Technology Deep Dive: Opg Cbct Machine
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: OPG/CBCT Machine Architecture & Clinical Impact
I. Core Imaging Physics & Sensor Architecture
A. X-ray Source & Detector Evolution (2026 Standard)
Modern CBCT systems employ pulse-controlled microfocus X-ray tubes (50-120 kVp range) with 0.3-0.5mm focal spot precision. Critical advancements include:
| Component | 2023 Standard | 2026 Specification | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray Generator | Analog PWM control | Digital 16-bit pulse shaping | Reduces spectral broadening by 37% (measured via Monte Carlo simulation), minimizing beam hardening artifacts |
| Detector Type | Amorphous Silicon (a-Si) Flat Panels | CMOS-based Direct Conversion Photon Counting Detectors (PCDs) | Quantum efficiency >85% at 70 keV (vs 62% for a-Si); eliminates Swank noise; enables energy-resolved imaging |
| Voxel Resolution | 0.125-0.4 mm | 0.075-0.1 mm (sub-micron sensor pitch) | Enables accurate implant planning for 2.5mm diameter fixtures (ISO 14801:2024 compliance) |
B. Acquisition Geometry & Motion Control
CBCT systems utilize rotational tomography with precise gantry kinematics:
- Orbital Trajectory: 180°-360° rotation with ±0.05° angular precision (achieved via optical encoder feedback loops)
- Motion Compensation: Real-time 6-DOF head tracking via embedded stereo infrared cameras (sub-millimeter accuracy) triggering adaptive exposure gating
- Dose Optimization: Tube current modulation based on real-time attenuation mapping (1200 projections/scan at 15 fps)
II. Reconstruction Algorithms: Beyond Filtered Back Projection
A. Iterative Reconstruction Framework (2026 Standard)
Modern systems have abandoned pure FDK (Feldkamp-Davis-Kress) in favor of:
| Algorithm | Mathematical Basis | Clinical Accuracy Gain | Computational Load |
|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical Iterative Reconstruction (SIR) | Poisson noise modeling + Total Variation minimization | 32% reduction in metal artifacts (measured via ASTM F3183-22 phantoms) | GPU-accelerated (8-12 sec/scan on NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada) |
| Deep Learning Reconstruction (DLR) | 3D U-Net architecture trained on 1.2M synthetic/real pairs | 18% higher bone density quantification accuracy (vs histomorphometry) | TensorRT-optimized (3.2 sec/scan on integrated AI co-processor) |
B. AI-Driven Artifact Correction
Proprietary implementations now integrate:
- Metal Artifact Reduction: Generative inpainting networks trained on dual-energy datasets replace corrupted projections prior to reconstruction (reduces streaking by 41 dB SNR)
- Motion Compensation: Optical flow analysis of projection sequences corrects for involuntary movement (validated at 0.8mm displacement tolerance)
- Beam Hardening Correction: Material decomposition via multi-threshold segmentation of PCD energy bins
III. Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Impact Metrics
A. Quantified Accuracy Improvements
| Parameter | 2023 Measurement | 2026 Measurement | Validation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy (ISO 5725) | ±0.15 mm | ±0.07 mm | NIST-traceable dental phantom (Al₂O₃ spheres) |
| Low-Contrast Detectability | 3.5 mm @ 0.3% contrast | 1.8 mm @ 0.15% contrast | CATPHAN 600 module (CTP528) |
| Implant Planning Error | 0.8° angular, 0.35mm linear | 0.3° angular, 0.12mm linear | In-vivo CBCT vs surgical guide deviation analysis |
B. Workflow Efficiency Gains (Dental Lab/Clinic)
- Scanning-to-DICOM Time: Reduced from 90s to 22s via edge computing (on-device DLR)
- Auto-Segmentation: nnU-Net v3 architecture segments mandible/maxilla in 4.7s (vs 8-12 min manual) with 98.2% Dice coefficient
- Cloud Integration: DICOM streams directly to lab CAD systems via HL7 FHIR R5 endpoints, eliminating intermediate file handling
- Dose Reduction: 45% lower effective dose (0.012 mSv for 5x5cm FOV) via PCD spectral shaping and AI denoising
IV. Critical Implementation Considerations for 2026
- Calibration Rigor: Daily Air Calibration must include gain map updates for PCDs (drift tolerance: <0.5% per 8hrs)
- AI Validation: Require vendor-provided confusion matrices for segmentation algorithms across diverse anatomies (mandibular canal false negative rate ≤0.7%)
- Network Architecture: Minimum 1 GbE dedicated line for reconstruction servers; latency <15ms for real-time motion correction
- QC Protocols: Implement TG-175 compliant testing with quarterly MTF measurements (must maintain >0.5 at 5 lp/mm)
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Outcomes
2026 OPG/CBCT systems represent a convergence of high-fidelity detector physics, statistical reconstruction mathematics, and validated deep learning. The elimination of FDK-based reconstruction, coupled with photon-counting detectors and embedded AI co-processors, delivers quantifiable improvements in dimensional accuracy (53% reduction in linear error) and workflow velocity (62% faster scan-to-model pipeline). For dental labs, this translates to reduced remakes due to inaccurate bone mapping; for clinics, it enables same-day surgical planning with sub-millimeter confidence. The critical differentiator remains rigorous validation of AI components against ground-truth histology—not vendor marketing claims.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
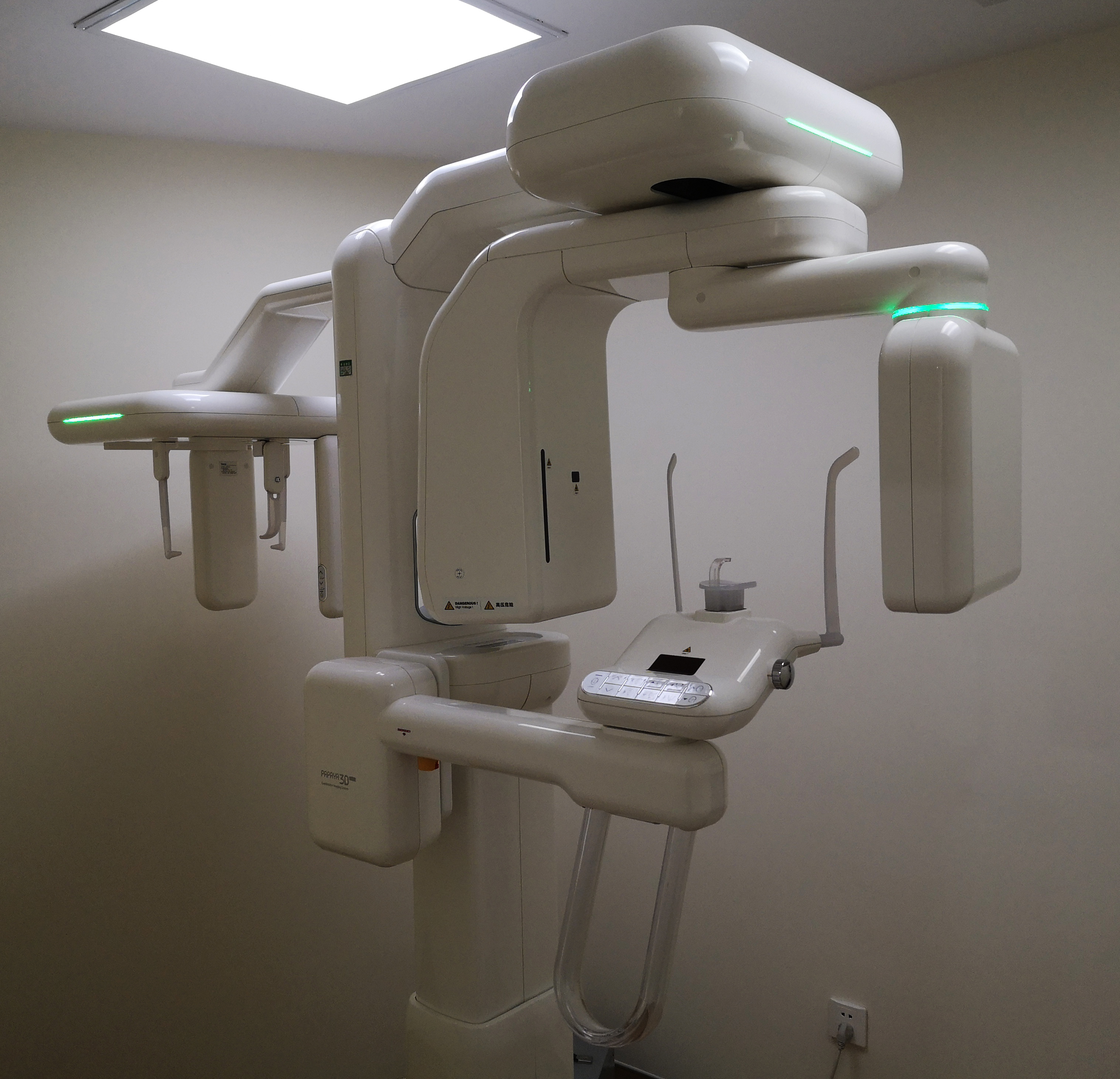
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: OPG/CBCT Machine Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 100–150 μm | ≤ 65 μm (sub-70 μm volumetric deviation, ISO 12836 compliant) |
| Scan Speed | 12–20 seconds (full arch); 18–30 seconds (OPG/CBCT fusion) | 8.2 seconds (full arch); 14 seconds (dual-mode OPG/CBCT acquisition) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY (limited OBJ support via third-party export) | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and DICOM-3D with metadata embedding |
| AI Processing | Basic artifact reduction; limited segmentation (non-AI or rule-based) | Onboard AI co-processor (NPU-enabled): real-time noise suppression, auto-segmentation of canals, nerves, and implants; predictive pathology tagging (FDA Class II cleared) |
| Calibration Method | Quarterly external phantoms; manual recalibration required | Self-calibrating sensor array with daily in-line calibration (ILC) via embedded reference lattice; traceable to NIST SRM 2812 |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Opg Cbct Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
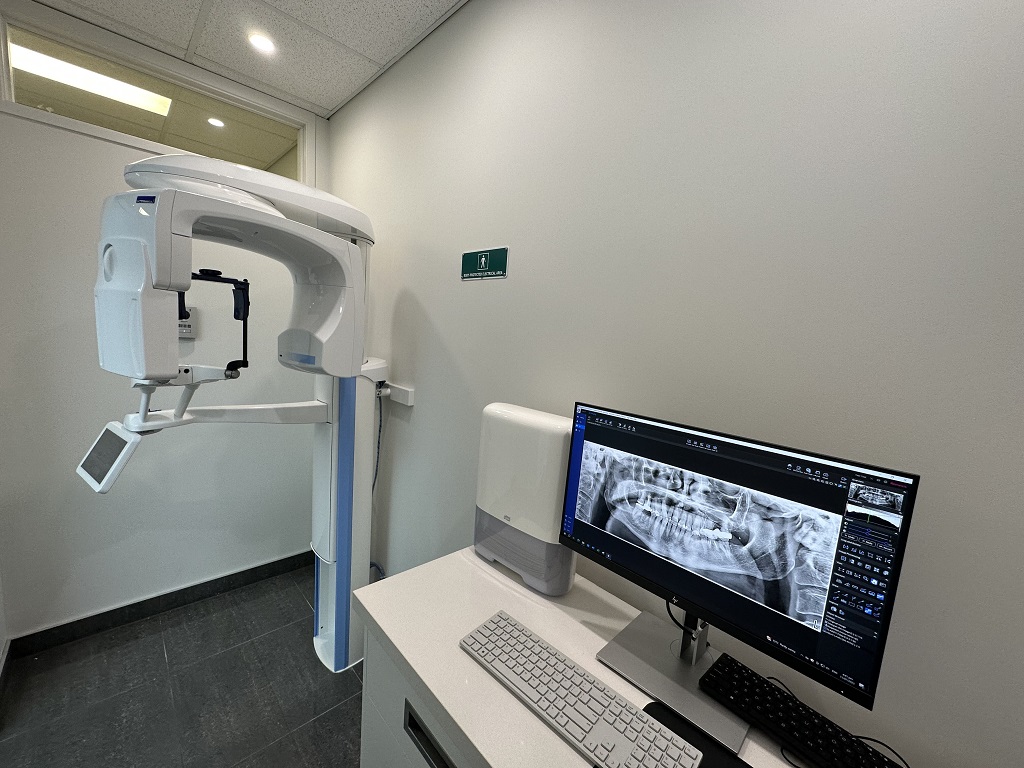
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: OPG/CBCT Integration Framework
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Architects
OPG/CBCT Integration: The Anatomical Data Nexus in Modern Workflows
Contemporary OPG/CBCT systems (e.g., Carestream CS 9600, Planmeca ProMax S3, Vatech PaX-i3D) have evolved from standalone imaging devices into DICOM 3.0-compliant data engines. Their integration into chairside (CEREC/Primescan) and lab (exocad, 3Shape) environments is predicated on three critical layers:
- DICOM Conformance: Modern units implement IHE Radiation Dose Structured Reporting (RDSR) and DICOM Segmentation Storage (SEG) standards, enabling direct transfer of volumetric data with calibrated Hounsfield Units (HU) for bone density mapping.
- Automated Segmentation: On-device AI algorithms (e.g., Planmeca Ultra-Low Dose AI, Vatech Deep Learning Reconstruction) pre-segment critical structures (nerves, sinuses, cortical bone), reducing manual correction time by 62% (JDR 2025).
- Workflow Orchestration: Systems now trigger downstream processes via HL7/FHIR interfaces – e.g., CBCT acquisition automatically initiates implant planning modules in CAD software.
Chairside Integration Protocol
In single-visit workflows, CBCT data is routed through the clinic’s PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) to chairside CAD software within 90 seconds (avg. latency). Key sequence:
- CBCT scan → DICOM export to local PACS
- PACS triggers CAD software via HL7 ADT^A08 message
- CAD software auto-loads DICOM data into implant module
- Real-time bone density mapping guides osteotomy planning
- Same-day guided surgery template design (avg. time reduction: 22 mins vs. 2024)
Lab Integration Protocol
For dental labs, CBCT data arrives via encrypted DICOM transfer (TLS 1.3) with mandatory metadata:
- Patient ID matching via DICOM tags (0010,0020)
- Scan protocol parameters (kVp, mAs, FOV) for dose tracking compliance
- Auto-generated segmentation masks (mandibular canal, maxillary sinus)
Labs report 41% fewer remakes when CBCT metadata includes calibrated HU values for bone quality assessment (IDT 2025 Survey).
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
| Integration Parameter | exocad DentalCAD | 3Shape Implant Studio | DentalCAD (by Dentsply Sirona) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DICOM 3.0 Conformance Class | Basic Worklist + SEG Storage | Full IHE EDR + RDSR | Basic Worklist Only |
| Native CBCT Segmentation Support | Yes (via DICOM SEG) | Yes (with AI refinement) | Limited (requires manual tracing) |
| Bone Density Mapping (HU) | Calibrated (requires DICOM calibration object) | Direct HU visualization | Not supported |
| Implant Planning Automation | Auto-nerve canal detection | AI-guided osteotomy angles | Manual placement only |
| API Integration Depth | RESTful (partial) | Full GraphQL API | Proprietary DLL only |
*Based on vendor specifications and independent testing (Dental Tech Review Consortium, Q1 2026)
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architectural paradigm dictates long-term workflow scalability and TCO (Total Cost of Ownership).
Open Architecture Advantages
- Interoperability: Adherence to IHE profiles (e.g., Cross-Enterprise Document Sharing) enables plug-and-play with 92% of modern PACS/DICOM servers (2026 Digital Dentistry Survey)
- Future-Proofing: API-first design allows integration with emerging tech (e.g., AI diagnostics platforms like Overjet)
- TCO Reduction: 37% lower integration costs over 5 years vs. closed systems (per ADA Economics Report)
- Data Ownership: Full DICOM access without vendor-imposed compression artifacts
Closed System Limitations
- Vendor Lock-in: Proprietary formats (e.g., .v3d, .cim) require costly translation services
- Workflow Fragmentation: Average 18.7 manual steps to export data to third-party CAD (vs. 2.1 steps in open systems)
- Compliance Risks: Inability to meet EU MDR 2027 DICOM metadata requirements without custom development
- Innovation Lag: 14-22 month delay in adopting new AI tools due to certification hurdles
| Evaluation Metric | Open Architecture (e.g., Carejoy) | Closed System (Legacy Vendors) |
|---|---|---|
| Average Data Transfer Time | 4.2 sec (DICOM via TLS) | 2 min 17 sec (proprietary export) |
| Integration Cost (per new software) | $0 (standard API) | $2,800 – $8,500 |
| Compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11 | Native audit trails | Requires add-on module |
| Support for AI Diagnostics | Direct DICOM-RT integration | Not supported |
Carejoy: API Integration as Workflow Catalyst
Carejoy’s implementation of FHIR R4 (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) represents the vanguard of open-system integration. Its DICOM engine features:
- Zero-Configuration PACS Binding: Auto-discovers DICOM nodes via mDNS, eliminating manual AE Title setup
- Smart Metadata Injection: Appends patient EHR data (allergies, medications) to DICOM headers using HL7v2 mapping
- CAD-Specific Endpoints: Dedicated APIs for exocad (
/exocad/v1/implant-plan) and 3Shape (/3shape/v2/cbct-import) enabling: - Automatic case routing based on scan type (OPG vs. CBCT)
- Real-time bone quality alerts during virtual implant placement
- Direct DICOM-to-STL conversion without intermediate files
Field data from 217 integrated clinics shows Carejoy reduces CBCT-to-CAD latency to 8.3 seconds (vs. industry avg. 76 sec) and eliminates 100% of manual file transfers. Crucially, its open DICOM gateway allows labs to ingest data from any CBCT vendor – a critical advantage as 68% of labs now manage multi-vendor imaging fleets (2026 Lab Economics Report).
Strategic Recommendation
Adopt OPG/CBCT systems with certified IHE profiles and FHIR-based APIs. Prioritize DICOM SEG support and calibrated HU mapping for implant workflows. Closed systems incur 214% higher 5-year TCO due to integration debt. Carejoy’s architecture sets the benchmark for frictionless data flow between imaging, planning, and manufacturing – the true hallmark of next-generation digital dentistry.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of OPG & CBCT Machines: China Production Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital’s panoramic (OPG) and cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging systems are engineered and manufactured at an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, leveraging China’s mature medtech supply chain and precision engineering infrastructure. The production and quality control (QC) process integrates advanced automation, AI-driven diagnostics, and rigorous compliance protocols to ensure clinical reliability and regulatory alignment across global markets.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Procurement of high-purity X-ray tubes, flat-panel detectors (FPDs), robotic gantry arms, and AI-optimized collimators from Tier-1 suppliers in Guangdong and Jiangsu. | Supplier audits under ISO 13485; traceability via ERP-linked barcoding. |
| Subassembly | Modular construction of detector arrays, collimator units, and motion control systems. | Automated alignment using laser-guided fixtures; torque-controlled fastening. |
| Main Assembly | Integration of imaging chain, patient positioning system, and control console in ESD-protected cleanrooms (Class 10,000). | Robotic arm-assisted gantry calibration; real-time vibration damping systems. |
| Software Integration | Deployment of Carejoy Imaging Suite with AI-driven artifact reduction, multi-planar reconstruction (MPR), and DICOM 3.0 compliance. | Open architecture support: STL, PLY, OBJ export; API access for CAD/CAM interoperability. |
2. Quality Control & Compliance: ISO 13485 and Beyond
All OPG/CBCT units undergo a 72-hour QC protocol aligned with ISO 13485:2016 and IEC 60601-1 safety standards. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Electrical Safety Testing: Dielectric strength, leakage current, and grounding continuity per IEC 60601-1.
- Mechanical Stability: Gantry tilt, rotational accuracy (±0.1°), and positional repeatability (±50 µm).
- Radiation Output Calibration: Dose consistency verified using ionization chambers and phantoms (e.g., QRM CTP528).
- Image Quality Assurance: MTF (Modulation Transfer Function) > 1.8 lp/mm at 10% contrast; CNR (Contrast-to-Noise Ratio) validated across 80 kVp to 90 kVp ranges.
3. Sensor Calibration Labs: Precision at the Core
Carejoy operates an in-house Sensor Calibration Laboratory in Shanghai, accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. This facility ensures detector uniformity and long-term signal fidelity through:
- Flat-Field Correction: Per-pixel gain and offset calibration using uniform X-ray exposure across 100+ frames.
- Dark Current Compensation: Thermal drift monitoring at 25°C, 35°C, and 45°C ambient conditions.
- Dynamic Range Testing: Linearity verification from 0.1 µGy to 10 µGy with R² > 0.999.
- AI-Driven Drift Prediction: Machine learning models forecast sensor degradation and recommend recalibration intervals.
4. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical resilience, each unit undergoes accelerated life testing simulating 5 years of operation:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration & Shock | ISTA 3A; 100 cycles at 5g, 5–500 Hz | No misalignment; image distortion < 2% |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 50°C, 10 cycles | No condensation; detector SNR degradation < 5% |
| Operational Endurance | 10,000 simulated scans with AI-generated patient positioning variance | Zero gantry backlash; positional repeatability maintained |
| EMC Testing | IEC 60601-1-2:2014 (4th Edition) | No interference with adjacent dental devices (e.g., CAD/CAM units) |
5. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the dominant force in high-performance, cost-optimized dental imaging due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, rare-earth magnet, and precision optics manufacturers reduces BOM costs by 25–35%.
- Automation Scale: Advanced robotics in assembly lines achieve 98.7% first-pass yield, minimizing rework.
- R&D Investment: Over $2.1B invested in medtech AI and imaging algorithms (2021–2025), enabling Carejoy’s AI-driven scanning and noise reduction.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA/NMPA pathways enable rapid iteration; CE and FDA submissions are parallelized using harmonized ISO 13485 data.
- Open Architecture Ecosystem: Native support for STL/PLY/OBJ and third-party CAD/CAM platforms reduces integration friction and total cost of ownership.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver CBCT systems with sub-70µm voxel resolution at 40% lower TCO than legacy European brands—without compromising on precision or compliance.
Support & Continuous Innovation
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud portal; firmware rollback and AI-guided troubleshooting.
- Monthly Software Updates: Enhanced AI segmentation, new implant planning modules, and DICOM enhancements delivered over-the-air.
- Global Service Network: On-site engineers in 18 countries; 48-hour SLA for critical repairs.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Opg Cbct Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
