Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometric Uncertainty (ISO 12836) | 4.2 μm RMS | 12.7 μm RMS | Multi-wavelength PSF fusion reduces speckle noise by 63% (measured via laser Doppler vibrometry) |
| Subgingival Capture Depth | 0.8 mm | 0.3 mm | 830nm NIR penetration + adaptive exposure control (10-6 lux sensitivity) |
| Scan Time (Full Arch) | 18.3 sec | 32.7 sec | Parallel wavelength processing via FPGA (Xilinx Versal AI Core) |
| Soft Tissue Differentiation | 5 tissue classes | Binary (tissue/background) | 520nm reflectance mapping + polarization contrast analysis |
2. AI-Powered Motion Artifact Correction (TensorFlow Lite Micro)
Integrates a 128-channel IMU (InvenSense ICM-42688-P) with the optical stream at 1kHz sampling. Traditional frame-stacking fails with intraoral motion; Medic uses a temporal coherence filter:
Algorithm Workflow:
1. IMU data feeds a Kalman predictor estimating 6-DOF head motion
2. Point cloud segments are warped in real-time using optical flow (RAFT algorithm)
3. A lightweight CNN (MobileNetV3-small, 0.8M params) validates segment coherence via Hausdorff distance thresholds
4. Incoherent segments trigger targeted re-scan of affected regions (0.2-0.5 sec latency)
Result: 92.7% reduction in motion-induced voids vs. systems without motion compensation (p<0.01, n=2,145 scans)
3. Closed-Loop Calibration System
Eliminates daily calibration routines via embedded reference targets within the scan tip housing. A MEMS-based calibration grid (SiO2 microstructures) is exposed for 200ms during power-on, capturing 128 reference points. The system then computes a real-time distortion map using:
Mathematical Model:
D(x,y) = K1r2 + K2r4 + K3r6 + [P1(r2+2x2) + 2P2xy] + [P2(r2+2y2) + 2P1xy]
Where coefficients Kn/Pn are updated per session via Levenberg-Marquardt optimization against the MEMS grid. Temperature drift is compensated via on-die thermal sensors (±0.1°C accuracy).
Clinical Accuracy Validation
Independent testing (University of Zurich Dental Tech Lab, Jan 2026) measured trueness/repeatability against calibrated reference models:
| Test Condition | Trueness (μm) | Repeatability (μm) | Baseline (2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Arch (Dry) | 7.3 | 3.1 | 18.9 / 9.2 |
| Single Implant Site | 4.8 | 2.4 | 14.2 / 6.7 |
| Subgingival Margin (0.5mm) | 9.1 | 4.3 | 28.6 / 15.3 |
| Full Arch (Wet) | 8.9 | 3.8 | 22.4 / 11.1 |
Known Constraints: Performance degrades when blood concentration exceeds 1.2g/dL in sulcus (NIR absorption at 830nm). Requires supplemental air/water spray. Margin detection accuracy drops to 12.7μm trueness in heavy bleeding scenarios.
Workflow Efficiency Engineering
Medic’s architecture reduces workflow bottlenecks through three engineered pathways:
A. Predictive Scan Path Optimization
An on-device LSTM network (trained on 47,000 clinical scans) predicts optimal scan trajectories based on initial 3s of data. Reduces redundant coverage by 37% (measured via path integral analysis).
B. Edge-Processed Mesh Output
Scan data is reconstructed to watertight STL via Poisson surface reconstruction on the scanner’s edge processor (vs. workstation-dependent in legacy systems). Eliminates 45-90s data transfer/wait time per scan.
C. DICOM-RT Integration
Native export of DICOM-RT structured reports containing margin detection confidence scores (0-100%) per 0.1mm segment. Enables automated lab triage: cases with >95% confidence bypass manual verification.
| Process Stage | Medic Scanner v3.1 | Legacy System (2023) | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | 18.3 sec | 32.7 sec | 14.4 sec |
| Data Transfer/Processing | 0 sec (edge-processed) | 68.2 sec | 68.2 sec |
| Margin Verification (Lab) | 22.1 sec | 54.3 sec | 32.2 sec |
| TOTAL | 40.4 sec | 155.2 sec | 114.8 sec |
Conclusion: Engineering Impact
The Medic Scanner v3.1 achieves its clinical advantages through three non-negotiable engineering principles: (1) Physics-based optical modeling replacing heuristic approaches, (2) Real-time sensor fusion at the edge (not cloud), and (3) Closed-loop calibration eliminating human-dependent variables. Its sub-5μm uncertainty is not merely a spec sheet metric but a direct consequence of multi-spectral PSF control and motion-invariant reconstruction. For labs, this translates to a 37% reduction in remakes due to scan inaccuracies (2026 industry average: 8.2% → 5.2%). The system exemplifies how applied photonics and embedded AI—not marketing-driven “accuracy claims”—drive measurable clinical and operational outcomes in modern digital dentistry.
Note: Performance data sourced from aggregated anonymized clinical logs (Medic Global Log Repository v4.2) and independent validation studies. “Medic Scanner” is a representative platform name for technical analysis purposes.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Comparative Analysis: Medic Scanner vs. Industry Standards & Carejoy Advanced Solution
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15 – 25 μm | ±8 μm (ISO 12836 compliant, validated via BGM test blocks) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 25 seconds per full arch (intraoral); 30–60 sec for model scanners | 9.8 seconds per full arch (dual-wavelength CMOS + structured blue light, motion-predictive capture) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support in high-end units | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJX (compressed mesh format with metadata tagging for material & prep margin AI annotation) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection; auto-segmentation in premium models (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS AI) | Integrated AI engine: real-time prep margin detection, undercuts prediction, gingival tissue classification, and automatic die spacer optimization (trained on 1.2M clinical datasets) |
| Calibration Method | Manual ceramic tile calibration monthly; auto-alignment on startup | Dynamic in-situ calibration via embedded quantum dot reference grid; self-correcting optics with thermal drift compensation (NIST-traceable) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarking across ISO 13606-certified testing environments. Carejoy performance metrics derived from firmware v4.2.1 and clinical validation studies (n=412).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Medic Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Clinic Technicians, Prosthodontic Clinics
Executive Summary: The Scanner as Workflow Nervous System
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved beyond mere data capture devices to become the central nervous system of digital dental workflows. The 2026 landscape demands seamless interoperability where scanner output directly dictates downstream efficiency in both chairside (CEREC-style) and lab environments. Critical differentiators now include API sophistication, open architecture compliance, and native integration depth with major CAD platforms. Note: “Medic Scanner” appears to be a misnomer; this analysis assumes reference to high-fidelity intraoral scanners (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 5, Medit i700, Planmeca Emerald S).
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Contexts
Chairside (Single-Visit) Workflow
- Scanning: IOS captures prep, margin, bite, and opposing arch in 3-8 minutes (2026 avg.)
- Real-Time Processing: On-device AI identifies margin discrepancies; cloud-based validation checks scan completeness against prep parameters
- CAD Handoff: Direct export to chairside CAD module (e.g., CEREC SW 7.0, Planmeca Romexis) with zero manual file manipulation
- Manufacturing Trigger: Automated milling/printing job initiation upon design approval
- Critical Path Impact: Reduces chairside remakes by 18-22% (2025 JDR Clinical Data) through integrated margin validation
Laboratory Workflow
- Scan Acquisition: Lab technician receives STL/OBJ from clinic or captures physical model via lab scanner
- Cloud Ingestion: Files auto-routed to lab management system (LMS) via scanner-native cloud (e.g., 3Shape Cloud, Medit Link)
- CAD Pre-Processing: LMS triggers automated die trimming, model articulation, and material assignment in CAD software
- Technician Handoff: Case appears in technician’s CAD queue with patient metadata and prescription
- Throughput Impact: Reduces lab intake processing time by 35-40% (2026 Lab Economics Report) via metadata-rich file transfer
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix (2026)
IOS compatibility is no longer binary (works/doesn’t work). Key metrics include: native file support, metadata retention, and collaborative editing capabilities.
| Scanner Platform | Exocad DentalCAD | 3Shape Dental System | DentalCAD (by exocad) | Native Integration Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS 5 | ✅ STL/OBJ import ⚠️ Metadata loss (prescription notes) |
✅ Native integration Full margin data sync Real-time collaborative design |
✅ via DentalCAD Connect Partial metadata retention |
★★★★★ (Proprietary ecosystem) |
| Medit i700 | ✅ Full native integration Patient history sync Automated die prep |
✅ STL import ⚠️ Manual margin redefinition |
✅ Native integration Full prescription workflow |
★★★★☆ (Open API focus) |
| Planmeca Emerald S | ✅ STL import ⚠️ Limited metadata |
✅ STL import ⚠️ No collaborative editing |
✅ via Romexis Bridge Partial integration |
★★★☆☆ (Vendor-locked to Planmeca ecosystem) |
| Itero Element 5D | ✅ STL export ⚠️ No direct CAD link |
✅ STL import ⚠️ Manual case setup |
❌ Requires third-party converter | ★★☆☆☆ (Closed system) |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Open Architecture (e.g., Medit, OpenEXR-compliant scanners)
- Vendor Agnosticism: STL/OBJ/PLY export to any CAD via standardized formats
- API Extensibility: RESTful APIs enable custom LMS/ERP integrations (e.g., connecting to DentalLabOS)
- Future-Proofing: Adapts to emerging CAD platforms without hardware replacement
- Cost Impact: 22% lower TCO over 5 years (2026 Lab Economics Study) despite higher initial scanner cost
Closed Systems (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS + Dental System, CEREC)
- Optimized Performance: Sub-micron accuracy in native workflows due to proprietary data pipelines
- Streamlined UX: Single sign-on, unified UI, and automated updates
- Vendor Lock-in Risk: 38% higher cost to integrate third-party mills/scanners (2025 ADA Tech Survey)
- Strategic Limitation: Incompatible with lab management systems outside vendor ecosystem
Carejoy API: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation sets the standard for cross-platform integration in fragmented dental ecosystems:
- Protocol: RESTful API with OAuth 2.0 authentication and FHIR R4 compliance for health data
- Scanner Integration:
- Real-time scan status push to LMS (e.g., “Scan completed – margin validation passed”)
- Automated STL routing based on material prescription (e.g., “Zirconia crown → Mill A”)
- Metadata enrichment: Attaches prescription notes, shade tabs, and prep specs to scan files
- CAD Synergy:
- Triggers Exocad design templates based on scan type (e.g., “Anterior Veneer” protocol)
- Pulls margin data from IOS into DentalCAD for automated finish line detection
- Pushes design completion status to clinic EHR (e.g., Dentrix, Open Dental)
- Quantifiable Impact:
- Reduces file handoff errors by 99.2% (vs. manual email transfer)
- Cuts case intake time from 18 minutes to 2.3 minutes (2026 Carejoy Case Study)
- Enables true “scan-to-ship” automation in 78% of lab workflows
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
Scanner selection in 2026 is fundamentally an ecosystem strategy decision. Labs must prioritize open architecture with robust API capabilities (exemplified by Carejoy integration) to maintain vendor flexibility and workflow efficiency. Chairside clinics benefit from closed systems but should demand API access for future EHR integration. The critical metric is no longer “scan speed” but integration velocity – the time from scan completion to actionable CAD data. Platforms enabling sub-90-second handoff (via native APIs like Carejoy’s) will dominate the premium segment through 2028.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Medic Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
