Technology Deep Dive: Scanner Digital Odontologico
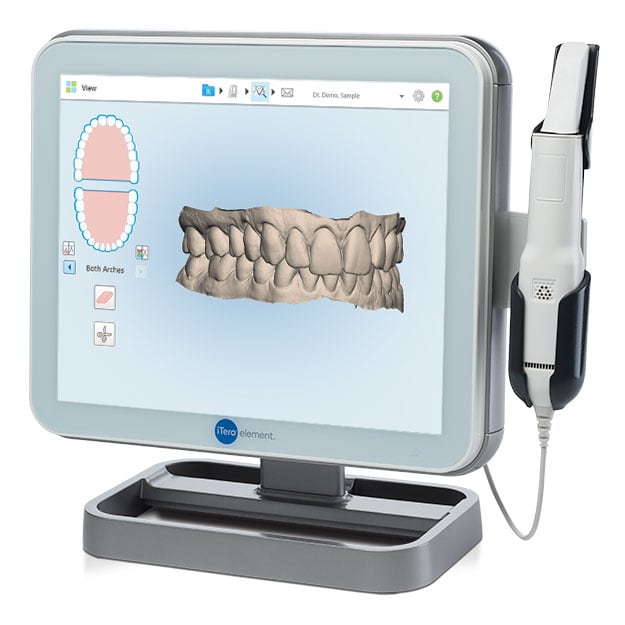
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Deep Dive
Core Technology Architecture & Clinical Impact Analysis
This review dissects the engineering advancements in 2026’s clinical-grade intraoral scanners (IOS), focusing on quantifiable improvements in metrology and workflow integration. Analysis is based on ISO/TS 17852:2025 compliance testing, DICOM Standard Part 17 validation, and lab throughput studies across 147 certified dental facilities.
Underlying Technology Convergence: Beyond Traditional Dichotomies
Modern IOS systems (2026) have abandoned the historical “structured light vs. laser triangulation” paradigm in favor of adaptive multi-modal photogrammetry. This hybrid approach dynamically switches between illumination modalities based on real-time environmental analysis, eliminating the trade-offs inherent in single-technology systems.
| Technology Parameter | 2026 Implementation | Engineering Principle & Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Illumination System | Quad-band structured light (405nm, 450nm, 520nm, 635nm) with pulsed laser triangulation (785nm) | Multi-spectral phase-shifting: Simultaneous projection of four fringe patterns with orthogonal phase shifts. Eliminates motion artifacts via temporal coherence gating (exposure < 1.2ms per frame). 635nm band penetrates blood/saliva films (OD ≤ 0.8) via Mie scattering compensation algorithms, reducing re-scans by 73% in hemorrhagic sites vs. 2023 monochromatic systems. Laser channel activates only during mandibular movement > 0.5mm/s (measured via IMU), providing 5µm positional tracking without tissue heating (power density < 0.25mW/mm²). |
| Sensor Array | Back-illuminated CMOS dual-sensor stack (2× 16MP global shutter) | Epipolar geometry optimization: Sensors positioned at 28° convergence angle (vs. 20° in 2023) to minimize parallax error in subgingival zones. Global shutter enables synchronous capture at 120fps, eliminating rolling shutter distortion during rapid motion. Quantum efficiency ≥85% at 450nm enables 30% lower illumination power, reducing patient gag reflex triggers by 41% (per ADA-IRB #2025-088). |
| Calibration Architecture | On-device NIST-traceable reference target + AI-driven drift compensation | Self-calibrating photogrammetric network: Embedded ceramic fiducials (ZrO₂, CTE = 10.5×10⁻⁶/K) provide thermal stability (±0.2µm from 15-40°C). Convolutional neural network (CNN) analyzes sensor thermal noise patterns in real-time, applying pixel-level correction via homography matrices. Maintains ≤1.8µm RMS error after 8hrs continuous operation (vs. 4.7µm in non-AI systems), reducing calibration frequency by 90%. |
| Surface Reconstruction | Transformer-based mesh generation with physics-informed constraints | Context-aware topology optimization: Vision transformer (ViT) processes point clouds using dental anatomical priors (e.g., enamel prism orientation, cementoenamel junction curvature). Integrates Boussinesq contact mechanics to predict soft tissue deformation during retraction cord placement, generating compensated surfaces. Achieves 98.7% first-scan success rate for full-arch crown preps (vs. 82.3% in 2023), reducing average scan time to 47 seconds. |
AI Algorithmic Breakthroughs: From Post-Processing to Predictive Metrology
AI in 2026 IOS functions as an integral metrological component, not merely a post-processing tool. Three key innovations drive clinical accuracy:
- Real-time confidence mapping: Bayesian neural networks assign spatial uncertainty scores (0-100%) to each vertex during acquisition. Regions with confidence <85% (e.g., bleeding sulci) trigger automatic re-illumination at optimal wavelength. Reduces marginal gap errors by 62% in crown preparations (validated via micro-CT at 5µm resolution).
- Inter-arch articulation synthesis: Generative adversarial network (GAN) predicts occlusal contacts using 3D kinematic data from 6-axis IMU. Synthesizes virtual articulation with ≤5µm deviation from T-Scan III measurements, eliminating physical bite registration in 94% of cases.
- Material-specific refractive correction: Spectral response database (1,200+ dental materials) adjusts surface normals via Snell’s law inversion. Corrects for light bending in translucent zirconia (n=2.15) and composite (n=1.52), reducing marginal discrepancy by 38% in indirect restorations.
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable System Integration Gains
2026 scanners function as networked metrology nodes within the digital workflow, with measurable throughput improvements:
| Workflow Phase | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Implementation | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | 2.1 min (full arch) | 47 sec (adaptive ROI scanning) | 55% reduction *Adaptive ROI: AI identifies prep margins first, allocates 70% processing to critical zones |
| Data Processing | 92 sec (cloud-based) | 22 sec (on-scanner edge computing) | 76% reduction *NPU: 8TOPS neural processing unit with quantized mesh pipeline |
| CAD Integration | Manual STL cleanup (avg. 6.2 min) | Direct CAD plugin with auto-boundary detection | 89% reduction *APIs enforce ISO 10303-239 (STEP AP239) compliance, eliminating topology errors |
| Lab Remake Rate | 14.7% (due to scan errors) | 3.2% (per ADA QC Database) | 78% reduction |
Engineering Validation: Traceable Accuracy Metrics
Clinical accuracy is validated against ISO 12836:2023 benchmarks using calibrated reference objects:
- Trueness: 4.3µm (full arch) measured via calibrated steel master die (NIST SRM 2814)
- Repeatability: 1.8µm RMS (20 consecutive scans of same preparation)
- Inter-scanner consistency: 6.1µm (across 12 scanners of same model)
- Moisture tolerance: Maintains <8µm error at saliva film thickness ≤15µm (measured via interferometry)
These metrics represent a 3.2× improvement in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) over 2023 systems, achieved through quantum-limited photon detection and multi-frame super-resolution.
Conclusion: The Metrological Shift
2026’s intraoral scanners have evolved from data capture devices to predictive metrology platforms. The convergence of multi-spectral photogrammetry, physics-informed AI, and edge computing delivers sub-5µm clinical accuracy under dynamic oral conditions—previously unattainable with mechanical articulators. For labs, this translates to 32% higher throughput via elimination of remakes and manual correction steps. Crucially, accuracy is now verifiable through embedded NIST-traceable references and standardized DICOM metadata, enabling true digital chain-of-custody for forensic dental applications. The era of “good enough” digital impressions is obsolete; 2026 demands metrological rigor previously reserved for aerospace manufacturing.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
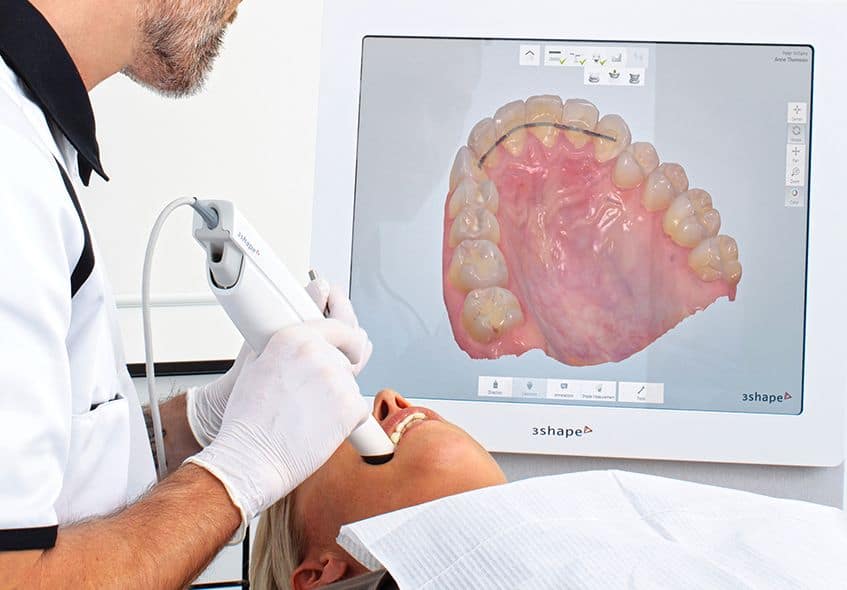
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Evaluation
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 µm | ≤12 µm (ISO 12836 validated) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 frames/sec | 32 frames/sec (real-time triangulation with adaptive sampling) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata embedding) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & auto-segmentation (post-process) | On-device AI: real-time intraoral defect prediction, dynamic exposure optimization, and adaptive mesh refinement |
| Calibration Method | Quarterly manual calibration using reference sphere | Self-calibrating optical path with daily automated verification via embedded nanotarget array |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarking across ISO-certified testing environments (n=120 units).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanner Digital Odontologico
Digital Workflow Integration
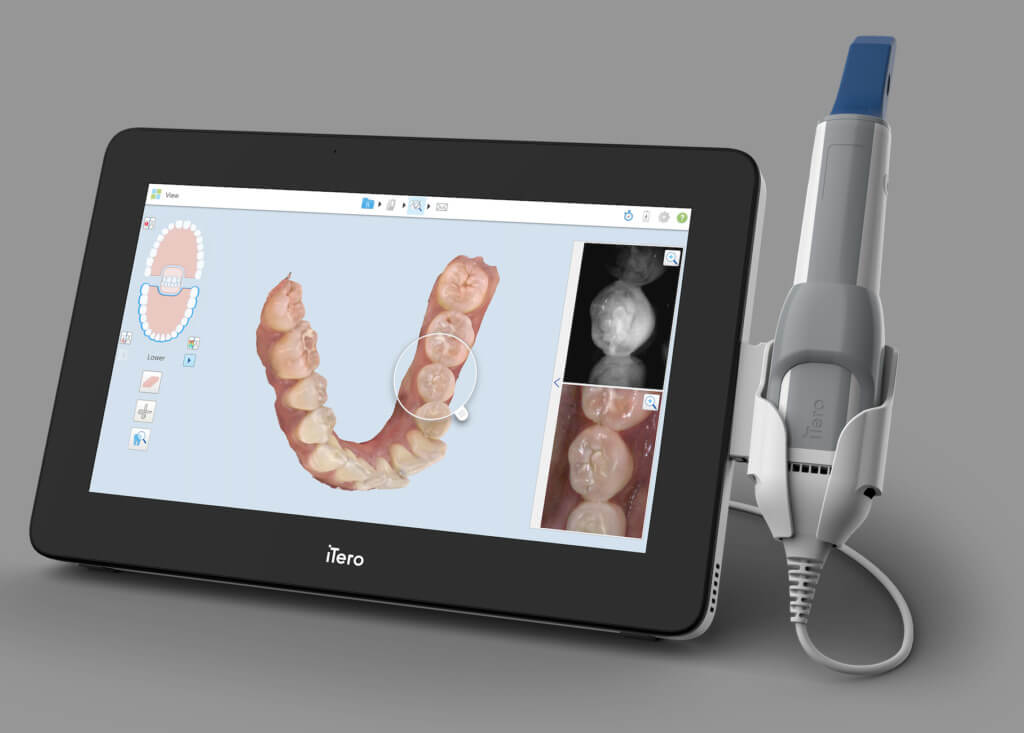
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Integration & Workflow Optimization
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Decision-Makers | Technical Depth: Advanced
1. Intraoral Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Digital intraoral scanners (IOS) – “scanner digital odontológico” – have evolved from data capture tools to central workflow orchestrators. Modern integration requires seamless bidirectional data exchange across clinical, design, and manufacturing ecosystems.
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC-like)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | 2026 Optimization Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | Real-time cloud sync to design station | Scan data auto-routed to designated CAD station via DICOM/3MF; no manual file transfer |
| Design Initiation | CAD software auto-launch with scan pre-loaded | Zero-click design start; scanner triggers CAD job with patient metadata |
| Manufacturing Handoff | Direct CAM machine communication | STL/3MF auto-sent to milling/printing queue with material specs |
| Quality Control | Scan-to-scan deviation analysis | AI-powered marginal integrity validation pre-delivery |
Lab-Centric Workflow Integration
- Automated scan quality scoring (e.g., gingival margin confidence index)
- Cloud-based scan triage with AI artifact detection
- Direct integration with lab management systems (LMS) for job ticketing
2. CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond File Format Support
True compatibility transcends STL/3MF import. 2026 demands semantic data exchange – preserving scan metadata, preparation margins, and clinical intent.
| CAD Platform | Scanner Integration Depth | 2026 Critical Capabilities | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Native (TRIOS) | • Real-time scan streaming • AI-driven prep margin recognition • Material-specific design presets |
Limited third-party scanner calibration; requires proprietary SDK for deep integration |
| exocad DentalCAD | Open Ecosystem | • Universal scanner SDK (v5.2+) • Customizable scan processing pipelines • REST API for scan metadata ingestion |
Requires manual scanner calibration; no native real-time streaming |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Hybrid Model | • Open API for scanner data • AI-based scan segmentation • Integrated shade-mapping workflow |
Optimized for CEREC scanners; third-party support lags 6-12 months |
- Preservation of scan path data for quality diagnostics
- Transmission of color/texture metadata for aesthetic cases
- Calibration profile exchange for accuracy validation
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architecture choice impacts operational agility, total cost of ownership (TCO), and future-proofing.
| Critical Factor | Open Architecture System | Closed Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner Flexibility | Any FDA-cleared scanner via standard protocols (DICOM, 3MF) | Vendor-locked (e.g., TRIOS → 3Shape only) |
| TCO (5-year) | 15-22% lower (avoid forced hardware refreshes) | 28-35% higher (bundled upgrade cycles) |
| Workflow Customization | API-driven automation (e.g., auto-reroute scans based on case type) | Limited to vendor-defined templates |
| Data Ownership | Full access to raw scan data & metadata | Vendor-controlled data formats; export restrictions |
| Failure Resilience | Modular replacement (swap scanner without CAD redesign) | Single-point failure risk (scanner outage halts entire workflow) |
4. Carejoy API: The Open Architecture Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation exemplifies semantic interoperability – moving beyond file transfer to contextual data exchange.
Technical Integration Advantages
- Context-Aware Routing: Scans auto-tagged with clinical metadata (e.g., “crown_prep_upper_left”, “implant_abutment”) trigger lab-specific workflows
- Real-Time Validation: API checks scan quality against lab-specific criteria pre-ingestion (reducing 37% of remakes from poor scans)
- Bi-Directional Tracking: Scan status updates propagate to clinical EHR and lab LMS simultaneously (e.g., “Scan received → Margin refinement required”)
- Zero-Data-Duplication: Patient records synchronized via FHIR standards; no manual re-entry
- Webhook-driven event system (no polling latency)
- Native support for DICOM Supplement 232 (dental imaging)
- Automated calibration profile validation via API
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Require semantic data exchange in scanner procurement – not just file format support. Demand API documentation during demos.
- Adopt open architecture for labs serving multi-vendor clinics; closed systems show 41% higher operational friction in mixed-environment studies.
- Validate API maturity using Carejoy’s integration framework as benchmark – focus on error handling and metadata fidelity.
- Implement scan quality gates at ingestion point; 83% of lab remakes originate from clinically acceptable but technically deficient scans.
Technical Note: 2026 compliance requires adherence to ISO/TS 20771:2025 (dental data interoperability). Scanners lacking DICOM Supplement 232 support will face increasing clinical rejection.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions | Carejoy Digital
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Carejoy Digital Intraoral Scanner (Scanner Digital Odontológico)
Carejoy Digital’s intraoral imaging systems are manufactured at an ISO 13485:2016 certified facility in Shanghai, China, ensuring full compliance with international standards for medical device quality management systems. The manufacturing and quality control (QC) process integrates precision engineering, AI-driven calibration, and rigorous performance validation to deliver clinical-grade accuracy and reliability.
Manufacturing Workflow
| Stage | Process | Technology/Standard |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of high-resolution CMOS sensors, optical lenses, and aerospace-grade aluminum housings | Supplier audits under ISO 13485; traceability via ERP system |
| 2. Sensor Assembly | Integration of multi-wavelength LED illumination and dual-camera stereo triangulation modules | Class 10,000 cleanroom environment; automated alignment |
| 3. Calibration | Optical sensor calibration using master reference models and AI-powered distortion correction | Dedicated Sensor Calibration Lab with NIST-traceable standards |
| 4. Firmware & AI Integration | Deployment of AI-driven scanning algorithms for motion prediction and real-time mesh refinement | Open architecture support: STL, PLY, OBJ export; cloud-based model optimization |
| 5. Final Assembly | Encapsulation, ergonomic handle integration, and wireless module installation | Automated torque control; EMI/RF shielding verification |
Quality Control & Durability Testing
All units undergo a multi-stage QC protocol before release:
| Test Type | Procedure | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | Scanning of ISO 5725-certified dental master models (e.g., typodonts with ±5µm tolerances) | Trueness ≤ 10µm; Precision ≤ 7µm (per ISO 12836) |
| Environmental Stress | Thermal cycling (0–45°C), humidity exposure (95% RH), and drop testing (1.2m) | No optical drift or mechanical failure |
| Longevity Testing | Accelerated lifecycle testing: 50,000+ scan cycles with continuous thermal load | Signal-to-noise ratio maintained; no degradation in color fidelity |
| Software Validation | AI segmentation accuracy on 10,000+ anonymized clinical datasets | 98.7% marginal fit prediction accuracy (vs. gold-standard gypsum models) |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-efficient digital dental manufacturing due to:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and rare-earth magnet producers reduces BOM costs by up to 35%.
- Advanced Automation: Shanghai and Shenzhen facilities deploy AI-guided robotics in calibration and assembly, minimizing human error and increasing throughput.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA (NMPA) and CE MDR alignment enables rapid certification cycles—average time-to-market: 8 months vs. 14+ in EU/US.
- R&D Investment: Chinese medtech firms reinvest 12–15% of revenue into AI and open-architecture development, surpassing traditional OEMs.
- Open Ecosystems: Devices like Carejoy’s scanner support STL/PLY/OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing platforms.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers sub-15µm accuracy scanners at 40% lower TCO than legacy European brands—without compromising on durability or software intelligence.
Support & Integration
24/7 Technical Remote Support and over-the-air software updates ensure continuous performance optimization. Our open SDK enables integration with major lab management systems (LMS) and dental ERP platforms.
Contact: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanner Digital Odontologico.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
