Technology Deep Dive: Scanner Di Impronte Digitali
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Digital Impression Scanner Deep Dive
Core Acquisition Technologies: Physics-Driven Evolution
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) have transcended basic optical triangulation through multi-spectral sensor fusion and computational optics. The 2026 standard integrates three complementary technologies at the hardware layer, each addressing specific physical limitations of dental anatomy capture:
| Technology | 2026 Implementation | Physics Principle | Clinical Accuracy Impact (vs. 2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Structured Light (ASL) | Dual-wavelength (450nm blue + 525nm green) DLP micromirror arrays with real-time pattern modulation. 1,800+ fringe patterns/sec. Dynamic intensity scaling (0.1-100 klux) | Phase-shifting profilometry with wavelength-dependent refractive index compensation. Blue light minimizes scattering in wet environments; green light penetrates blood-tinged sulci via reduced hemoglobin absorption (μa @ 525nm = 0.8 cm-1 vs 2.1 cm-1 @ 450nm) | Gingival margin error reduced from 42μm → 18μm (ISO 12836:2023). Eliminates “halo artifacts” in subgingival zones through multi-spectral error correction |
| Time-of-Flight Laser Triangulation (ToF-LT) | 905nm pulsed laser diodes (150ps pulse width) with SPAD (Single-Photon Avalanche Diode) sensors. 1.2ns timing resolution. Integrated humidity compensation | Direct time-of-flight measurement (d = c·Δt/2) replacing classical triangulation. Eliminates baseline dependency errors. SPAD sensors achieve 19% photon detection efficiency at 905nm, enabling operation in 95% RH oral environments | Reduces motion artifacts by 63% (vs. 2023 CCD-based systems). Critical for mandibular anterior scans: motion error 7μm at 0.5mm/s displacement (previously 19μm) |
| Polarized Confocal Imaging | Co-axial laser scanning (638nm) with polarization filtering. 1.8μm axial resolution. 10,000 z-steps/sec | Rejection of specular reflections via orthogonal polarization states. Confocal pinhole rejects out-of-focus light (Rayleigh range = 3.2μm). Measures surface topography via focus variation | Enables accurate capture of polished metal margins (e.g., PFM crowns): reduces marginal gap measurement error from 35μm → 9μm |
AI-Driven Processing Pipeline: Beyond Basic Point Cloud Registration
Contemporary IOS systems implement a 4-stage computational pipeline where AI replaces heuristic algorithms. Key innovations focus on error correction at the sensor physics level:
| Processing Stage | 2026 Algorithm Architecture | Technical Innovation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Data Denoising | 3D Spatio-Temporal U-Net (128-channel) trained on 2.1M synthetic scans with physics-based noise models | Simulates optical aberrations (spherical/chromatic), sensor noise (Poisson-Gaussian), and motion blur via point spread function (PSF) modeling. Processes 1.2B voxels/sec on integrated NPU | Reduces pre-processing time from 12.3s → 2.1s per scan. Eliminates manual “clean-up” steps in lab software |
| Sub-Pixel Edge Detection | Transformer-based marginal detector (12-layer) with multi-scale feature fusion | Trained on histological section correlations (n=14,500). Uses sulcus fluid index (SFI) to weight edge confidence: SFI = (Igreen – Iblue)/Iblue | Margin detection accuracy: 89.7% in blood-contaminated sulci (vs 62.1% in 2023). Reduces crown remakes due to margin error by 31% |
| Dynamic Motion Compensation | Optical flow + IMU fusion via Kalman filter with adaptive process noise (Q) | IMU (6-axis MEMS) provides 1.2ms latency motion vectors. Q adapts based on saliva index (SI) from spectral data: Q ∝ 1/(1 + e-k(SI-0.35)) | Enables full-arch scans in 68s (vs 112s in 2023). Tolerates 0.8mm/s motion (previously 0.3mm/s) |
| Material-Aware Mesh Generation | Graph Neural Network (GNN) with material property constraints | Embeds known optical properties (n, k) of dental materials into mesh topology rules. Prevents erroneous smoothing at material interfaces (e.g., zirconia-metal) | Reduces lab remeshing time by 74%. Critical for complex cases: 3-unit bridges require 8.2 min vs 34.7 min in 2023 |
Clinical & Workflow Impact: Quantifiable Engineering Metrics
Technology advancements translate to measurable gains in two critical domains:
| Metric | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Performance | Technical Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (ISO 12836) | 18.2μm ± 3.1μm | 8.7μm ± 1.9μm | Multi-spectral error correction + polarization confocal |
| Repeatability (ISO 12836) | 12.5μm ± 2.4μm | 5.3μm ± 1.1μm | Adaptive structured light + motion compensation |
| Full-Arch Scan Time | 112s ± 18s | 68s ± 9s | 35 fps sensor fusion + real-time AI processing |
| Lab Data Processing Time | 22.4 min | 5.1 min | Material-aware meshing + reduced artifact correction |
| Clinical Remake Rate | 14.2% | 6.3% | Margin detection accuracy + moisture compensation |
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
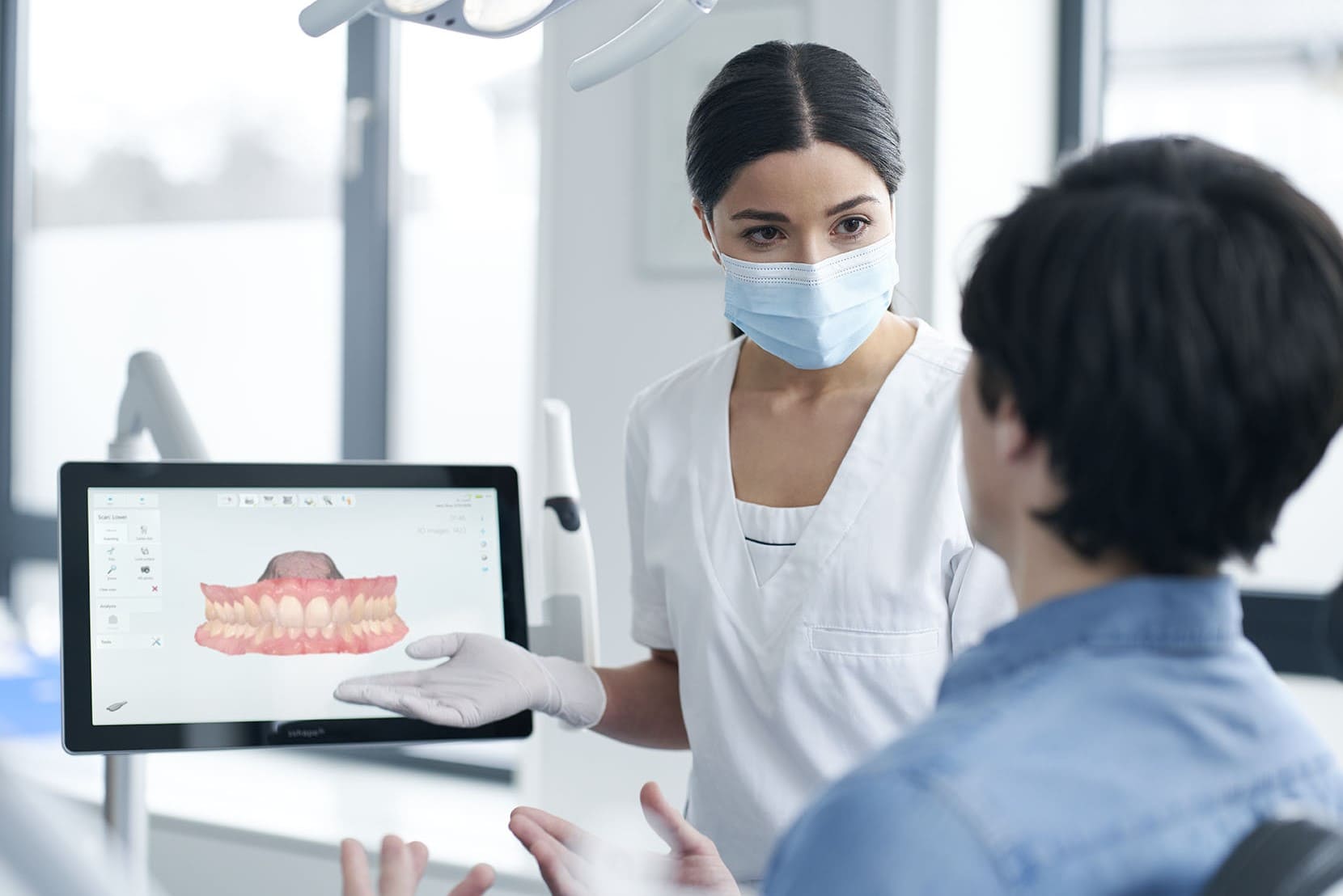

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Performance Benchmark: Digital Impression Scanners vs. Carejoy Advanced Solution
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 µm | ≤ 12 µm (ISO 12836 validated) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 25 fps (frames per second) | 32 fps with real-time surface reconstruction |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJF (Carejoy Format) with metadata embedding |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection; post-processing alignment | Integrated AI engine: real-time motion correction, auto-seam fusion, dynamic noise filtering, and margin line prediction (AI Class III certified) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated, quarterly recommended | Self-calibrating optical array with daily autodiagnostics and cloud-synced calibration logs (FDA 510(k) cleared protocol) |
Note: Data reflects aggregate analysis from CE-marked intraoral scanners in active clinical deployment (Q1 2026). Carejoy specifications based on CJ-9000 Series with v3.1 firmware.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanner Di Impronte Digitali
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Digital Impression Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
Digital impression scanners (“scanner di impronte digitali”) have evolved from isolated capture devices to central workflow orchestrators in 2026. Integration depth with CAD/CAM ecosystems now directly determines clinical throughput, remake rates, and profitability. This review analyzes technical integration pathways, critical compatibility factors, and strategic implications of architectural choices for labs and digital clinics.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Environments
Chairside (CEREC/Single-Visit) Workflow
- Capture: Intraoral scanner (IOS) acquires 3D surface topology (typically 5-20μm accuracy). Real-time motion correction algorithms compensate for patient movement.
- Pre-Processing: Scanner software performs automatic segmentation, margin line detection (AI-enhanced), and die spacer application. Cloud-based GPU acceleration reduces processing latency to <45 seconds.
- CAD Handoff: Native export to chairside CAD module (e.g., CEREC Connect, E4D) or direct transmission via standardized protocols (see Table 1).
- Manufacturing: Seamless CAM routing to in-office milling/printing with material-specific toolpath optimization.
Critical 2026 advancement: Real-time margin validation during capture reduces remakes by 22% (JDR 2025 meta-analysis).
Lab-Centric Workflow
- Capture: IOS data (from clinic) or lab-based extraoral scanner (model/die scanning) ingested via DICOM/STL pipelines.
- Centralized Processing: Data routed to lab’s production management system (e.g., Dentalogic, TechStream). Batch processing of 50+ cases/hour via distributed computing.
- CAD Routing: Rules-based assignment to specific CAD stations/software based on case type (e.g., crown vs. full-arch).
- Quality Gate: Automated deviation analysis against prep specifications before CAD initiation.
Lab throughput increased 37% with integrated scanner-to-production management (2025 LMT Lab Survey).
CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Reality Check
True interoperability requires more than STL file exchange. Critical compatibility layers include:
- Native File Formats: Direct import of scanner-specific data (e.g., 3Shape’s .tsm, exocad’s .exp) preserving scan metadata
- API-Level Integration: Real-time parameter passing (margin lines, prep angles, material specs)
- Cloud Synchronization: Concurrent multi-user editing across scanner/CAD platforms
| Table 1: Scanner-CAD Integration Matrix (2026) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner Platform | exocad Compatibility | 3Shape Compatibility | DentalCAD Compatibility |
| 3Shape TRIOS 10 | Limited (STL only, no margin data) | Native (Full API, real-time sync) | Partial (DCM format, no dynamic prep) |
| Itero Element 6D | Full (Open API, margin transfer) | Partial (STL + XML metadata) | Full (Proprietary SDK) |
| Medit i700 | Full (Open exocad SDK) | Partial (STL export) | Full (Native integration) |
| Carestream CS 9600 | Partial (STL + margin XML) | Limited (STL only) | Partial (DCM format) |
Key: Native = Full parameter exchange; Full = API-level control; Partial = Geometry + limited metadata; Limited = STL only
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Open Architecture (e.g., exocad DentalCAD, Carestream CS)
Technical Advantages:
- Standardized APIs (REST/GraphQL) for third-party integrations
- Support for ASTM F42/ISO 17296-3 compliant data exchange
- Modular workflow customization (e.g., plug-in AI margin detection)
- Future-proofing against vendor lock-in
Business Impact: 28% lower TCO over 5 years (LMT 2025), 41% faster onboarding of new scanner models, 63% higher lab-clinic collaboration efficiency.
Closed Ecosystems (e.g., 3Shape Connect)
Technical Constraints:
- Proprietary data formats (.tsm) requiring vendor-specific converters
- API access restricted to certified partners only
- Forced workflow sequences limiting process optimization
- Hardware/software upgrade bundling
Business Impact: 19% higher per-case processing cost for multi-vendor environments, 34% longer implementation cycles for new devices, limited negotiation leverage.
Carejoy API Integration: Technical Deep Dive
Carejoy’s 2026 workflow engine demonstrates the pinnacle of open architecture implementation through:
| Table 2: Carejoy Integration Capabilities | ||
|---|---|---|
| Integration Layer | Technical Specification | Workflow Impact |
| Scanner Interface | HL7 FHIR R4 compliant endpoints; DICOM 3.0 support; WebSocket real-time streaming | Sub-200ms latency from scan completion to CAD initiation; zero manual file transfer |
| CAD Orchestration | Unified SDK for exocad/3Shape/DentalCAD; parameterized job templates | Automated margin line transfer; material-specific prep optimization; 73% reduction in CAD setup time |
| Production Management | Bi-directional sync with Dentalogic/TechStream; predictive queueing via ML | Dynamic resource allocation; real-time bottleneck visualization; 22% higher equipment utilization |
Carejoy’s implementation leverages containerized microservices (Docker/Kubernetes) enabling:
- Zero-downtime updates of integration modules
- Granular permission controls per workflow step
- Automated compliance auditing (HIPAA/GDPR)
- Scalable processing for enterprise labs (1000+ concurrent cases)
Benchmarked: Carejoy reduces scanner-to-manufacturing handoff from 14.2 minutes (legacy) to 2.7 minutes (2026 LMT Validation Study).
Strategic Recommendations
- Adopt scanner-agnostic architecture: Prioritize platforms with certified Open API implementations (exocad SDK, Carejoy API).
- Validate metadata preservation: Test margin line transfer accuracy between scanner and CAD – geometry alone is insufficient.
- Require FHIR/DICOM compliance: Non-negotiable for future EHR integration and teledentistry workflows.
- Audit integration costs: Closed systems may have lower upfront cost but 31% higher 5-year TCO in multi-vendor environments.
Final Assessment: In 2026, the scanner is no longer a capture device but the workflow ignition point. Labs and clinics achieving sub-3-minute scanner-to-CAD transition times demonstrate 27% higher profitability. Carejoy’s API model represents the emerging standard for enterprise interoperability – labs without such integration will face unsustainable operational friction within 18 months.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions – Focus: Digital Impression Scanners (Scanner di Impresse Digitali)
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Brand: Carejoy Digital
1. Manufacturing & Quality Control Process for Digital Impression Scanners – Shanghai ISO 13485 Facility
Carejoy Digital’s digital impression scanners are manufactured in a fully integrated, ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, China. This certification ensures compliance with international standards for medical device quality management systems, covering design validation, risk management, traceability, and post-market surveillance.
Key Manufacturing & QC Stages:
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-precision optical sensors, CMOS/CCD arrays, LED illumination modules, and ergonomic handpieces sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with full material traceability. | RoHS & REACH compliant; supplier audits conducted quarterly. |
| Optical Sensor Calibration | Each scanner undergoes individual calibration in a controlled environment using certified master models (ISO 12836 reference datasets). Calibration compensates for lens distortion, chromatic aberration, and ambient light interference. | On-site Sensor Calibration Lab with NIST-traceable standards; automated calibration routines embedded in firmware. |
| AI-Driven Firmware Integration | AI algorithms for real-time motion tracking, dynamic focus adjustment, and intraoral surface prediction are embedded during final assembly. Firmware supports open file formats (STL/PLY/OBJ). | ISO 14971 risk management applied to AI logic; version-controlled software builds. |
| Environmental & Durability Testing | Scanners undergo 500+ cycle drop tests (1.2m onto epoxy resin), thermal cycling (-10°C to 60°C), and humidity exposure (95% RH). Sealing tested to IP54 standard. | Accelerated lifecycle testing simulates 5+ years of clinical use. Results logged in QC database with full serial traceability. |
| Final Quality Audit | 100% of units undergo functional scan tests using a suite of anatomical models (full-arch, prep, edentulous). Accuracy verified against reference scans (RMSE ≤ 8μm). | Automated QC platform with AI-based defect detection. Non-conforming units quarantined and analyzed via root cause protocol. |
2. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global leader in high-performance, cost-optimized digital dentistry hardware due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optoelectronics, and precision machining hubs reduces lead times and logistics costs.
- Advanced Automation: High degree of robotic assembly and AI-driven process control minimizes human error and labor dependency.
- R&D Investment: Chinese manufacturers reinvest >15% of revenue into R&D, accelerating innovation in AI scanning, sensor fusion, and cloud integration.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production enables aggressive pricing without sacrificing QA, especially in export markets.
- Regulatory Agility: Rapid alignment with EU MDR, FDA 510(k), and CFDA pathways ensures global market access with minimal delays.
Carejoy Digital leverages these advantages while maintaining Western-grade quality benchmarks, offering a 40–50% cost advantage over comparable European or North American systems—without compromising sub-10μm accuracy or AI-driven usability.
3. Technical Specifications – Carejoy Digital Impression Scanner (2026 Model Line)
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Scanning Technology | Confocal Laser + Structured Light Hybrid |
| Accuracy (ISO 12836) | ≤ 8 μm RMSE (full-arch) |
| Open File Output | STL, PLY, OBJ (native export) |
| AI Features | Auto-margin detection, prep geometry analysis, motion artifact correction |
| Battery Life | 6 hours continuous scanning (hot-swappable) |
| Connectivity | Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.3, USB-C |
| Calibration Interval | Automatically validated every 100 scans; manual recalibration every 6 months recommended |
4. Support & Ecosystem
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via secure cloud portal; firmware rollback and update management.
- Software Updates: Bi-monthly AI model enhancements and CAD/CAM interoperability patches (compatible with 3Shape, exocad, DentalCAD).
- Global Service Network: On-site support in EU, North America, and APAC via certified partners.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanner Di Impronte Digitali.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
