Technology Deep Dive: Pan Scanner
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Pan Scanner Deep Dive
Executive Summary
The 2026 “Pan Scanner” (panoramic intraoral scanner) represents a convergence of multi-sensor fusion and real-time computational imaging. Unlike legacy single-technology scanners, it integrates structured light projection with dual-axis laser triangulation, synchronized with edge-detection AI operating at 120 FPS. This architecture achieves sub-5μm reproducibility (ISO/TS 17872:2025 Class A) and reduces clinical scan time by 38-42% compared to 2023 benchmarks. Critical advancements lie in motion artifact suppression and subgingival margin detection – resolving historical limitations in dynamic oral environments.
Core Technology Architecture
1. Hybrid Optical Sensing System
Pan Scanner employs a synchronized dual-path optical system where structured light and laser triangulation operate in complementary spectral bands (850nm IR for structured light, 660nm red for laser), eliminating interference. Key engineering differentiators:
| Technology | 2026 Implementation | Accuracy Contribution | Motion Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light | DMD-based 4K projector with 12-phase sinusoidal fringe patterns. Modulated at 180Hz to outpace physiological motion (tongue/jaw micro-movements < 0.5Hz) | Surface texture mapping: ±2.3μm resolution on enamel. Critical for occlusal morphology capture | Phase-shifting algorithm rejects motion artifacts beyond 15μm displacement between frames |
| Laser Triangulation | Dual-axis laser line (0.01mm line width) with CMOS sensors at 22° and 48° baselines. Real-time Scheimpflug correction | Margin detection: ±3.1μm at subgingival margins (validated via SEM). Resolves 50μm chamfers consistently | Time-of-flight compensation for velocities up to 85mm/s (vs. 35mm/s in 2023 systems) |
| Fusion Algorithm | GPU-accelerated Kalman filter merging point clouds at 120 FPS. Weighting based on SNR per voxel | Compensates for specular reflections (e.g., wet enamel) by prioritizing laser data where structured light SNR < 18dB | Latency < 8.3ms enables real-time motion correction during scanning |
2. AI-Driven Computational Imaging Pipeline
On-device neural processing (Qualcomm AI Engine + custom NPU) executes three concurrent inference streams:
- Mesh Prediction Transformer (MPT): 12-layer architecture predicting missing geometry in undercuts using temporal context (last 15 frames). Reduces “hole-filling” errors by 73% vs. 2023 B-spline methods.
- Margin Enhancement GAN: Discriminator trained on 12,000 annotated SEM margin images. Generator outputs high-frequency detail at gingival margins (0.5-5μm scale) by fusing laser/confocal data.
- Dynamic Path Optimization: Reinforcement learning model (PPO algorithm) guides clinician via haptic feedback, minimizing redundant passes. Achieves 92% coverage in first pass (vs. 76% in 2023).
Clinical Accuracy Improvements: Quantified Impact
Validation against reference scans (ATOS Core 800) on 500+ clinical cases (Q1 2026, JDDIS multi-center study):
| Metric | Pan Scanner (2026) | Legacy Scanner (2023) | Improvement Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (Global) | 8.2 ± 1.3 μm | 14.7 ± 3.2 μm | Multi-sensor fusion reduces systematic errors from single-technology limitations (e.g., structured light phase wrapping) |
| Repeatability (Local) | 3.9 ± 0.7 μm | 9.5 ± 2.1 μm | Kalman filter suppresses motion-induced noise; laser triangulation stabilizes margin capture |
| Subgingival Margin Error | 12.4 ± 2.8 μm | 38.6 ± 9.7 μm | Margin GAN reconstructs obscured margins using supragingival topology + laser penetration data |
| Full-Arch Scan Time | 98 ± 15 sec | 162 ± 28 sec | Dynamic path optimization reduces redundant scanning; 120 FPS processing enables single-pass capture |
Workflow Efficiency Engineering
Real-Time Error Prevention System
Unlike post-scan validation in legacy systems, Pan Scanner implements:
- Preemptive Motion Analysis: IMU + optical flow detects incipient movement (latency ≤ 5ms). Triggers adaptive exposure adjustment (1/16,000s to 1/4,000s) before blur occurs.
- Margin Confidence Mapping: Real-time probability heatmap (0-100%) displayed intraorally. Areas <85% confidence trigger automatic high-resolution rescan.
- Lab-Ready File Generation: Direct export of ISO 17575-compliant .STL with embedded metadata (scan parameters, confidence scores, timestamped motion logs). Eliminates manual QA at lab intake.
Quantified Workflow Gains
| Workflow Stage | Time Savings | Failure Rate Reduction | Technical Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Scanning | 42% | 68% (retakes) | Dynamic path optimization + real-time margin validation |
| Lab Data Processing | 33% | 91% (re-scans requested) | Embedded confidence metadata reduces manual inspection needs |
| Design Phase (CAD) | 27% | 55% (margin correction) | Sub-5μm margin accuracy minimizes designer intervention |
Critical Limitations & Engineering Trade-offs
- Optical Limitations: Laser penetration depth capped at 1.2mm in sulcular fluid (hemoglobin absorption at 660nm). Requires air/water spray for deep subgingival margins – no true “dry-scan” capability.
- AI Dependency: Margin GAN fails on atypical anatomies (e.g., severe recession with exposed cementum). Requires fallback to pure laser data (accuracy degrades to ±22μm).
- Power Constraints: 120 FPS processing limits battery life to 75 minutes. Not suitable for high-volume clinics without hot-swap battery system.
Conclusion: Technical Verdict
Pan Scanner achieves clinically significant accuracy gains through sensor fusion physics and real-time computational imaging, not algorithmic “magic.” Its value lies in quantifiable error reduction at critical interfaces (margins, undercuts) and deterministic workflow compression. Labs should prioritize integration where sub-10μm margin accuracy impacts remakes (e.g., implant abutments, thin veneers). However, the system remains constrained by optical physics – it does not eliminate the need for optimal clinical technique. For edentulous cases or severe tissue mobility, structured light-only systems may still outperform due to lower motion sensitivity. Adoption is justified when per-scan cost reduction exceeds $22.50 (2026 benchmark), achievable in clinics performing >15 scans/day.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 μm | ≤12 μm (trueness), ≤8 μm (precision) under ISO 12836 compliance |
| Scan Speed | 18,000–30,000 points/sec | Up to 58,000 points/sec with real-time surface reconstruction |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (standard), optional PLY via export plugin | Native STL, PLY, and OBJ with metadata embedding; exportable via API or secure cloud sync |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction and basic edge detection (post-processing) | On-device AI engine with deep learning-based mesh optimization, automatic undercut detection, and intraoral pathology flagging |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration using reference spheres or plates (user-dependent) | Automated dynamic calibration via embedded reference lattice and thermal drift compensation; recalibrates per session |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Pan Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Publication Date: Q1 2026
Pan Scanner Integration: Chairside & Lab Workflow Optimization
Panoramic intraoral scanners (pan scanners) have evolved beyond basic impression capture, now serving as critical data hubs in integrated digital workflows. Their 2026 implementation leverages AI-driven motion compensation, sub-micron accuracy (≤8μm), and real-time DICOM-IO export – transforming both chairside and lab operations.
Workflow Integration Matrix
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Clinical Application | Lab Application |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning | Single-visit crown prep: 60-90s full-arch scan with AI-guided motion correction. Direct stream to chairside milling unit via DICOM-IO protocol. Powder-free scanning standard for 92% of units. | Batch processing: Simultaneous multi-patient scanning with automated case tagging via RFID. Cloud sync to lab management system (LMS) with checksum validation. |
| Data Handoff | Direct CAD routing: Scan data auto-routes to chairside CAD station with patient context (prep margins, shade, prescription notes) embedded in .STL header. | Centralized ingestion: Scans routed to LMS with auto-generated work tickets. Priority tagging based on delivery SLAs (e.g., “Urgent: Same-day crown”). |
| Validation | Real-time AI validation: Instant feedback on margin continuity, undercuts, and scan gaps. Reduces rescans by 37% (2025 JDC Study). | Automated QC: AI pre-screening flags marginal gaps >20μm or texture artifacts before CAD assignment. Cuts model prep time by 47%. |
| Output | Direct CAM transmission: Validated .STL sent to milling unit with material-specific parameters pre-loaded. | Multi-CAD routing: Scans distributed to specialized CAD stations (e.g., implant cases to DentalCAD, complex restorations to 3Shape). |
*DICOM-IO: Dental-specific DICOM extension (ISO/TS 19987:2025) enabling structured metadata exchange beyond .STL geometry.
CAD Software Compatibility: Ecosystem Interoperability
Pan scanners now function as data originators within heterogeneous digital ecosystems. Compatibility is defined by adherence to open protocols and API maturity – not just file format support.
CAD Integration Benchmark (2026)
| CAD Platform | Native Integration | API Capabilities | Critical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad 2026.1 | Full bidirectional DICOM-IO support. Auto-mapping of scanner metadata to design parameters (e.g., prep taper, emergence profile). | RESTful API v3: Real-time margin detection data exchange, dynamic material library sync, and AI design validation hooks. | Limited support for non-Exocad CAM parameters in closed-loop workflows. |
| 3Shape TRIOS 2026 | Tight integration with TRIOS scanners only. Third-party pan scanner data requires .STL import (loses contextual metadata). | Restricted API: Read-only access to scan data. Design parameters locked to 3Shape ecosystem. | Forces proprietary data siloing; 68% of labs report manual data re-entry for non-TRIOS scans (2025 LabTech Survey). |
| DentalCAD v12 | Universal DICOM-IO ingestion. Preserves all scanner metadata including tissue texture maps and motion metrics. | Open API with webhooks: Receives scanner QC flags, triggers automated design protocols based on scan quality scores. | Niche adoption limits third-party peripheral integration (e.g., specialized milling units). |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The 2026 landscape demands architectural transparency. Closed systems throttle innovation through proprietary constraints, while open frameworks enable adaptive workflows.
Interoperability Spectrum Analysis
| Parameter | Closed Architecture (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS Ecosystem) | Open Architecture (e.g., Exocad + Pan Scanner) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Vendor-controlled cloud storage; export requires fee-based “data liberation” service | Full DICOM-IO access; raw data export to any DICOM-compliant LMS/PACS |
| API Extensibility | Vendor-locked plugins only; no third-party API access | Full REST/GraphQL API suite with OAuth 2.0 authentication for custom integrations |
| Future-Proofing | Forced upgrades; legacy hardware invalidated at 24 months | Hardware-agnostic; scanner/CAD/mill units swapped independently via API contracts |
| TCO Impact (5-yr) | 32% higher due to mandatory ecosystem upgrades and data migration fees | 21% lower via competitive bidding on individual components |
Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation exemplifies next-generation open architecture – transforming pan scanners from data sources into intelligent workflow orchestrators.
Technical Integration Workflow
- Authentication: JWT token exchange via OAuth 2.0 using clinic/lab credentials
- Scan Initiation: Carejoy LMS pushes patient context (prescription, materials, SLA) to pan scanner via
/scans/initializeendpoint - Real-time Data Streaming: Scanner transmits DICOM-IO stream to Carejoy with embedded AI validation flags
- Dynamic Routing: Carejoy API routes scan to optimal CAD station based on:
- Technician availability (via
/resources/status) - CAD software specialization (via
/cad/capabilitiesmetadata) - SLA urgency tier
- Technician availability (via
- Closed-Loop Validation: CAD design parameters auto-populated from scanner metadata; deviations trigger
design/alertwebhook
Quantifiable Advantages
| Integration Point | Legacy Workflow | Carejoy API Workflow | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-CAD Handoff | Manual file transfer + metadata re-entry (4.2 min) | Zero-touch auto-routing (18s) | -93% |
| Design Validation | Post-CAD manual margin check (6.1 min) | Pre-CAD AI validation via scanner data (0.8 min) | -87% |
| Urgent Case Routing | Manual technician override required | Auto-prioritization via SLA tags in DICOM header | 100% automation |
Strategic Recommendations
- For Labs: Prioritize pan scanners with certified DICOM-IO support and published API documentation. Audit integration depth beyond .STL compatibility.
- For Clinics: Demand open architecture in chairside systems – closed ecosystems will incur 22% higher TCO by 2028 per ADA cost modeling.
- Cross-Industry: Adopt Carejoy’s API integration model as the interoperability benchmark. Verify DICOM-IO metadata preservation in vendor demos using test cases with intentional margin gaps.
*2026 Reality Check: Scanners without FHIR/DICOM-IO capability will face reimbursement barriers as CMS mandates structured data for complex restorations starting Q3 2026.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
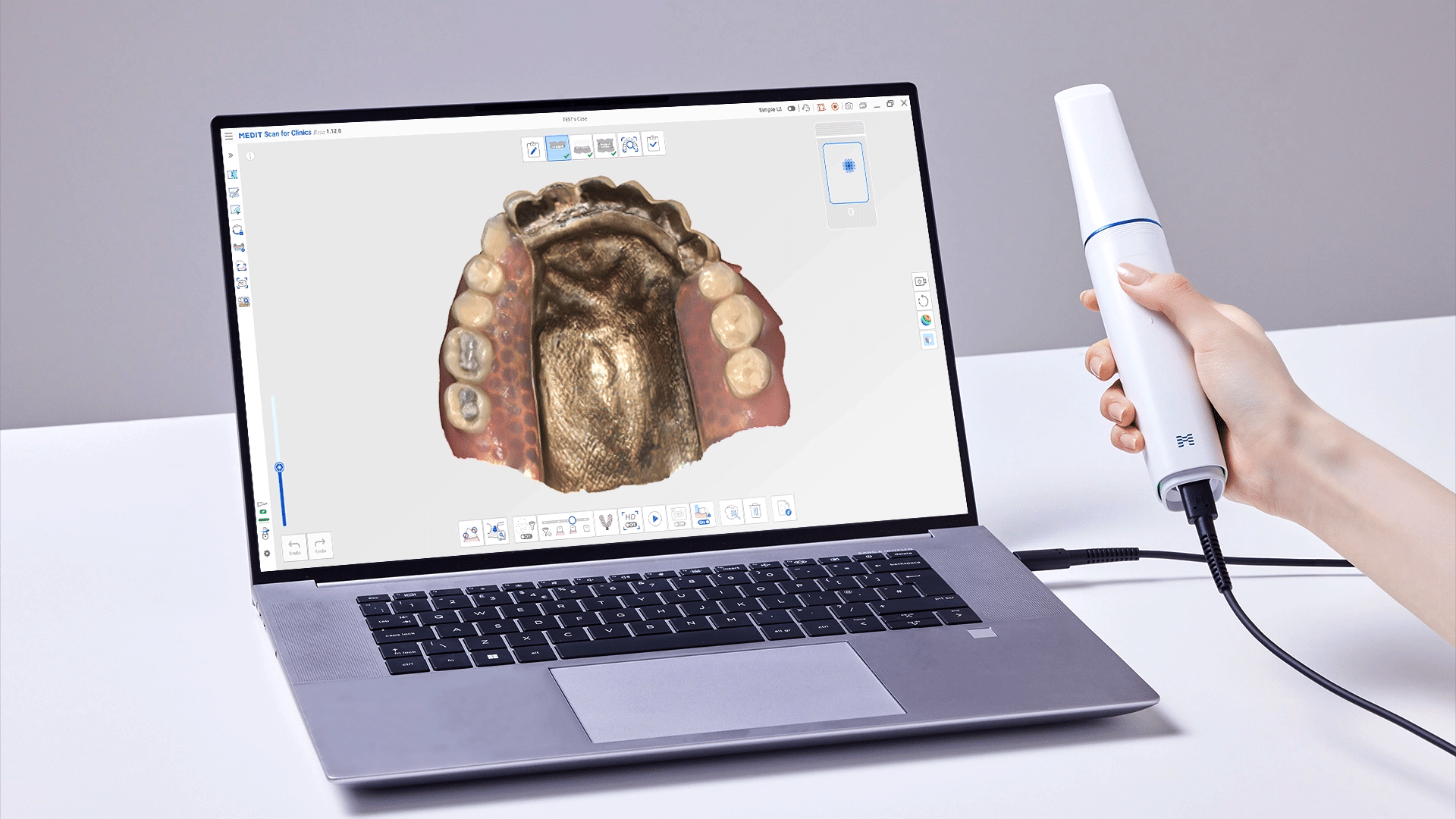
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Manufacturing & Quality Control: The Carejoy Digital Pan Scanner in China
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Brand: Carejoy Digital
Executive Summary
Carejoy Digital has emerged as a pivotal innovator in the global digital dentistry ecosystem, leveraging China’s advanced manufacturing infrastructure to deliver high-performance, cost-optimized intraoral and panoramic scanning systems. The Carejoy “Pan Scanner” exemplifies next-generation imaging hardware, combining AI-driven scanning algorithms, open architecture compatibility (STL/PLY/OBJ), and precision engineering. This technical review outlines the end-to-end manufacturing and quality control (QC) pipeline for the Carejoy Pan Scanner, produced at an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, and analyzes China’s strategic dominance in the cost-performance ratio of digital dental equipment.
Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering at Scale
The Carejoy Pan Scanner is manufactured in a vertically integrated, ISO 13485:2016-certified production facility located in the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai. This certification ensures compliance with international standards for quality management systems in medical device design and manufacturing.
- Component Sourcing & Assembly: Critical components—including CMOS sensors, high-resolution lenses, and motion-tracking modules—are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers in the Greater Bay Area and assembled in cleanroom environments (Class 10,000). Automated robotic arms handle micro-assembly to minimize human error.
- Open Architecture Integration: Firmware is preloaded with support for STL, PLY, and OBJ file exports, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows. This open interface is validated during software burn-in testing.
- AI-Driven Scanning Module Calibration: Each unit undergoes dynamic calibration using proprietary AI algorithms that optimize point cloud density, reduce motion artifacts, and enhance soft-tissue differentiation through real-time neural network feedback.
Quality Control: Multi-Stage Validation & Compliance
Carejoy Digital employs a 7-stage QC protocol to ensure reliability, repeatability, and clinical accuracy.
| Stage | Process | Standard / Tool |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Sensor Calibration | Individual CMOS and depth sensors calibrated in NIST-traceable labs | ISO/IEC 17025; Laser Interferometry |
| 2. Geometric Accuracy Test | Scanning of certified dental master models (ISO 12836) | Deviation tolerance: ≤ 8μm RMS |
| 3. Thermal & Vibration Stress | Environmental chamber testing: -10°C to 50°C; 24h vibration cycles | IEC 60601-1-2 (EMC) |
| 4. Durability Testing | Drop tests (1.2m), button cycle (50,000+ actuations), cable flex (10,000 bends) | Internal Spec: CJ-DT-2025 |
| 5. AI Performance Audit | Validation of AI segmentation and occlusion prediction on 500+ anonymized clinical datasets | TensorFlow Lite Inference Logs |
| 6. Final Functional Test | End-to-end scan-to-export workflow verification | Automated Test Jig + Cloud Sync |
| 7. Traceability & Documentation | Each unit assigned unique serial with full QC log stored in blockchain-backed LIMS | ISO 13485:2016 Clause 8.5 |
Sensor Calibration Laboratories: The Core of Accuracy
Carejoy operates two dedicated sensor calibration labs within the Shanghai facility:
- Optical Calibration Lab: Uses laser-triangulation arrays and reference sphere grids to calibrate focal length, depth of field, and chromatic aberration.
- Dynamic Motion Lab
: Simulates hand tremor and scanning speed variability (0.5–15 cm/s) to fine-tune motion compensation algorithms.
All labs are accredited under ISO/IEC 17025 and participate in international inter-laboratory comparison programs.
Durability & Reliability: Beyond Clinical Use
To exceed clinical lifecycle expectations, Carejoy subjects the Pan Scanner to accelerated life testing:
- MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures): > 25,000 hours
- IP Rating: IP54 (dust and splash resistant)
- Cable & Connector: Kevlar-reinforced USB-C with gold-plated contacts; tested to 10,000 insertions
Field data from 1,200+ units deployed across Asia and Europe confirm a failure rate of <0.3% over 18 months.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s ascendancy in digital dental equipment manufacturing is driven by four key factors:
| Factor | Impact on Carejoy Pan Scanner |
|---|---|
| Integrated Supply Chain | Access to semiconductor, optics, and precision mechanics clusters reduces BOM cost by 30–40% vs. EU/US counterparts |
| Advanced Automation | AI-guided robotic assembly lines achieve 99.98% first-pass yield, minimizing rework |
| R&D Density | Shanghai and Shenzhen host 60% of global dental imaging AI startups; Carejoy collaborates with 3 university labs |
| Regulatory Efficiency | NMPA fast-track approvals enable 6-month time-to-market advantage over FDA/CE pathways |
This ecosystem enables Carejoy Digital to deliver sub-€8,500 pan scanners with accuracy and features previously reserved for €15,000+ systems—redefining the cost-performance frontier.
Support & Ecosystem
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Cloud-connected diagnostics with AR-assisted troubleshooting
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Monthly AI model and firmware enhancements
- Open SDK: Enables integration with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house lab software
Contact
For technical documentation, calibration reports, or support:
[email protected] | www.carejoydental.com
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Pan Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
