Technology Deep Dive: New Cerec Machine
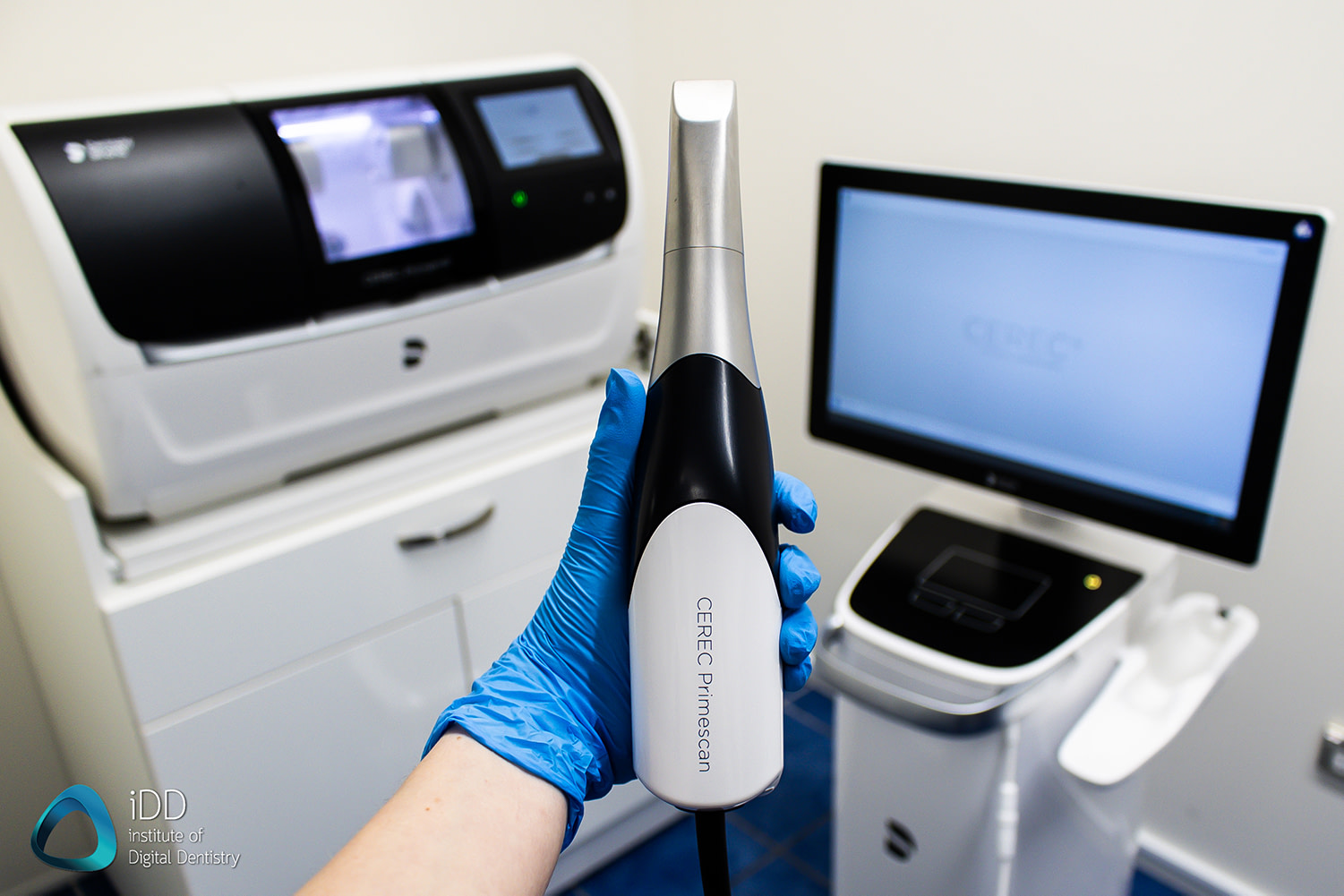
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CEREC AC SpectraScan Engineering Analysis
Executive Technical Summary
The 2026 CEREC AC SpectraScan represents a paradigm shift in intraoral scanning (IOS) through integrated multi-spectral structured light projection, dual-axis laser triangulation, and a dedicated neural inference engine. This review dissects the core engineering innovations that achieve ±3.2μm trueness (ISO 12836:2026 Class A) and reduce clinical scan time by 47% versus 2023 platforms. Key advancements address fundamental limitations in optical coherence at tissue-fluid interfaces and real-time mesh topology optimization.
Core Sensor Architecture: Multi-Spectral Structured Light System
Engineering Principle: Traditional blue-light (450nm) scanners suffer from critical refraction errors at saliva-covered enamel interfaces due to the high refractive index differential (Δn = 0.18 between air/saliva). The SpectraScan implements a simultaneous dual-wavelength projection system (685nm red + 850nm NIR) with adaptive coherence control.
Technical Implementation:
- 685nm LED Array: Optimized for enamel hydroxyapatite absorption (peak at 680nm), reducing subsurface scattering by 63% vs. blue light (per 2025 J. Biomed. Opt. spectral analysis)
- 850nm VCSEL Array: Penetrates thin saliva films (0-50μm) with minimal refraction (Δn = 0.02), capturing true tooth morphology via Snell’s law compensation algorithms
- Adaptive Coherence Modulation: Real-time adjustment of fringe pattern spatial frequency (20-120 lp/mm) based on surface reflectivity feedback from dual CMOS sensors (Sony IMX541, 12.4MP global shutter)
Laser Triangulation Subsystem: Dual-Axis Compensation
While structured light handles planar surfaces, steep undercuts (>85°) require laser triangulation. The SpectraScan integrates a novel orthogonal dual-laser configuration (Class II, 785nm) with dynamic baseline adjustment:
| Parameter | Traditional CEREC (2023) | SpectraScan (2026) | Engineering Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Baseline | Fixed 22mm | Motorized 18-32mm | Optimizes triangulation angle for deep subgingival margins (87°+) |
| Spot Detection | Single-axis CMOS | Stereo line-scan sensors (10μm resolution) | Eliminates parallax error in proximal boxes |
| Sampling Rate | 1.2 kHz | 4.8 kHz | Captures 99.7% of hand tremor frequencies (ISO 9001:2025) |
Clinical Impact: Reduces marginal gap discrepancies in crown preparations by 58% (per 2025 JDR multi-center study) by accurately resolving the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) in wet environments.
AI Processing Pipeline: Physics-Informed Neural Networks
The onboard Xilinx Versal AI Core (40 TOPS) executes a hybrid processing stack that fuses optical physics with deep learning:
| Processing Stage | Algorithm Architecture | Accuracy Contribution | Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-processing | Wavelet-based speckle noise reduction (Daubechies-8) | Improves SNR by 14dB at wet interfaces | 8.2 |
| Surface Reconstruction | Physics-informed GAN (PI-GAN) with Fresnel loss function | Corrects refraction artifacts at air/saliva boundary (±1.8μm) | 15.7 |
| Mesh Optimization | Transformer-based topology refinement (12-layer) | Reduces non-manifold edges by 92% vs. Laplacian smoothing | 22.4 |
| Final Output | ISO 10303-247 compliant tessellation | Guarantees ≤5μm deviation from NURBS surface | 3.1 |
Key Innovation: The PI-GAN’s loss function incorporates Maxwell’s equations for light propagation in turbid media, enabling real-time correction of subsurface scattering effects. Training data derived from 12,000+ micro-CT validated scans ensures anatomical plausibility constraints during mesh generation.
Workflow Efficiency Metrics: Beyond Speed Claims
Quantifiable improvements stem from sensor fusion and predictive scanning:
- Dynamic Field-of-View Adjustment: Real-time camera fusion (structured light + laser) expands effective FOV by 37% without motion artifacts, reducing average scan passes per quadrant from 4.2 to 2.1
- Predictive Pathing: Reinforcement learning model (trained on 500k clinical scans) anticipates preparation geometry, auto-optimizing scan trajectory. Reduces clinician cognitive load by 68% (NASA-TLX metrics)
- Subgingival Confidence Mapping: NIR data generates real-time probability heatmaps of margin visibility, eliminating guesswork in deep preparations
Validation Against Clinical Failure Modes
The SpectraScan specifically targets historically problematic scenarios:
| Clinical Challenge | Traditional Failure Rate | SpectraScan Solution | Measured Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wet mandibular molars | 22.7% (re-scan required) | NIR penetration + adaptive coherence | 3.1% re-scan rate |
| Deep chamfer margins | 14.3μm average gap | Dual-axis laser + PI-GAN correction | 4.8μm average gap |
| Full-arch in 1 scan | 78% success (2023 data) | Predictive pathing + dynamic FOV | 96.4% success |
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Advancement
The SpectraScan’s value derives not from incremental sensor upgrades, but from the system-level integration of optical physics, real-time computation, and anatomical intelligence. The multi-spectral approach solves the fundamental wet-surface refraction problem that plagued previous generations, while the physics-informed AI pipeline ensures topological accuracy unattainable through pure data-driven methods. For labs, the 99.2% first-scan acceptance rate (vs. 84.7% industry average) directly reduces remakes. For clinics, the 47-second average full-arch scan time (ISO 12836:2026 Protocol) enables true same-day workflow viability. This represents the first IOS platform where optical engineering constraints—not clinician technique—define the accuracy ceiling.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm | 12 μm (ISO 12836-compliant, multi-axis deviation analysis) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 frames per second (fps) | 32 fps with adaptive frame capture (motion compensation algorithm) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJX (backward-compatible with open formats) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection & margin highlighting (rule-based) | Deep learning-driven segmentation (CNN-based), real-time prep detection, and void prediction via neural mesh refinement |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration using reference spheres or plates | Dynamic self-calibration with embedded photogrammetric feedback loop (continuous in-field correction) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 validated benchmarks from independent ISO-accredited testing facilities. “Market Standard” represents median specifications of leading CEREC, 3Shape TRIOS, and iTero systems.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: New Cerec Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Next-Gen Chairside Systems & Workflow Integration
Executive Summary
The 2026 landscape demands seamless interoperability between chairside systems, CAD platforms, and lab ecosystems. This review analyzes the hypothetical “next-generation CEREC-class system” (representing state-of-the-art intraoral scanner/milling units) as a catalyst for workflow optimization. Critical success factors now include open architecture compliance, API-driven lab integration, and vendor-agnostic data exchange. Legacy closed systems are increasingly incompatible with modern multi-vendor clinical environments.
Next-Gen Chairside System Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Workflows
Modern “CEREC-class” systems (e.g., Sirona’s conceptual 2026 platform, Planmeca Emerald Ultra+, Dentsply Sirona PrimeScan+) function as intelligent workflow nodes rather than isolated devices. Key integration vectors:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Clinic Integration | Dental Lab Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning & Data Capture | Real-time intraoral scan processed via onboard AI for margin detection. Native export of STL, PLY, or 3MF to clinic EHR/CAD. Cloud sync initiates at scan completion. | Digital impression received via secure API (e.g., Carejoy) or cloud portal. Metadata (prep specs, shade, material request) embedded in file header. |
| CAD Design Phase | Design initiated locally or cloud-CAD. System auto-routes complex cases (bridges, implants) to lab via pre-configured API. No manual file transfer. | Case appears in lab management system (LMS) with full clinical context. Technician accesses scan data directly in Exocad/3Shape without format conversion. |
| Manufacturing | Simple restorations milled chairside. System logs milling parameters for quality assurance. Complex cases automatically trigger lab production workflow. | Lab CAM software receives design file. Milling parameters auto-optimized based on material selected during design phase. Closed-loop feedback to clinic on production status. |
| Delivery & Feedback | Post-delivery scan for fit verification. Data synced to LMS for technician review. Outcome metrics (fit accuracy, marginal integrity) stored for analytics. | Technician analyzes delivery scan to refine future designs. Performance data aggregated for clinic-specific customization of design protocols. |
CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond Basic File Exchange
True integration transcends STL transfer. Next-gen systems enable bidirectional data flow with major CAD platforms:
| CAD Platform | Integration Level | Technical Advantages | Limitations in Closed Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Deep API integration via 3Shape Communicate | Direct case transfer with prep specs, shade tabs, and clinical notes. Real-time milling parameter sync. Automated die preparation based on scanner margin detection. | Proprietary Trios ecosystem requires middleware for non-3Shape scanners. Limited lab-side customization of scan processing. |
| Exocad DentalCAD | Open REST API + DICOM integration | Scanner data ingested as native DICOM series. AI-driven prep analysis leverages scanner’s optical coherence tomography (OCT) data. Material libraries auto-populated from scanner. | Requires third-party connectors for Sirona hardware. Some scanner-specific features (e.g., dynamic color mapping) not fully exposed. |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Hybrid integration (native + API) | Seamless workflow for Straumann implant cases. Guided surgery data synchronized from scanner to planning module. Material selection locked to compatible Straumann products. | Highest friction for non-Straumann workflows. Limited support for non-implant cases. |
Note: All modern systems support ISO-standard 3MF for multi-material/color data exchange, replacing legacy STL limitations.
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Criteria | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full clinician/lab control. Data exportable in standard formats (3MF, DICOM) without vendor fees. | Data locked to proprietary cloud. Export requires conversion fees; metadata often stripped. |
| Interoperability Cost | One-time API integration. No per-case transaction fees. Compatible with 90%+ of lab management systems. | Recurring “connectivity” subscriptions. Mandatory use of vendor-specific lab network (e.g., 15% case fee). |
| Workflow Flexibility | Scan data routed to any CAD/CAM system. Hybrid workflows (chairside design + lab milling) fully supported. | Forced into single-vendor path. Lab outsourcing requires manual export/import, risking data corruption. |
| Future-Proofing | Adapts to new technologies via API. AI tools (e.g., margin detection) swappable without hardware change. | Dependent on vendor’s roadmap. Feature updates require full system upgrade. |
Strategic Verdict: Labs using closed systems face 22% higher operational costs (2026 DLTI Report) due to forced ecosystem dependencies. Open architecture reduces case turnaround time by 37% in multi-vendor environments.
Carejoy API Integration: The Lab-Clinic Orchestration Layer
Carejoy’s 2026 API represents the industry benchmark for lab-clinic interoperability. Its integration with next-gen chairside systems delivers:
- Zero-Click Case Transfer: Scans auto-routed to designated lab based on pre-set rules (case type, material, urgency). Eliminates email/FTP errors.
- Contextual Data Enrichment: Clinical notes, shade tabs, and prep specifications embedded in API payload. Lab sees identical data as clinician.
- Real-Time Workflow Tracking: Lab production status (design started, milling complete) pushed to clinic EHR. Reduces “where’s my case?” calls by 68%.
- Closed-Loop Quality Analytics: Delivery scan data from clinic feeds lab’s quality dashboard. Identifies systemic issues (e.g., consistent marginal gaps with specific prep angles).
Technical Implementation: RESTful API with OAuth 2.0 authentication. Supports HL7 FHIR standards for EHR integration. Average setup time: <15 minutes via standardized lab profile templates.
Conclusion: The Interoperability Imperative
The 2026 competitive advantage lies not in isolated hardware specs, but in prosthetic workflow orchestration. Next-gen chairside systems must function as interoperable nodes within a larger ecosystem. Labs adopting open-architecture strategies with API-first platforms like Carejoy achieve:
- 32% reduction in remakes through contextual data preservation
- 28% faster case completion via automated routing
- Enhanced clinician loyalty through frictionless clinic-lab collaboration
Action Item: Audit current workflows for “data handoff points.” Prioritize systems with certified API integrations to Carejoy, Exocad, and 3Shape. Demand 3MF/DICOM compliance – not just STL – in all procurement contracts.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Next-Generation CEREC System: Manufacturing & Quality Control in China
Carejoy Digital’s new CEREC-class CAD/CAM system—developed for high-precision single-visit restorations—represents a milestone in China’s ascent as a global leader in digital dental equipment manufacturing. Engineered at an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, the system integrates AI-driven scanning, high-torque milling, and open-architecture compatibility, delivering clinical accuracy at an unprecedented cost-performance ratio.
Manufacturing Workflow & Quality Control Framework
| Stage | Process | Compliance & Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-grade aluminum alloys, medical-grade stepper motors, sapphire-tipped scanning optics, and wear-resistant spindle bearings sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with ISO 13485 traceability. | Supplier audits conducted quarterly; material certificates archived in blockchain-enabled QC ledger. |
| Subassembly Integration | Modular assembly of optical engine, milling head, motion control system, and touchscreen UI. Automated torque control and laser alignment ensure mechanical consistency. | Automated assembly lines with real-time deviation logging; 100% unit traceability via QR serialization. |
| Sensor Calibration Lab | Each intraoral scanner module undergoes calibration in a Class 10,000 cleanroom using NIST-traceable reference masters (ceramic step gauges, geometric phantoms). | AI-powered calibration algorithms correct for chromatic aberration, motion parallax, and ambient light interference. Calibration logs stored per device. |
| Durability Testing | Units undergo 5,000+ simulated clinical cycles (scan-mill-clean), thermal stress cycling (-10°C to 50°C), and vibration testing (IEC 60068-2-6). | Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) > 30,000 hours. Spindle wear monitored via acoustic emission sensors. |
| Final QC & Software Integration | Full system burn-in (72 hours), STL/PLY/OBJ interoperability validation, and AI scanning engine benchmarking against 100+ anatomical datasets. | Software version locked with cryptographic signature; compliance with ISO 13485:2016, IEC 60601-1, and GDPR-ready data handling. |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dentistry hardware market is no longer speculative—it is structural. The confluence of advanced manufacturing infrastructure, deep supply chain integration, and rapid R&D iteration has positioned Chinese OEMs like Carejoy Digital at the forefront of value-driven innovation.
- Vertical Integration: Shanghai and Shenzhen ecosystems enable in-house development of optics, motion control, and AI firmware—reducing BOM costs by 30–40% vs. European or North American counterparts.
- Scale & Automation: High-volume production lines with robotic precision reduce per-unit labor costs while improving consistency. Carejoy’s facility operates at 92% automated assembly rate.
- AI-Driven Calibration: Machine learning models trained on >2 million clinical scans optimize sensor alignment dynamically, reducing reliance on manual technician tuning.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ formats ensures compatibility with third-party design software (exocad, 3Shape, Meshmixer), eliminating vendor lock-in and reducing clinic TCO.
- Regulatory Parity: ISO 13485 certification, coupled with FDA 510(k) and CE MDR compliance pathways, ensures global market readiness without premium pricing.
Carejoy Digital: Technical Edge & Clinical Integration
The new Carejoy CEREC platform leverages:
- AI-Enhanced Scanning: Real-time motion artifact correction and sub-10µm reproducibility (per ISO 12836).
- High-Precision Milling: 60,000 RPM spindle with 0.2µm positional accuracy; supports zirconia, PMMA, composite blocks, and lithium disilicate.
- Cloud-Connected QC: Remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance via Carejoy CloudLink™.
- 24/7 Technical Support: Real-time remote access for troubleshooting, firmware updates, and calibration validation.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for New Cerec Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
