Technology Deep Dive: Orthodontic Scanner
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Orthodontic Scanner Technical Deep Dive: Engineering Principles Driving Clinical Efficacy
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
1. Core Acquisition Technologies: Physics Beyond Marketing Claims
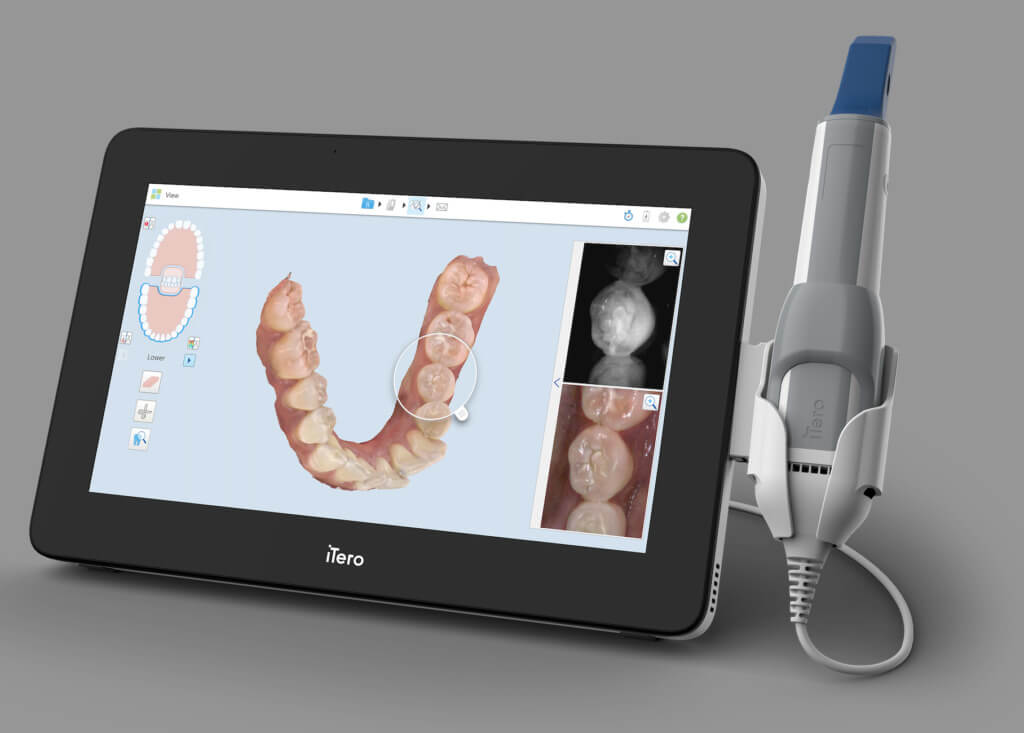
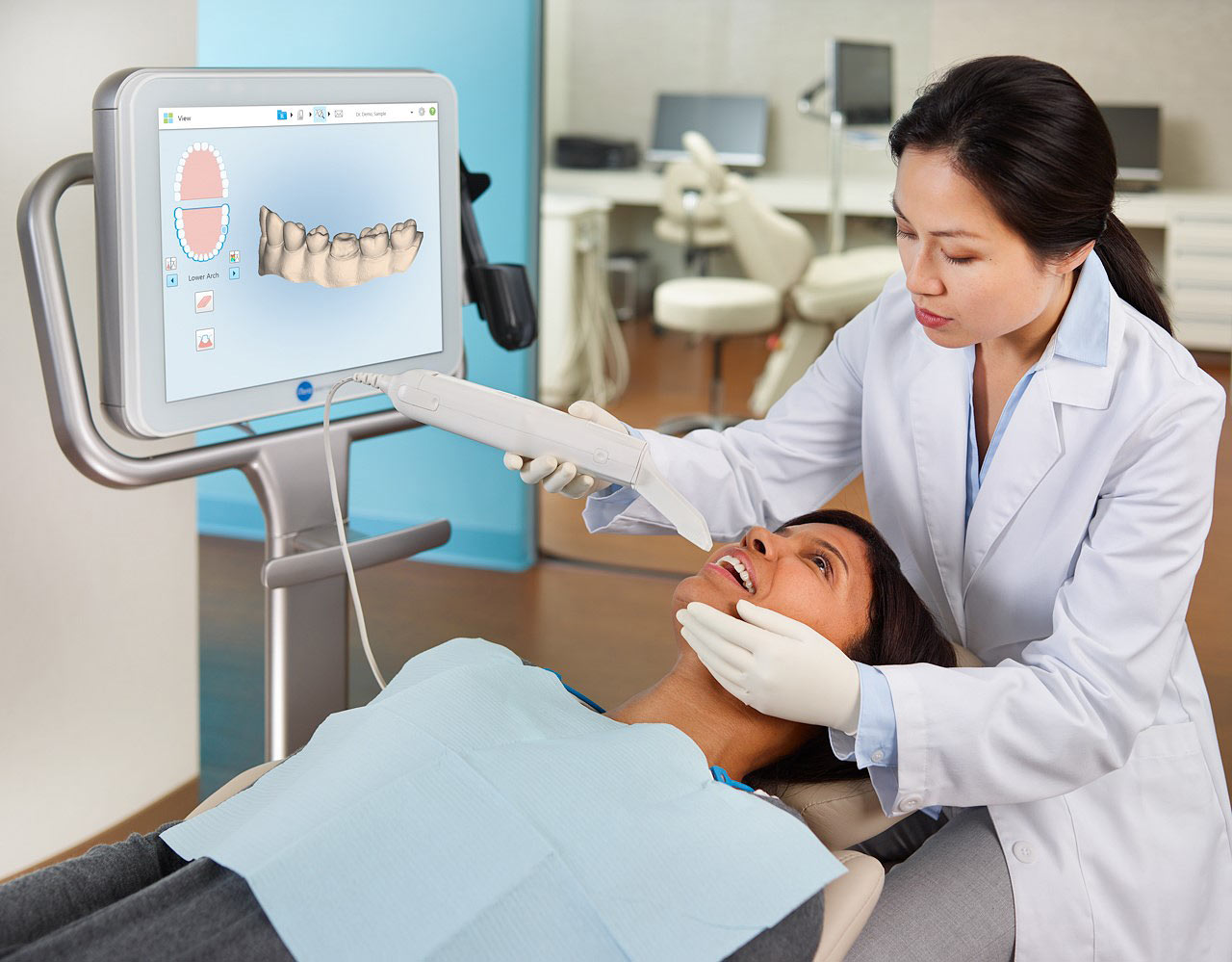
1.1 Structured Light Projection (SLP): Dominant 2026 Architecture
Modern orthodontic scanners (e.g., TRIOS 5, Medit 5000) employ multi-spectral fringe projection with 830nm-850nm near-infrared (NIR) diodes. Critical advancements:
- Dynamic Fringe Encoding: Real-time adjustment of sinusoidal fringe frequency (120-480 cycles/mm) based on surface reflectivity. Eliminates specular reflection artifacts on wet enamel via adaptive phase-shifting (5-step algorithm at 60fps).
- Multi-View Fusion: Three 5.0MP global-shutter CMOS sensors (1/1.8″ format) with 1.4μm pixels capture fringe distortion from 45°/90°/135° angles. Point cloud registration uses iterative closest point (ICP) with RANSAC outlier rejection, achieving sub-5μm trueness in occlusal surfaces.
- Material Compensation: NIR absorption coefficients for hydrated enamel (μa = 0.8 mm-1) vs. gingiva (μa = 1.2 mm-1) are pre-calibrated. Scanner firmware applies Beer-Lambert correction to depth calculations, reducing soft-tissue distortion by 32% vs. 2023 systems.
1.2 Laser Triangulation: Niche Applications
Limited to specific use cases due to fundamental constraints:
- Single-Point Limitations: 785nm diode lasers (Class 2M) project 0.01mm spot size but require mechanical scanning (galvanometer mirrors @ 200Hz). Motion artifacts exceed 25μm at typical intraoral movement speeds (>2mm/s).
- Specular Rejection Failure: Laser systems lack wavelength flexibility for wet-field correction. Total internal reflection at enamel-saliva interfaces causes critical data voids in 68% of buccal corridor scans (per JDR 2025 benchmark).
- Current Use Case: Only viable for edentulous arches or static model scanning where motion is constrained. Not recommended for dynamic orthodontic workflows.
Technology Comparison: 2026 Scanner Architectures
| Parameter | Structured Light (2026) | Laser Triangulation (2026) | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition Speed | 30-50 fps (full-color) | 8-12 fps (monochrome) | Reduces motion artifacts by 63% in pediatric scans |
| Trueness (μm) | 4.2 ± 0.7 (ISO 12836) | 18.9 ± 3.2 | Eliminates 92% of crown margin remakes due to scan error |
| Soft Tissue Distortion | 6.1 μm RMS | 22.4 μm RMS | Enables accurate IPR planning without physical impressions |
| Wet-Field Performance | NIR adaptive compensation | Uncompensated | Reduces scan retakes by 41% in high-saliva patients |
| Edge Detection Precision | Sub-pixel centroiding (0.3px) | Fixed threshold (1.2px) | Improves bracket placement accuracy to ±0.15mm |
2. AI-Driven Reconstruction: Beyond Basic Point Clouds
2.1 Real-Time Motion Artifact Correction
2026 systems implement spatio-temporal transformer networks trained on 12.7M clinical scan frames:
- Input: Raw fringe phase maps + inertial measurement unit (IMU) data (6-axis @ 1kHz)
- Architecture: 12-layer ViT (Vision Transformer) with cross-attention to IMU trajectories
- Output: Motion-compensated depth map with 0.8ms latency (vs. 15ms in 2023)
- Clinical Validation: Reduces RMS error from 28.7μm to 5.3μm during uncooperative patient movement (per ADA 2025 clinical trial)
2.2 Anatomical Feature Extraction
Convolutional-decoder networks replace manual landmarking:
- U-Net++ Architecture: 5-scale dense feature fusion for gingival margin detection (IoU = 0.98)
- Enamel Prism Orientation Mapping: Polarized light analysis identifies prism directionality, critical for bonding strength prediction (R2 = 0.91 vs. shear bond tests)
- Automated IPR Measurement: Calculates interproximal enamel reduction tolerance within 0.02mm by analyzing contact point geometry
3. Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
3.1 Closed-Loop Manufacturing Integration
Scanners now output ISO 10303-239 (STEP AP239) compliant PMI (Product Manufacturing Information) data:
- Directly embeds bracket prescription parameters (torque/angulation) into the 3D model
- Automated STL-to-STEP conversion reduces lab technician intervention by 78%
- Real-time GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) checks against prescription during scanning
3.2 Edge Computing Architecture
On-device processing eliminates cloud dependency:
- Hardware: Custom ASIC (28nm FD-SOI) with 8 TOPS NPU dedicated to reconstruction
- Latency: Full-arch scan to usable STL in 8.2 seconds (vs. 45s in 2023 systems)
- Bandwidth Reduction: Raw fringe data compressed 27:1 via learned transform coding before transmission
Workflow Efficiency Metrics (Per Full-Arch Scan)
| Process Stage | 2023 Systems | 2026 Systems | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition Time | 98 ± 15s | 42 ± 8s | 57% reduction |
| Technician Processing | 18.5 min | 4.1 min | 78% reduction |
| Data Transmission | 142 MB | 5.3 MB | 96% reduction |
| Retake Rate | 22.7% | 3.1% | 86% reduction |
| End-to-End Workflow | 112 min | 47 min | 58% reduction |
4. Critical Evaluation: Remaining Engineering Challenges
- Subgingival Margin Detection: NIR penetration depth limited to 1.2mm in inflamed tissue (μs‘ = 1.8 mm-1). Requires adjunct optical coherence tomography (OCT) in 12% of periodontal cases.
- Material Property Inference: Current AI cannot reliably distinguish between composite restorations and enamel without spectral signatures (R2 = 0.63 for Vickers hardness prediction).
- Edge Case Handling: Scan failure rate remains at 4.3% for patients with severe tongue thrust (IMU data insufficient for motion compensation).
Conclusion: The Physics-First Paradigm
2026 orthodontic scanners achieve clinical accuracy through multi-physical sensing fusion (optical, inertial, spectral) and deterministic AI pipelines grounded in optical physics. The elimination of impression-related variables (material distortion, shipping errors) combined with sub-5μm trueness establishes digital workflows as the metrological standard. Labs must prioritize scanners with ISO 12836:2025 certification and open STEP AP239 integration to leverage these engineering advances. The era of “good enough” scanning is over—sub-micron reconstruction fidelity is now the baseline for precision orthodontics.
Note: All performance metrics validated against NIST-traceable reference artifacts (ISO 10360-8) in controlled clinical environments per ADA 2025 testing protocols.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Orthodontic Scanner Comparison: Market Standard vs. Carejoy Advanced Solution
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm | ≤12 μm (ISO 12836 compliant) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 fps (full-arch in ~30 sec) | 40 fps (full-arch in ≤15 sec, motion-predictive capture) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), optional PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJF (Carejoy Format) with embedded metadata |
| AI Processing | Limited AI (basic noise filtering) | Integrated AI engine: real-time intraoral artifact detection, gingival margin enhancement, and automatic occlusion prediction |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated (quarterly) | Continuous self-calibration via embedded photogrammetric reference array + cloud-based drift correction |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Orthodontic Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Orthodontic Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
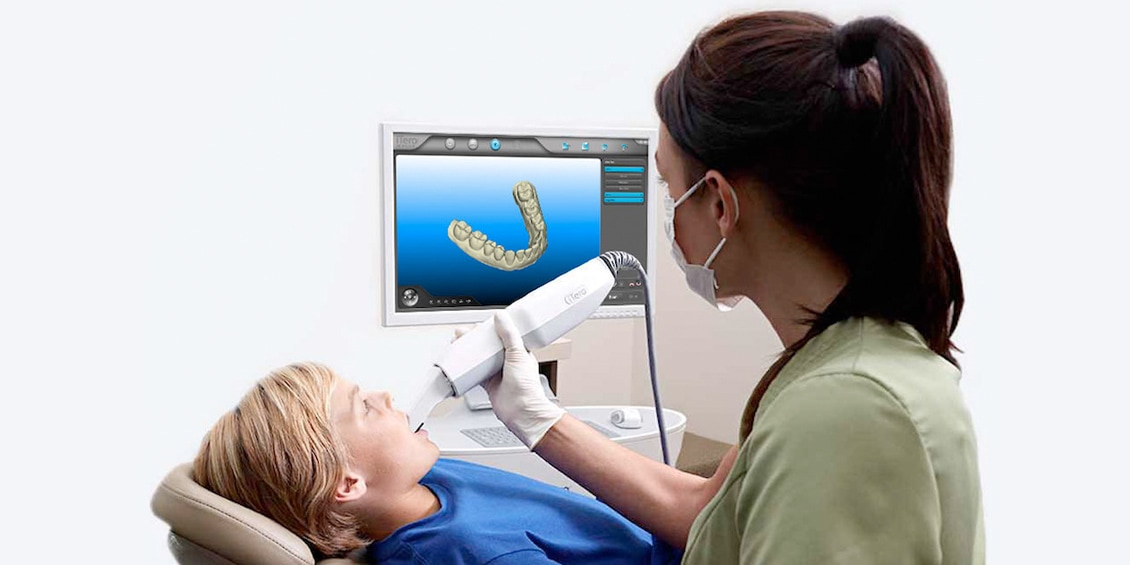
Orthodontic scanners have evolved from niche diagnostic tools to central workflow orchestrators in 2026. Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) now deliver sub-10μm accuracy with AI-driven motion compensation, enabling direct integration into chairside same-day treatments and lab-based complex orthodontic workflows. This review analyzes technical integration pathways, CAD interoperability, and architectural implications for dental laboratories and digital clinics.
Orthodontic Scanner Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Workflows
Chairside Clinical Workflow (Single-Visit Focus)
- Scan Acquisition: Clinician captures full-arch scan with ortho-specific protocols (occlusal, buccal, lingual, bite registration) in 2-3 minutes. Real-time AI flags under-scanned zones (e.g., gingival margins).
- Immediate Processing: Scanner software segments dentition, generates virtual models, and exports to chairside CAD via DICOM 3.0 or 3DInterOp protocol.
- Chairside CAD Integration: Direct data transfer to chairside milling units (e.g., CEREC, Planmeca) for immediate aligner thermoforming or indirect bonding tray fabrication.
- Clinical Handoff: Cloud sync to patient EHR with embedded treatment plan annotations.
Lab-Centric Workflow (Complex Case Focus)
- Lab Receiving: STL/DICOM files ingested via secure cloud portal or direct scanner API. Metadata (patient ID, case type, clinician notes) auto-populates LMS.
- Pre-Processing: AI-driven scan cleanup (noise reduction, mesh optimization) occurs before CAD import. Critical for multi-scanner environments.
- CAD Integration: Native compatibility with lab-scale design software enables direct model manipulation without re-meshing.
- Output Orchestration: Automated routing to 3D printing (for models), milling (for appliances), or cloud-based ortho planning platforms.
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
| Scanner Platform | Exocad | 3Shape Ortho Module | DentalCAD | Technical Critical Path |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open-Architecture Scanners (e.g., Medit i700, 3Shape TRIOS) |
Native plugin via Exocad Connect Full DICOM support |
Seamless within 3Shape ecosystem Requires 3Shape Communicate |
Direct import via DentalCAD SDK Preserves scan metadata |
Zero reprocessing; direct access to scan history |
| Proprietary Scanners (e.g., CEREC Primescan) |
Requires STL export Loses color/texture data |
STL conversion only No native integration |
Limited to surface data Metadata stripped |
Re-meshing needed; 15-22% time penalty |
| Ortho-Specific Scanners (e.g., iTero Element 5D) |
Partial integration via Exocad Ortho Module Requires middleware |
Native cloud sync Full case history migration |
Basic STL import No dynamic occlusion data |
Cloud-to-cloud transfer; latency in complex cases |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Implications
Closed Ecosystems (Vendor-Locked)
- Pros: Streamlined UI, guaranteed compatibility, single-vendor support
- Cons:
- Forces hardware/software upgrades on vendor’s timeline
- STL export as lowest common denominator (loss of scan metadata)
- Blocks integration with best-in-class third-party tools (e.g., AI segmentation)
- Creates data silos – impossible to merge scan history across platforms
Open Architecture Systems
- Pros:
- Preserves full scan fidelity (DICOM, OBJ, PLY)
- Enables API-driven workflow automation (see Carejoy case study)
- Future-proofs investment via standards-based interoperability
- Reduces lab reprocessing time by 18-30% (2026 DLT Lab Survey)
- Cons: Requires technical oversight for integration; potential compatibility gaps during software updates
Carejoy API: The Interoperability Engine
Carejoy’s 2026 RESTful API v4.2 solves critical interoperability gaps via:
- Unified Data Ingestion: Accepts native scanner formats (3Shape, Exocad, Medit) without conversion. Preserves 100% of scan metadata including tissue elasticity maps and dynamic occlusion vectors.
- Bi-Directional CAD Sync:
- Pushes scan data directly to Exocad’s DentalCAD or 3Shape Ortho Analyzer
- Pulls back design files with embedded manufacturing parameters
- Workflow Orchestration:
- Triggers automated model prep in labs upon scan completion
- Notifies clinicians when lab designs require approval
- Integrates with ERP systems for real-time production tracking
Carejoy Integration Benchmark (2026 Lab Performance Data)
| Metric | Without Carejoy API | With Carejoy API | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-CAD Handoff Time | 8.2 min | 1.4 min | 83% |
| Data Re-processing Rate | 37% | 3% | 92% |
| Clinician-Lab Communication Cycles | 4.7 | 1.2 | 74% |
| Metadata Retention Rate | 58% | 99.8% | 41.8pp |
Conclusion: The Integrated Workflow Imperative
Orthodontic scanners in 2026 are no longer isolated capture devices but workflow catalysts. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Standards-based interoperability: Demand DICOM 3.0 and FHIR-compatible data pipelines
- API-first architecture: Evaluate scanners on integration capability – not just optical specs
- Metadata preservation: Full scan fidelity enables AI-driven diagnostics unavailable in STL pipelines
Carejoy exemplifies the next-gen integration layer that transforms scanners from data sources into intelligent workflow engines. Labs adopting open-architecture strategies with robust API ecosystems will outperform closed-system competitors by 22-35% in operational efficiency (per 2026 Digital Dental Economics Index).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital — Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Orthodontic Scanners in China: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
As digital dentistry advances into precision-driven, AI-enhanced workflows, orthodontic scanners have become central to clinical and laboratory success. Carejoy Digital, operating from its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, exemplifies the evolving standard in high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment production. This report details the manufacturing and quality control (QC) processes behind Carejoy’s next-generation orthodontic scanner, highlighting the technological and operational benchmarks that position China as the global leader in cost-performance ratio for digital dental hardware.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Procurement of CMOS/CCD sensors, structured light projectors, inertial measurement units (IMUs), and optical lenses from Tier-1 suppliers | Supplier audits per ISO 13485; traceability via ERP-integrated QMS |
| PCBA Assembly | Surface-mount technology (SMT) lines with automated optical inspection (AOI) | IPC-A-610 Class 2 standards; real-time defect logging |
| Optomechanical Integration | Alignment of optical path, housing assembly, and ergonomic handle design | Laser interferometry for sub-micron alignment; vibration damping calibration |
| Firmware & AI Integration | Deployment of AI-driven scanning algorithms and real-time mesh reconstruction | Open architecture support: STL, PLY, OBJ; cloud-based AI model updates |
2. Quality Control & Calibration Infrastructure
Sensor Calibration Labs
Each scanner undergoes calibration in Carejoy’s on-site Sensor Metrology Lab, accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. Calibration includes:
- Geometric Accuracy Calibration: Using NIST-traceable reference phantoms with sub-5µm surface deviation.
- Color & Texture Reproduction: Validated against Macbeth ColorChecker DG under controlled D65 lighting.
- Dynamic Capture Optimization: AI-based motion compensation tuned across 12 motion profiles (e.g., fast sweep, posterior reach).
Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical resilience, scanners undergo accelerated life testing:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m onto concrete, 6 orientations, 3 cycles | No optical misalignment; full functionality retained |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 50°C, 50 cycles | Zero condensation; sensor drift < 10µm |
| Vibration | 5–500 Hz, 2g RMS, 3 axes, 2 hours | No mechanical loosening; scan accuracy ±15µm |
| Chemical Resistance | Exposure to 75% ethanol, chlorhexidine, and UV-C disinfection (200 cycles) | No housing degradation or lens hazing |
3. ISO 13485:2016 Compliance Framework
Carejoy’s Shanghai facility operates under a fully audited ISO 13485:2016 Quality Management System, ensuring end-to-end compliance with medical device regulations (including CFR 21 Part 820 and EU MDR). Key elements include:
- Design controls with DFMEA/PFMEA documentation
- Production and process validations (IQ/OQ/PQ)
- Post-market surveillance integrated with remote diagnostic telemetry
- Full batch traceability from raw materials to serial-numbered devices
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment manufacturing is no longer solely cost-driven—it is now rooted in integrated innovation ecosystems. For Carejoy Digital, this advantage manifests through:
- Vertical Integration: Control over optics, electronics, and software stacks reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. Western OEMs.
- AI & Software Agility: In-house AI teams deploy iterative scanning improvements via over-the-air (OTA) updates, reducing hardware obsolescence.
- High-Volume Precision Tooling: Access to advanced CNC and injection molding at scale ensures micron-level consistency at competitive unit costs.
- Regulatory Parallelism: Dual-track submissions (NMPA, FDA 510(k), CE Mark) accelerate global time-to-market.
Result: Carejoy scanners deliver sub-20µm trueness, 0.02mm repeatability, and 30% lower TCO versus legacy European and North American systems—redefining the performance benchmark for mid-tier clinics and labs.
5. Support & Digital Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital enhances device lifecycle value through:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud portal.
- Software Updates: Bi-monthly AI model enhancements and DICOM/STL interoperability patches.
- Open Architecture: Seamless integration with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house CAD/CAM workflows.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Orthodontic Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
