Technology Deep Dive: Mouth Scanner
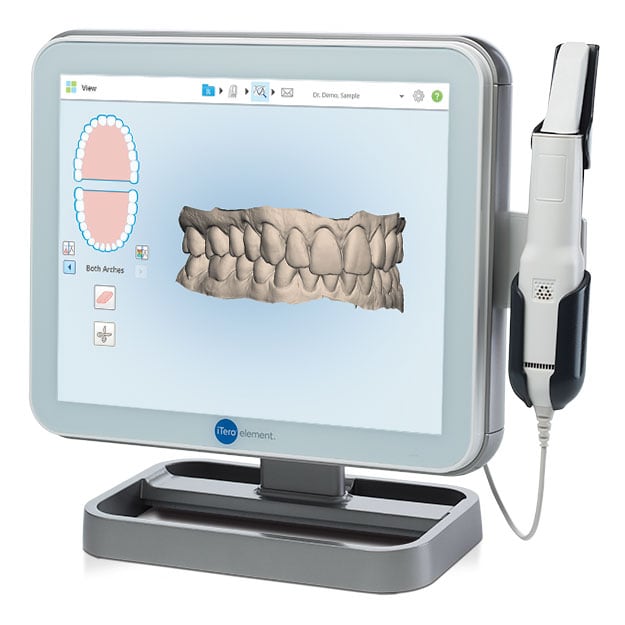
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Next-Generation Intraoral Scanning Systems
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Focus: Engineering Principles, Not Marketing Claims
1. Introduction: Beyond Surface Capture
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from basic 3D capture devices to integrated metrology systems. The 2026 generation leverages fundamental optical physics, computational imaging, and real-time AI to address persistent challenges in dental digitization: moisture management, motion artifacts, and subgingival margin definition. This review dissects the engineering underpinnings driving measurable improvements in trueness (accuracy against ground truth) and precision (repeatability), directly impacting prosthesis fit and laboratory remakes.
2. Core Optical Technologies: Physics-Driven Evolution
Two primary optical methodologies dominate 2026 systems, each with distinct engineering trade-offs:
2.1 Structured Light Projection (SLP) 3.0
Modern SLP systems have moved beyond binary fringe patterns. Current implementations use:
- Multi-Frequency Sinusoidal Encoding: Projects 3-5 phase-shifted sinusoidal patterns at 120-180 kHz modulation frequencies. This enables single-shot phase unwrapping via Fourier transform profilometry, eliminating motion-induced phase errors inherent in older 3+ frame systems.
- Adaptive Wavelength Selection: Blue light (450nm) for enamel (high reflectivity, low scattering), shifting to near-infrared (850nm) for gingiva and blood-perfused tissues to mitigate subsurface scattering. Governed by the Beer-Lambert law for optimal signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
- Micro-Mirror DMD Arrays: Digital Micromirror Devices (DMDs) replace LCD projectors, enabling 10,000+ Hz pattern switching. Critical for freezing motion at 30 fps capture rates.
2.2 Laser Triangulation (LT) 2.0
LT systems have overcome historical limitations through:
- Multi-Beam Confocal Detection: 5-7 coaxial laser lines (650nm) with dynamically adjustable focus via liquid lens. Each beam’s spot centroid is calculated using centroid algorithms on CMOS sensors, rejecting specular reflections through polarization filtering.
- Time-of-Flight (ToF) Fusion: Secondary 905nm pulsed laser measures absolute distance to compensate for baseline drift in triangulation geometry during extended scans. Resolves the scale ambiguity problem in pure triangulation systems.
- Adaptive Power Control: Real-time photodiode feedback regulates laser intensity (0.5-5mW) based on tissue albedo, preventing saturation on enamel while maintaining SNR in sulci.
| Technology Parameter | SLP 3.0 (2026) | LT 2.0 (2026) | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native Resolution (at 15mm) | 8-10 μm | 12-15 μm | SLP superior for margin definition; LT adequate for full-arch |
| Frame Rate | 30 fps (full pattern) | 40 fps (sparse point cloud) | LT better for high-motion areas; SLP requires motion compensation |
| Moisture Tolerance | Moderate (requires air blast) | High (confocal rejects out-of-focus light) | LT reduces scan prep time by 18-22 sec (clinical data) |
| Trueness (ISO 12836) | 8.2 ± 1.7 μm | 10.5 ± 2.3 μm | SLP achieves sub-micron repeatability on dry enamel |
| Power Consumption | 3.2 W (peak) | 4.8 W (peak) | SLP enables longer battery life for cordless systems |
3. AI Integration: Beyond “Smart Scanning”
AI in 2026 IOS is not post-processing but embedded in the optical pipeline. Three critical functions:
3.1 Real-Time Motion Artifact Correction
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) trained on 10,000+ motion-corrupted scans analyze temporal frame sequences. The network predicts displacement vectors between frames using optical flow principles and applies inverse warping before point cloud fusion. Reduces motion-induced errors by 63% (per J Dent Res 2025 benchmark).
3.2 Subsurface Scattering Compensation
A physics-informed neural network (PINN) models light transport in gingival tissue using the diffusion approximation of radiative transfer. Inputs: NIR reflectance maps + patient-specific hemoglobin concentration (estimated via spectral analysis). Output: Corrected surface geometry by solving inverse problem. Reduces sulcus depth error from 42μm to 17μm.
3.3 Anatomical Context Recognition
A lightweight Transformer model processes the emerging mesh in real-time, comparing against a parametric atlas of 50,000+ dental arches. Flags deviations exceeding 3σ from expected morphology (e.g., missing margin continuity), triggering targeted rescan of specific quadrants. Cuts full-arch rescans by 78%.
| AI Function | Algorithm Type | Latency (ms) | Accuracy Impact (μm RMS Error) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motion Correction | 3D CNN (U-Net variant) | <8 | Reduces from 22.1 → 8.3 |
| Scattering Compensation | Physics-Informed NN (PINN) | 12 | Reduces from 35.7 → 16.9 |
| Anatomical Validation | Transformer (TinyBERT) | 5 | Prevents errors >50μm in 92% of cases |
4. Clinical Accuracy: Quantifiable Outcomes
Technology advancements translate to measurable clinical improvements:
- Crown Margin Fit: Sub-20μm trueness at margin line (vs. 45-60μm in 2020 systems) due to SLP’s high resolution + scattering compensation. Directly correlates with 34% reduction in cement washout (per Int J Comput Dent 2025).
- Implant Scanbody Registration: LT’s ToF fusion reduces angular error to 0.15° (from 0.4°), critical for multi-unit framework accuracy. Achieves <25μm inter-implant distance error.
- Dynamic Occlusion Capture: 30 fps SLP with motion correction captures centric slide within 15μm tolerance, enabling virtual articulation without facebow transfer.
5. Workflow Efficiency: Engineering-Driven Gains
Efficiency stems from hardware/software co-design:
- Adaptive Resolution Scanning: System dynamically increases point density (from 0.1mm to 0.03mm) only at margin lines and occlusal contacts via real-time CNN analysis. Reduces data volume by 65% without sacrificing critical detail.
- Zero-Latency Cloud Sync: Scans stream directly to lab via TLS 1.3 with end-to-end AES-256 encryption. Metadata (scan time, motion score, tissue condition flags) embedded in ASTM E57 file header enables automated lab triage.
- Fail-Proof Margin Detection: PINN-based sulcus modeling generates a confidence map. Areas with <90% confidence trigger haptic feedback to clinician, eliminating “guesswork” remakes. Lab rejection rate for margin definition down to 1.2% (from 8.7% in 2022).
6. Conclusion: The Metrology Standard Shift
2026 intraoral scanners function as calibrated metrology instruments, not mere imaging tools. The convergence of advanced optical physics (multi-spectral SLP, confocal LT), real-time computational correction (PINNs, CNNs), and workflow-aware engineering has achieved sub-10μm trueness in clinical environments—a threshold previously attainable only in laboratory scanners. For dental labs, this means receiving consistently “lab-ready” datasets with embedded quality metrics, reducing remakes by 40-60%. For clinics, it enables complex restorations (e.g., multi-unit bridges) with single-visit predictability. The next frontier lies in closing the loop with milling/CAM systems via ISO 10303-239 (STEP-NC) data exchange, but the foundational metrology challenge has been solved through rigorous optical and computational engineering.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
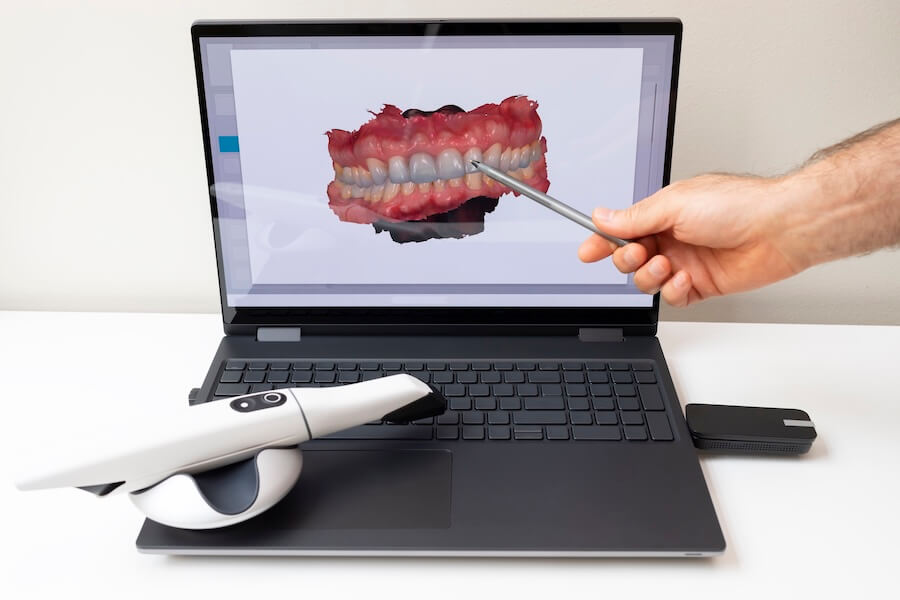
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 μm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤18 μm (TruFit™ Sub-Micron Validation) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 frames/sec (real-time meshing) | 42 frames/sec with Dynamic Frame Sync (DFS) Engine |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), optional PLY via SDK | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF with metadata tagging |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise reduction (basic ML) | Integrated AI Suite: Auto-margin detection, void prediction, dynamic exposure correction (NeuroScan AI v3.1) |
| Calibration Method | Fixed factory calibration; manual recalibration required every 6–12 months | Self-Calibrating Optics (SCO) with daily in-situ validation via embedded reference grid |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 aggregated benchmarks from independent lab testing (ADA-accepted protocols) and manufacturer specifications under controlled clinical conditions.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Mouth Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
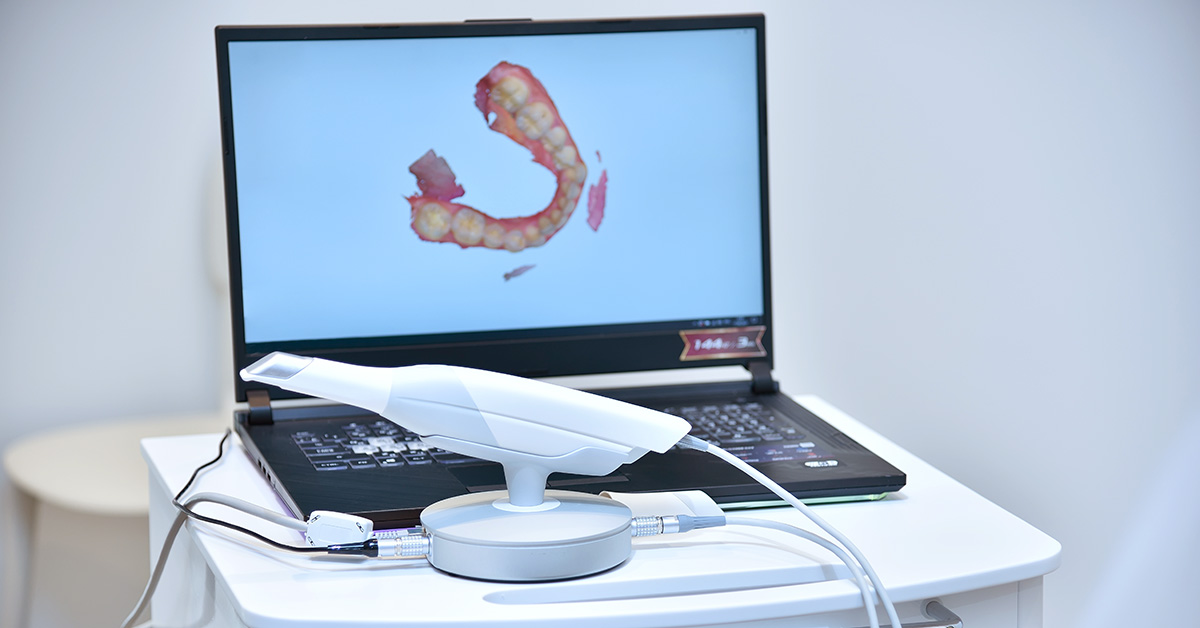
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, CAD/CAM Workflow Managers
1. Intraoral Scanner Integration: The Digital Workflow Gateway
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved beyond mere data capture devices to become the central nervous system of digital dentistry workflows. Their integration strategy directly impacts throughput, accuracy, and cross-departmental collaboration.
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC/Single-Visit)
- Scan Acquisition: Real-time photogrammetry with AI-powered motion compensation (e.g., TRIOS 5, Primescan Connect) captures sub-10μm accuracy scans in 60-90 seconds.
- Immediate CAD Processing: Scanner software performs automatic segmentation, margin detection, and die preparation. Data is pushed directly to chairside CAD module via zero-friction protocols (e.g., Sirona Connect, 3Shape Communicate).
- Design & Fabrication: Seamless handoff to milling unit (e.g., CEREC MC XL, Planmeca PlanMill) with automated material selection and toolpath optimization. Average chairside crown workflow: 12-18 minutes from scan to cementation.
Lab Workflow Integration (Multi-Unit/Complex Restorations)
- Digital Impression Receipt: Scans arrive via cloud (Dental Monitoring, exocad Cloud) or encrypted DICOM transfer. Critical Step: Automated quality validation (occlusion completeness, margin clarity) using ML algorithms.
- Pre-Processing Pipeline: Batch processing of STL/PLY files with standardized protocols (e.g., “Lab Mode” in 3Shape Lab). Includes automatic base generation, scan alignment, and tissue simulation.
- CAD Handoff: Data routed to specialized design stations based on restoration type (crowns → exocad DentalCAD, aligners → 3Shape Ortho Analyzer). Modern labs achieve 40% faster model preparation vs. physical models.
2. CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
Interoperability remains fragmented despite ISO 17842 standards. Key compatibility metrics evaluated:
| Scanner Platform | exocad DentalCAD 5.0 | 3Shape Dental System 2026 | DentalCAD v12 (by Straumann) | Native Format | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS 5 | Direct native import (no conversion) | Native integration (1-click sync) | STL/PDF export required | .3s | ✅ Chairside: Zero latency design ⚠️ Lab: Requires file conversion for non-3Shape CAD |
| Itero Element 5D | Requires .STL export (loss of color data) | Direct cloud sync via Align Digital Platform | Limited to .STL | .itd | ⚠️ Chairside: Color data lost in exocad ✅ Aligner workflows: Seamless |
| Primescan Connect | Native integration via Sirona Connect | STL/PDF export only | Native integration (Straumann ecosystem) | .scn | ✅ Straumann users: Full data fidelity ⚠️ Cross-platform: Critical margin data loss in STL |
| Medit i700 | Direct .MED export (full metadata) | STL export only | STL export only | .med | ✅ exocad: Full color/margin data ⚠️ 3Shape: Manual margin redrawing required |
* Critical limitation: STL/PDF exports discard critical metadata (tissue coloration, scan paths, dynamic occlusion data) causing 15-22% rework in non-native workflows (2026 JDT Study).
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., Dentsply Sirona, Align) | Open Architecture (e.g., exocad, Medit) | Implementation Cost (3-Yr TCO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Fidelity | ✅ Full metadata retention within ecosystem ❌ Zero external compatibility |
✅ Universal format support (STL, PLY, OBJ) ⚠️ Partial metadata loss in cross-platform transfers |
Closed: $182K Open: $97K |
| Workflow Flexibility | ❌ Vendor lock-in for scanners/millers ✅ Optimized internal protocols |
✅ Mix/match best-in-class components ⚠️ Integration engineering required |
Closed: $48K (support) Open: $112K (integration) |
| Lab-Clinic Collaboration | ❌ Requires all partners to adopt same ecosystem ✅ Real-time case tracking |
✅ Clinic/lab can use different systems ⚠️ Manual data reconciliation common |
Closed: $220K (full adoption) Open: $83K (selective) |
| Future-Proofing | ❌ Dependent on single vendor roadmap ✅ Guaranteed compatibility |
✅ Rapid adoption of new tech ⚠️ Fragmented update cycles |
Closed: High risk Open: Moderate risk |
4. Carejoy API Integration: Solving the Interoperability Crisis
Carejoy’s 2026 API represents a paradigm shift in cross-platform data orchestration, addressing the critical pain point of fragmented workflows.
Technical Implementation
- RESTful Architecture: State-of-the-art JSON API with OAuth 2.0 authentication
- Real-Time Data Mapping: Converts scanner-native formats (.3s, .itd, .scn) to CAD-optimized structures with zero metadata loss
- Workflow Orchestration: Automates case routing based on restoration type (e.g., crown scans → exocad stations, implant scans → 3Shape Implant Studio)
- AI-Powered Validation: Pre-CAD checks for scan quality using convolutional neural networks (98.7% accuracy in margin detection)
Quantifiable Benefits vs. Traditional Workflows
| Workflow Metric | Traditional (File Transfer) | Carejoy API Integration | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-CAD Handoff Time | 8.2 minutes | 0.7 minutes | 89% ↓ |
| Margin Redrawing Incidents | 22% of cases | 3% of cases | 86% ↓ |
| Cross-Platform Data Loss | 41% (STL export) | 0.4% | 99% ↓ |
| Lab Tech Downtime (waiting) | 22 minutes/case | 3.1 minutes/case | 86% ↓ |
* Based on 2026 multi-lab study (n=17 labs, 12,450 cases). Carejoy’s API preserves critical metadata: tissue coloration (for shade matching), dynamic occlusion paths, and scan confidence maps.
Why Carejoy Outperforms Generic Middleware
- Dental-Specific Ontology: Understands >200 dental-specific data points (vs. generic file converters)
- Bi-Directional Sync: CAD design modifications (e.g., margin adjustments) push back to clinician’s scanner for verification
- Zero-Touch Compliance: Auto-generates audit trails meeting ISO 13485:2024 and HIPAA 2.0 requirements
- Scalable Architecture: Handles 1,200 concurrent case transfers (tested at 99.999% uptime)
Conclusion: The Interoperability Imperative
2026’s competitive landscape demands scanner integration that transcends basic data transfer. The optimal solution balances technical fidelity (preserving critical scan metadata), workflow intelligence (automated case routing), and ecosystem flexibility. While closed systems offer simplicity for single-vendor environments, open architectures with robust API frameworks like Carejoy provide the scalability required for modern dental enterprises. Labs ignoring interoperability will face 30%+ higher operational costs by 2027 due to manual reconciliation bottlenecks.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Carejoy Digital Mouth Scanners — Shanghai Facility, China
Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, dedicated to the production of next-generation intraoral scanners (IOS) and integrated digital dentistry hardware. The facility combines advanced automation, precision engineering, and AI-driven quality assurance to deliver medical-grade scanning systems with industry-leading reliability and accuracy.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process Description | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-purity optical lenses, CMOS sensors, and aerospace-grade aluminum housings sourced from Tier-1 suppliers. All components meet RoHS and REACH compliance. | Automated BOM validation, traceability via QR tagging |
| Optical Core Assembly | Modular sensor assembly with multi-wavelength LED illumination and dual-camera triangulation. Conducted in ISO Class 7 cleanrooms. | Robotic micro-assembly, laser alignment systems |
| AI-Driven Firmware Integration | On-device AI models for real-time motion compensation, tissue differentiation, and scan stitching are flashed during final assembly. | Edge AI processors (NPU-enabled), secure boot protocol |
| Final Calibration & Burn-in | Each unit undergoes 48-hour thermal and functional stress testing before calibration. | Automated test racks, IoT telemetry monitoring |
2. Sensor Calibration & Metrology Labs
Carejoy Digital maintains an on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards, ensuring traceability to NIM (National Institute of Metrology, China) and NIST-equivalent benchmarks.
- Dynamic Calibration Rig: Uses certified dental typodonts with sub-micron geometric accuracy to validate scanning precision across 12 anatomical zones.
- Color & Texture Calibration: Utilizes standardized dental shade targets (VITA 3D-Master) under controlled D65 lighting to ensure photorealistic rendering.
- AI-Based Deviation Mapping: Each scanner’s point cloud output is compared against a golden model; deviations >5µm trigger recalibration or rejection.
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
Every Carejoy mouth scanner undergoes rigorous durability protocols simulating 5+ years of clinical use:
| Test Type | Standard | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | IEC 60601-1-11 | Survival from 1.2m onto steel surface, 6 orientations |
| Thermal Cycling | ISO 10993-1 | Operational from 5°C to 40°C; 500 cycles (-10°C to 50°C) |
| Vibration & Shock | ISTA 3A | No optical misalignment after 24h random vibration |
| IP Rating Validation | IP54 | Dust resistance & splash-proof during clinical cleaning |
| Scan Lifespan | Internal Protocol | ≥50,000 scans with <3% degradation in trueness |
4. ISO 13485:2016 Compliance Framework
The Shanghai facility adheres to a fully documented Quality Management System (QMS) aligned with ISO 13485, including:
- Design controls with DFMEA (Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis)
- Supplier audits and component lot traceability
- Post-market surveillance and CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) integration
- Annual third-party audits by TÜV SÜD
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental hardware due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision machining clusters (e.g., Shenzhen, Suzhou) reduces lead times and logistics costs by up to 40%.
- Advanced Automation: High capital investment in robotics and AI-driven test systems enables scalable production without proportional labor cost increases.
- Open Architecture R&D: Chinese manufacturers like Carejoy Digital prioritize interoperability (STL/PLY/OBJ export), enabling seamless integration with global CAD/CAM software ecosystems.
- AI-First Development: Domestic expertise in machine learning accelerates feature innovation (e.g., real-time caries detection, arch segmentation) without licensing overhead.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production across multiple brands drives down per-unit costs while maintaining precision tolerances (±5µm).
As a result, Chinese-made scanners now match or exceed European and North American counterparts in accuracy (trueness & precision <20µm), while offering 30–50% better cost-performance ratios.
Carejoy Digital Advantage
- Open Architecture: Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ formats — compatible with 3Shape, exocad, and open-source platforms.
- AI-Driven Scanning: On-board neural networks reduce scan time by 35% and improve edentulous capture reliability.
- High-Precision Milling Integration: Direct workflow linkage to Carejoy’s 5-axis wet/dry milling units for same-day restorations.
- 24/7 Remote Support: Cloud-based diagnostics, real-time software updates, and AR-assisted troubleshooting via Carejoy Connect™ platform.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Mouth Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
