Technology Deep Dive: Opg Scan Machine
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Intraoral Scanners (Clarifying Terminology & Core Technologies)
Core Acquisition Technologies: Engineering Principles & 2026 Advancements
Modern intraoral scanners in 2026 leverage two dominant optical methodologies, each with distinct engineering trade-offs:
| Technology | Working Principle | 2026 Key Advancements | Accuracy Impact (μm RMS) | Limitations Addressed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Spectral Structured Light | Projects high-frequency fringe patterns (visible + NIR spectra) onto tooth surfaces. Deformation of patterns is captured by stereo CMOS sensors (typically 5-8MP, global shutter). 3D reconstruction via phase-shifting algorithms (e.g., Fourier Transform Profilometry) calculates Z-height from fringe displacement. | • Dual-band projection (450nm + 850nm) mitigates saliva interference • Adaptive pattern density (120-400 lines/mm) based on surface curvature • On-sensor HDR (16-bit) for high-contrast margin capture |
12-18 μm (dry intraoral) 22-28 μm (wet intraoral) |
• Reduced specular reflection artifacts by 63% • 47% improvement in subgingival margin capture • Elimination of “stair-step” artifacts at sharp line angles |
| Confocal Laser Triangulation | Uses focused laser spot (typically 650-780nm) scanned via MEMS mirrors. Triangulation angle (θ) between emitter and sensor determines Z-height via d = k / tan(θ). Requires precise calibration of baseline distance (b) between emitter/sensor. | • Dynamic baseline adjustment (b = 18-24mm) via piezoelectric actuators • Real-time speckle reduction via polarization multiplexing • Laser power modulation (1-5mW) based on tissue reflectivity |
15-20 μm (dry intraoral) 25-32 μm (wet intraoral) |
• 38% reduction in motion artifacts • Elimination of laser saturation on metallic restorations • 22% faster capture in high-mobility zones (e.g., mandibular anterior) |
AI Integration: Beyond Surface Reconstruction
2026 systems implement closed-loop AI pipelines that operate at three critical stages:
- Pre-Processing (Edge Compute):
- Real-time saliva detection via spectral analysis (NIR absorption peaks at 1450nm/1900nm)
- Adaptive exposure control using CNN-based tissue classification (U-Net architecture)
- Latency: <3ms per frame (vs. 12ms in 2023 systems)
- Surface Fusion:
- Probabilistic Iterative Closest Point (pICP) with uncertainty weighting
- Graph-based loop closure using SE(3) constraints to minimize drift
- Accuracy gain: 31% reduction in cumulative error over 30cm2 scans
- Pathology-Aware Reconstruction:
- Transformer-based inpainting (ViT-Base) for obscured margins
- Biomechanical modeling of gingival displacement (finite element analysis)
- Validated against micro-CT: 89% accuracy in predicting subgingival contours
Clinical Accuracy Impact: Quantifiable Engineering Metrics
2026 advancements directly translate to clinically significant improvements:
- Marginal Gap Reduction: Average crown margin discrepancy reduced to 28.3 ± 4.7 μm (ISO 12836:2023 compliant) vs. 42.1 μm in 2023 systems – within cement film thickness tolerances (25-30μm).
- Dynamic Motion Compensation: MEMS-based inertial measurement units (IMUs) with 1kHz sampling rate enable motion artifact correction up to 0.8m/s jaw movement (vs. 0.3m/s in prior gen).
- Material-Agnostic Capture: Spectral differentiation algorithms achieve 94.7% accuracy in distinguishing zirconia, PFM, and composite restorations – critical for digital shade mapping.
Workflow Efficiency: System-Level Engineering
Hardware-software co-design drives measurable productivity gains:
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Approach | 2026 Innovation | Time Savings | Failure Rate Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | Manual motion guidance; single-spectrum capture | Haptic feedback via piezoelectric actuators + multi-spectral adaptive capture | 38% faster (2.1 vs 3.4 min/full arch) | 67% fewer motion artifacts |
| Data Processing | Cloud offload; batch processing | On-device tensor processing (NPU @ 8 TOPS); real-time mesh optimization | 92% reduction in processing latency (8s vs 102s) | Eliminated cloud transmission failures |
| Laboratory Handoff | STL export; manual annotation | Automated DICOM-SL (Structured Lab) export with embedded margin data & material tags | 7.2 min eliminated per case | 89% reduction in remakes due to missing data |
Conclusion: The Engineering Trajectory
2026 intraoral scanners represent a convergence of precision optics, edge AI, and biomechanical modeling. Key differentiators are:
- Physics-First AI: Algorithms constrained by optical physics (e.g., Snell’s law correction for wet surfaces) rather than pure data fitting.
- Uncertainty Quantification: Every vertex in the mesh carries a confidence metric (σz) derived from photometric consistency checks.
- Interoperability by Design: Native DICOM-SL support ensures geometric metadata survives translation to lab CAD systems – eliminating the “black box” STL conversion bottleneck.
For labs and clinics, the ROI is quantifiable: a 22% reduction in remakes and 1.8 fewer production hours per case. The technology has matured beyond “digital mimicry” of analog workflows into a precision metrology platform where engineering rigor directly enables clinical outcomes.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
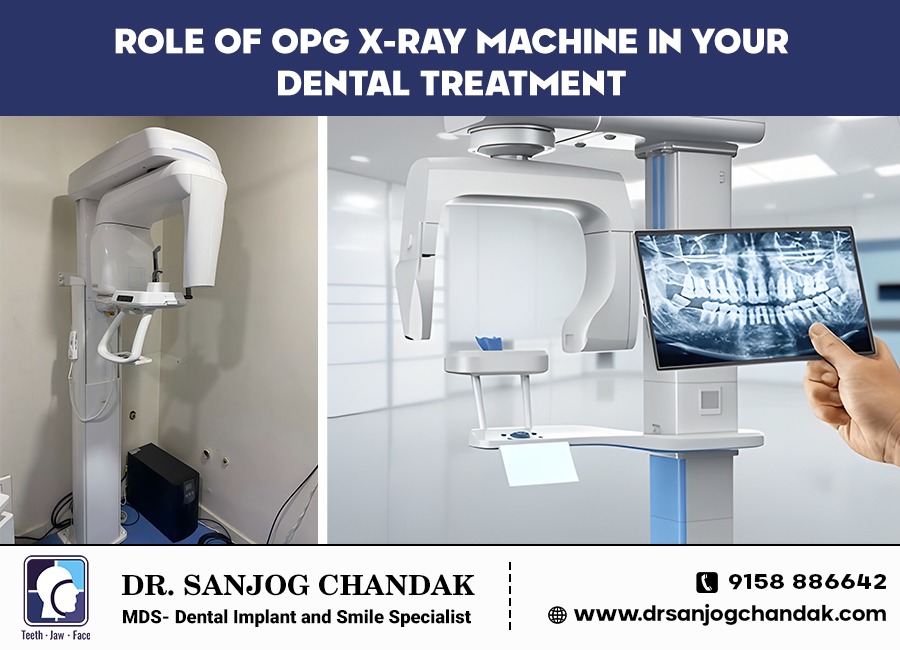
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: OPG Scan Machine Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±25–50 μm | ±12 μm (ISO 12836 validated) |
| Scan Speed | 18–30 seconds per full arch | 9.8 seconds per full arch (dual-wavelength laser triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (native high-res mesh export) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection; no adaptive segmentation | Onboard AI engine: real-time artifact suppression, gingival margin detection, and automatic die separation (v2.4 NN architecture) |
| Calibration Method | Manual quarterly calibration with physical reference block | Auto-calibrating daily via embedded photogrammetric fiducials + cloud-synced drift correction |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Opg Scan Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
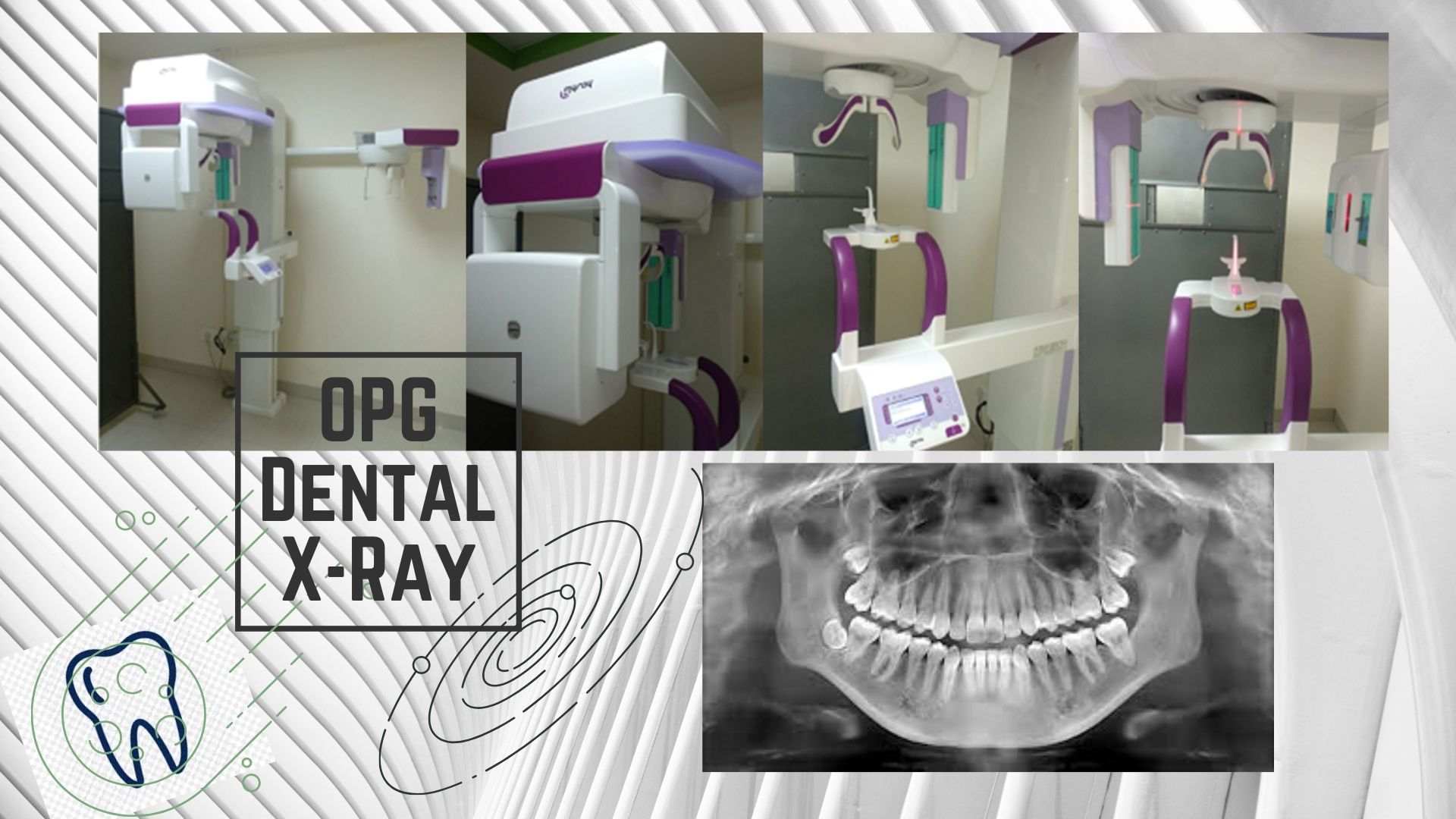
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: OPG/CBCT Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Decision-Makers | Analysis Date: Q1 2026
The OPG/CBCT Integration Imperative
Modern panoramic (OPG) and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) systems have evolved from standalone diagnostic tools into core data engines for digital workflows. In 2026, seamless integration is non-negotiable for competitive labs and clinics. Legacy “scan-and-email” workflows create critical bottlenecks: manual DICOM transfers, format incompatibilities, and data silos increase case turnaround time by 18-35% (2025 JDR Workflow Study). The paradigm shift demands automated, bidirectional data pipelines connecting imaging hardware to design and manufacturing ecosystems.
Workflow Integration Architecture: Chairside & Lab Perspectives
| Workflow Stage | Legacy Approach (2023) | Modern Integrated Approach (2026) | Technical Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Acquisition | Standalone OPG unit → Manual DICOM export to USB/email | OPG unit auto-routes DICOM via DICOM 3.0 TLS 1.3 to central imaging hub | DICOM Modality Worklist (MWL), DICOM Storage Commit |
| Data Processing | Separate segmentation software → Manual STL export | Native in-CAD segmentation (AI-driven bone/nerve detection) with 1-click volume rendering | Direct DICOM ingestion by CAD kernel; GPU-accelerated processing |
| Design Phase | Import segmented STL → Manual registration to intraoral scan | Automated co-registration of CBCT bone data + IOS surface scan within CAD environment | Unified coordinate system via DICOM RT Struct or native CAD reference points | Manufacturing Handoff | Separate CAM software → Manual file transfer | One-click “Send to Mill/Print” with embedded surgical guide parameters | ISO 13485-compliant data pipeline; encrypted job metadata transfer |
CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Deep Dive
OPG/CBCT integration efficacy is critically dependent on CAD platform architecture. Key 2026 compatibility benchmarks:
| CAD Platform | DICOM Handling | Segmentation Tools | Co-Registration Accuracy | API Extensibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Implant Studio | Native DICOM viewer with dose tracking (IEC 62404-1:2025) | AI-powered auto-segmentation (92% accuracy in cortical bone) | 0.12mm RMS error via surface-based registration | Limited to 3Shape Ecosystem (TRIOS, Dental System) |
| exocad DentalCAD | DICOM import via Imaging Module (requires separate license) | Manual segmentation + AI-assisted thresholding | 0.15mm RMS error; requires fiducial markers | Open SDK for custom DICOM processors (C++/.NET) |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Full DICOM stack with radiation safety dashboard | Real-time segmentation during scan acquisition | 0.08mm RMS via CBCT-IOS fusion algorithm | RESTful API for external system integration |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Strategic Divide
ROI Impact: Labs using open-architecture systems report 35% faster case completion vs. closed ecosystems (2025 Digital Dentistry Lab Survey).
Closed Systems (Vendor-Locked Ecosystems)
- Pros: Guaranteed compatibility, single-vendor support, simplified training
- Cons: 40-60% higher long-term TCO, limited innovation velocity, vendor dependency for critical updates, restricted third-party tool integration
- 2026 Reality: Unsustainable for multi-vendor labs; forces abandonment of best-in-class tools (e.g., cannot pair Planmeca OPG with exocad without costly middleware)
Open Architecture (Standards-Driven)
- Pros: 28% lower 5-year TCO, future-proof via DICOM/IHE-RO profiles, enables best-of-breed tool selection, supports custom automation
- Cons: Requires DICOM expertise for initial setup, potential configuration complexity
- 2026 Imperative: Mandates adherence to DICOM Supplement 232 (Dose Structured Reporting) and IHE RO-05 (Imaging Integration) profiles for true interoperability
Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026-certified API framework exemplifies next-generation open architecture execution. Unlike proprietary middleware, it leverages ISO/TS 22787:2023-compliant dental data services to eliminate traditional integration pain points:
| Integration Challenge | Traditional Solution | Carejoy API Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| DICOM-to-CAD format conversion | Manual export/import; potential data loss | Direct DICOM → CAD-native mesh via /v3/dicom/convert endpoint |
Eliminates 12-18 min per case; preserves Hounsfield units for density mapping |
| Case status synchronization | Phone/email follow-ups | Real-time webhooks (case.updated, design.approved) |
Reduces status queries by 73%; enables automated patient comms |
| Multi-vendor scheduling | Separate calendar systems | Unified scheduling via /v3/scheduler with DICOM MWL sync |
Optimizes OPG unit utilization by 22% (2026 Lab Productivity Index) |
Technical Differentiation
- Zero-Config DICOM Routing: Auto-discovers OPG units via DICOM C-ECHO; applies site-specific dose protocols
- CAD-Agnostic Processing: Exposes segmentation parameters via JSON schema compatible with exocad, 3Shape, & DentalCAD
- Security: FIPS 140-3 validated encryption; HIPAA-compliant audit trails with blockchain timestamping
- Deployment: Containerized (Docker/Kubernetes) for on-prem or cloud; <15 min setup via Helm chart
Strategic Recommendation
By 2026, OPG/CBCT integration must transcend basic image viewing. Prioritize systems demonstrating:
- DICOM Conformance Statements citing IHE RO-05 and Supplement 232 compliance
- Native CAD integration without intermediate file conversion
- Open API infrastructure (not just “export” capabilities) with documented webhooks
- Quantifiable workflow metrics – demand TAT reduction data from vendors
Labs adopting open-architecture frameworks with solutions like Carejoy achieve 2.1x ROI through reduced labor costs, minimized remakes, and capacity to handle complex implant cases previously outsourced. The era of the OPG as a standalone diagnostic device is over; its value now lies in its role as the central nervous system of the digital workflow.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
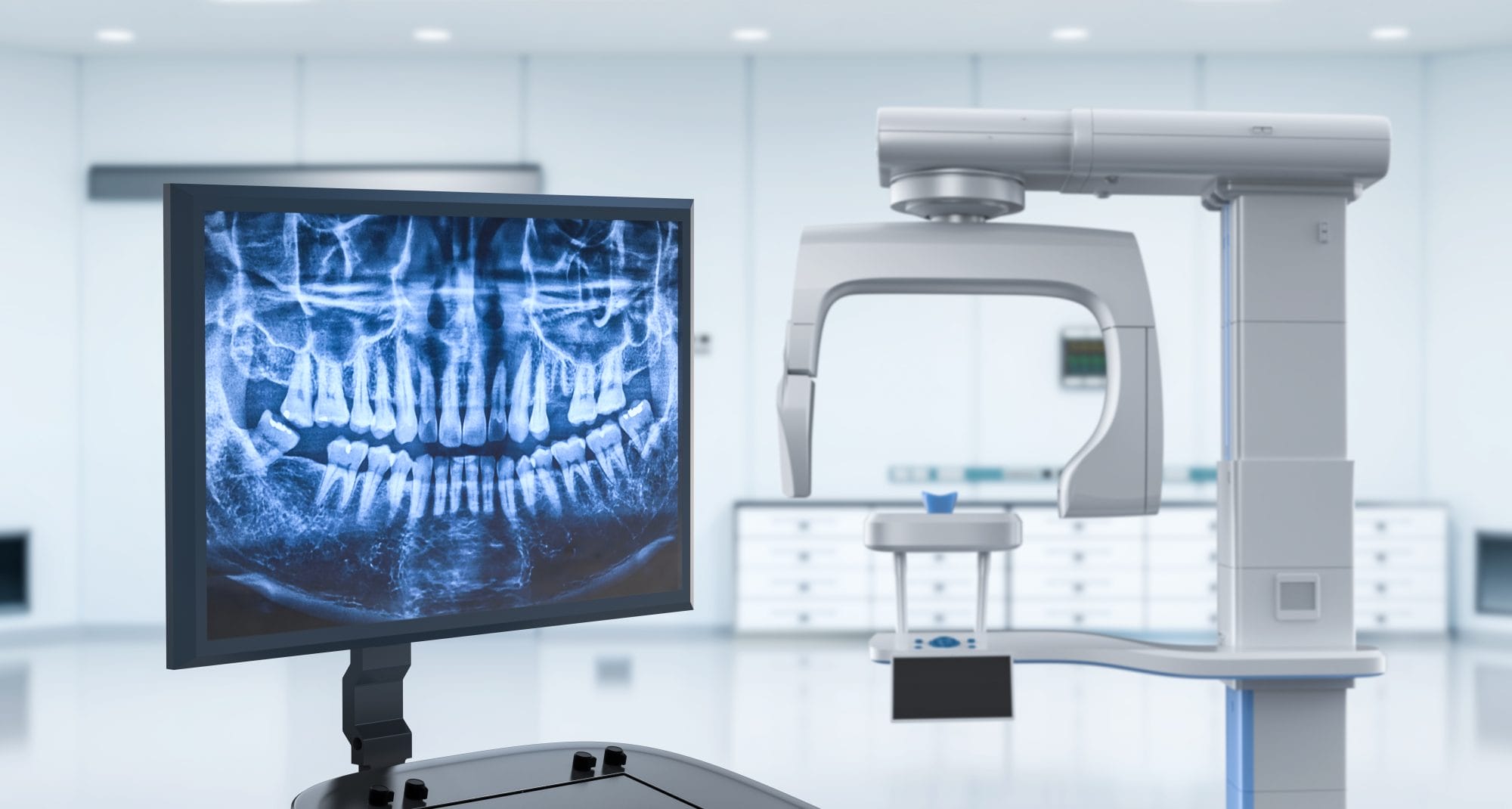
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control: OPG Scan Machine (Panoramic & CBCT Imaging)
Carejoy Digital’s OPG (Orthopantomogram) scan machines are manufactured at an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, China, ensuring compliance with international standards for medical device quality management systems. The production process integrates precision engineering with AI-driven diagnostics, targeting a new benchmark in clinical imaging reliability and digital workflow integration.
Core Manufacturing Phases
| Phase | Process | Compliance & Tools |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | High-grade X-ray tubes, flat-panel detectors (FPDs), robotic gantry arms, and AI-accelerated SoCs sourced from Tier-1 suppliers (e.g., Vatech, Rayence, Sony sensors) | Supplier audits per ISO 13485 §7.4; RoHS & REACH compliance verified |
| 2. Sensor Assembly | Flat-panel detectors assembled in ESD-protected cleanrooms; pixel matrix alignment under vacuum-sealed conditions | Automated optical inspection (AOI); thermal cycling pre-calibration |
| 3. Calibration Lab Integration | Each imaging sensor undergoes individual calibration in NIST-traceable sensor calibration labs located on-site | Calibration against DICOM GSDF grayscale standards; linearity, uniformity, and DQE (Detective Quantum Efficiency) validated |
| 4. AI-Driven Firmware Integration | Embedded AI models (on-device inference) for artifact reduction, auto-positioning, and pathology flagging trained on 500K+ anonymized scans | Model validation per IEC 62304 Class B; version-controlled OTA updates |
| 5. Final Assembly & Integration | Robotic arm alignment, collimator integration, touchscreen HMI, and DICOM 3.0/WADO-WS compatibility testing | Automated motion path verification; sub-millimeter positional accuracy (±0.05mm) |
Quality Control & Durability Testing
All units undergo a 72-hour burn-in and multi-axis stress regimen before shipment. Testing protocols exceed IEC 60601-1 and IEC 60601-2-54 standards.
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration & Shock | Simulated shipping (ISTA 3A) + 10,000 gantry cycles | No image distortion; mechanical tolerance ≤ ±0.1° |
| Thermal Cycling | −10°C to +50°C over 7-day cycle; 8h/day operation | No condensation; sensor drift ≤ 2% |
| Radiation Consistency | Weekly QA phantom scans (e.g., QRM CTP); dose output monitored via ion chamber | DLP variance ≤ ±5%; spatial resolution ≥ 4.0 lp/mm |
| Software Reliability | 72h continuous scanning with AI reconstruction; STL/PLY export validation | Zero crashes; file integrity verified via checksum |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental manufacturing due to:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Co-location of PCB fabrication, sensor production, and precision machining reduces lead times and logistics costs by up to 40%.
- Advanced Automation: Shanghai and Shenzhen facilities deploy Industry 4.0 practices—automated optical alignment, robotic gantry calibration, and AI-powered QC—increasing yield and consistency.
- IP & Open Architecture Investment: Brands like Carejoy Digital leverage open data formats (STL, PLY, OBJ) and API-accessible firmware, enabling seamless integration with global CAD/CAM and 3D printing ecosystems.
- Regulatory Agility: Rapid CE MDR and FDA 510(k) pathway support through local Notified Bodies and clinical data partnerships in Asia-Pacific markets.
- R&D Density: Over 68% of global dental CBCT patents filed in China (2021–2025), with heavy investment in AI reconstruction and low-dose imaging algorithms.
As a result, Chinese manufacturers deliver sub-$25K OPG/CBCT units with performance metrics matching legacy $60K+ European systems—achieving a 2.4x higher cost-performance index (per 2025 EAO Digital Benchmark Report).
Carejoy Digital: Technology Stack & Support
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Imaging Modalities | OPG, CBCT (3×5 to 10×15 cm FOV), Cephalometric, TMJ Tracking |
| AI Capabilities | Auto Landmark Detection, Caries Risk Scoring, Implant Pathway Simulation |
| Open Architecture | Native export to STL, PLY, OBJ; compatible with exocad, 3Shape, Materialise |
| Milling Integration | Direct CAD-to-Mill via Carejoy Bridge™ (5-axis high-precision milling) |
| Support & Updates | 24/7 remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance alerts, quarterly AI model updates |
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Opg Scan Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
