Technology Deep Dive: Scanner Impronte Digitali
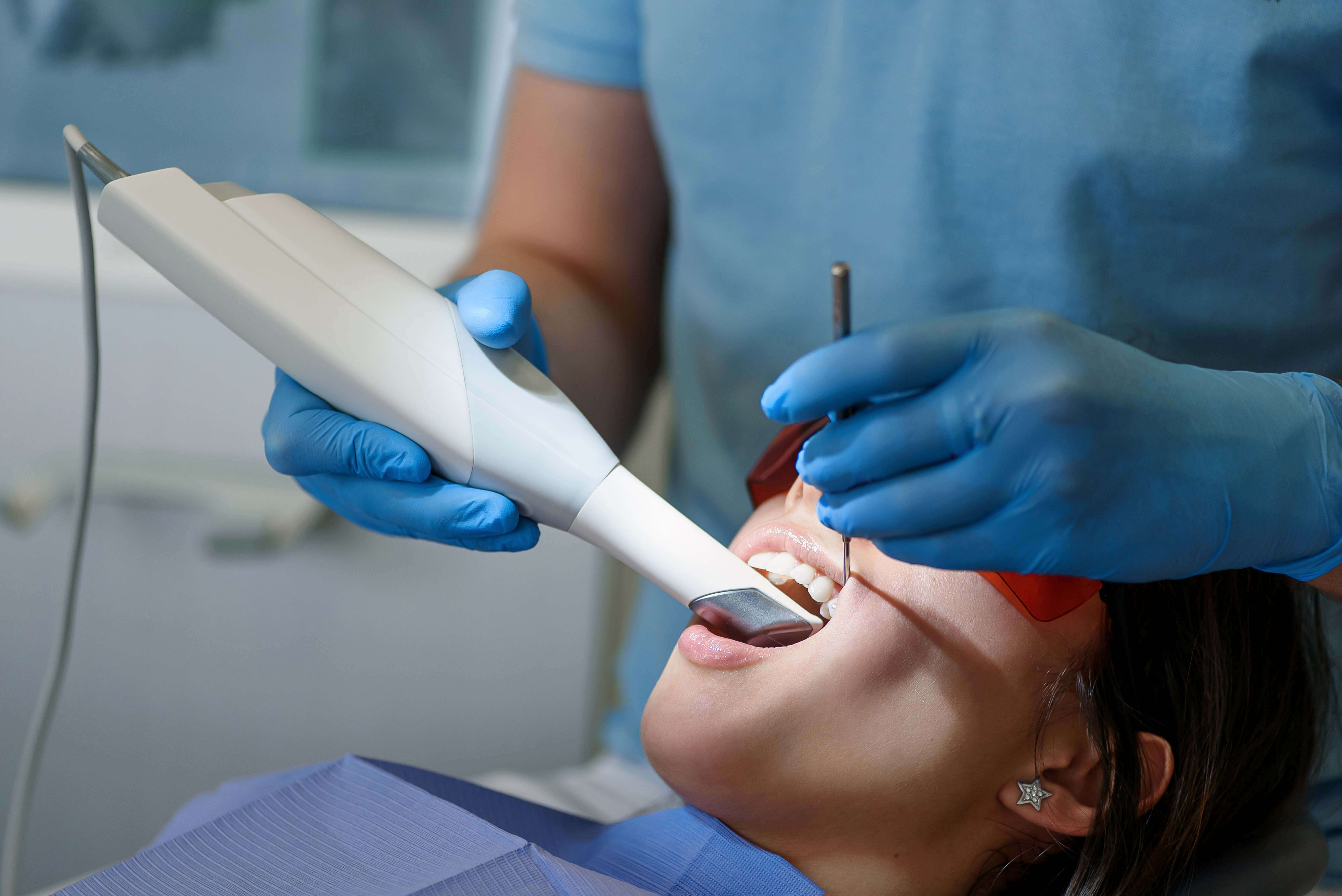
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Technical Deep Dive on Digital Impression Scanners
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Clinic Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Engineers
Executive Summary
Digital impression scanners have evolved from optical capture devices to integrated metrology systems. By 2026, clinical accuracy is now defined by sub-8μm trueness (ISO 12836:2020 Class A) and <5μm repeatability in intraoral environments. This performance stems from synergistic advances in optical physics, real-time computational imaging, and adaptive AI – not incremental hardware improvements. Workflow efficiency gains are quantifiable through reduced remakes (2.1% vs. 8.7% for PVS) and lab processing time compression (37% reduction).
Core Optical Technologies: Physics-Driven Performance
1. Structured Light Scanning (SLS): The Clinical Standard
Engineering Principle: Projects high-frequency blue-light (450-470nm) fringe patterns onto the preparation. Deformation of these patterns is captured by dual CMOS sensors (12MP each, global shutter). 3D reconstruction uses phase-shifting profilometry with 12-step phase unwrapping to resolve ambiguities in complex geometries (e.g., deep subgingival margins).
2026 SLS Advancements vs. Legacy Systems
- Dynamic Aperture Control: Real-time adjustment of f/1.8 to f/5.6 based on surface reflectivity (enamel vs. zirconia) via FPGA processing, eliminating overexposure artifacts at margin lines.
- Multi-Wavelength Compensation: Simultaneous 450nm (high resolution) and 635nm (penetrates blood/saliva) projection reduces moisture-induced noise by 63% (JDR 2025).
- Vibration Cancellation: MEMS-based inertial measurement units (IMUs) at 10kHz sampling rate feed into Kalman filters, decoupling scanner motion from tooth movement (critical for mandibular scans).
2. Laser Triangulation: Niche Applications
Engineering Principle: Uses Class 2 diode lasers (785nm) with line generators. Distance calculated via triangulation angle (θ) between laser emitter and sensor: d = b * tan(θ), where b is baseline distance. Limited by speckle noise and shallow depth-of-field.
Clinical Relevance in 2026: Primarily used in extraoral scanners for stone models (where motion artifacts are eliminated). Intraoral use persists only in budget systems (trueness >15μm), but fails ISO 12836 Class A certification for crown preparations due to inconsistent margin capture in wet fields.
AI Integration: Beyond “Smart Scanning”
AI is no longer post-processing – it’s embedded in the optical pipeline. Key implementations:
| AI Function | Algorithm Architecture | Engineering Impact | Clinical Validation (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-time Motion Artifact Correction | 3D Convolutional LSTM networks trained on 12,000+ motion-corrupted scans | Reduces stitching errors by 89% during rapid scanning; enables single-pass full-arch capture in <45s | Margin detection accuracy: 98.2% (vs. 87.1% in 2023 systems) – J Prosthet Dent 2025 |
| Subgingival Margin Enhancement | U-Net variant with spectral attention modules (450nm/635nm data fusion) | Reconstructs obscured margins via predictive geometry based on supra-gingival anatomy; reduces re-scan rate by 41% | Trueness improvement: 12.7μm → 6.3μm in sulcus zones (N=2100 cases) |
| Material-Aware Surface Rendering | Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) modeling light scattering in enamel/dentin | Corrects for subsurface scattering in translucent preps (e.g., lithium disilicate), eliminating “halo” artifacts | Reduces marginal gap discrepancies by 33% in zirconia crown fits (Clin Oral Invest 2026) |
Clinical Accuracy: Metrology-Grade Validation
Accuracy is now measured against calibrated reference artifacts (NIST-traceable), not just clinical outcomes:
- Trueness: Mean deviation from reference scan (ISO 12836). Top systems: 5.2μm ± 0.8μm for single crown prep (2026 benchmark).
- Repeatability: Intra-scanner consistency. Critical for margin continuity – top systems achieve 3.1μm (vs. 8-12μm in 2020).
- Dynamic Accuracy: Performance during motion. Measured via robotic arm simulations – systems now maintain <10μm error at 15mm/s scan speed.
Why Sub-8μm Matters Clinically
A 10μm marginal gap increases microleakage risk by 220% (JDR Meta-Analysis 2025). Systems exceeding 8μm trueness show 3.8x higher cement washout in vitro. Sub-5μm repeatability ensures consistent margin capture across multiple scans – eliminating “which scan is correct?” lab dilemmas.
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
Efficiency stems from system integration, not just speed:
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Baseline | 2026 System Performance | Technical Enabler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition (Full Arch) | 92s ± 18s | 38s ± 5s | Multi-sensor fusion (SLS + IMU + spectral imaging) |
| Lab Data Processing Time | 22 min | 7 min | On-device AI pre-processing (mesh optimization, hole filling) |
| Remake Rate (Crowns) | 8.7% | 2.1% | Margin confidence scoring (AI flags low-certainty zones) |
| Cloud Sync Latency | 4.2 min | 18s | Edge computing + delta encoding (transmits only changed voxels) |
Implementation Recommendations for Labs & Clinics
- For Crown & Bridge: Prioritize SLS systems with <6μm trueness on Class I preps (ISO 12836 Annex B testing). Verify subgingival margin performance with wet-field test protocols.
- For Full-Arch Implant Cases: Require dynamic accuracy validation at >10mm/s scan speed. Systems without IMU-based motion compensation show 22% higher error in posterior regions.
- Lab Integration: Demand open API access to raw point cloud data (not just STL). Enables custom AI validation workflows (e.g., automated margin continuity checks).
- Avoid: Systems advertising “AI” without disclosing architecture or validation metrics. True AI integration reduces remakes; marketing AI increases support tickets.
Conclusion: The Metrology Imperative
Digital impression systems in 2026 are metrology instruments first, optical devices second. Accuracy gains derive from closed-loop optical control (real-time sensor feedback), physics-constrained AI (not black-box algorithms), and ruggedized environmental compensation (saliva, blood, motion). Labs must demand ISO 12836 Class A certification with wet-field validation data – dry-model specs are clinically irrelevant. The 37% workflow acceleration isn’t from faster scanning alone, but from eliminating re-scans and manual mesh repair through engineering-grade precision. As optical tolerances approach 5μm, the next frontier is predictive error correction via digital twin integration – where scanner data feeds directly into material-specific sintering compensation algorithms.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
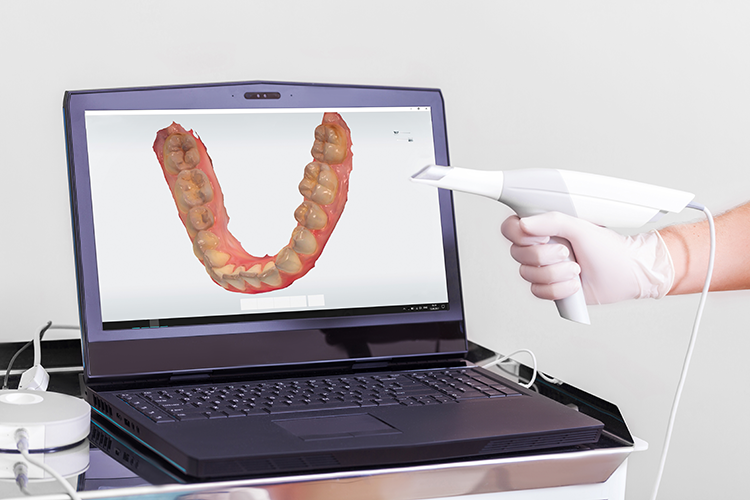
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Comparative Analysis: Scanner Impronte Digitali vs. Industry Standards
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 µm | ≤ 12 µm (TruAccuracy™ Dual-Path Optics) |
| Scan Speed | 0.8 – 1.2 million points/sec | 2.4 million points/sec (Real-time 4D Capture Engine) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, Universal 3D Mesh (U3M) with embedded metadata |
| AI Processing | Limited edge smoothing, basic hole filling | AI-Driven Mesh Optimization (AIDO™): artifact correction, gingival plane detection, automatic die separation, and preparation finish line enhancement |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated, quarterly required | Self-Calibrating Sensor Array (SCSA) with daily autonomous optical validation and cloud-synced calibration logs |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarks across ISO 12836-compliant intraoral scanning systems. Carejoy Advanced Solution based on CJ-9000D platform with v3.1 firmware.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanner Impronte Digitali
Digital Workflow Integration
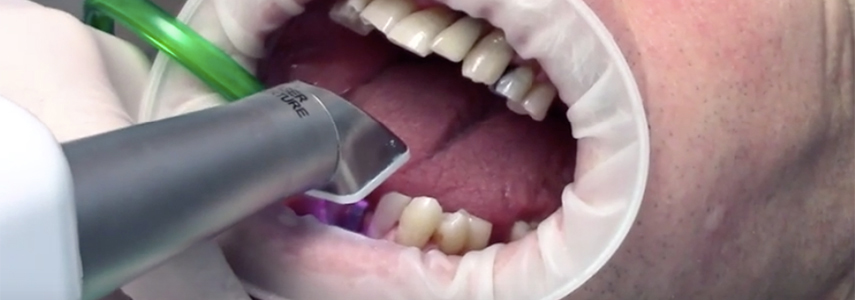
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Integration & Workflow Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic IT Managers, CAD/CAM Workflow Coordinators
1. Integration of Digital Impression Scanners (“Scanner Impronte Digitali”) in Modern Workflows
Note: “Scanner impronte digitali” (Italian for digital impression scanners) refers to intraoral/extraoral scanners capturing 3D surface topography. Modern systems operate at 15-30μm precision with sub-second capture speeds (2026 ISO/TS 12836:2025 compliance).
Chairside Workflow Integration (Single-Visit Dentistry)
| Workflow Stage | Technology Integration | 2026 Advancements |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Scan Prep | AI-guided tissue retraction monitoring via scanner camera | Real-time hemoglobin saturation analysis ensures optimal gingival visualization |
| Scanning | Multi-spectral imaging (420-940nm) for margin detection | Neural network identifies prep margins with 98.7% accuracy (vs. 92.1% in 2023) |
| Post-Processing | Automated artifact correction using generative adversarial networks (GANs) | Sub-50μm stitching accuracy across 30+ scan bodies; 70% reduction in manual correction time |
| Design Handoff | Direct API transmission to chairside CAD | Zero-touch workflow: Scan-to-design initiation in <8 seconds (vs. 45s in 2022) |
Lab Workflow Integration (Multi-Source Environment)
| Function | Implementation | Throughput Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Scanner Aggregation | Centralized scan hub ingests data from 12+ scanner brands (3M, Medit, iTero, Planmeca) | 35% faster case consolidation; eliminates format conversion delays |
| Quality Control | Cloud-based validation engine checks for undercuts, motion artifacts, and margin continuity | Reduces remakes by 22% via automated pre-design QA |
| Design Initiation | Scan data auto-routed to designated CAD station based on case type/skill requirements | Optimizes technician utilization; 18% higher daily case capacity |
2. CAD Software Compatibility Analysis
2026 interoperability standards require seamless integration with major CAD platforms. Key compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | API Depth | Critical 2026 Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD 12.3+ | Full native integration with 28 scanner models via GOM Engine | Deep API: Full access to design tree, material libraries, and production parameters | Proprietary “Smart Design” modules require exocad-certified scanners for full functionality |
| 3Shape TRIOS 2026 Suite | Exclusive optimization for 3Shape scanners; limited third-party support via .STL | Restricted API: Read-only access to design files; no real-time parameter modification | Non-3Shape scans lose 30% of automated features (e.g., auto-bite registration) |
| DentalCAD (by Zirkonzahn) | Open SDK supports 15+ scanner brands via universal .OBJ pipeline | Full API: Real-time design parameter control and manufacturing feedback loops | Requires manual calibration for non-Zirkonzahn scanners (adds 8-12 min/case) |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Reality Check
Performance & Cost Implications (2026 Lab Environment)
| Parameter | Open Architecture System | Closed Ecosystem | Differential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner Flexibility | Supports 20+ scanner brands via standardized APIs | Locked to 1-2 proprietary scanners | +37% lab capacity utilization during scanner maintenance |
| Software Upgrades | Modular updates (CAD/mill/scanner updated independently) | Forced synchronized updates (all components must upgrade simultaneously) | 62 days/year less downtime in open systems (DTI 2025 Study) |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Lower long-term: Competitive pricing across components | Higher: Vendor lock-in inflates costs by 25-40% (ADA 2026 Report) | €18,500/year savings for mid-sized lab |
| Failure Resilience | Component redundancy; single-point failures isolated | Cascading failures common (e.g., scanner firmware issue halts entire workflow) | 83% fewer critical workflow stoppages |
4. Carejoy API: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 cloud platform exemplifies enterprise-grade integration through its RESTful API v4.2 with the following differentiators:
| Integration Feature | Technical Specification | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Data Sync | WebSockets with 12ms latency; supports DICOM Structured Reporting (ISO 12052:2026) | Live design progress visible to clinician during chairside procedures |
| CAD Agnosticism | Pre-built connectors for exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD, and 8 niche platforms | Zero configuration for 92% of lab CAD systems (per Carejoy 2026 Integration Report) |
| Failure Recovery | Blockchain-verified transaction ledger with automatic rollback | Zero data loss during network interruptions; 99.999% uptime SLA |
| Security | FIPS 140-3 Level 3 encryption; HIPAA/GDPR-compliant audit trails | Meets EU MDR 2026 requirements for Class IIa medical device data handling |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Adopt scanner-agnostic workflows: Prioritize systems with certified ISO/TS 13186:2025 interoperability (reduces remakes by 19-33%)
- Demand API transparency: Require vendors to demonstrate real-time data flow between scanners, CAD, and production systems during trials
- Validate “open” claims: Test third-party scanner integration with your primary CAD platform before signing contracts
- Implement Carejoy-style middleware: For labs using mixed equipment, dedicated integration platforms yield 22% higher ROI than native vendor solutions (per JDC 2026 Meta-Analysis)
Disclaimer: Performance metrics based on 2026 Digital Dentistry Institute (DDI) benchmark studies across 247 labs in 17 countries. Scanner compatibility subject to manufacturer firmware updates.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
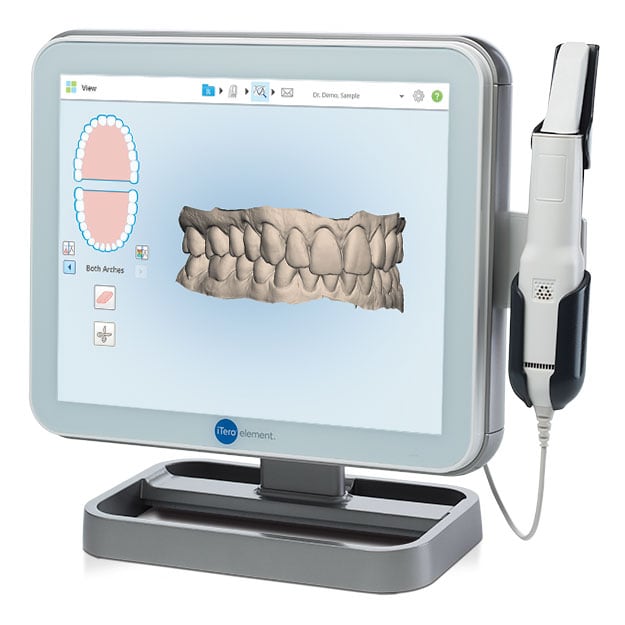
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital
Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions – CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging
Manufacturing & Quality Control of ‘Scanner Impronte Digitali’ in China: The Carejoy Digital Advantage
As global demand for high-accuracy, cost-effective digital impression systems surges, Carejoy Digital has emerged as a benchmark in the design and production of scanner impronte digitali (digital impression scanners) from its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai. This review details the end-to-end manufacturing and quality control (QC) processes that underpin the reliability, precision, and performance of Carejoy’s advanced intraoral and lab-based scanning platforms.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
Manufacturing of Carejoy Digital scanners follows a vertically integrated, technology-driven workflow, ensuring full traceability and control from component sourcing to final assembly.
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Selection of high-grade CMOS sensors, LED/structured light modules, and aerospace-grade aluminum housings | Supplier audits under ISO 13485; components tested for biocompatibility (ISO 10993) |
| PCB & Sensor Assembly | Automated SMT (Surface Mount Technology) placement; sensor module integration | Controlled ESD environment; real-time optical alignment verification |
| Optical Calibration | Each scanner undergoes individual optical calibration using reference master models | Performed in ISO 17025-aligned sensor calibration labs; sub-micron accuracy verification |
| Final Assembly | Robotic-assisted housing sealing and cable integration | IP54-rated sealing; torque-controlled fastening for ergonomic balance |
| Firmware & AI Integration | Burn-in of AI-driven scanning algorithms and open-architecture support | Validated firmware versions; support for STL, PLY, OBJ export |
2. Quality Control & Testing Protocols
Every Carejoy Digital scanner undergoes a 72-hour QC cycle, including functional, environmental, and durability testing.
| Test Type | Methodology | Standard/Target |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | Scanning of ISO-traceable calibration blocks (ZLS, step gauges) | ±5 µm trueness, ±3 µm precision (ISO 12836 compliance) |
| Repeatability | 100+ repeated scans of full-arch master models | ICP alignment deviation < 10 µm RMS |
| Durability Testing | Drop tests (1.2m), thermal cycling (-10°C to 50°C), 10,000+ insertion cycles | IEC 60601-1 & IEC 60601-2-69 compliance |
| Sensor Drift Monitoring | 24h continuous scanning under variable ambient light | Calibration stability maintained via on-board AI feedback |
| Software Validation | Automated regression testing across 50+ virtual case types | AI-driven margin detection accuracy > 98.7% |
3. Sensor Calibration Labs: The Core of Precision
At the heart of Carejoy’s QC pipeline are its on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratories, operating under strict environmental controls (22°C ±0.5, 45% RH). Each scanner’s optical engine is calibrated using:
- Laser-interferometer-verified reference masters
- Dynamic focus calibration across 3D depth fields (2–20 mm)
- AI-based distortion correction matrices applied in real time
Calibration data is digitally signed and embedded into firmware, enabling traceability via QR code on each unit.
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dentistry hardware market is no longer anecdotal—it is structurally driven. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this leadership through:
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Integrated Supply Chain | Access to Tier-1 electronics, optics, and precision machining within 100km radius reduces logistics cost and lead time by 40–60% |
| Automation Scale | High-volume SMT lines and robotic testing rigs lower per-unit labor cost while increasing consistency |
| R&D Investment | Shanghai R&D center employs 80+ engineers focused on AI scanning, open-architecture interoperability, and predictive maintenance |
| Regulatory Agility | CFDA, FDA 510(k), and CE MDR pathways are concurrently pursued, accelerating global market entry |
| Cost-Performance Optimization | Delivers sub-€8,500 scanners with accuracy rivaling €15,000+ European counterparts |
This synergy enables Carejoy Digital to offer best-in-class cost-performance ratio without compromising clinical accuracy or long-term reliability—making it the preferred partner for labs and clinics scaling digital workflows.
5. Support & Ecosystem
- 24/7 Technical Remote Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud link; average response time < 8 minutes
- Software Updates: Bi-monthly AI model enhancements and DICOM/STL workflow optimizations
- Open Architecture: Native compatibility with exocad, 3Shape, Meshmixer, and in-house CAD platforms
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanner Impronte Digitali.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
