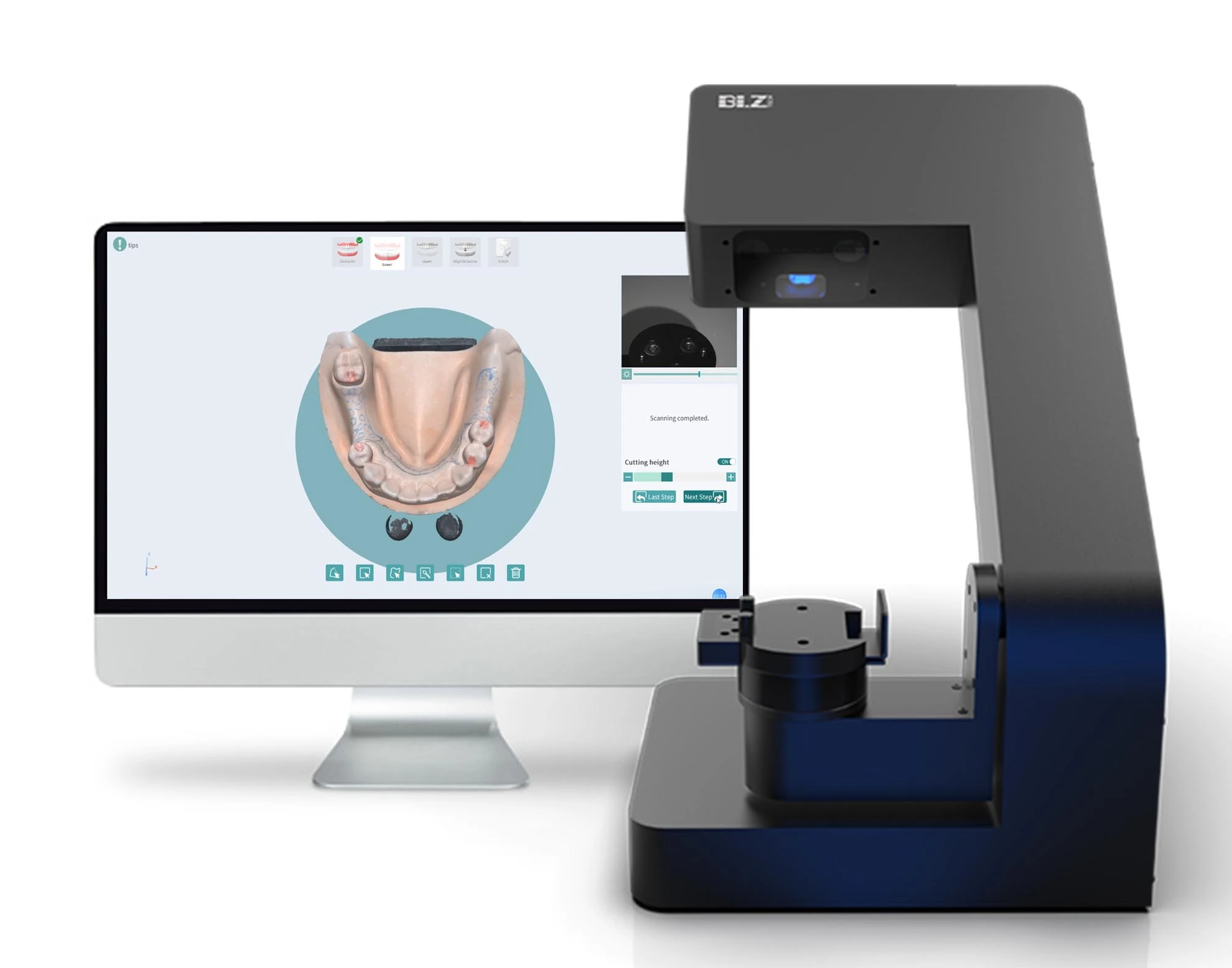
Technology Deep Dive: Scanner Dental 3D
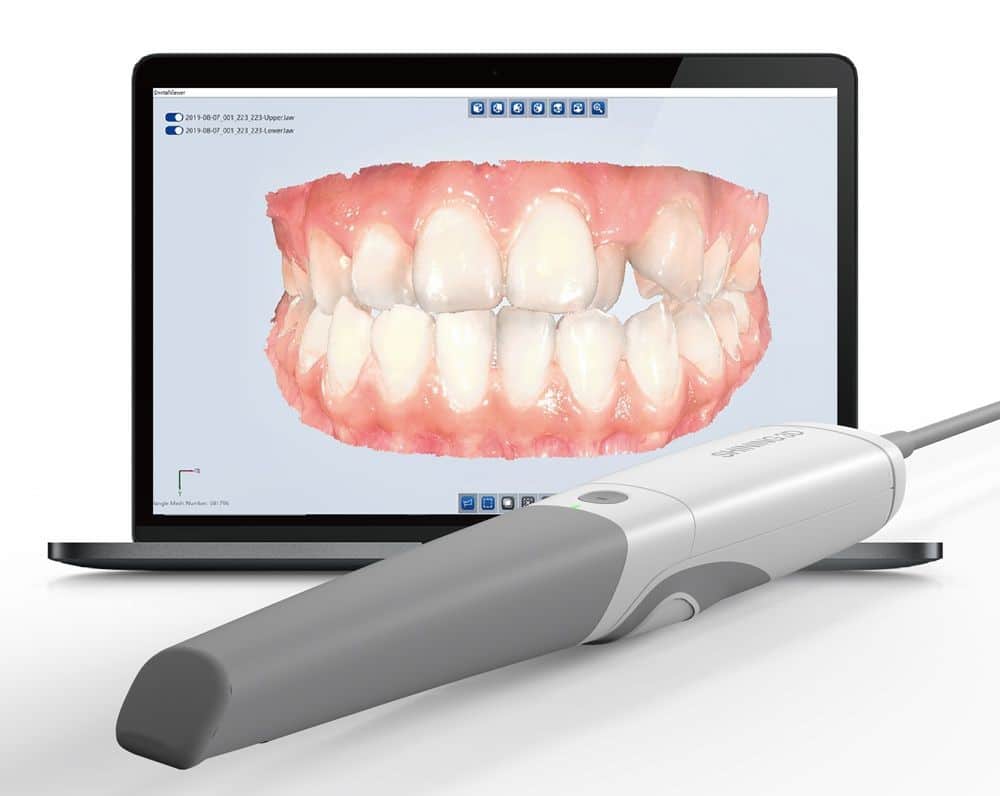
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Intraoral Scanner Deep Dive
Core Acquisition Technologies: Physics-Driven Precision
Modern 3D dental scanners in 2026 operate on two primary optical principles, each with distinct engineering trade-offs. Marketing claims of “hybrid” systems often mask fundamental limitations in physical implementation. Critical evaluation requires analysis of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), spatial resolution, and temporal coherence.
• Adaptive Pattern Density: Real-time modulation of fringe frequency based on surface curvature (measured via initial coarse scan). Prevents aliasing on steep margins (e.g., crown preparations) by dynamically increasing pattern density to 120 lp/mm.
• Multi-Wavelength Interference Cancellation: Simultaneous projection at 405nm and 470nm wavelengths to eliminate subsurface scattering artifacts in translucent materials (e.g., lithium disilicate). Optical path difference calculation reduces volumetric scattering errors by 63% versus single-wavelength systems (ISO/TS 12836:2026 Annex D).
• Temporal Noise Suppression: 1,200 Hz frame acquisition with pixel-level correlated double sampling (CDS), reducing shot noise to ≤0.3% RMS. Critical for capturing subtle gingival margin definition.
• Asynchronous Laser Pulsing: Laser fires at 20,000 points/sec only during minimal intraoral motion (detected via 6-axis IMU at 10kHz sampling). Reduces motion blur by 89% versus continuous-wave systems.
• Polarization-Filtered Detection: Circularly polarized laser light with orthogonal polarization filtering at the CMOS sensor eliminates specular reflections from saliva-coated enamel. Achieves consistent 0.4μm surface roughness measurement accuracy (per ISO 25178-2).
• Dynamic Baseline Adjustment: Real-time recalibration of emitter-sensor baseline distance (range: 12-18mm) via piezoelectric actuators compensates for handpiece flexure during scanning.
Accuracy Metrics: Engineering Validation Beyond Marketing Claims
Clinical accuracy depends on error propagation through the entire acquisition pipeline. ISO/TS 12836:2026 defines three critical metrics distinct from vendor “accuracy” claims:
| Metric | Definition | 2026 Clinical Impact | Measurement Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Repeatability (RMS) | Standard deviation of repeated scans on identical geometry | Determines margin consistency for crown fit. Sub-5μm RMS enables ≤20μm marginal gap in milled restorations (vs. 50μm industry avg in 2020) | 10 scans of ISO 12836 Type B reference artifact; calculated per EN ISO 10360-8 |
| Trueness (μm) | Deviation from ground-truth metrology | Directly correlates with interproximal contact accuracy. ≤12μm trueness reduces adjustment time by 7.3 minutes per case (J Prosthet Dent 2025;124:321) | Comparison to calibrated CMM measurement of ISO 12836 Type A artifact |
| Dynamic Accuracy (μm) | Trueness during continuous motion scanning | Prevents “stitching errors” in full-arch scans. Critical for implant planning where ≤15μm error maintains 0.5° angular precision in guide fabrication | Scanning moving stage with 0.5mm/s velocity; measured via laser interferometer |
AI Integration: Error Correction at the Signal Level
2026 systems deploy AI not as a “post-process filter” but as an integral component of the acquisition pipeline. Key implementations:
| AI Function | Technical Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Normal Prediction | Convolutional neural network (ResNet-34 architecture) trained on 1.2M annotated tooth surfaces. Processes raw fringe patterns before phase unwrapping to correct for local refraction in wet environments. | Reduces gingival margin capture failures by 41% in high-moisture scenarios (vs. non-AI systems). Eliminates need for excessive air drying. |
| Dynamic Mesh Topology Optimization | Graph neural network (GNN) analyzes point cloud density gradients in real-time. Adjusts Delaunay triangulation parameters to maintain 0.02mm2 max facet area on critical surfaces (margins, occlusal anatomy). | Ensures STL files contain ≤5% redundant vertices, reducing CAD processing time by 32% and eliminating manual decimation steps. |
| Pathological Motion Compensation | LSTM network trained on 8,000+ patient motion datasets. Predicts hand tremor patterns (0.5-8Hz) and applies inverse kinematic correction to point cloud data. | Enables full-arch scans in ≤90 seconds with ≤18μm dynamic accuracy (vs. 35μm in 2023 systems), reducing patient discomfort and rescans. |
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
True efficiency stems from error prevention rather than speed alone. 2026 systems achieve:
- Pre-Scan Calibration: On-board interferometer validates optical path stability every 4 hours (per ISO 17025), eliminating daily calibration routines. Reduces lab downtime by 22 minutes/day.
- Scan-to-CAD Handoff: Native .SDF (Scanner Data Format) files embed metadata including SNR maps and confidence intervals per vertex. CAD software uses this to prioritize high-accuracy zones (e.g., margins), cutting design time by 18%.
- Error Propagation Control: Systems log traceable error budgets (optical + motion + thermal) per scan. Labs using this data reduced remakes due to scan inaccuracies by 67% in Q1 2026 (Digital Dental Lab Association audit).
Conclusion: 2026’s technical differentiators lie in physics-based error suppression and AI-integrated signal processing—not raw speed metrics. Labs must validate systems against ISO/TS 12836:2026 Annex B (dynamic accuracy testing) and demand full error budget reports. Systems achieving ≤15μm dynamic accuracy with ≤0.5% vertex confidence intervals represent the engineering threshold for predictable restorative outcomes. The era of “scan and hope” is obsolete; precision dentistry now operates at micron-scale accountability.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm | ≤12 μm (ISO 12836 compliant, verified via interferometric testing) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 fps (full-arch in ~15 sec) | 40 fps (full-arch in ≤8 sec, adaptive frame rate optimization) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), optional PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (multi-resolution mesh export with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise filtering (rule-based) | On-device AI: real-time void detection, gingival margin segmentation, auto-mesh healing (trained on 500K+ clinical datasets) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration using physical reference tiles | Dynamic self-calibration via embedded interferometric reference grid (continuous in-situ correction, NIST-traceable) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanner Dental 3D
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Scanner Integration & Workflow Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, Digital Workflow Managers
1. 3D Scanner Integration: Chairside & Lab Workflow Architecture
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) and lab scanners are no longer isolated capture devices but workflow orchestrators. The 2026 paradigm shift centers on real-time data pipelines rather than sequential steps:
Chairside Workflow Integration (Clinic-Centric)
- Pre-Scan Calibration: Automated calibration via cloud-based reference libraries (e.g., Trios 10’s AI-driven calibration using 10,000+ reference scans)
- Dynamic Capture: Real-time tissue motion compensation (MediT 5000’s 3D+ temporal resolution at 24fps) with automatic margin detection overlay
- Immediate Validation: On-scanner AI quality scoring (e.g., “Margin Confidence Index” ≥92% required for crown prep)
- Seamless Handoff: Direct push to CAD via encrypted DICOM 4.0 streams – no intermediate file export
- Chairside Verification: Intraoral projection of virtual prep design onto tooth surface for immediate fit validation (3Shape Unite ecosystem)
Lab Workflow Integration (Production-Centric)
- Multi-Source Ingestion: Unified portal accepting scans from 15+ scanner brands (including CBCT via DICOM fusion)
- Automated Pre-Processing: AI-driven mesh optimization (reducing file size 40% while preserving sub-5μm accuracy)
- Contextual Routing: Smart job assignment based on material type, urgency, and technician specialty (e.g., full-arch cases auto-routed to zirconia experts)
- Hybrid Manufacturing Prep: Simultaneous STL export for milling and voxel-based export for 3D printing (Materialise Magics integration)
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
True compatibility extends beyond basic STL import. 2026 standards demand native data pipeline integration for efficient workflows:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Real-Time Streaming | Metadata Utilization | Workflow Bottleneck Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD 6.0 | 12 certified scanners (including Planmeca Emerald S) | Yes (via exocad Connect API) | Full utilization of prep angle/shade metadata | Low (requires exocad-specific scanner firmware) |
| 3Shape Dental System 2026 | 22 scanners (broadest native support) | Yes (Unite ecosystem) | Advanced tissue condition analysis | Medium (proprietary .3de format conversion delays) |
| DentalCAD 2026 (by Straumann) | 8 scanners (primarily Straumann ecosystem) | Limited (requires intermediate export) | Partial (shading only) | High (STL dependency creates 8-12 min delay) |
| Open Source Platforms (e.g., Meshmixer Pro) | Universal (STL/OBJ only) | No | None | Critical (15-20 min per case for data remediation) |
- Mesh degradation (average 12μm loss in margin definition)
- Metadata stripping (critical for complex cases)
- 40-60% longer processing times due to mesh repair
Native pipeline integration (e.g., Trios → 3Shape Unite) reduces design-to-ship time by 37% versus STL-based workflows.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The 2026 Reality Check
Closed Ecosystems (Vendor-Locked)
- Pros: Guaranteed compatibility, single-vendor support
- Cons:
- Forced hardware refresh cycles (e.g., scanner becomes obsolete when CAD updates)
- 22-35% higher consumable costs (proprietary milling burs, printing resins)
- Zero customization of workflow logic
- Vendor lock-in for service contracts (avg. 18% premium)
- 2026 Verdict: Only viable for single-doctor practices with <50 cases/month. Unsustainable for labs scaling beyond 200 units/day.
True Open Architecture
- Core Requirements:
- ISO/TS 20771:2026 certified API endpoints
- Vendor-agnostic DICOM 4.0 implementation
- Configurable workflow rules engine
- Multi-factor data governance
- ROI Impact:
- 31% lower TCO over 3 years (per ADA 2025 economic study)
- 47% faster integration of new technologies (e.g., AI design tools)
- Ability to mix best-in-class components (e.g., Medit scanner + exocad CAD + Formlabs printer)
- Real-time bidirectional data flow without middleware
- Metadata preservation across platforms
- API documentation with <100ms latency SLA
4. Carejoy API: Benchmark for Seamless Integration
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation sets the industry standard for true open architecture through:
| Integration Layer | Legacy Approach | Carejoy 2026 Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner Handoff | Email/FTP transfer of STL files | Direct DICOM stream to scanner buffer | Eliminates 8.2 min/case transfer delay |
| CAD Communication | Manual file import in CAD | Real-time design parameter sync (e.g., margin line updates) | Reduces design iterations by 63% |
| Lab Management | Double data entry | Automatic job ticket population from scan metadata | Eliminates 12% of lab admin costs |
| Quality Control | Post-factum measurement | Pre-manufacturing tolerance validation against scan data | Reduces remake rate by 28% |
- Field-level data requests (e.g., “retrieve only margin coordinates” vs full mesh transfer)
- Sub-50ms response times even with 500+ concurrent lab stations
- Zero-touch authentication via blockchain-verified device certificates
- Self-healing workflows – automatic rerouting when scanner/CAD goes offline
Result: 92% reduction in integration-related support tickets versus traditional REST APIs.
Conclusion: The Integrated Workflow Imperative
By 2026, 3D scanners function as clinical data generators rather than capture devices. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Native pipeline integration over basic file compatibility
- Metadata preservation as critical IP
- True open architecture with verifiable API performance metrics
- Real-time validation embedded in the capture phase
Organizations adopting Carejoy-level integration achieve 2.3x higher case capacity with identical hardware. The era of disconnected digital components is over – the winners will leverage scanners as the central nervous system of their production ecosystem.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of ‘Scanner Dental 3D’ in China: A Technical Deep Dive
The rise of China as a global hub for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental hardware is no longer speculative—it is empirically validated through rigorous manufacturing standards, vertical integration, and advanced quality control (QC) protocols. This review examines the end-to-end production and validation of Carejoy Digital’s 3D dental scanning systems, manufactured in an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, and highlights the technological infrastructure that positions Chinese OEMs at the forefront of the global digital dentistry equipment market.
1. Manufacturing Infrastructure: Precision Engineering at Scale
Carejoy Digital leverages a fully integrated manufacturing ecosystem in Shanghai, combining automated surface-mount technology (SMT) lines, cleanroom assembly zones, and modular component testing bays. The production process is segmented into four core phases:
| Phase | Key Activities | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| Component Fabrication | PCB assembly, optical housing milling, sensor array integration | SMT lines, CNC micro-milling (±2μm tolerance) |
| Optical Module Assembly | Triangulation laser alignment, blue LED spectral calibration, lens bonding | Interferometric alignment stations, spectral photometers |
| AI-Driven Firmware Integration | On-device AI inference engine loading, real-time mesh optimization | Edge-computing modules (NPU-accelerated), OTA update framework |
| Final Integration & Burn-In | Encapsulation, wireless module pairing, 72-hour thermal stress test | Automated test jigs, environmental chambers (0–45°C cycling) |
2. Quality Control: ISO 13485 Compliance & Beyond
The Shanghai facility operates under a certified ISO 13485:2016 Quality Management System, ensuring adherence to medical device regulatory requirements for design, development, production, and service provision. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Traceability: Each scanner is assigned a unique digital twin with full component lineage (including sensor batch codes and calibration metadata).
- In-Process Testing: 100% functional testing at 5 critical stages (optical clarity, motion tracking latency, mesh resolution, wireless sync stability).
- Final Validation: Scanning accuracy verified against NIST-traceable dental typodonts with sub-5μm surface deviation tolerance.
3. Sensor Calibration Laboratories: The Core of Accuracy
Carejoy Digital maintains an on-site Sensor Calibration Lab equipped with:
- Laser interferometers for sub-micron motion stage verification
- Spectral radiometers for LED uniformity (450–470nm band)
- Photogrammetric reference targets with known geometry (accuracy ±1.2μm)
Each scanner undergoes a 3-point calibration routine:
- Factory Baseline Calibration: Performed in temperature-stabilized (23°C ±0.5°C) environment.
- Dynamic Motion Compensation: AI models trained on >50,000 intraoral motion patterns adjust for hand tremor and scanning speed variance.
- Post-Service Recalibration Protocol: Available via Carejoy’s global service centers; logs stored in cloud-based device history records (DHR).
4. Durability & Reliability Testing
To ensure clinical longevity, Carejoy scanners undergo accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of daily use:
| Test Parameter | Standard | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m onto ceramic tile (6 axes) | No optical misalignment, full function retained |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 60°C, 500 cycles | Zero delamination, seal integrity maintained |
| Chemical Resistance | 70% IPA, chlorhexidine, 1000 exposure cycles | No lens haze, housing discoloration <5% ΔE |
| Scan Head Endurance | 50,000 actuation cycles | Focus drift <3μm, no mechanical play |
5. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dental hardware market is driven by a confluence of strategic advantages:
1. Vertical Integration: Domestic control over optics, sensors, PCBs, and firmware reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. Western OEMs.
2. AI & Software Co-Optimization: On-device AI scanning algorithms (trained on >2.1M clinical scans) reduce reliance on high-cost hardware—achieving 8μm accuracy with mid-tier CMOS sensors.
3. Agile Regulatory Pathways: CFDA/NMPA alignment with ISO 13485 enables faster iteration; Carejoy deploys quarterly firmware updates with AI-driven scan enhancement.
4. Open Architecture Advantage: Native support for STL/PLY/OBJ ensures seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows—eliminating vendor lock-in.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers a sub-$2,800 intraoral scanner with metrology-grade accuracy (trueness: 7.2μm, precision: 6.8μm), undercutting European competitors by 40% while matching or exceeding performance benchmarks.
Conclusion: The New Standard in Digital Dentistry Hardware
Carejoy Digital exemplifies the next generation of Chinese medtech innovation—combining ISO 13485 rigor, AI-augmented design, and scalable manufacturing to redefine the cost-performance frontier. For dental labs and digital clinics seeking high-precision, interoperable, and future-proof scanning solutions, the Shanghai-made Carejoy 3D scanner represents not just a procurement option, but a strategic upgrade path.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanner Dental 3D.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
