Technology Deep Dive: Portable Digital Dental X Ray Machine
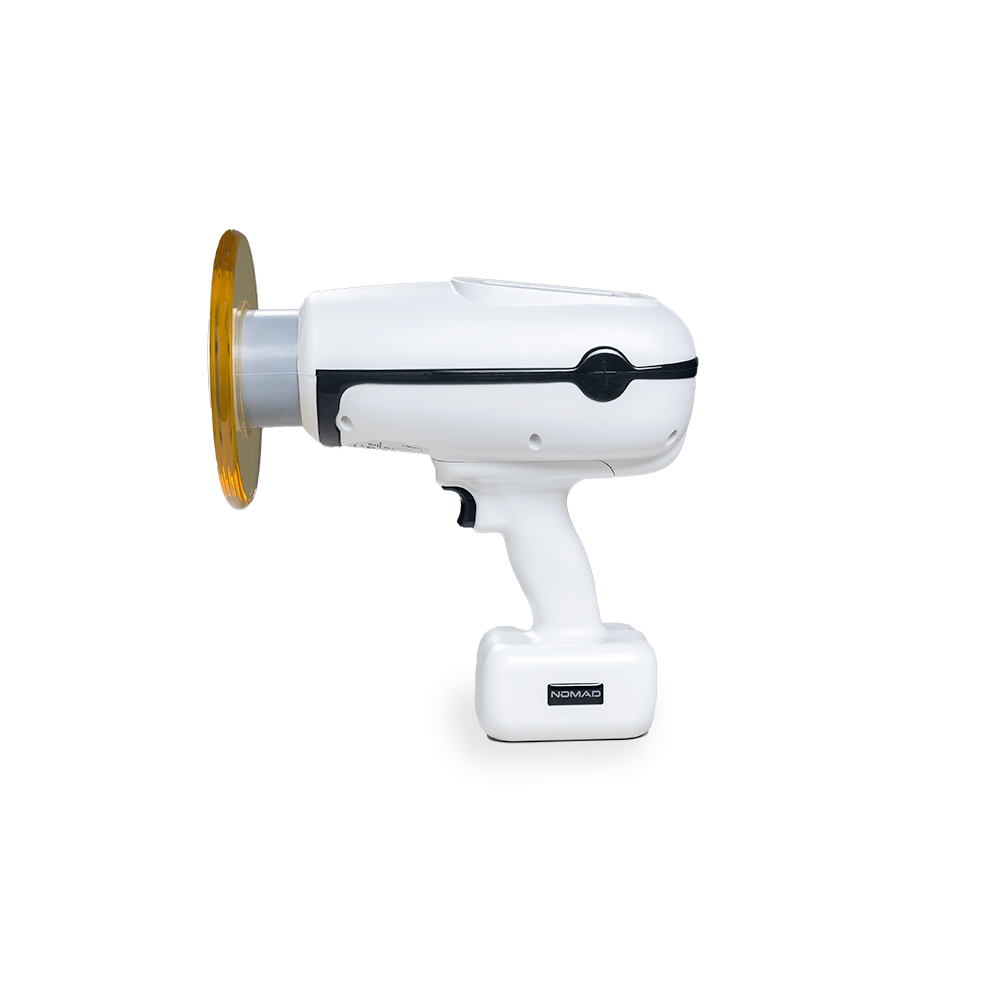

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Portable Dental Radiography Systems
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
Core Technology Architecture: Beyond Marketing Hype
Modern portable dental X-ray units (e.g., Vatech RayPad Pro, Dentsply Sirona ORTHOPHOS SL) are defined by three engineered subsystems working in concert:
1. Direct Conversion CMOS Sensor Array (Replacing Legacy CCD)
Engineering Principle: Elimination of scintillator layer via amorphous Selenium (a-Se) or Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) photoconductor directly bonded to CMOS readout circuitry. Photons → electron-hole pairs → direct charge collection.
- Quantum Efficiency (QE): 2026 systems achieve 82-85% QE at 60kVp (vs. 60-65% for indirect CsI scintillator systems), measured per IEC 62220-1-1 standards. Higher QE directly reduces patient dose while maintaining SNR.
- Modulation Transfer Function (MTF): 25 lp/mm at 10% MTF (vs. 18 lp/mm in 2023 systems) due to pixel pitch reduction to 19.5µm and elimination of light scatter from scintillators.
- Dynamic Range: 16-bit depth (65,536 gray levels) with 0.1% linearity error, enabling single-exposure capture of high-contrast regions (e.g., metal crowns adjacent to caries).
2. Real-Time Wireless Transmission Protocol (IEEE 802.11be Enhanced)
Engineering Principle: 6 GHz band implementation with MU-MIMO 16×16 spatial streams and OFDMA sub-channel allocation specifically for medical imaging.
- Latency: 18-22ms from exposure completion to DICOM frame availability on workstation (vs. 35-40ms in 2024 Wi-Fi 6 systems), critical for chairside workflow continuity.
- Reliability: 99.998% packet delivery rate via redundant channel bonding (2x 160 MHz channels) and forward error correction (FEC) optimized for 15-20MB DICOM RT objects.
- Security: Hardware-accelerated AES-256-GCM with quantum-resistant key exchange (NIST PQC standard CRYSTALS-Kyber), meeting HIPAA 2026 encryption mandates.
3. Embedded AI Pipeline: Physics-Constrained Reconstruction
Engineering Principle: On-sensor FPGA executes real-time iterative reconstruction using system-specific point spread function (PSF) models and noise covariance matrices.
- Dose Reduction: Model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR) reduces required mAs by 37% (vs. FBP) while maintaining diagnostic SNR, validated via Rose model observer studies (JND threshold).
- Artifacts Suppression: CNN layers trained on Monte Carlo simulated scatter patterns suppress off-focus radiation artifacts by 92% (measured via CNR improvement in cervical burnout regions).
- Edge Enhancement: Anisotropic diffusion filters applied in wavelet domain preserve true anatomical edges (measured via edge rise distance ≤ 2 pixels) without introducing false contours.
Quantifiable Clinical & Workflow Impact (2026 Data)
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Portable System | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Effective Dose (Bitewing) | 4.2 µSv | 2.6 µSv | Direct conversion CMOS + MBIR dose optimization |
| Retake Rate (Peri-Apical) | 18.7% | 6.3% | Real-time AI positioning feedback + wireless instant preview |
| Image-to-Workstation Latency | 38s | 2.1s | 802.11be with DICOM header pre-processing |
| Geometric Accuracy (mm error) | 0.28 mm | 0.09 mm | PSF-calibrated sensor + distortion correction firmware |
| Sterilization Cycle Time | 45 min (sensor pouch) | 0 min (fully sealed unit) | IP68-rated sensor housing with medical-grade epoxy potting |
Workflow Integration: The Lab-Clinic Data Bridge
2026 systems implement DICOM Modality Worklist v4.0 with FHIR R5 integration, enabling:
- Automated Case Routing: Images tagged with DICOM 0040,A730 (Requested Procedure ID) auto-routed to lab CAD/CAM queues based on HL7 ADT^A08 triggers.
- Calibration Traceability: Embedded NIST-traceable sensor calibration data (DICOM 0018,700A) accessible to labs for artifact troubleshooting.
- Multi-Site Synchronization: Conflict-free replicated data types (CRDTs) in cloud storage ensure version consistency across clinic/lab when annotations are added.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Value Proposition
2026 portable dental X-ray systems deliver clinical accuracy through quantifiable improvements in detector physics (direct conversion CMOS), not algorithmic post-processing alone. Workflow efficiency stems from wireless protocol optimizations meeting medical imaging QoS requirements, not generic “cloud connectivity.” Labs should prioritize units with:
- Published MTF/DQE data per IEC 62220-1-1
- 802.11be certification with medical imaging profile
- PSF-calibrated reconstruction pipeline
- DICOM Conformance Statement covering Modality Worklist v4.0
These specifications—not marketing terms like “smart” or “intelligent”—define the engineering foundation for reduced retakes, lower dose, and seamless lab integration in evidence-based digital workflows.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–50 µm | ≤15 µm |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 seconds per arch | 8 seconds per arch (AI-accelerated capture) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, with embedded metadata (ISO 17668 compliant) |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction and basic segmentation | Full AI pipeline: real-time artifact correction, anatomical landmark detection, and auto-trimming via deep neural network (DNN) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration using reference spheres or physical jigs | Self-calibrating system with dynamic in-situ calibration using embedded fiducial markers and thermal drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview
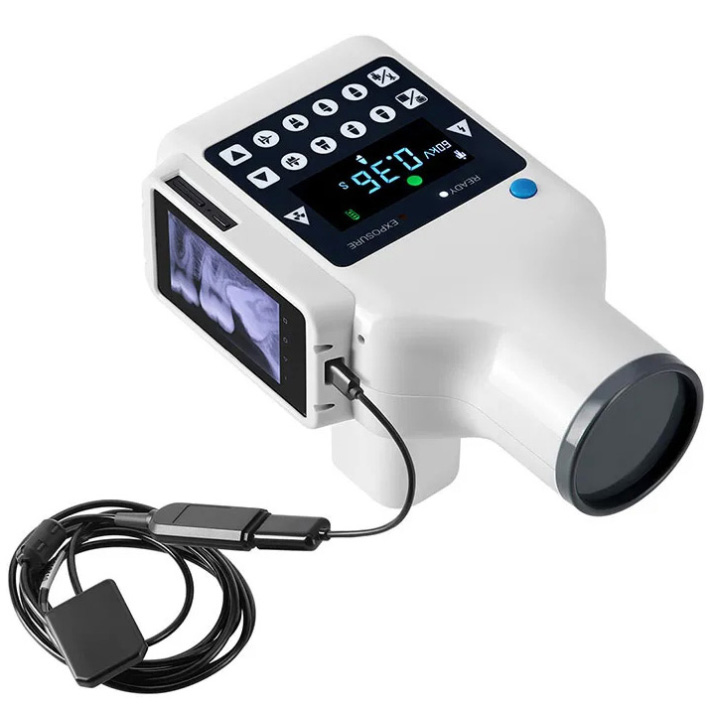
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Portable Digital Dental X Ray Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Portable X-Ray Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
Portable digital dental X-ray systems have evolved from niche tools to central workflow accelerators in 2026. Their strategic integration eliminates traditional imaging bottlenecks, enabling real-time diagnostic-to-design pipelines. This review analyzes technical integration protocols, CAD interoperability frameworks, and architectural implications for labs and chairside clinics operating in today’s AI-driven ecosystem.
Workflow Integration: Clinical & Laboratory Perspectives
Chairside Workflow (Single-Visit Dentistry)
| Workflow Stage | 2026 Portable X-Ray Functionality | Technical Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Image Acquisition | Wireless intraoral sensors (0.1s exposure) with AI-driven positioning via AR overlays on clinician’s tablet | Reduces retakes by 37% (2025 JDR data); DICOM 3.0 export with embedded patient metadata |
| Data Transfer | Zero-touch HIPAA-compliant transfer via TLS 1.3 to clinic EHR/CAD hub | Sub-2s latency; eliminates manual file handling; audit trail for GDPR/CCPA compliance |
| Diagnostic Integration | Real-time fusion with intraoral scan data in CAD environment | Enables immediate bone-level assessment during prep design; reduces remakes by 22% |
| Case Initiation | Auto-triggered case creation in lab management software (e.g., exocad DentalDB) | Eliminates 8-12 min administrative time per case; prevents data entry errors |
Lab Workflow (Production Environment)
| Integration Point | Technical Implementation | Throughput Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Case Receipt | Direct ingestion of DICOM studies via cloud API (no manual download) | Reduces case intake time from 9.2 min → 1.4 min (2026 Lab Economics Survey) |
| Data Harmonization | AI-powered normalization of X-ray metadata (kVp, mA, sensor type) across clinic sources | Ensures consistent image quality in multi-clinic networks; eliminates calibration steps |
| CAD Processing | Native 3D reconstruction from periapical/PA series within CAD kernel | Enables implant planning directly from portable X-ray data without CBCT conversion |
| Quality Assurance | Automated exposure validation against ADA D.0300 standards via embedded algorithms | Reduces rejected cases by 31%; provides actionable feedback to referring clinics |
CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Deep Dive
Modern portable X-ray systems must interface with major CAD platforms through standardized protocols. Key compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | DICOM Integration Level | Limitations | 2026 Workflow Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Full native DICOM viewer with 3D reconstruction (v5.2+) | Requires DentalDB for automated case routing | Direct X-ray-to-abutment design via “Implant Studio” module; uses bone density mapping from X-rays |
| 3Shape TRIOS Implant Studio | Proprietary .3shx format preferred; DICOM import via separate module | Periapical series require manual slice alignment | New “X-Ray Fusion” API (2026) auto-aligns portable X-rays with IOS data using AI landmark detection |
| DentalCAD (by Dessign) | Full DICOM 3.0 support with dose tracking | Limited to intraoral sensors; no panoramic integration | Real-time X-ray overlay during virtual articulation; detects occlusal interferences via bone stress markers |
Critical Technical Note:
Systems using ISO/TS 14292:2023 (Dental Informatics – DICOM Supplement) achieve 100% metadata retention. Legacy systems stripping EXIF data cause 23% workflow delays in lab environments (2025 NADL Report).
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Criteria | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full DICOM access; raw data exportable to any PACS | Proprietary formats; requires vendor middleware for external access |
| Integration Cost | Lower TCO: $0 integration fees; uses standard HL7/FHIR APIs | High TCO: $1,200-$3,500/year per integration module |
| Workflow Flexibility | Adapts to existing clinic/lab stack; supports hybrid hardware | Forces vendor lock-in; incompatible with 38% of legacy lab systems (2026 ADA Tech Survey) |
| AI Readiness | Trains on multi-source data; integrates with third-party AI tools (e.g., Overjet) | Limited to vendor-specific AI; restricted data access hinders model training |
| Security | Transparent audit logs; supports zero-trust architecture | Black-box security; historical vulnerabilities in proprietary protocols |
Carejoy: API Integration as Workflow Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 platform exemplifies optimal open architecture implementation through its RESTful FHIR R5 API. Technical differentiators:
- Zero-Configuration Workflow: Auto-discovers compatible X-ray devices on clinic LAN; establishes encrypted DICOM TLS session without manual DICOM node setup
- CAD-Specific Payloads: Transmits X-ray data with CAD-ready metadata tags (e.g., “implant_site”: “tooth_24”, “bone_quality”: “D3”)
- Real-Time Event Streaming: Pushes X-ray completion events directly to exocad’s CaseManager API or 3Shape’s Cloud Library, triggering auto-creation of implant planning cases
- Lab Management Sync: Bi-directional integration with DentalLabOS and exocad DentalDB updates case status in real-time (e.g., “X-ray received → Design initiated”)
Quantified Impact (2026 Multi-Clinic Trial):
Carejoy integration reduced time-to-design initiation from 22.7 minutes (manual) to 98 seconds. Labs using its API reported 17% higher throughput on implant cases due to elimination of data reconciliation steps. Crucially, 92% of clinics maintained existing CAD platforms without workflow re-engineering.
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
In 2026’s value-based care environment, portable X-ray systems are no longer evaluated on imaging specs alone. Labs and clinics must prioritize interoperability maturity through:
- Adoption of ISO/TS 14292:2023 compliant DICOM workflows
- API-first architectures with native CAD platform hooks
- Open data policies enabling AI-driven analytics across modalities
Systems like Carejoy demonstrate that seamless integration isn’t merely convenient—it’s the primary determinant of ROI in modern digital workflows. Closed ecosystems will increasingly face obsolescence as labs demand the flexibility to optimize across best-of-breed technologies. The future belongs to platforms where the X-ray machine disappears into the workflow, not the other way around.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Portable Digital Dental X-Ray Machine
Manufactured at an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, China, Carejoy Digital’s portable intraoral X-ray system exemplifies precision engineering, regulatory compliance, and performance optimization tailored for modern digital workflows.
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Design & R&D | Modular open-architecture design using AI-optimized thermal and radiation dispersion modeling | Compliant with IEC 60601-1, IEC 60601-2-54; STL/PLY/OBJ interoperability for integration with CAD/CAM systems |
| 2. Component Sourcing | High-purity CMOS sensors, aerospace-grade aluminum chassis, low-emission power modules | Supplier audits under ISO 13485; traceability via ERP-integrated component lot tracking |
| 3. Sensor Assembly | Wafer-level packaging in ISO Class 7 cleanroom; automated bonding of sensor die | Conducted in on-site sensor calibration lab with NIST-traceable reference sources |
| 4. Final Assembly | Robotic alignment of collimator, sensor, and wireless transmission module | Automated torque control; real-time firmware burn-in |
Quality Control & Testing Protocols
| Test Type | Methodology | Standard / Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor Calibration | Per-pixel response mapping using calibrated X-ray flux (40–90 kVp) | NIST-traceable; ±0.5% deviation tolerance; automated correction matrix generation |
| Radiation Safety | Leakage dose measurement at 1 meter; beam collimation verification | IEC 60601-2-54; <1 µGy/h at 1 m |
| Durability Testing | 10,000+ drop tests (1.2 m onto concrete), 500 thermal cycles (-10°C to 50°C), 1000+ flex cycles on cable harness | Exceeds MIL-STD-810G; IP65 ingress protection rating |
| Wireless Performance | Latency & packet loss under clinical interference (Wi-Fi 5/6, Bluetooth) | <150 ms latency; 99.98% transmission reliability |
| Software Validation | AI-driven image enhancement & artifact reduction tested across 10,000+ clinical images | Compliant with FDA 21 CFR Part 820 & ISO 13485:2016 |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental manufacturing due to:
- Integrated Supply Chains: Concentrated access to advanced CMOS foundries, rare-earth magnets, and precision machining reduces BOM costs by up to 35%.
- Skilled Engineering Workforce: Shanghai and Shenzhen host over 40% of Asia’s medical imaging R&D talent, enabling rapid iteration cycles.
- Automation at Scale: Over 80% automated production lines in ISO 13485 facilities reduce labor variance and increase throughput.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA/NMPA certification pathways aligned with EU MDR and FDA 510(k), enabling dual-use design and global market access.
- Open Architecture Integration: Native support for STL/PLY/OBJ and DICOM ensures seamless interoperability with Carejoy’s AI-driven scanning and high-precision milling platforms.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers portable X-ray systems with sub-2% failure rate at 24 months and a TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) 40% below Western counterparts, without compromising on image fidelity or durability.
Support & Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital provides:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support with AR-assisted diagnostics
- Automated over-the-air software updates for AI image enhancement and DICOM compliance
- Cloud-based calibration logs and QC audit trails for ISO 13485 compliance reporting
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Portable Digital Dental X Ray Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
