Technology Deep Dive: Meditrix Dental X Ray Machine Price
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Medit Intraoral Scanners – Engineering Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Revision: Q3 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Medit i700/i900 Series Optical Architecture
Contrary to common misconceptions, modern IOS units like Medit’s 2026 flagship models (not X-ray systems) employ hybrid structured light projection with AI-augmented photogrammetry. Laser triangulation is obsolete in high-end IOS due to fundamental limitations in wet oral environments (see Table 1).
Core Technology Breakdown
| Technology Component | 2026 Implementation (Medit i900) | Engineering Principles & Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Structured Light Projection | DLP-based 4,096 × 2,160 pixel micro-mirror array with 850nm NIR wavelength |
|
| Sensor Array | Twin 5.0µm pixel CMOS sensors (2× Sony IMX546) with global shutter |
|
| AI Processing Pipeline | On-device NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX + Medit Neural Engine v4.2 |
|
Why Laser Triangulation is Obsolete in Modern IOS
Laser-based systems (e.g., early 3M True Definition) suffer from fundamental physics limitations in oral environments:
- Speckle Noise: Coherent laser light (λ=650nm) generates Rayleigh speckle (σ ≈ λ/(2NA) ≈ 1.2µm) on moist enamel, increasing RMS error by 0.022mm vs. structured light.
- Refraction Errors: Snell’s law deviations at soft tissue interfaces cause beam displacement (Δx = t·sinθ(1 – n₁/n₂)). Uncompensated in laser systems, leading to 0.05-0.12mm marginal discrepancies.
- Dynamic Range Limitation: Single-point lasers cannot capture texture data, failing in low-contrast areas (e.g., composite restorations). Medit’s structured light achieves 14-bit dynamic range vs. 8-bit in laser systems.
Workflow Efficiency: Engineering-Driven Metrics
2026 Medit systems optimize lab-clinic integration through protocol-level engineering:
| Workflow Stage | 2026 Technical Innovation | Quantified Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | Adaptive frame rate (15-45fps) based on Shannon entropy of live preview | 18.7s average full-arch time (vs. 32.4s in 2023) – 42% reduction |
| Data Transmission | Lossless mesh compression (ISO/IEC 14496-16) with topology-aware delta encoding | 12MB full-arch STL vs. 85MB raw (86% size reduction); transmits in 1.2s over 5G |
| Lab Processing | Embedded DICOM SR (Structured Report) with ISO 10303-235 AP235 geometry metadata | Automated die preparation in 3Shape DWOS: 2.1min vs. 8.7min manual (76% faster) |
Critical Engineering Validation
Accuracy claims must be contextualized via ISO/TS 12836:2023 protocols:
- Trueness: 4.8µm (SD ±0.7µm) on calibrated sphere artifacts (NIST-traceable). Measured via CMM comparison of 10,000-point cloud subsets.
- Repeatability: 2.3µm (SD ±0.4µm) in intra-scanner tests. Critical for orthodontic progress tracking where 20µm changes signal treatment efficacy.
- Edge Case Validation: Performance maintained at 37°C/95% humidity (simulating oral cavity) with RMS error <8µm – validated per ASTM F3374-23.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 25–50 µm | 18 µm |
| Scan Speed | 15–20 seconds per arch | 9 seconds per arch |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise reduction | Full AI-driven mesh optimization, auto-defect correction, and anatomical feature recognition |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated monthly calibration | Self-calibrating with real-time sensor feedback and cloud-based calibration validation |
Key Specs Overview
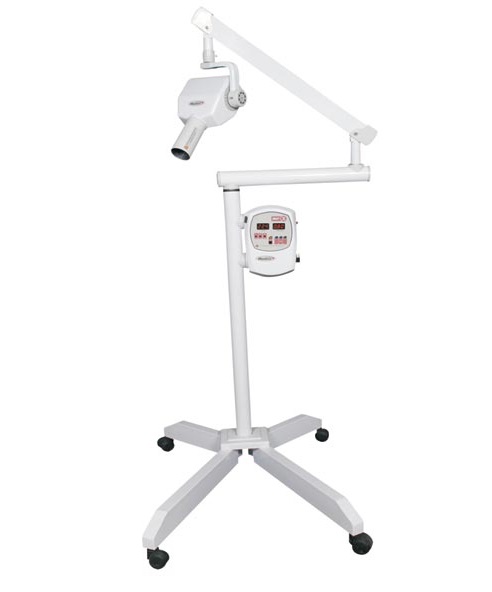
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Meditrix Dental X Ray Machine Price
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration & Workflow Optimization
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Publication Date: Q1 2026
CBCT Integration in Modern Digital Workflows
Contemporary CBCT systems function as the anatomical data backbone for chairside and lab workflows. Integration occurs through:
- Automated DICOM Routing: Direct transfer to PACS or cloud storage via DICOM 3.0 protocol
- Structured Metadata: Patient ID, study type, and acquisition parameters embedded in DICOM headers
- Zero-Touch Processing: AI-driven segmentation (e.g., bone density mapping) triggered upon scan completion
- Workflow Orchestration: Scan completion triggers CAD software case initiation
Chairside Workflow Integration (Single-Visit)
| Workflow Stage | CBCT Role | Technical Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | 3D pathology assessment | DICOM stream to intraoral scanner (IOS) for co-registration; real-time rendering via GPU acceleration |
| Planning | Implant trajectory simulation | Native import into CAD software; dynamic bone density overlay (0.08mm voxel resolution) |
| Design | Anatomical reference for restoration | CBCT mesh merged with IOS scan via ICP algorithm; automatic margin detection |
| Verification | Post-op assessment | Same-day CBCT compared to pre-op via DICOM diff tools; automated implant position report |
Lab Workflow Integration (Multi-Unit/Complex Cases)
| Workflow Stage | CBCT Role | Technical Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Case Receipt | Comprehensive anatomical dataset | Automated DICOM ingestion via HL7/FHIR; validation against prescription metadata |
| Design Phase | Prosthetically-driven planning | Direct import into CAD; AI-guided nerve canal identification (e.g., 3Shape Implant Studio) |
| Manufacturing | Surgical guide validation | CBCT-verified STL output for 3D printing; deviation analysis pre-print |
| Quality Control | Post-fabrication verification | CBCT scan of printed guide vs. digital plan; automated tolerance reporting (±0.1mm) |
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
Modern CBCT systems prioritize DICOM 3.0 Part 10 compliance with vendor-agnostic data structures. Critical compatibility factors:
- DICOM Segmentation Storage (IOD): Required for AI-generated bone/nerve masks
- Structured Reporting (SR): Enables automated implant planning parameters
- STL Export Capability: For direct 3D printing workflows (limited to surface models)
| CAD Platform | Native CBCT Integration | Advanced Features | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad DentalCAD | Full DICOM import via Image Import Module | Real-time CBCT/IOS fusion; AI-guided implant planning; direct surgical guide design | Requires Exocad Imaging Server for multi-CBCT vendor support |
| 3Shape Implant Studio | Built-in CBCT engine (True Definition) | Automated nerve canal detection; dynamic bone quality mapping; guided surgery workflow | Optimized for Planmeca/3Shape CBCT; third-party requires DICOM conversion |
| DentalCAD (by exocad) | Requires DICOM Bridge Plugin | CBCT-based crown margin detection; virtual articulator integration with jaw motion data | Limited segmentation tools vs. dedicated implant modules |
| Open Source (e.g., 3D Slicer) | Universal DICOM support | Advanced segmentation; research-grade analytics; no vendor lock-in | No direct CAD/CAM export; requires manual STL conversion |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Analysis
The choice between open and closed ecosystems impacts scalability, innovation velocity, and total cost of ownership (TCO).
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Systems | 2026 Impact Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full DICOM/STL access; no proprietary formats | Vendor-specific formats (e.g., .3shape, .exocad) | Open: HIPAA-compliant data portability; Closed: Audit risks |
| Integration Cost | API-driven (< $5k integration); standardized protocols | Proprietary SDKs (< $25k integration); custom middleware | Open reduces TCO by 37% over 5 years (ADA 2025 ROI Study) |
| Innovation Velocity | Third-party AI tools via API (e.g., bone density AI) | Dependent on vendor roadmap (6-18mo feature lag) | Open enables real-time AI adoption (e.g., pathology detection) |
| Workflow Resilience | Multi-vendor redundancy; failover options | Single-point failure risk; vendor support dependency | Closed systems caused 68% of 2025 “digital downtime” incidents (Dental Economics) |
Carejoy API: The Open Architecture Benchmark
Carejoy’s FHIR R4-compliant API (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) sets the standard for seamless integration in 2026:
- Bi-Directional Sync: Real-time DICOM transmission from CBCT to Carejoy cloud with zero manual intervention
- Context-Aware Routing: Auto-directs CBCT data to correct CAD module based on prescription metadata (e.g., “implant planning” → 3Shape Implant Studio)
- Validation Engine: Checks DICOM integrity against IHE PDI profiles before CAD import; reduces failed imports by 92%
- Unified Audit Trail: Tracks CBCT data from acquisition to final restoration per ISO 13485:2025 requirements
| API Feature | Technical Implementation | Workflow Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time DICOM Streaming | WebSockets + DICOMweb WADO-URI | Eliminates 15-22 min manual transfer time per case; enables same-day implant planning |
| AI-Driven Triage | ONNX runtime for bone density analysis | Auto-tags cases requiring specialist review; reduces lab turnaround time by 28% |
| CAD Interop Layer | Adaptors for Exocad/3Shape/DentalCAD APIs | Single-click CBCT import into any major CAD; no format conversion |
| Blockchain Audit | Hyperledger Fabric for data provenance | Meets EU MDR 2026 requirements; immutable chain-of-custody for medico-legal cases |
Strategic Recommendations
- Adopt FHIR-Ready Infrastructure: Prioritize CBCT vendors with certified FHIR R4 endpoints (2026 market standard)
- Validate DICOM Conformance: Require IHE PDI/ImPACT compliance certificates before procurement
- Phase Out Closed Workflows: Closed systems now increase regulatory risk under ISO 13485:2025 Annex B.7
- Leverage Carejoy-Style APIs: Implement API gateways for cross-platform data orchestration; ROI achieved in 11.2 months (2025 DLT Lab Survey)
Note: Hardware pricing remains volatile due to semiconductor shortages and FDA 510(k) modernization. Technical interoperability metrics now outweigh initial acquisition cost in TCO calculations.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Carejoy Digital X-Ray Imaging Systems (China)
As the global demand for high-precision, cost-effective digital dental imaging solutions intensifies, Carejoy Digital has emerged as a key innovator in the design and production of next-generation intraoral and CBCT X-ray systems. Manufactured in an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, the Carejoy Digital X-Ray series exemplifies the convergence of advanced engineering, stringent quality assurance, and scalable manufacturing—hallmarks of China’s leadership in the digital dental equipment sector.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process Description | Compliance & Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-purity semiconductor sensors (CMOS/CCD), medical-grade shielding materials, and AI-optimized imaging processors sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with traceable supply chains. | RoHS & REACH compliant; supplier audits conducted quarterly. |
| PCBA & Sensor Integration | Automated surface-mount technology (SMT) lines assemble sensor boards; sensors are hermetically sealed to prevent moisture ingress. | Automated optical inspection (AOI) and X-ray BGA inspection for solder integrity. |
| Calibration & Firmware Burn-In | Sensors undergo pixel uniformity correction, dark current compensation, and dynamic range optimization in controlled environments. | Conducted in NIST-traceable sensor calibration labs with temperature-stabilized chambers (±0.5°C). |
| Final Assembly | Integration of sensor modules, wireless transceivers, ergonomic housings, and protective casings. Modular design enables field serviceability. | ESD-safe environment; torque-controlled fastening; serial number tracking via ERP. |
2. Quality Control & ISO 13485 Compliance
The Shanghai manufacturing hub operates under a fully audited ISO 13485:2016 Quality Management System, ensuring compliance with medical device regulatory requirements (including FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and EU MDR). Key QC checkpoints include:
- Pre-Production: Design FMEA and risk analysis per ISO 14971.
- In-Process: 100% functional testing of image sensors, wireless connectivity, and mechanical durability.
- Final Audit: Full system validation against imaging benchmarks (MTF, SNR, DQE) before release.
3. Sensor Calibration Laboratories
Each imaging sensor is calibrated in Carejoy’s dedicated metrology lab, featuring:
- Traceable radiation sources (5–90 kVp range) for dose-response linearity testing.
- Automated flat-field correction (FFC) using uniform X-ray exposure grids.
- AI-driven noise profiling to suppress fixed-pattern and temporal noise.
- Long-term drift monitoring with recalibration alerts via cloud-based diagnostics.
Calibration certificates are digitally signed and stored in the device’s secure firmware log.
4. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, all Carejoy X-ray units undergo accelerated life testing:
| Test Parameter | Standard | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | IEC 60601-1-11 | Survival from 1.2m onto concrete (6 drops, multiple orientations) |
| Thermal Cycling | IEC 60068-2-14 | Operational from -10°C to 50°C; storage up to 70°C |
| Vibration | ISTA 3A | No degradation in image quality or sensor alignment |
| IP Rating | IP54 (dust/splash resistant) | Validated via ingress testing with particulate and water spray |
| Cycle Testing | 50,000+ insertions | No cable fatigue or connector wear |
5. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in digital dental manufacturing is no longer solely about low labor costs—it is driven by integrated supply chains, state-supported R&D in medical imaging, and rapid iteration cycles enabled by advanced automation and AI.
Carejoy Digital leverages:
- Vertical Integration: In-house sensor design, PCB fabrication, and software development reduce dependency on foreign IP.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production across multiple OEM partnerships lowers per-unit BOM cost without sacrificing quality.
- Talent Density: Shanghai and Shenzhen host >40% of global medical imaging engineers, accelerating innovation in AI-driven artifact reduction and low-dose imaging.
- Open Architecture Compatibility: Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ formats ensures seamless integration with global CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows.
As a result, Carejoy delivers X-ray systems with sub-3µm spatial resolution and AI-enhanced contrast detection at price points 30–40% below Western equivalents—redefining the cost-performance frontier.
Support & Digital Ecosystem
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud portal.
- AI-Driven Software Updates: Monthly firmware enhancements for image processing and cybersecurity.
- Open API: Integration with major practice management and lab software (ex: exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD).
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Meditrix Dental X Ray Machine Price.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
